Punjab State Board PSEB 9th Class Hindi Book Solutions Hindi Grammar varn वर्ण Exercise Questions and Answers, Notes.
PSEB 9th Class Hindi Grammar वर्ण
(क) निम्नलिखित शब्दों का वर्ण-विच्छेद कीजिए:
अंकुर ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… ।
उत्तर:
अं + कु + उ + र् + अ
अनुभव : ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… ……… + ……… +
त्तर:
अ + न् + उ + भ् + अ + व् + अ
आराम: ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… ।
उत्तर:
आ + र् + आ + म् + अ

इच्छा : ……… + ……… + ……… + ………।
उत्तर:
इ + च् + छ् + आ
ईश्वर : ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + ………।
उत्तर:
ई + श् + व् + अ + र + अ
उपाधि : ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… +
उत्तर:
उ + प् + आ + ध + इ
ऊर्जा : ……… + ……… + ………. + ……… + ………
उत्तर:
ऊ + र + ज् + आ
ऋतु : ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… ।
उत्तर:
ऋ + इ + त् + उ
एकांत : ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… ।
उत्तर:
ए + + आ + त् + अ
ऐतिहासिक : ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + ………
उत्तर:
ऐ + त् + इ + ह् + आ + स् + इ + क् + अ
ओजस्वी : ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + ………।
उत्तर:
ओ + ज् + अ + स् + व + ई
औपचारिक : ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + ……….
उत्तर:
औ + प + अ + च + आ + र् + इ + क् + अ
क्रमानुसार : ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + ………
उत्तर:
क् + र् + म् + आ + न् + उ + स् + र् + अ
खिन्न : ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… ।
उत्तर:
ख् + इ + न् + न् + अ
गर्दन : ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + ……..
उत्तर:
ग् + अ + र् + द् + अ + न् + अ
घमासान : ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + ………
उत्तर:
घ + म् + आ + स् + आ + न् + अ
चतुर्भुज : ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + ………
उत्तर:
च् + अ + त् + उ + र् + भ + उ + ज् + अ
छियानवे : ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + ………
उत्तर:
छ् + इ + य् + आ + न् + अ + व + ए
जिह्वा : ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… ।
उत्तर:
ज् + इ + ह् + व् + आ
ज्ञानवर्धक : ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + …………. + …….. ….. + ……… + ………।
उत्तर:
ज + अ + आ + न् + अ + व + अ + द् + र् + ध् + अ + क् + अ
झंझट : ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + ………।
उत्तर:
झ + अं + झ् + अ + ट् + अ
ट्रैफिक : ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + ………….
उत्तर:
ट् + र् + ऐ + फ् + इ + क् + अ
ठंडक : ……… + ……… + ……… + …………. + ………।
उत्तर:
ठं + अं + ड् + अ + क् + अ
ड्राइवर : ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… ।
उत्तर:
ड् + र् + आ + इ + व् + अ + र् + अ

ढूंढ़ना : ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + ………….. + ………।
उत्तर:
द + ऊ + अं+ ढ् + अ + न् + आ
त्याग : ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… ।
उत्तर:
त् + य् + आ + ग् + अ
थिरकना : ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + ………।
उत्तर:
थ् + इ + र् + अ + क् + अ + न् + आ
दुग्ध : ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… ।
उत्तर:
द् + उ + ग् + ध् + अ
धोखेबाज़ : ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + ………।
उत्तर:
ध् + ओ + ख् + ए + ब + आ + ज + अ
न्यून : ……… +………. + ……… + ……… + ………
उत्तर:
न् + य + ऊ + न् + अ
पर्वत : ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + ………।
उत्तर:
प् + अ + र् + व् + अ + त् + अ
फरीटकोट : ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + …………. ।
उत्तर:
फ्+ अ + र् + ई + द् + अ + क् + ओ + ट् + अ
बर्मा : ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… ।
उत्तर:
ब् + अ + र् + म् + आ
भ्रष्टाचार : ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + …….।
उत्तर:
भ् + र् + अ + ष् + ट् + आ + च् + आ + र् + अ
मनोव्यथा : ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + …….
उत्तर:
म् + अ + न् + ओ + व् + य् + अ + थ् + आ
योद्धा : ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… ।
उत्तर:
य् + ओ + द् + ध् + आ
रहस्य : ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… ।
उत्तर:’
र + अ + ह् + अ + स् + य + अ
लिखवाना : ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + ………।
उत्तर:
ल् + इ + ख + अ + व् + आ + न + आ
विज्ञान : ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + ………।
उत्तर:
व् + इ + ज् + ब + आ + न् + अ
व्यवहार : ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + ………।
उत्तर:
व् + य + अ + व् + अ + ह् + आ + र् + अ
श्रृंगार : ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + ………।
उत्तर:
श् + क्रं + ग् + आ + र् + अ
श्रीमती : ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + ………।।
उत्तर:
श् + र् + ई + म् + अ + त् + ई

सूक्ष्म : ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + ………
उत्तर:
स् + ऊ + क् + क्ष् + म् + अ
हृदय : ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… + ……… ………।
उत्तर:
ह् + ऋ + द् + अ + य् + अ
(ख) निम्नलिखित वर्णों को जोड़कर शब्द बनाइए:
1. उ + प् + आ + य् + अ =
उत्तर:
उपाय
2. ऊ + ष् + म् + आ =
उत्तर:
ऊष्मा
3. औ + ष + अ + ध् + इ =
उत्तर:
औषधि
4. + अं+ च् + अ + न् + अ =
उत्तर:
कंचन
5. ग् + य् + आ + र् + अ + ह् + अ =
उत्तर:
ग्यारह
6. न् + इ + श् + च् + इ + त् + अ =
उत्तर:
निश्चित
7. प् + र् + अ + द् + अ + र् + श् + अ + न् + अ =
उत्तर:
परादर्शन
8. प् + र् + अ + स् + अ + न् + न् + अ + त् + आ =
उत्तर:
प्रसन्नता
9. स् + व् + अ + र् + ग् + ई + य् + अ =
उत्तर:
स्वर्गीय
10. स् + अ + र् + व् + ओ + च् + च् + अ =
उत्तर:
सर्वोच्च
11. प् + अ + र् + इ + श् + र् + अ + म् + अ =
उत्तर:
परिश्रम
12. प् + अ + त् + र् + इ + + आ =
उत्तर:
पत्रिका
13. व् + अ + र + त् + अ + म् + आ + न् + अ =
उत्तर:
वर्तमान
14. ग् + अ + र् + इ + म् + आ =
उत्तर:
गरिमा
15. च् + इ + + इ + त् + स् + आ + ल् + य् + अ =
उत्तर:
चिकित्सालय
16. ल् + अ + + उ + र् + आ + इ + न् + अ =
उत्तर:
ठकुराइन
17. त् + ई + व् + र् + अ =
उत्तर:
तीव्र
18. थ् + आ + न् + ए + द् + अ + र् + अ =
उत्तर:
थानेदार
19. द् + उ + र् + भ् + आ + ग् + य् + अ =
उत्तर:
दुर्भाग्य

20. आ + श् + च् + अ + र् + य् + अ =
उत्तर:
आश्चर्य
परीक्षोपयोगी वर्णविच्छेद संबंधी अन्य उदाहरण
अशोक = अ + श् + ओ + क् + अ
प्रेम = प् + र् + ए + म् + अ
कर्म = क् + अ + र् + म् + अ
विद्यालय = व् + इ + द् + य् + आ + ल + अ + य् + अ
विद्या = व् + इ + द् + य् + आ
कृष्ण = कृ + ऋ + ष् + ण् + अ
विश्वास = व् + इ + श् + व् + आ + स् + अ
उत्तीर्ण = उ + त् + त् + ई + र् + ण् + अ
दिल्ली = द् + इ + ल् + ल् + ई
केंद्र = क् + ए + न् + द् + र् + अ
चंडीगढ़ = च + अ + ण् + इ + ई + ग्र + अ + ढ़ + अ
यज्ञ = य् + अ + ज् + ञ् + अ
क्षमा = क् + ष् + अ + म् + आ
त्राता = त् + र् + आ + त् + आ
पिता = प् + इ + त् + आ
माता = म + आ + त् + आ
आश्रय = आ + श् + र् + अ + य् + अ
ट्रक = ट् + र् + अ + क् + अ
यात्रा = य् + आ + त् + र् + आ
श्रीमान = श् + र् + ई + म् + आ + न् + अ
कर्म = क् + अ + र् + म् + अ
ग्वाला = ग् + व् + आ + ल् + आ
सत्य = स् + अ + त् + य् + अ
मच्छर = म् + अ + च् + छ् + अ + र् + अ
प्याऊ = प् + य् + आ + ऊ.
मक्खी = म् + अ + क् + ख + ई
मक्खन = म् + अ + क् + ख् + अ + न् + अ
दैत्याकार = द् + ऐ + त् + य् + आ + क् + आ + र् + अ
अच्छाई = अ + च् + छ + आ + ई
मोटर = म् + ओ + ट् + अ + र् + अ
कठिन = क् + अ + ल् + इ + न् + अ
स्कूल = स् + क् + ऊ + ल् + अ
गृहकार्य = गृ + ऋ + ह् + अ + क् + आ + र् + य् + अ
खिचड़ी = ख् + इ + च् + अ + ई
मानस = म् + आ + न् + अ + स् + अ
पूनम = प् + ऊ + न + अ + म् + अ
रजत = र + अ + ज् + अ + त् + अ
प्रतिकूल = प् + र् + अ + त् + इ + क् + ऊ + ल् + अ
सूर्योदय = स् + ऊ + र् + य् + ओ + द् + अ + य् + अ
तृप्ति = त् + ऋ+ प + त् + इ
तिमिर = त् + इ + म् + इ + र् + अ
खिलाफ़त = ख् + इ + ल् + आ + फ् + अ + त् + अ
जलाशय = ज् + अ + ल् + आ + श् + अ + य् + अ
काव्यात्मक = क् + आ + व् + य् + आ + त् + म् + अ + क् + अ
स्वाभाविकता = स् + व + आ + भ् + आ + व् + इ + क् + अ + त् + आ
नेतृत्व = न् + ए + त् + ऋ + त् + व् + अ
महिषकुल = म् + अ + ह + इ + ष् + अ + क् + उ + ल् + अ
संस्करण = स् + अं+ स् + क् + अ + र् + आ + ण् + अ
प्रयोगशाला = प् + र् + अ + य् + ओ + ग् + अ + श् + आ + ल् + आ
वाद्ययंत्र = व् + आ + द् + य् + अ + य् + अं + त् + र् + अ
आविष्कार = आ + व् + इ + ष् + क् + आ + र् + अ
उद्वेलिंत = उ + द् + व् + ए + ल + इ + त् + अ
दुर्दात = द् + उ + र् + द् + आ + त् + अ
कलाभिज्ञ = क् + अ + ल + आ + भ् + इ + ज् + ञ् + अ
आह्लादित = आ + ह् + ल् + आ + द् + इ + त् + अ
चिह्न = च + इ + इ + न् + अ
आह्वान. = आ + ह् + व् + आ + न् + अ
चाँदनी = च् + आँ + द् + अ + न + ई
विडंवना व + इ + ड् + अं + ब् + अ + न् + आ
श्रेणियों = श् + र् + ए + ण् + इ + य् + ओं
विचित्र = व् + इ + च + इ + त् + र् + अ
विज्ञापित = व + इ + ज + अ + आ + प + इ + त् + अ
यथार्थवादी = . य + अ + थ् + आ + र् + थ् + अ + व् + आ + द् + ई
प्रधानाध्यापक = प् + र् + अ + ध् + आ + न + आ + ध् + य् + आ + प् + अ + क् + अ
न्योछावर = न् + य् + ओ + छ् + आ + व् + अ + र् + अ
पर्यावरण = प् + अ + र् + य् + आ + व् + अ + र् + अ + ण् + अ
प्रकृति = प् + र् + अ + क् + ऋ + त् + इ
द्रवित = द् + र् + अ + व् + इ + त् + अ
मोमबत्ती = म् + ओ + म् + अ + ब् + अ + त् + ई
एक वाक्य में उत्तर दीजिए
प्रश्न 1.
वर्ण किसे कहते हैं?
उत्तर:
भाषा में प्रयुक्त होने वाली सबसे छोटी ध्वनि को वर्ण कहते हैं।

प्रश्न 2.
उच्चारण की दृष्टि से वर्ण के कितने भेद होते हैं?
उत्तर:
उच्चारण की दृष्टि से वर्ण के तीन भेद होते हैं-स्वर, अयोगवाह और व्यंजन।
प्रश्न 3.
स्वर के भेद कौन-कौन से होते हैं?
उत्तर:
हस्व, दीर्घ और प्लुत।
प्रश्न 4.
ओ३म्, राम और श्या३म् में स्वर का कौन-सा भेद है?
उत्तर:
प्लुत स्वर।
प्रश्न 5.
व्यंजन किसे कहते हैं?
उत्तर:
जिन वर्णों का उच्चारण करते समय हमारे मुँह से हवा थोड़ा रुक कर बाहर निकलती है उसे व्यंजन कहते हैं।
प्रश्न 6.
व्यंजनों के कितने भेद होते हैं?
उत्तर:
व्यंजनों के तीन भेद होते हैं-स्पर्श, अन्त:स्थ, ऊष्म।
प्रश्न 7.
अयोगवाह कितने और कौन-से होते हैं?
उत्तर:
अयोगवाह संख्या में दो होते हैं-‘अं’, ‘अः’।
प्रश्न 8.
संयुक्त व्यंजन किसे कहते हैं?
उत्तर:
जब स्वर रहित व्यंजन किसी स्वर रहित व्यंजन से मिलाकर लिखा जाता है तो उसे संयुक्त व्यंजन कहते हैं।
प्रश्न 9.
संयुक्त व्यंजनों के चार उदाहरण लिखिए।
उत्तर:
श्रीमती, विज्ञापन, विक्षिप्त, नेत्र।
प्रश्न 10.
मात्रा किसे कहते हैं?
उत्तर:
जब स्वर किसी व्यंजन से मिलते हैं तो उनके बदले हुए रूप को ‘मात्रा’ कहते हैं।
प्रश्न 11.
संयुक्त व्यंजन किसे कहते हैं?
उत्तर:
जो व्यंजन दो वर्गों के संयोग से बनते हैं उन्हें संयुक्त व्यंजन कहते हैं। ये स्वतंत्र नहीं होते।
प्रश्न 12.
संयुक्त व्यंजनों के चार उदाहरण दीजिए।
उत्तर:
विज्ञापन, पवित्र, श्रीमान, अत्रिय।
प्रश्न 13.
द्वित्व वर्ण किसे कहते हैं ?
उत्तर:
जब किसी एक शब्द में कोई व्यंजन दो बार आ जाता है तो उसे द्वित्व वर्ण कहते हैं; उदाहरण-हड्डी, डिब्बा, धक्का
प्रश्न 14.
अयोगवाह किसे कहते हैं?
उत्तर:
हिंदी वर्णमाला में जो न स्वर होते हैं और न ही व्यंजन उन्हें अयोगवाह कहते हैं।
एक शब्द में उत्तर दीजिए
प्रश्न 1.
हिंदी में किस स्वर का प्रयोग लगभग नहीं होता?
उत्तर:
प्लुत स्वर।
प्रश्न 2.
दीर्घ स्वर के दो उदाहरण दीजिए।
उत्तर:
आ, ई।

प्रश्न 3.
वर्णमाला में न स्वर न व्यंजन क्या कहलाते हैं?
उत्तर:
अयोगवाह।
प्रश्न 4.
अनुनासिक का उदाहरण दीजिए।
उत्तर:
आँख।
प्रश्न 5.
विसर्ग के प्रयोग से बना एक शब्द लिखिए।
उत्तर:
प्रातः।
प्रश्न 6.
त् + ई + व् + र् + अ से बनने वाला शब्द लिखिए।
उत्तर:
तीव्र।
प्रश्न 7.
उच्चारण में ह्रस्व स्वर से तिगुना समय किस स्वर में लगता है?
उत्तर:
प्लतु स्वर में।
हाँ/नहीं में उत्तर दीजिए
प्रश्न 1.
भाषा में सब से छोटी ध्वनि को वर्ण कहते हैं।
उत्तर:
हाँ।
प्रश्न 2.
उच्चारण की दृष्टि से वर्णों के तीन भेद होते हैं।
उत्तर:
हाँ।
प्रश्न 3.
ह्रस्व स्वरों की संख्या चार होती है?
उत्तर:
हाँ।
प्रश्न 4.
हिन्दी में अब दीर्घ स्वर का प्रयोग नहीं किया जाता?
उत्तर:
नहीं।
प्रश्न 5.
स्पर्श व्यंजन संख्या में 25 होते हैं।
उत्तर:
हाँ।
प्रश्न 6.
अयोगवाह ध्वनि का वहन करते हैं।
उत्तर:
हाँ।
प्रश्न 7.
विसर्ग का प्रयोग प्रायः संस्कृत शब्दों में किया जाता है।
उत्तर:
हाँ।
प्रश्न 8.
हिंदी में प्रयुक्त अंग्रेजी, उर्दू, अरबी, फ़ारसी आदि के शब्दों को आगत शब्द कहते हैं।
उत्तर:
हाँ।
प्रश्न 9.
द्वित्व वर्ण में एक शब्द में कोई व्यंजन दो बार आते हैं।
उत्तर:
हाँ।
रिक्त स्थानों की पूर्ति करें
प्रश्न 1.
वर्णभेद का उच्चारण ……….. के आधार पर किया जाता है।
उत्तर:
अव्ययों की भिन्नता।
प्रश्न 2.
स्वरों के ……….. भेद होते हैं।
उत्तर:
तीन।
प्रश्न 3.
व्यंजनों के ………. भेद होते हैं।
उत्तर:
तीन।
प्रश्न 4.
विसर्ग का प्रयोग प्रायः ……… भाषा में किया जाता है।
उत्तर:
संस्कृत।
प्रश्न 1.
वर्ण किसे कहते हैं?
उत्तर:
भाषा में प्रयुक्त होने वाली सबसे छोटी ध्वनि को वर्ण कहते हैं। उदाहरण-अ, इ, उ, ज्, र, म्, आदि।
प्रश्न 2.
वर्णमाला से आपका क्या तात्पर्य है?
उत्तर:
वर्णमाला शब्द का सामान्य अर्थ है-वर्णों की माला या वर्गों का समूह। किसी भी भाषा के वर्गों के व्यवस्थित समूह को वर्णमाला कहते हैं।

प्रश्न 3.
उच्चारण की दृष्टि से वर्गों के कितने भेद होते हैं?
उत्तर:
उच्चारण की दृष्टि से वर्गों के तीन भेद होते हैंस्वर, अयोगवाह और व्यंजन।
प्रश्न 4.
हिंदी की वर्णमाला लिखिए।
उत्तर:
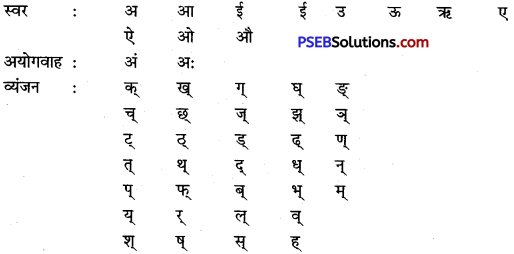
प्रश्न 5.
वर्ण-भेद किस आधार पर किया जाता है? स्पष्ट करें।
उत्तर:
भाषा की ध्वनियों का उच्चारण अव्ययों की भिन्नता के आधार पर किया जाता है। इसी आधार पर भाषा के वर्गों का विभाजन दो भागों में किया जाता है-स्वर और व्यंजन।
प्रश्न 6.
स्वर किसे कहते हैं? ये कितने प्रकार के होते हैं?
उत्तर:
जिन वर्णों के उच्चारण करते समय हमारे मुँह से हवा किसी भी प्रकार की रुकावट के बिना बाहर निकलती है, उन्हें स्वर कहते हैं।
स्वर तीन प्रकार के होते हैं-ह्रस्व, दीर्घ और प्लुत।
प्रश्न 7.
स्वरों के तीन भेदों का वर्णन कीजिए।
उत्तर:
उच्चारण में लगे हुए समय के आधार पर स्वरों का वर्गीकरण किया जाता है; जैसे-
(I) ह्रस्व स्वर-जिन स्वरों के उच्चारण में कम समय लगता है, उन्हें ह्रस्व स्वर कहते हैं। ये संख्या में चार होते हैं-अ, इ, उ, ऋ।
(II) दीर्घ स्वर-जिन स्वरों के उच्चारण में दुगुना समय लगता है, उन्हें दीर्घ स्वर कहते हैं। ये संख्या में सात होते है-
आ, ई, ऊ, ए, ऐ, ओ, औ।
(III) प्लुत स्वर-जब किसी स्वर के उच्चारण में ह्रस्व स्वर से तिगुना समय लगता है, उन्हें प्लत स्वर कहते हैं। इनका प्रयोग दूर से पुकारने या आवाज़ को लंबा खींचने की आवश्यकता पड़ने पर किया जाता है। संस्कृत में इसे लिखने के लिए स्वर विशेष के आगे ‘३’ (तीन) का अंक लिख दिया जाता है; जैसे- ओ३म्, गोपाइल, रा३म्, श्या३म् आदि। हिंदी में प्लुत स्वर का प्रयोग अब प्राय: नहीं किया जाता।
प्रश्न 8.
व्यंजन किसे कहते हैं?
उत्तर:
जिन वर्णों का उच्चारण करते समय हमारे मुँह से हवा थोड़ा रुक कर बाहर निकलती है, उन्हें व्यंजन कहते हैं। व्यंजन सदा स्वरों की सहायता से बोले जाते हैं, जैसे-
क् + अ = क, ल् + अ = ल, ट् + अ = ट आदि।
प्रश्न 9.
व्यंजनों के कितने भेद होते हैं? उनका वर्णन कीजिए।
उत्तर:
व्यंजनों के तीन भेद हैं। स्पर्श, अन्तःस्थ, ऊष्म।
(I) स्पर्श-जिन वर्णों का उच्चारण करते समय वायु कंठ, तालू, जिह्वा आदि उच्चारण स्थानों का स्पर्श करती है, उन्हें स्पर्श व्यंजन कहते हैं। ये संख्या में 25 होते हैं; जैसे-

(II) अन्तःस्थ-जिन व्यंजनों का उच्चारण करते समय जिह्वा पूरी तरह मुख के किसी भी भाग का स्पर्श नहीं करती उन्हें अन्तःस्थ व्यंजन कहते हैं। इनका उच्चारण स्वर और व्यंजन के बीच का-सा होता है। ये संख्या में चार होते हैं-य, र, ल, व्।
(III) ऊष्म-जिन वर्णों के उच्चारण के समय मुख से ऊष्मा अर्थात् गर्म हवा बाहर निकले और हल्की सीटी जैसी ध्वनि उत्पन्न हो, उन्हें ऊष्म व्यंजन कहते हैं, इनके उच्चारण में श्वास की प्रबलता रहती है। ये संख्या में चार होते हैंश्, ष, स्, ह। .
प्रश्न 10.
अयोगवाह किसे कहते हैं?
उत्तर:
हिंदी वर्ण माला में अयोगवाह न स्वर होते हैं और न ही व्यंजन। इनकी संख्या दो है- ‘अं’, ‘अः’। ‘अं’ को अनुस्वार और ‘अ’: को विसर्ग कहते हैं। इन्हें स्वतंत्र गति न होने के कारण स्वर नहीं कहा जा सकता। इनका प्रयोग स्वरों के साथ होने के कारण इन्हें व्यंजन भी नहीं कहा जा सकता। ये ध्वनि का वहन करते हैं; इसलिए इन्हें ‘अयोगवाह’ कहते हैं।
प्रश्न 11.
अनुस्वार किसे कहते हैं?
उत्तर- अनुस्वार (.) एक नासिक्य ध्वनि है। जब इसका उच्चारण किया जाता है। तब हवा केवल नाक से निकलती है। यह अपने से पहले आने वाले वर्ण के ऊपर बिंदु (.) रूप में लगता है; जैसे-
अंकित, अंत, रंक, पंक, डंक, गंद, कंस, आदि।
अनुस्वार का प्रयोग सभी वर्गों के पाँचवें नासिक्य व्यंजन (ङ्, ञ्, ण, न, म्) के स्थान पर किया जाता है; जैसे-
| शब्द |
उच्चरित रूप |
वर्ग विशेष से पूर्व |
| (I) कंघी, गंगा |
कङ्घी, गङ्गा |
कवर्ग से पहले ‘ङ’ रूप में |
| (II) चंचल, आंचल |
चञ्चल, आञ्चल |
चवर्ग से पहले ‘ज्’ रूप में |
| (III) डंडा, ठंडी |
डण्डा, ठण्डी |
टवर्ग से पहले ‘ण’ रूप में |
| (IV) निंदा, संध्या |
निन्दा, सन्ध्या |
तवर्ग से पहले ‘न्’ रूप में |
| (V) असंभव, अंबर |
असम्भव, अम्बर |
पवर्ग से पहले ‘म्’ रूप में |

प्रश्न 12.
अनुस्वार से संबंधित विशेष नियमों को लिखिए।
उत्तर:
(1) हिंदी में सरलता, सुविधा और एकरूपता के लिए अनुस्वार को वर्ण के ऊपर बिंदु (.) रूप में प्रयुक्त किया जाने लगा है। संस्कृत में अभी भी इसका प्रयोग बिंदु और परंपरागत रूप में किया जाता है।
(II) यदि ‘म्’ के पश्चात् व्यंजनों के अतिरिक्त अंत:स्थ (य, र, ल, व) या ऊष्म व्यंजन (श, ष, स, ह) में से कोई भी व्यंजन प्रयुक्त करना हो तो ‘म्’ अनुस्वार रूप में ही लिखते हैं; जैसे-संचार, संहार, संलग्न, संरचना, संयम, संयत, संशय, संसार आदि।
(III) ऊष्म व्यंजन श, ष, स् से पहले अनुस्वार अपने मूल रूप में प्रयुक्त होता है; जैसे–संसद्, संशय, कंस, वंश।
(IV) हिंदी में शब्द के अंत में ‘म्’ अनुस्वार में बदल जाता है; जैसे-अहं, स्वयं आदि।
(V) जहाँ नासिक्य व्यंजन संयुक्त रूप में होते हैं, वहाँ अनुस्वार का प्रयोग नहीं होता; जैसे-जन्म, वाङ्मय, मन्मथ, षण्मास आदि।
(VI) न, म्, आदि पंचम वर्ण जब संयुक्त रूप में प्रयुक्त होते हैं। तब अनुस्वार का प्रयोग नहीं किया जाता, जैसे गन्ना, पन्ना, धम्म, धन्ना, सम्मान, खुन्नस आदि।
(VII) यदि पंचम स्वर य, व, ह से पहले आता हो तो वहाँ अनुस्वार का प्रयोग नहीं होता; जैसे- पुण्य, गण्य, लावण्य आदि।
प्रश्न 13.
अनुनासिक किसे कहते हैं?
उत्तर:
जब किसी शब्द के उच्चारण में हवा, नाक और मुँह दोनों से ही निकलती है तो उसे अनुनासिक कहते हैं। यह अपने से पहले आने वाले वर्ण के ऊपर-चंद्रबिंदु () के रूप में लगाया जाता है; जैसे-काँख, आँख, गाँव, चाँद, मुँह आदि।
प्रश्न 14.
अनुनासिक को किस अवस्था में अनुस्वार के रूप में लिखा जा सकता है ? उदाहरण सहित लिखिए।
उत्तर:
जब किसी शब्द में स्वरों या मात्राओं का कोई भी अंश शिरोरेखा के ऊपर चला जाता है तो अनुनासिकता (*) के स्थान पर अनुस्वार (‘) का प्रयोग किया जाता हैं; जैसे- मैं, चौंक, गेंद, छींक आदि । इनमें ‘ऐ’, ‘औ’, ‘ए’ ‘इ’ की मात्राएँ शिरारेखा के ऊपर प्रयुक्त की गई है।
प्रश्न 15.
अनुस्वार और अनुनासिक में अंतर लिखिए।
उत्तर:
| अनुस्वार |
अनुनासिक |
| 1. यह एक व्यंजन है। |
1. यह एक स्वर है। |
| 2. इसका चिह्न बिंदु (.) है। |
2. इसका चिह्न चंद्रबिंदु (*) है। |
| 3. इसमें ‘न्’ ध्वनि ज़ोर देकर बोला जाता है। |
3. इसमें ‘न्’ ध्वनि ज़ोर देकर नहीं बोला जाता। |
| 4. इससे वर्ण दीर्घ हो जाता है। |
4. इसमें वर्ण दीर्घ नहीं होता। |
प्रश्न 16.
विसर्ग किसे कहते हैं? इसका प्रयोग कहाँ किया जाता है?
उत्तर:
विसर्ग (:) एक ध्वनि चिह्न है जिसका उच्चारण ‘इ’ व्यंजन के समान किया जाता है। इसका प्रयोग संस्कृत या हिंदी में प्रयुक्त किए जाने वाले संस्कृत शब्दों में किया जाता है। जैसे- स्वतः, प्रातः, दुःख, अतः, पुनः आदि।
प्रश्न 17.
हल और हलंत किसे कहते हैं? उदाहरण सहित लिखिए।
उत्तर:
स्वर के प्रयोग के बिना किसी व्यंजन के प्रयोग के लिए उसके नीचे लगी तिरछी-सी रेखा को हल कहते हैं और हल से युक्त व्यंजन या शब्द को हलंत कहते हैं; जैसे-
व = व् + अ
लेकिन व् = ‘अ’ स्वर में रहित ‘व’।
उदाहरण-विद्या, द्वारा, विद्यालय, रद्दी, आद्या।
हिंदी में हलंत का प्रयोग अब धीरे-धीरे कम होता जा रहा है।
प्रश्न 18.
आगत स्वर किसे कहते हैं? उदाहरण देकर लिखिए।।
उत्तर:
अंग्रेज़ी में अनेक शब्द ऐसे हैं जिनके शुद्ध उच्चारण और लेखन के लिए हिंदी में औ’ (अर्धचंद्राकार) ध्वनि को जोड़ा गया है। यह हिंदी की ‘आ’ और ‘ओ’ ध्वनि से अलग है। यह ओष्ठों की स्थिति के अनुसार वृत्तमुखी और जीभ के अनुसार अर्ध विवृत स्वर है। उदाहरण-टॉफी, मॉनीटर, बॉल, नॉलेज, डॉक्टर, कॉलेज, टॉय, कॉफी, बॉक्स, कॉलोनी, मॉडल आदि।
प्रश्न 19.
हिंदी में विकसित ध्वनियाँ कौन-कौन सी हैं? इनका विकास किन व्यंजनों से हुआ है?
उत्तर:
हिंदी में ‘ङ’ और ‘ढ’ विकसित ध्वनियाँ हैं जो क्रमशः ‘ड’ और ‘ढ’ से बनी हैं। ये दोनों टवर्ग से संबंधित
उदाहरण-बढ़, कढ़ाई, उड़ान, बढ़ना, सड़क, जड़, उजाड़, बुढ़िया, चढ़ाई, गुड़िया आदि।
हिंदी शब्दों के आरंभ में ‘ड’ और ‘ढ’ का प्रयोग कभी नहीं होता। इन्हें शब्दों के बीच और अंत में प्रयोग किया जाता है; जैसे-शब्द के बीच में-बढ़ना, लड़ाई, लड़ना, उजड़ना, सड़ना, पढ़ना, बढ़ना।
शब्द के अंत में-उजाड़, झाड़, सड़, ताड़, बाढ़, पढ़, मारवाड़।
प्रश्न 20.
आगत व्यंजन किसे कहते हैं?
उत्तर:
हिंदी में जिन अंग्रेज़ी, उर्दू, अरबी, फ़ारसी आदि शब्दों का प्रयोग प्रायः होता है उन्हें आगत शब्द कहते हैं। इन्हें शुद्ध रूप से बोलने और लिखने के लिए ‘क’, ‘ख’, ‘ग’, ‘ज’, और ‘फ’ व्यंजनों के नीचे बिंदु (नुक्ता) लगाया जाता है और उन्हें आगत व्यंजन कहते हैं। यदि ऐसा न किया जाए तो ध्वनियों के परिवर्तन के कारण अर्थ में बदलाव आ जाता है; जैसे-
| राज-शासन |
राज-रहस्य |
| फन–साँप का सिर |
फ़न-कौशल |
| फलक-लकड़ी का तख्ता |
फ़लक-आकाश |
| जरा-बुढ़ापा |
ज़रा-थोड़ा |
| कदर-आँख, अंकुश |
क़दर-प्रतिष्ठा, मान |
| खुदा-उत्कीर्ण |
खुदा-भगवान् |
| खाना-भोजन |
ख़ाना-घर, मकान, अलमारी, आदि का ख़ाना |
| गौर-उज्ज्वल |
गौर-सोच-विचार। |
प्रश्न 21.
अंग्रेज़ी और उर्दू में प्रयोग किए जाने वाले ‘ज़’ और ‘फ़’ वर्ग वाले कुछ शब्दों के उदाहरण दीजिए जो हिन्दी में भी प्रयुक्त किए जाते हैं।
उत्तर:
I. उर्दू से आए ‘ज’ वर्ग वाले शब्द-ज़ोर, नाज़, मज़ेदार, ज़बान, ज़माना, हमराज़, जिंदा, ज़मीन, ज़बरदस्त, जेवर, जब्त, बाजी, फर्ज, कर्ज, ज़फ़र, प्याज़, ज़िक्र।
अंग्रेज़ी से आए ‘ज़’ वर्ण वाले शब्द-ज़ीरो, क्विज़, मेज़र, इज़ी, ट्रेजरर, क्रेज़ी, ट्रेज़टी, पीज़ा, जोन, फ़िज़िक्स, प्राइज़, जेब्रा, अंग्रेज़ी, रोज़, रिवीज़न, फिज़िकल।
II. उर्दू से आए ‘फ़’ वर्ण वाले शब्द-फ़ाका, फ़रियाद, फ़लसफा, फारसी, फ़रज़ी, फ़रेब, फ़जूल, फ़जीहत, गिलाफ़, फ़रमान, सिफ़ारिश, सफ़ेद, बरफ़, शराफ़त, फ़ौजी, हफ़्ते, फ़र्क, फ़ायदा, काफ़ी।
अंग्रेज़ी से आए ‘फ़’ वर्ण वाले शब्द-फ़न, कॉफ़ी, फ्रूट, फ़िल्म, फ्री, फ्रेक्चर, कफ़, फ़न, फुटबॉल, फ़ाइव, फ़ील, फ़ाइल, फ़िटर, फ़ीचर, फ़िल्टर, फ़ेल, फ़ार्म, फ़ादर, फ़ोर, फ़ारेन, फ़िजिक्स, फ़ार्मूला, फ़ार्मेसी, फ़ायर।
प्रश्न 22.
‘मात्रा’ किसे कहते हैं? स्वरों का जब व्यंजन वर्गों में मेल होता है तो उनके रूप कैसे बन जाते हैं? लिख कर स्पष्ट करें।
उत्तर:
किसी वर्ण के उच्चारण में लगने वाले समय के अंश को मात्रा कहते हैं। इन्हें निम्नलिखित ढंग से लिखा जा सकता है-
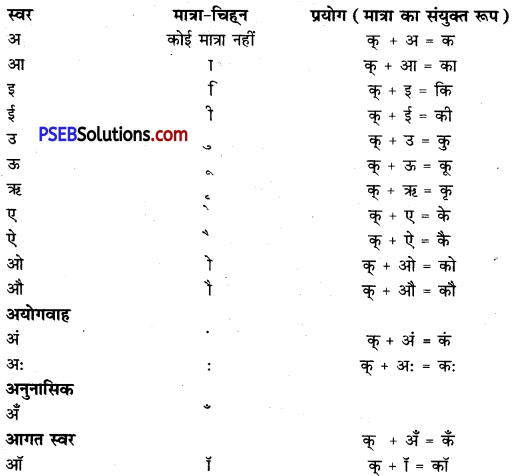
प्रश्न 23.
‘र’ व्यंजन में ‘उ’ और ‘ऊ’ मात्राएँ कैसे लगाई जाती हैं ? उदाहरण सहित स्पष्ट करें।
उत्तर:
‘र’ व्यंजन में ‘उ’ और ‘ऊ’ मात्राएँ नीचे न लग कर सामने की ओर लगती हैं; जैसे-र + उ = रुचि, रुपया, रुबी, रुमाल, र + ऊ = रुपया, रूखा, अमरूद, बारूद।
प्रश्न 24.
संयुक्त व्यंजनों को किस-किस प्रकार लिखा जा सकता है? स्पष्ट कीजिए।
उत्तर:
जब व्यंजन को दूसरे व्यंजन से मिला कर लिखा जाता है तो संयुक्त ध्वनियों की रचना होती है। स्वर-रहित व्यंजन को हलंत किया जाता है या अगले व्यंजन के साथ मिलाकर लिख दिया जाता है। प्रायः संयुक्त व्यंजनों को दो प्रकार से लिखा जाता है-
I. खड़ी पाईं (1) के साथ-देवनागरी लिपि में जिन व्यंजनों के साथ खड़ी रेखा मिलती है। उन्हें पाई (1) कहते हैं, जैसे-ख्, ग, घ, च्, ज, झ्, ण, त्, थ, ध्, न्, प, ब्, भ, म्, य, ल, व्, श, ष, स्। जब इन्हें आगे वाले व्यंजन से मिलाया जाता है तो इनकी पाई हटा दी जाती है, जैसे-
ग् + व = ग्व (ग्वाला), प् + य = प्य (प्यार) ल् + क = ल्क (शुल्क), न् + न = न्न (गन्ना), थ् + य = थ्य (तथ्य), त् + थ = त्थ (पत्थर), म् + म = म्म (सम्मान), स् + ट = स्ट (स्टूल), व् + य = व्य (व्यस्क), य् + य = य्य (नैय्या), ल् + ल = ल्ल (हल्ला), ष् + ठ = ष्ठ (वशिष्ठ), ध्, य = ध्य (संध्या), ण् + ड = ण्ड आदि। (तुण्ड), ज् + व = ज्व (ज्वार), च् + च = च्च (जच्चा) आदि। देवनागरी लिपि में ‘क’ और ‘फ’ व्यंजनों के बीच में खड़ी पाई का प्रयोग किया जाता है। इन्हें अगले वर्ण से मिलाकर लिखा जाता है। खड़ी पाई के बाद के हिस्से से नीचे के भाग को हटा दिया जाता है, जैसे-
क् + य = क्य (वाक्य), क् + ल = क्ल (शक्ल), क् + त = क्त (सूक्त), फ़् + ल = पल (फ़्लास्क), फ़् + ल = फ़्ल (फ़्लू) आदि।
II. बिना पाई वाले व्यंजन–देवनागरी लिपि में ‘छ’, ‘ट’, ‘ठ’, ‘ड’, ‘ढ’, ‘ढ’, ‘ट’, ‘ट’ बिना पाई वाले व्यंजन हैं। जब इन्हें अगले व्यंजनों (‘र’ के अतिरिक्त) से मिला कर लिखा जाता है तो हलंत का प्रयोग किया जाता है; जैसे— द् + य = द्य (विद्यालय), ट् + ट = ट्ट (मिट्टी), ट् + ठ = ट्ठ (मट्ठी), ठ् + य = ठ्य (सुपाठ्य), ड् + ढ = ड् (गड्ढा ) = ह् + य = ह्य (दुःसह्य)।
प्रश्न 25.
हिन्दी में प्रचलित मानक और मानकेतर शब्दों की एक सारणी तैयार कीजिए।
उत्तर:
हिन्दी में संयुक्त व्यंजनों के मानक और मानकेतर रूप प्रचलन में हैं। वर्तमान में एकरूपता के लिए मानक व्यंजनों को अधिक महत्त्व दिया जाता है। लेकिन मानकेतर रूप को अशुद्ध भी नहीं माना जाता। यह संभव हो सकता है कि भविष्य में मानकेतर रूप का धीरे-धीरे प्रचलन समाप्त हो जाए। वर्तमान में भी इनका प्रयोग अपेक्षाकृत कम हो गया है, जैसे-
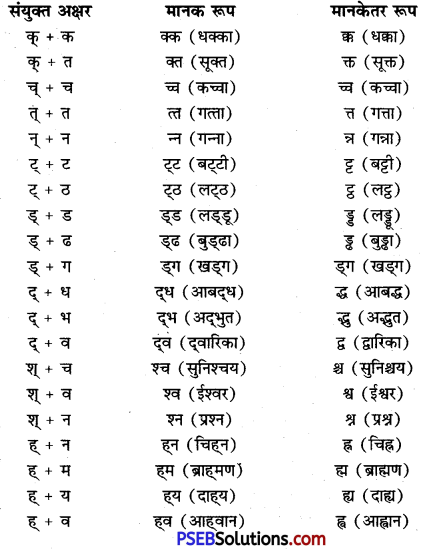
प्रश्न 26.
द्वित्व वर्ण किसे कहते हैं? स्पष्ट कीजिए।
उत्तर:
जब किसी एक शब्द में कोई व्यंजन दो बार आ जाए तो उसे द्वित्व वर्ण कहते हैं। इनमें पहला व्यंजन स्वर रहित और दूसरा स्वर युक्त होता है; जैसे-
पक्का, धक्का, टट्ट, हड्डी, फट्टा, गत्ता, चक्का, मुक्का, डिब्बा, लट्ट, बिट्ट आदि।
प्रश्न 27.
द्वित्व वर्ण की रचना में किन बातों का ध्यान रखना चाहिए?
उत्तर-वर्णमाला के दूसरे और चौथे वर्णों को द्वित्व नहीं हो सकता। जब किसी स्थिति में दूसरे और चौथे वर्णों के द्वित्व होने का आभास होता है तो वहाँ वर्ग के पहले-दूसरे तथा तीसरे-चौथे वर्गों का मेल माना जाना चाहिए; जैसे-
(क) पहले-दूसरे वर्गों का मेल-पत्थर, मच्छर, अच्छाई, अक्खड़, मक्खी आदि शब्दों में दूसरे वर्ण के द्वित्व होने का होने का आभास होता है। नियमानुसार इनमें दूसरे वर्ण के साथ उसी वर्ग का पहला वर्ण जोड़ दिया गया है।
(ख) तीसरे-चौथे वर्गों का मेल-शुद्ध, बौद्ध, बुड्ढा, घग्घर आदि शब्दों में चौथे वर्ण से द्वित्व होने का आभास होता है लेकिन नियम के अनुसार उसके साथ उसी वर्ग का तीसरा वर्ण लगा दिया गया है।
प्रश्न 28.
‘र’ और ‘ऋ’ में क्या अंतर है?
उत्तर:
‘र’ एक व्यंजन है और ‘ऋ’ स्वर है। हिन्दी में ‘ऋ’ का उच्चारण ‘रि’ के रूप में किया जाता है।
प्रश्न 29.
व्यंजनों के साथ ‘र’ लगाने के नियम लिखिए।
उत्तर:
(क) स्वर ‘ऋ’ के अतिरिक्त किसी भी स्वर ‘र’ के बाद आता है तो ‘र’ पूरा लिखा जाता है; जैसे- रख, राम, रिक्शा, रीढ़, रुपया, रूठना, रेखा, रैली, रोना, रौब।
(ख) स्वर से रहित ‘र’ रेफ (‘) कहलाता है जो अपने से अगले व्यंजन के ऊपर लगता है, जैसे कर्म, गर्म, चर्म, टर्न, वर्ष, पूर्वज, पर्वत, कर्क, बर्फ आदि।
(ग) ‘र’ से पहले यदि ‘क्’, ‘ग्’, ‘घ’, ‘थ्’, ‘ब’, ‘भ्’, ‘ध्’ ‘प्’, ‘फ्’ हों तो यह ‘प्र’ (पदेन ‘र’) के रूप में दिखाई देता है, जैसे-क्रम, ग्रास, घ्राण, थ्रो, ब्राह्मण, भ्रांति, ध्रुवीय, प्रेम, फ्रॉक।
(घ) यह त्, श् और स् के साथ क्रमशः ‘त्र’, ‘श्र’, ‘स’ रूप में दिखाई देता है; जैसे-
त् + र = त्र (तत्र, सत्र)
श् + र = श्र (श्रवण, श्रद्धा)
स् + र = स्र (स्रोत, सहस्र)।
(ङ) जब ‘स्’ के साथ त्र मिलता है तो ‘स्त्र’ बनता है, जैसे शस्त्र, शास्त्र।
(च) बिना पाई वाले व्यंजनों ‘ट्’ और ‘ठ’ के र () रूप में लिखा जाता है; जैसे-
ट् + र = ट्र (राष्ट्र, ट्राम, ड्रम, ट्रिन-ट्रिन)
(ज) ‘द’ के साथ ‘र’ पदेन र का रूप ले लेता है; जैसे-
द् + र = द्र (द्रव, द्राक्षासव, विद्रुम, उपद्रव, विद्रोह, द्रोणाचार्य, द्रोही, द्रविड़, रुद्र आदि)
(झ) यदि ‘र’.से पहले ‘ह’ हो तो ‘ह्’ बनता है; जैसे
ह् + र = ह् (ह्रस्व)
उदाहरण-ह्रास, ह्रासोन्मुख, ह्री।।
प्रश्न 30.
संयुक्त व्यंजन किसे कहते हैं? स्पष्ट कीजिए।
उत्तर:
कुछ व्यंजन दो वर्गों के संयोग से बनते हैं। ये स्वतंत्र नहीं होते। जब स्वर रहित व्यंजन किसी स्वर सहित व्यंजन से मिलकर लिखे जाते हैं तो उन्हें संयुक्त व्यंजन कहते हैं। जैसे-
क् + ष = क्ष – क्षमा, रक्षा, क्षत्रिय,
विक्षिप्त। त् + र = त्र – नेत्र, नेतायुग, पवित्र, पुत्र।
ज् + उ = ज्ञ – ज्ञान, विज्ञान, ज्ञापित, विज्ञापन।
श् + र = श्र – श्रीमान, श्रीमती, श्रीफल, श्रमिक।
प्रश्न 31.
संस्कृतनिष्ठ भाषा बोलने वाले विद्वान् ‘ज्ञ’ का उच्चारण कैसे करते हैं और क्यों?
उत्तर:
संस्कृतनिष्ठ भाषा बोलने वाले विद्वान् ‘ज्ञ’ को ‘ज्व’ रूप में उच्चारित करते हैं जबकि हिन्दी भाषी इसे ‘ग्य’ रूप में बोलते हैं। ये दोनों रूप मानक हैं। हिन्दी भाषा यदि ‘विज्ञान’ को ‘विज्यान’ बोलते हैं तो संस्कृत भाषी ‘विज्ञान’ बोलते हैं।
प्रश्न 32.
यदि ‘ऋ’ से पहले स्वर रहित ‘श्’ आ जाए तो संयुक्त रूप में क्या परिवर्तन हो जाता है? उदाहरण भी दीजिए।
उत्तर:
यदि ‘ऋ’ से पहले स्वर रहित ‘श्’ आ जाए तो वह संयुक्त रूप में शृ’ बन जाता है; जैसे-शृंगार, श्रृंगी, श्रृंखला, शृंगाल, श्रृंगारिक, विश्रृंखल।
प्रश्न 33.
वर्ण विच्छेद से क्या तात्पर्य है?
उत्तर:
वास्तव में ‘वर्ण’ का विच्छेद कभी नहीं हो सकता लेकिन यहाँ ‘वर्ण विच्छेद’ से तात्पर्य है-किसी शब्द के वर्गों को अलग-अलग करना।
प्रश्न 34.
वर्ण विच्छेद करते समय किन-किन बातों की ओर ध्यान में रखा जाना चाहिए?
उत्तर:
वर्ण, विच्छेद करते समय निम्नलिखित बातों की ओर ध्यान रखा जाना चाहिए
I. स्वर से रहित व्यंजनों को हलंत () रूप में लिखा जाना चाहिए; जैसे-
पुस्तक = प + उ + स् + त् + अ + क् + अ
कलम = क् + अ + ल् + अ + म् + अ।
टमाटर = ट् + अ + म् + आ + ट् + अ + र् + अ
शलजम = श् + अ + ल् + अ + ज् + अ + म् + अ
II. स्वरों का मूल रूप में विच्छेद नहीं होता और न ही उनके नीचे कभी हलंत लगता है; जैसे-
उल्लू = उ + ल् + ल् + ऊ
उदय = उ + द् + अ + य् + अ
ऐनक = ऐ + न् + अ + क् + अ
इमली = इ + म् + अ + ल् + ई
III. मात्राओं वाले शब्दों का विच्छेद ध्यानपूर्वक करना चाहिए। स्वरों को हलंत नहीं लगाना चाहिए, जैसे यदि किसी शब्द में कोई स्वर मूल रूप में हो तो उसका विच्छेद नहीं किया जाना चाहिए; जैसे-
एकता = ए + क् + अ + त् + आ
अनुपम = अ + न् + उ + प् + अ + म् + अ
कूल = क् + ऊ + ल् + अ
कृपा = क् + ऋ + प् + आ
उपयोगिता – उ + प् + य् + ओ + ग् + इ + त् + आ
केरल = क + ए + र् + अ + ल् + अ
कृपावान = क् + ऋ + प् + आ + व् + आ + न् + अ
किला = क् + इ + ल् + आ
किसान = क् + इ + स् + आ + न् + अ
कौरव = क् + औ + र् + अ + व् + अ
कैसा = क् + ऐ + स् + आ ..
हृदय = ह् + ऋ + द् + अ + य् + अ
हार्दिक = ह् + आ + र् + द् + इ + क् + अ
IV.(क) अनुस्वार (स्पर्श व्यंजनों के साथ) वाले शब्दों के वर्ण विच्छेद में पंचम स्वर के स्थान पर अनुस्वार () का ही प्रयोग होता है लेकिन कुछ विद्वान् अभी भी पंचम अक्षर का प्रयोग करते हैं जिसे गलत नहीं माना जाता; जैसे-
पतंगा = प् + अ + त् + अं + ग् + आ
चंचल = च् + अं + च् + अ + ल् + अ
तंदूर = त् + अं + द् + ऊ + र् + अ
दंडित = द + अं + ड् + इ + त् + अ .
कंजूस = क् + अं + ज् + ऊ + स् + अ
(ख) सम्’ उपसर्ग के बाद अंत: स्थ (य, र, ल, व) या ऊष्म (श, स, ह) व्यंजन आने पर अनुस्वार (‘) का प्रयोग किया जाता है; जैसे-
संशय = स् + अं + श् + अ + य् + अ
संसार = स् + अं +. स् + आ + र् + अ
संवादात्मकता = स् + अं + व् + आ + द् + आ + त् + म् + अ + क् + अ + त् + आ
विसंहार = व् + इ + स् + अं + ह् + आ + र् + अ
संयत = स् + अं + य् + अ + त् + अ
संयोग = स् + अं + य् + ओ + ग् + अ
5. पूरा रूप बदलने वाले संयुक्त व्यंजनों (ज्ञ, त्र, क्ष) का वर्ण-विच्छेद करते हुए उनके मूलरूप को ध्यान में रखा जाना चाहिए, जैसे-
पवित्रता = प् + अ + व् + इ + त् + र् + त् + आ
कक्षा = क् + अ + क् + ष् + आ
ज्ञानवान = ज् + ञ् + आ + न् + अ + व् + आ + न् + अ
श्रमिक = श् + र् + म् + इ + क् + अ
श्रीमान = श् + र् + ई + म् + आ + न् + अ
जयश्री = ज् + अ + + अ + श् + र् + ई
6. अन्य संयुक्त अक्षरों का वर्ण विच्छेद करते समय खड़ी मध्य और बिना पाई वाले व्यंजनों के संयोग की ओर ध्यान दिया जानना चाहिए; जैसे-
विख्यात = व् + इ + ख् + य् + आ + त् + अ
ज्वर = ज् + व् + अ + र् + अ
ग्वालिन = ग् + व् + आ + ल् + इ + न् + अ।
क्लांति = क् + ल् + आ + त् + इ
फ्लै शबैक = फ् + ल् + ऐ + श् + अ + ब + ऐ + क् + अ
समन्वय = स् + अ + म् + अ + न् + व् + अ + य् + अ
गड्ढा = ग् + अ + ड् + ल् + आ
दृश्यमान = द् + ऋ + श् + य् + अ + म् + आ + न् + अ
बाह्य = ब् + आ + ह् + य् + अ
सुपाठ्य = स् + उ + प् + आ + ल् + य् + आ
7. द्वित्व व्यंजन वाले शब्दों के वर्ण विच्छेद में विशेष ध्यान देने की आवश्यकता होती है। जैसे-
कच्चा = क् + च् + च् + आ
पक्की = प् + अ + क् + क् + ई.
खट्टी = ख् + अ + ट् + ट् + ई
सुशैय्या = स् + उ + श् + ऐ + य् + य् + आ
पत्थरीला = प् + अ + त् + थ् + अ + र् + ई + ल् + आ
मच्छर = म् + अ + च् + छ् + अ + र् + अ
8. ‘र’ के विभिन्न रूपों वाले शब्दों का वर्ण विच्छेद करते समय ‘र’ के रूप की ओर ध्यान दिया जाना चाहिए; जैसे-
राम = र् + आ + म् + अ
राजेश्वर = र् + आ + ज् + ए + श् + व् + अ + र् + अ
रात = र् + आ + त् + अ
मर्म = म् + अ + र् + म् +. अ
कार्मिक = क् + आ + र् + म् + इ + क् + अ
अधर्म = अ + ध् + अ + र् + म् + अ
क्रम = क् + र् + अ + म् + अ
प्रीतम = प् + र् + ई + त् + अ + म् + अ
अतिशीघ्र = अ + त् + इ + श् + ई + घ् + र् + अ
मेलट्रेन = म् + ए + ल् + अ + ट् + र् + ए + न् + अ
द्रविड़ = द् + र् + अ + व् + इ + ङ् + अ
सुपुत्र = स् + उ + प् + उ. + त् + त् + अ
ह्रस्व = ह् + र् + अ + स् + व् + अ
हासोनुमुख = ह् + र् + आ + स् + ओ + न् + उ + म् + उ + ख् +अ
मित्रता = म् + इ + त् + र् + अ + त् + आ
श्रावण = श् + र् + आ + व् + अ + ण् + अ
विग्रह = व् + इ + ग् + र् + अ + ह् + अ
![]()
![]()