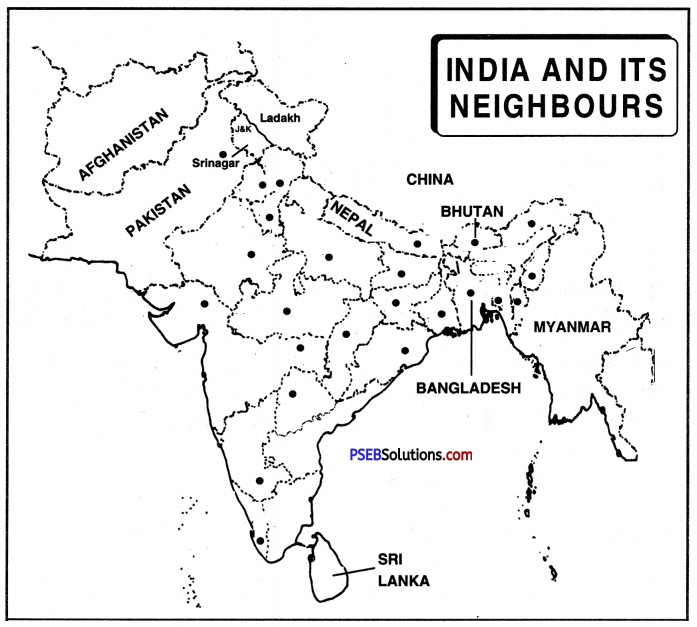
Punjab State Board PSEB 9th Class Social Science Book Solutions History Chapter 4 Sri Guru Arjan Dev Ji: Contribution in the Development of Sikhism and his Martyrdom Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
PSEB Solutions for Class 9 Social Science History Chapter 4 Sri Guru Arjan Dev Ji: Contribution in the Development of Sikhism and his Martyrdom
SST Guide for Class 9 PSEB Sri Guru Arjan Dev Ji: Contribution in the Development of Sikhism and his Martyrdom Textbook Questions and Answers
I. Multiple Choice Questions:
Question 1.
The name of Guru Arjan Dev Ji’s mother was .
(a) Bibi Bhani
(b) Shabrai Devi
(c) Bibi Amro
(d) Bibi Anokhi.
Answer:
(a) Bibi Bhani.
Question 2.
The name of the eldest son of Guru Ram Das Ji was
(a) Mahadev
(b) Arjan Dev
(c) Prithichand.
Answer:
(c) Prithichand.
Question 3.
In which fort Jahangir imprisoned Guru Hargobind Ji?
(a) Gwalior
(b) Lahore
(c) Delhi
(d) Jaipur.
Answer:
(a) Gwalior.
![]()
Question 4.
Where did Khusrau meet Guru Arjan Dev Ji?
(a) Goindwal
(b) Hargobindpur
(c) Kartarpur
(d) Santokhsar.
Answer:
(a) Goindwal.
Question 5.
When was Sri Guru Arjan Dev Ji martyred by Jahangir?
(a) 24 May, 1606 A.D.
(b) 30 May, 1606 A.D.
(c) 30 May, 1581 A.D.
(d) 24 May, 1675 A.D.
Answer:
(b) 30: May 1606. A.D.
II. Fill in the blanks :
Question 1.
Guru Arjan Dev Ji’s period was from __________ upto
Answer:
1581-1606 A.D.
Question 2.
In 1590, Sri Guru Arjan Dev Ji constructed a sarovar __________
Answer:
Tarn Taran.
III. Match the Columns:
Question 1.
|
A |
B |
| 1. Martyrdom of Sri Guru Arjan Dey Ji | (i) Jahangir |
| 2. MiriPiri | (ii) 30th May, 1606 |
| 3. Saint Mian Mir | (iii) Sri Guru Hargobind Sahib Ji |
| 4. Khusrau | (iv) Foundation stone of Harmandir Sahib Ji |
Answer:
|
A |
B |
| 1. Martyrdom of Sri Guru Arjan Dey Ji | (ii) 30th May, 1606 |
| 2. MiriPiri | (iii) Sri Guru Hargobind Sahib Ji |
| 3. Saint Mian Mir | (iv) Foundation stone of Harmandir Sahib Ji |
| 4. Khusrau | (i) Jahangir |
IV. Differentiate between:
Question 1.
Miri and Piri.
Answer:
Guru Hargobind Sahib put on two swords which he called one of Miri and the other of Piri. His sword of Miri symbolized his leadership of the Sikh followers in worldly affairs. The Piri sword represented his leadership of the Sikhs in spiritual affairs.
![]()
V. Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Who was the fifth Guru of the Sikhs?
Answer:
Sri Guru Arjan Dev Ji.
Question 2.
When and who laid the foundation of Harmandir Sahib Ji?
Answer:
The foundation of Harmandir Sahib Ji was laid by a famous Sufi Saint Mian Mir in 1588 A.D.
Question 3.
To whom Guru Arjan Dev Ji got dictate Adi Granth Sahib Ji?
Answer:
Bhai Gurdas Ji.
Question 4.
When was the compilation of Adi Shri Guru Granth Sahib Ji completed?
Answer:
In 1604 A.D.
Question 5.
Who was the leader of Naqshbandi?
Answer:
Shaikh Ahmad Sirhindi.
Question 6.
Who was the first Granthi of Harmandir Sahib?
Answer:
Baba Buddha Ji.
![]()
Question 7.
What do you mean by Daswandh?
Answer:
The meaning of Daswandh is each Sikh must give one tenth of his income in the name of Guru.
VI. Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
To whom did Sri Guru Ram Das Ji give Guruship and when?
Answer:
Guru Ram Das Ji wanted to give Guru Gaddi to one of his three sons. Guru Ji thought about it. Out of all three one (Mahadev) was a Faqir. He had no interest in worldly affairs. So Guru Ji did not give him Guru Gaddi. Guru Ji’s second son Prithi Chand was also considered incapable because he was not fit for Guru Gaddi. Under these circumstances, Guru Ji declared his younger son Arjan Dev as his successor in 1581 A.D.
Question 2.
Describe the Martyrdom of Sri Guru Arjan Dev Ji.
Answer:
The Mughal Emperor Akbar had very cordial relations with Guru Arjan Dev Ji. However, Jahangir the next Mughal emperor abandoned the policy of toleration after the death of Akbar. Jahangir was on the look out for an oppourtunity to give mortal blow to Sikh religion. In the meantime, Prince Khusro, the son of Jahangir, revolted against his father. After being defeated at the hand of his father, Khusro came to Guru Arjan Dev Ji. Guru Sahib blessed him. Jahangir imposed a fine of two lakh rupees on Guru Sahib on the charge of helping rebellious Khusro. Guru Sahib showed his inability to pay. As a result, Guru Sahib was detained and subjected to severe torture. It infuriated the Sikhs. The Sikhs learned that the only course then left open to them was to rise in arms for the protection of their religion.
Question 3.
What do you mean by religious intolerance of Jahangir?
Answer:
Unlike Akbar, Emperior Jahangir was a fundamentalist Muslim. He wanted to spread his religion. But people of all the religions and castes were very much influenced with the teachings and generosity of Sikhism and were adopting Sikhism. Jahangir did not tolerate the growing influence of Sikhism and started doing jealousy with Sikhism. That is why he martyred Guru Arjan Dev Ji.
Question 4.
Who was Chandu Shah? Why did he turn against Guru Arjan Dev Ji?
Answer:
Chandu Shah was a high ranking official of the Mughal administration in Punjab. Guru Arjan Dev Ji had declined to marry the daughter of Chandu Shah to his own son on the suggestion of Sikh Sangat. Chandu Shah felt insulted and tried to instigate Akbar against Guru Sahib with the motive of taking revenge. Akbar held Guru Sahib in high esteem and considered himself as a friend of Guru Sahib. Akbar did not give any importance to the grumbling of Chandu Shah. Chandu Shah did not stop conspiring against Guru Sahib. After the death of Akbar, Chandu Shah instigated Jahangir and convinced him that Guru Sahib had helped the rebellious Prince Khusro. Jahangir had already decided to end the religious movement of Guru Sahib. The instigation by Chandu Shah further provoked Jahangir to take a strong step against Guru Sahib.
![]()
Question 5.
What was the immediate cause of Sri Guru Arjan Dev Ji’s martyrdom?
Answer:
The martyrdom of Guru Arjan Dev Ji took place in May 1606 A.D. The major reason behind this martyrdom was Jahangir’s fundamentalist religious policy. He wanted to curb the growing popularity of Sikhism. Guru Ji gave blessings to Khusro, son of Jahangir. It was considered a political crime. Moreover, the compilation of Sri Adi Granth Sahib Ji by Guru Arjan Dev Ji further increased the suspicion of Jahangir. The opponents of Guru Ji told Jahangir that lot is written in Sri Adi Granth Sahib against Islam. So, Jahangir called Guru ji to his court. He ordered Guru Ji to write something on prophet Mohammad but Guru Ji refused his order. So Jahangir issued an order to put Guru Sahib to death by torture.
Question 6.
What was the role of Masand System in the development of Sikh religion?
Answer:
The Masand System played an important role in the development and organisation of the Sikh religion. The importance of the Masand System for Sikh religion was as under :
1. The system ensured regular and fixed donations for the Guru Gaddi. .With a fixed income from donations, Guru Sahib was able to undertake much constructive work for the development of Sikh religion. Guru Arjan Dev Ji not only built tanks at Amritsar and Santokhsar, but also built new cities, constructed ponds, dug wells, etc.
2. Masand System, not only ensured fixed donations, but also helped in spreading the message of Sikh religion more enthusiastically. Earlier, the work of spread of religion was done through Manji system. It was confined only to the Punjab during those days. However, Guru Arjan Dev Ji appointed Masands even outside Punjab. It helped in the spread of Sikh religion even outside.
3. Guru Sahib started holding his own court when he had an assured income through Masand System. The Masands and the devoted Sikhs brought donations and gifts to the court of Guru Arjan Dev Ji on every Baisakhi day and bowed their heads before him to seek his blessings. Gradually, the court of Guru Sahib acquired the status of a court of an emperor for the Sikhs and Sikh Sangat started calling Guru Arjan Dev Ji as Sachcha Padshah (The True Emperor) out of love and devotion for him.
VII. Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is the contribution of Guru Arjan Dev Ji in the development of Sikh religion? Discuss in detail.
Answer:
The history of Sikh religion entered a new phase with the coming of Guru Arjan Dev Ji to Guru Gaddi. It was the result of his efforts that Sikhs were blessed with Harmandir Sahib Ji and numerous other places of pilgrimage. Not only that, the Sikhs got their first sacred and divine book when Guru Arjan Dev Ji compiled the Adi Granth Sahib. The Hindus had their Ramayana, the Muslims their Quran Sharif, the Christians their Bible, and the Sikhs their Guru Granth Sahib Ji.
A brief description of the activities and contribution of Guru Arjan Dev Ji is given as follows :
1. Construction of Sri Harmandir Sahib: Guru Arjan Dev Ji completed the work of construction of Amritsar and Santokhsar Sarovars after the expiry of Guru Ram Das Ji. Guru Sahib constructed Sri Harmandir Sahib in the midst of Amritsar Sarovar. Guru Sahib constructed a door each in all the four directions of Sri Harmandir Sahib. These four doors convey the message that Sri Harmandir Sahib is open to all the religions, castes and tribes without any discrimination. Guru Sahib told his followers that a pilgrimage to Sri Harmandir Sahib would bestow the benefit of 68 places of pilgrimage of the Hindus. In this manner, Sri Harmandir Sahib became one of the most sacred and important religious places.
2. Foundation of Tarn Taran. Guru Arjan Dev Ji founded the city of Tarn Taran as well. The city was founded in the heart of Majha region. It is also an important place of pilgrimage like Amritsar for th§ Sikhs. Guru Ji also constructed many other buildings and Sarovars.
3. Construction of Baoli at Lahore. On his tour to Lahore, Guru Arjan Dev Ji got constructed a Baoli in the Dubbi Bazaar. The Baoli soon became an important place of pilgrimage for the Sikhs of the surrounding region..
4. Foundation of Hargobindpur and Chheratta. Guru Arjan Dev Ji founded the city of Hargobindpur on the banks of river Beas to celebrate the birth of his son Hargobind Ji. Apart from this he also got a well dug at Chheratta near Amritsar in order to provide water to the local people. Guru Sahib also arranged for six pulleys to draw water from the well and the area is known after those pulleys as Chheratta.
5. Foundation of Kartarpur. In 1593, Guru Arjan Dev Ji founded the city of Kartarpur and also built a Sarovar in Kartarpur which is called Gangsar.
6. Improvement in the Masand System. Guru Arjan Dev Ji felt the need to improve Masand system. Guru Sahib instructed the Sikh followers to deposit one- tenth (Daswandh) of their annual income with the Masands. The Masands deposited the collections in the main treasury (Guru Ki Golak) at Amritsar on every Baisakhi day. The Masands appointed their representatives to collect donations. Those representatives were called Sangatias. The one-tenth donation was called Daswandh. Apart from the work of collection of Daswandh, the Masands also spread the message of Sikh religion.
7. Compilation of the Adi Granth Sahib. Guru Arjan Dev Ji bestowed upon the Sikhs a sacred and religious book by compiling the Adi Granth Sahib. Guru Arjan Dev Ji compiled Adi Granth Sahib at Ramsar. Bhai Gurdas Ji assisted Guru Sahib in its compilation. The work of compilation was completed in 1604. Guru Sahib included the hymns of first four Gurus, followed by the hymns of Bhakti saints and finally the sayings of Bhatt Bahiyan. Guru Arjan Dev Ji also included his own Vani in the holy book.
8. Encouraged Horse Trade. Guru Arjan Dev Ji encouraged the Sikhs to start trading in horses. The Sikhs were benefited from the trading in horses in the following ways :
(1) Trading in horses was the most profitable business in those days. As a result, the Sikhs became very rich by trading in the horses. They contributed Daswandh regularly out of their income from this trade.
(2) The Sikhs became fully trained in making selection of good horses. It helped them in the long run in organising a Sikh cavalry.
9. Spread of Religious Teachings. Guru Arjan Dev Ji made many people his followers by his religious teachings. Guru Sahib impressed the people with his ideals, teachings, amiable personality, sweet temper, and toleration. Many Muslims also joined the Sikh religion under the influence of Guru Arjan Dev Ji.
Thus the Sikh religion progressed tremendously under the spiritual leadership of Guru Arjan Dev Ji. The Adi Granth Sahib, the most sacred book of the Sikhs, was compiled, the cities like Tarn Taran, Kartarpur,® Hargobindpur, were founded and the Sikh religion was blessed with Sri Harmandir Sahib.
![]()
Question 2.
What were the reasons behind Guru Arjan Dev Ji’s martyrdom? Discuss.
Answer:
Guru Arjan Dev Ji was one of those great saints of the world who sacrificed their lives for the sake of their religion. The circumstances which were responsible for the martyrdom of Guru Sahib were as follows :
1. Fanaticism of Jahangir. Jahangir became the Mughal Emperor in 1605. He hated the Sikhs. He had similar feelings for Guru Arjan Dev Ji. He wanted that either Guru Sahib should become a Musalman or else be put to death. He definitely played a big role in the martyrdom of Guru Arjan Dev Ji.
2. Hostility of Prithia. Guru Ram Das Ji had appointed Guru Arjan Dev Ji as his successor to Guru Gaddi because Guru Sahib was convinced of his intelligence and ability. Prithia, the elder brother of Guru Arjan Dev Ji, did not relish the decision of Guru Ram Das Ji. Then Prithia started conspiring against Guru Arjan Dev Ji in league with the governor of Punjab and his finance minister Chandu Shah. It is true that Prithia had died before the martyrdom of Guru Sahib but it was he who had done the maximum damage to Sikh religion by infusing hatred in the hearts of Mughals against Guru Arjan Dev Ji.
3. Splendour of Guru Arjan Dev Ji’s Court. The Sikhs had grown rich by the blessings of Guru Arjan Dev Ji. The Sangat set up a magnificent court for Guru Sahib, where Guru Sahib continued with his religious activities. The Sangat started addressing Guru Sahib as “Sachcha Padshah” out of love and devotion for him. Jahangir could not tolerate the rising strength of Sikh community within his empire. Hence, the Emperor decided to act against Guru Sahib.
4. Case of Prince Khusro. Khurso, the eldest son of Emperor Jahangir, was once even considered for succession to the throne of Mughal Empire by Akbar himself. Prince Khusro revolted against his father Emperor Jahangir. The Mughal army chased him. Khurso came to Punjab and sought shelter with Guru Sahib whom he considered as a friend of his grandfather Akbar. Guru Sahib, a saintly figure, expressed good wishes for Khusro. However, the Mughal Emperor took this act of Guru Sahib as a political offence and decided to sentence Guru Ji to death.
5. Hostility of Chandu Shah. Chandu Shah was a high ranking official of the Mughal administration in Punjab. Guru Arjan Dev Ji had declined to marry the daughter of Chandu Shah to his own son on the suggestion of Sikh Sangat. Chandu Shah felt insulted and tried to instigate Akbar against Guru Sahib with the motive of taking revenge. Akbar held Guru Sahib in high esteem and considered himself as a friend of Guru Sahib. Akbar did not give any importance to the grumbling of Chandu Shah. Chandu Shah did not stop conspiring against Guru Sahib. After the death of Akbar, Chandu Shah instigated Jahangir and convinced him that Guru Sahib had helped the rebellious Prince Khusro. Jahangir had already decided to end the religious movement of Guru Sahib. The instigation by Chandu Shah further provoked Jahangir to take a strong step against Guru Sahib.
6. Compilation of the Adi Granth Sahib. Guru Arjan Dev Ji had compiled the Adi Granth Sahib. The enemies of Guru Sahib told Jahangir that Guru Sahib had included such matter in the holy book which was against Islam. Jahangir asked Guru Sahib to remove all such matter from Adi Granth Sahib, which was supposed to be against Islam. Guru Sahib clearly told Jahangir that he was not going to delete anything from the Adi Granth Sahib as there was no such matter in it which could be considered against any religion. Then Jahangir proposed to Guru Sahib to add something in Adi Granth Sahib in praise of Prophet Muhammad. Guru Sahib refused to oblige Jahangir and told him that nothing could be entered in the Adi Granth except as directed by the Divine Voice itself. Jahangir was infuriated by such a reply.
7. Penalty imposed on Guru Sahib. The religious fanaticism of Jahangir reached its peak due to the reasons given above. Jahangir issued an order to put Guru Sahib to death by torture. Later, he changed his own orders and asked the Guru Sahib to pay a penalty of two lakh rupees. Guru Sahib refused to pay even a single paisa as penalty and claimed that all the money with him was meant only for the poor and orphans. Jahangir was enraged and again issued orders for the torture and execution of Guru Sahib.
Martyrdom. Guru Sahib was subjected to horrible physical torture. Guru Sahib was made to sit on red-hot iron plate and then hot sand was poured on his body. Guru Sahib was also made to enter boiling water. Finally, in May 1606 Guru Sahib was martyred. According to Sikh scholars, when Guru Sahib was being tortured, one day Guru Sahib expressed a desire to take bath in a river. When Guru Sahib entered the river Ravi, he suddenly disappeared.
Question 3.
What were impacts of Martyrdom of Guru Arjan Dev Ji in Sikh religion? Discuss.
Answer:
The martyrdom of Guru Arjan Dev Ji caused fundamental changes in the attitude of the Sikhs.
1. Guru Sahib had left a parting message for his son Guru Hargobind that read,
“The day is approaching fast when Good and Evil will clash Let him (Guru Hargobind Ji) sit fully armed on the throne and maintain army to the best of his ability.” The last message of Guru Sahib was the starting point of the military policy of “the Sikhs. The Sikh religion of ‘Saints’ became the religion of ‘Saint Soldiers’ (Sant Sipahi) with rosary in one hand and a sword in the other.
2. Before the martyrdom of Guru Arjan Dev Ji, the Sikhs and the Mughals had very cordial relations. However, the martyrdom of Guru Arjan Dev Ji injured the religious feelings of the Sikhs and they developed ill-will against the Mughal rule in their hearts.
3. The Sikh religion became more popular due to the martyrdom of Guru Arjan Dev Ji. The Sikh followers of Guru Sahib were now all out to sacrifice their lives for the cause of their religion. There is no doubt that the martyrdom of Guru Sahib had given a new direction to the history of Sikh religion. ‘
4. The martyrdom of Guru Arjan Dev Ji gave birth to .militant spirit among the Sikhs. The Sikh community was transformed into a sect of aggressive fighters for the cause of religion from being a community of pious and peace loving people. They had been transformed into Sant Sipahis.
5. Earlier, the Mughals and the Sikhs had very cordial relations but the martyrdom of Guru Sahib had hurt their religious sentiments and they became the bitter enemies of the Mughal rule.
6. The martyrdom of Guru Sahib raised the prestige and popularity of the Sikh religion. The Sikhs were bent upon the protection of their religion by all means.
Indeed, the martyrdom of Guru Sahib turned a new leaf in the history of Sikh religion. It transformed peace loving saintly Sikhs into Sant Sipahis. “The martyrdom of Guru Sahib convinced the Sikhs that they must arm themselves and fight if they want to live.”
PSEB 9th Class Social Science Guide Sri Guru Arjan Dev Ji: Contribution in the Development of Sikhism and his Martyrdom Important Questions and Answers
Multiple Choice Questions :
Question 1.
Sri Adi Granth Sahib was compiled by __________
(a) Guru Amar Das Ji (b) Guru Arjan Dev Ji
(c) Guru Ram Das Ji (d) Guru Teg Bahadur Ji.
Answer:
(b) Guru Arjan Dev Ji.
![]()
Question 2.
__________ was appointed the first Granthi of Harmandir Sahib.
(a) Bhai Prithia Ji
(b) Sh. Mahadev Ji
(c) Baba Buddha Ji
(d) Natha Mai Ji.
Answer:
(c) Baba Buddha Ji.
Question 3.
Chheratta was founded by
(a) Guru Teg Bahadur Ji
(b) Guru Hargobind Ji
(c) Guru Arjan Dev Ji
(d) Guru Ram Das Ji.
Answer:
(c) Guru Arjan Dev Ji.
Question 4.
Two swords of Miri and Piri were put on by _________________
(a) Guru Arjan Dev Ji
(b) Guru Hargobind Ji
(c) Guru Teg Bahadur Ji
(d) Guru Ram Das Ji.
Answer:
(6) Guru Hargobind Ji.
Question 5.
Which Guru got martyred during the times of Jahangir?
(a) Guru Angad Dev Ji
(6) Guru Amar Das Ji
(c) Guru Arjan Dev Ji
(d) Guru Ram Das Ji.
Answer:
(c) Guru Arjan Dev Ji.
Fill in the blanks :
Question 1.
Guru Hargobind Sahib spend last 10 years of his life at __________ in preaching religion.
Answer:
Kiratpur Sahib.
Question 2.
Guru Arjan Dev Ji was born at __________
Answer:
Goindwal Sahib.
Question 3.
__________ was the first Guru who got martyrdom.
Answer:
Guru Arjan Dev Ji.
![]()
Question 4.
The construction work of Harmandir Sahib was completed in __________ A.D.
Answer:
1601.
Question 5.
__________ was the sixth Guru of Sikhs.
Answer:
Guru Hargobind Ji.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
When and who laid the foundation of Harmandir Sahih?
Answer:
The foundation of Harmandir Sahib was laid in 1589 A.D. by the famous Sufi Saint Mian Mir.
Question 2.
What is the meaning of keeping four doors at Harmandir Sahib?
Answer:
It means that this place is equally open for all the classes, castes and religions.
Question 3.
When and which city was founded hy Guru Arjan Dev Ji between Ravi and Beas?
Answer:
Guru Arjan Dev Ji laid the foundation of Tarn Taran in 1590 A.D. between Ravi and Beas.
Question 4.
Name four cities founded by Guru Arjan Dev Ji.
Answer:
Tarn Taran, Kartarpur, Hargobindpur and Chheratta.
Question 5.
What is meant by Daswandh?
Answer:
It means that every Sikh will keep one tenth of his income in the name of the Guru.
Question 6.
Write about the Baoli Sahib (water source) of Lahore.
Answer:
Guru Arjan Dev Ji had constructed a large well (Baoli) in Dubbi Bazaar in Lahore. It became a place of pilgrimage for his Sikh followers.
![]()
Question 7.
What was the need of compilation of the Adi Granth Sahib by Guru Arjan Dev Ji?
Answer:
Guru Arjan Dev Ji wanted that his Sikhs should be benefited from the true and divine hymns of Guru Sahiban for which he found it necessary to make available a true and sacred religious book.
Question 8.
Write two advantages of trading in horses during Guru Arjan Dev Ji’s times.
Answer:
(1) The Sikhs became very rich by trading in horses and donations to the Guru also increased.
(2) It also helped in destroying the caste system among the Sikhs.
Question 9.
Write two social reforms brought about by Guru Arjan Dev Ji.
Answer:
(1) Guru Sahib tried to encourage widow remarriage.
(2) Guru Sahib prohibited the use of liquor and intoxicants by his Sikh followers.
Question 10.
Write about the relationship between Guru Arjan Dev Ji and Akbar.
Answer:
Akbar had very friendly relations with Guru Arjan Dev Ji.
Question 11.
Why did Jahangir want to kill Guru Arjan Dev Ji?
Answer:
- The Mughal Emperor Jahangir was jealous of the rising popularity of Guru Arjan Dev Ji.
- He was perturbed (troubled) by the fact that like the Hindus, many Muslims were coming under the influence of Guru Arjan Dev Ji.
Question 12.
Write the importance of the swords of ‘Miri’ and ‘Piri’.
Answer:
Guru Hargobind Ji put on two swords and called them ‘Miri’ and ‘Piri’. The ‘Miri’ sword represented the leadership of Guru Hargobind Ji over the Sikhs in their worldly affairs. The sword ‘Piri’ indicated the leadership of Guru Sahib in spiritual matters of the Sikhs.
Question 13.
Describe the royal symbols used by Guru Hargobind Sahib Ji.
Answer:
Guru Hargobind Sahib Ji put on a Crest (Kalgi), Umbrella (Chatra), and the two swords as his royal symbols. Guru Hargobind Ji kept 52 bodyguards. Guru Sahib also adopted the title ‘Sachcha Padhshah’ (True Emperor) and sat on a throne.
Question 14.
How did Guru Hargobind Sahib Ji fortify the city of Amritsar?
Answer:
Guru Hargobind Ji raised a thick wall all around the city of Amritsar. Guru Sahib also constructed a fort called ‘Lohgarh’ within the city and garrisoned it.
Question 15.
How and where did Guru Hargobind Sahib Ji spend his last ten years?
Answer:
Guru Hargobind Ji spent the last ten years of his life at Kiratpur. Guru Sahib devoted his time to popularise the teachings of the Sikh religion.
Question 16.
Which Sikh Guru got martyrdom during the reign of Jahangir?
Answer:
Guru Arjan Dev Ji.
Question 17.
Who was the fifth Guru of the Sikhs?
Answer:
Guru Arjan Dev Ji.
Question 18.
Who constructed Harmandir Sahib at Amritsar?
Answer:
Guru Arjan Dev Ji.
![]()
Question 19.
Which cities were founded by Guru Arjan Dev Ji?
Answer:
Tarn Taran, Kartarpur and Hargobindpur.
Question 20.
With which system is Daswandh related?
Answer:
Daswandh is related with the Masand system.’
Question 21.
When was the compilation work of Sri Adi Granth Sahib Ji completed? ’
Answer:
In 1604 A.D.
Question 22.
Who compiled Sri Adi Granth Sahib Ji?
Answer:
Guru Arjan Dev Ji.
Question 23.
When Guru Arjan Dev Ji got martyrdom?
Answer:
In 1606 A.D.
Question 24.
Which Guru adopted two swords called Miri and Piri?
Answer:
Guru Hargobind Ji.
Question 25.
Name the Pathan army General of Guru Hargobind Ji.
Answer:
Painda Khan.
Question 26.
Which Guru constructed Akal Takht, fort of Lohgarh and organised the Sikh army?
Answer:
Guru Hargobind Ji.
![]()
Question 27.
Which Guru fortified Amritsar?
Answer:
Guru Hargobind Ji.
Question 28.
Who gave the land for the city of Kiratpur?
Answer:
Raja Kalyan Chand.
Question 29.
Which Mughal emperor imprisoned Guru Hargobind Ji at Gwalior fort?
Answer:
Jahangir.
Question 30.
Describe any one difficulty which Guru Arjan Dev Ji encountered on coming to Guru Gaddi.
Answer:
Guru Sahib faced animosity and opposition of his eldest brother Bhai Prithia.
Question 31.
Write the name of Guru Sahib who was the first martyr.
Answer:
Guru Arjan Dev Ji.
Question 32.
Write any one effect of the martyrdom of Guru Arjan Dev Ji.
Answer:
The martyrdom of Guru Arjan Dev Ji provoked the Sikhs to rise in arms.
Question 33.
Which two persons had assisted Guru Arjan Dev Ji in the execution of his plans for the construction of Sri Harmandir Sahib?
Answer:
Bhai Buddha Ji and Bhai Gurdas Ji.
Question 34.
When was the construction of Sri Harmandir Sahib completed?
Answer:
In 1601 A.D.
![]()
Question 35.
What were the representatives of Guru Arjan Dev Ji called?
Answer:
The representatives of Guru Arjan Dev Ji were called the Masands.
Question 36.
Who completed the work of compilation of ‘Adi Granth Sahib’?
Answer:
Guru Arjan Dev Ji.
Question 37.
Where was Adi Granth Sahib placed?
Answer:
Adi Granth Sahib was placed in Sri Harmandir Sahib at Amritsar.
Question 38.
From whom did Guru Hargobind Ji receive the training in the use of arms and knowledge of religion?
Answer:
Bhai Buddha Ji.
Question 39.
How many hymns of Guru Nanak Dev Ji, Guru Angad Dev ji, Guru Amar Das Ji and Guru Ram Das Ji have been included in Sri Adi Granth Sahib?
Answer:
Guru Nanak Dev Ji-976, Guru Angad Dev Ji-61, Guru Amar Das Ji-907, Guru Ram Das Ji-679.
Question 40.
Write any one cause for the adoption of “New Policy” by Guru Hargobind Ji.
Answer:
For self-defence of the Sikh community.
Question 41.
Which four places emerged as sacred cities for the Sikh religion by the time of Guru Hargobind Ji?
Answer:
Goindwal, Amritsar, Tarn Taran and Kartarpur.
Question 42.
Which four Sikh institutions had played major role in the consolidation and progress of Sikh religion?
Answer:
The institutions of Pangat, Sangat, Manji System and Masand System. Question 5. Write the names of any four commanders of Guru Hargobind Ji. Answer:Bhai Bidhi Chand, Bhai Pheru, Bhai Jetha and Bhai Paida.
Question 43.
Which two singers were instructed by Guru Hargobind Ji to sing heroic deeds songs (vir rasa) on high notes in his presence?
Answer:
Nathamal and Abdullah.
Question 44.
Write any one cause which resulted in the confinement of Guru Hargobind Ji.
Answer:
Jahangir was irritated by his ‘New Policy’.
![]()
Question 45.
Why was the title of “Bandi Chhor Baba” (a holy deliverer) given to Guru Hargobind Ji?
Answer:
Guru Sahib got released 52 Rajput chiefs imprisoned in the Gwalior Fort.
Question 46.
How many battles were fought between the Sikhs and the Mughals during the period of Guru Hargobind Ji?
Answer:
Three battles.
Question 47.
Write the names of four main missionary preachers of the period of Guru Hargobind Ji.
Answer:
Almast, Phul, Gonda and Balu Hassan.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Write about Sri Harmandir Sahib.
Answer:
Guru Arjan Dev Ji had raised Sri Harmandir Sahib in the centre of the Sarovar Amritsar after the final union of Guru Ram Das Ji with the Divine Power. Sufi fakir, Mian Mir laid the foundation stone of Sri Harmandir Sahib in 1589. Guru Sahib had constructed doors in each of the four directions of Sri Harmandir Sahib. It was done to declare that the doors of Sri Harmandir’Sahib were open to the people of all the castes and religious without distinction. Bhai Budda Ji supervised the work of construction of Sri Harmandir Sahib and completed it in 1601. In 1604, Adi Granth Sahib was placed in Sri Harmandir Sahib and Bhai Budda Ji was appointed as the first Granthi of Sri Harmandir Sahib.
Question 2.
What do you know about Tarn Taran Sahib?
Answer:
The town of Tarn Taran was founded by Guru Arjan Dev Ji. Tarn Taran has great significance in the history of Sikhs. Tarn Taran is an important place of pilgrimage like Amritsar for the Sikhs. A large number of Sikh pilgrimage come to Tarn Taran and take bath in the Sarovar. It was because of Tarn Taran that the Jats of Majha region of Punjab adopted Sikh religion during the period of Guru Arjan Dev Ji. The Jats of the Majha region proved to be most courageous and fearless while fighting against the Mughals in the battles. Indu Bushan Banerjee remarks that the history of the Sikhs took a new turn with the entry of the Jats into Sikh religion.
Question 3.
What were the benefits of the Masand System for the Sikh religion?
Answer:
The Masand System played an important role in the development and organisation of the Sikh religion. The importance of the Masand System for Sikh religion was as under :
1. The system ensured regular and fixed donations for the Guru Gaddi. With a fixed income from donations, Guru Sahib was able to undertake much constructive work for the development of Sikh religion. Guru Arjan Dev Ji not only built tanks at Amritsar and Santokhsar, but also built new cities, constructed ponds, dug wells, etc.
2. Masand System not only ensured fixed donations but also helped in spreading the message of Sikh religion more enthusiastically. Earlier, the work of spread of religion was done through Manji system. It was confined only to the Punjab during those days. However, Guru Arjan Dev Ji appointed Masands even outside Punjab. It helped in the spread of Sikh religion even outside.
3. Guru Sahib started holding his own court when he had an assured income through Masand System. The Masands and the devoted Sikhs brought donations and gifts to the court of Guru Arjan Dev Ji on every Baisakhi day and bowed their heads before him to seek his blessings.
![]()
Question 4.
Describe the organisation of the army by Guru Hargobind Sahib Ji.
Answer:
Guru Hargobind Ji raised an army for self-defence. There were a number of armed soldiers and volunteers in his army. Many courageous and war-loving young men of Majha region joined his army. According to one record, there were 60 musketeers, 300 horse riders, and 800 horses in his army. There were also five hundred volunteers who were paid nothing as salary and even then, they loved to be in his army out of their devotion to Guru Sahib. The army was divided into five sections (jathas). The five famous commanders (Jathedars) were Bidhi Chand, Perana, Jetha, Paida and Langha. Apart from this army, there was a separate company of Afghan (Pathan) soldiers, headed by Painda Khan.
Question 5.
Write about the daily life of Guru Hargobind Ji.
Answer:
Guru Hargobind Ji had changed his life style according to his ‘New Policy’. According to his new daily routine, after taking his bath early morning, Guru Sahib visited Sri Harmandir Sahib to give religious instruction. After the discourse, the Langar was served every day. After the Langar, Guru Sahib used to take rest for some time before leaving for hunting. Guru Hargobind Ji had instructed Abdul and Nathmal to sing songs of heroism (songs of vir rasa) on high notes in order to infuse courage into the Sikh Sangat. Guru Sahib organised special troupes of singers (Dhadis). In this manner, Guru Sahib created a new awareness among the Sikhs and created in them the spirit of courage.
Question 6.
What do you know about the ‘Akal Takht’?
Answer:
Guru Hargobind Ji used to give religious instructions at Sri Harmandir Sahib. Guru Sahib had constructed a new building called ‘Akal Takht’ (the Throne of Supreme God) in the western part of the premises of Sri Harmandir Sahib to give advice to the Sikhs in the worldly matters. There was raised a platform about 12 feet high. Guru Sahib used to solve the military and political problems of the Sikhs while sitting there. Guru Sahib also listened to heroic songs (songs of vir rasa) from his followers at Akal Takht. Guru Sahib also imparted physical training to his Sikh followers near Akal Takht.
Question 7.
What is the importance of the Adi Granth Sahib in the history of Sikh religion?
Answer:
The compilation of Adi Granth Sahib provided the strong foundation for the Sikh religion. Adi Granth Sahib became the most reliable and holy book of the Sikhs. All the social ceremonies concerning the life of the Sikhs, like birth, marriage, initiation to adulthood, death, etc. were performed in divine presence of the Adi Granth Sahib. The Sikhs who had deep faith in the holiness of Adi Granth Sahib, developed a feeling of being one with the fellow believers, giving rise to class consciousness and ultimately to the rise of a distinct Sikh Panth. Later, the holy book was raised to the status of Guru itself and the holy book became the Guru of the Sikh religion. The Sikhs and numerous other people believe that the hymns of Guru Granth Sahib are divine utterances.
Question 8.
Write the historical significance of Adi Granth Sahib.
Answer:
Adi Granth Sahib is the holy book of the Sikhs. It was not written with any historic perspective or motive. However, it has great historical importance also. It is one of the major sources of political, social, religious, economic and cultural history of the 16th and the 17th century Punjab. Guru Nanak Dev Ji had severely condemned the rule of Lodhis and oppression of Babur over the people of Punjab in his sayings. It is a source of information about the dominance of caste system, the exploitation of women, and other shortcomings of Indian society like irrational customs, rites and traditions during those days. The religion had lost its sanctity. Guru Nanak Dev Ji had declared “No one is a Hindu or a Muslim,” suggesting that religion had lost its actual meaning and people were treading a wrong path.
![]()
Question 9.
Write down any four causes of the martyrdom of Guru Arjan Dev Ji.
Answer:
The circumstances which led to the martyrdom of Guru Arjan Dev Ji were as follows:
1. Intolerant Religious policy of Jahangir. Jahangir, the Mughal Emperor, was hostile to Guru Arjan Dev Ji. He was planning to convert him to Islam or to kill him.
2. The Enmity of Prithia. Guru Ram Das Ji had appointed Guru Arjan Dev Ji as his successor because Guru Sahib was much impressed with the intelligence and ability of Bhai Arjan Dev Ji. However, Bhai Prithi Chand did not like his decision. Prithi Chand started conspiring against Guru Arjan Dev Ji.
3. The Grandeur of Guru Arjan Dev Ji’s court. The Guru Sahib held a splendid court. The Sangat had also increased the grandeur of his court and out of their respect and love for him had started addressing him as their “Sachcha Padshah”. The Mughal emperor could not tolerate all these developments so he decided to take some severe action against him.
4. Penalty imposed on Guru Arjan Dev Ji. Jahangir imposed a penalty on Guru Sahib and detained him. The fanaticism of Jahangir crossed all limits and he passed the orders to execute Guru Sahib by inflicting tortures on his person.
Question 10.
What was the reaction against the martyrdom of Guru Arjan Dev Ji?
Answer:
The martyrdom of Guru Arjan Dev Ji caused fundamental changes in the attitude of the Sikhs.
1. Guru Sahib had left a parting message for his son Guru Hargobind that read, “The day is approaching fast when Good and Evil will clash Let him (Guru Hargobind Ji) sit fully armed on the throne and maintain army to the best of his ability.” The last message of Guru Sahib was the starting point of the military policy of the Sikhs. The Sikh religion of ‘Saints’ became the religion of ‘Saint Soldiers’ (Sant Sipahis) with rosary in one hand and a sword in the other.
2. Before the martyrdom of Guru Arjan Dev Ji, the Sikhs and the Mughals had very cordial relations. However, the martyrdom of Guru Arjan Dev Ji injured the religious feelings of the Sikhs and they developed ill-will against the Mughal rule in their hearts.
3. The Sikh religion became more popular due to the martyrdom of Guru Arjan Dev Ji. The Sikh followers of Guru Sahib were now all out to sacrifice their lives for the cause of their religion. There is no doubt that the martyrdom of Guru Sahib had given a new direction to the history of Sikh religion.
Question 11.
Write any four important aspects of the personality and character of Guru Arjan Dev Ji.
Answer:
The fifth Guru, Guru Arjan Dev Ji was a man of high character and pleasing manners. The four main aspects of his personality are as under :
1. Guru Sahib was a successful organiser and religious leader. Guru Sahib vigorously spread the message of Sikh religion and gave an organised form to the Sikh community by making necessary reforms in the Masand System.
2. Guru Sahib was a great builder. Guru Sahib completed the work of building the city of Amritsar, constructed Sri Harmandir Sahib, and founded cities like Tarn Taran, Hargobindpur etc. Guru Sahib also constructed a Baoli at Lahore.
3. Guru Sahib completed the work of compilation of Adi Granth Sahib.
4. Guru Sahib was a great social reformer. Guru Sahib encouraged widow remarriage and checked the use of intoxicants among the Sikhs. Guru Sahib also established a centre where free medicines and clothes were provided to the sick.
Question 12.
Name any four causes which forced Guru Hargobind Ji to adopt the “New Policy”.
Answer:
1. Hostility and Interference of the Mughals. The Mughal Emperor Jahangir adopted the policy of oppression towards Sikhs after the martyrdom of Guru Arjan Dev Ji. Consequently, it became necessary for the next Guru Sahib, Guru Hargobind Ji to adopt New Policy for the defence of the Sikh religion.
2. The martyrdom of Guru Arjan Dev Ji. It became clear to the Sikhs after the martyrdom of Guru Arjan Dev Ji that they had to bear the arms along with the rosaries for the protection of Sikh religion. Hence, Guru Hargobind Ji adopted the New Policy with the same aim in view.
3. Parting Message of Guru Arjan Dev Ji. In his last message, Guru Arjan Dev Ji had instructed the Sikhs to bear arms. Hence, Guru Hargobind Ji started imparting the training in arms along with spiritual knowledge to the Sikhs.
4. Entry of the Jats in Sikhism. Guru Hargobind Ji was encouraged to adopt the new policy on the entry of Jats in the Sikh religion. The Jats were freedom loving by nature and had great aptitude for fighting battles.
![]()
Question 13.
Write briefly the contribution of Guru Hargobind Ji to Sikhism.
Answer:
1. Guru Sahib put on two swords when he occupied Guru Gaddi. One sword represented his Miri and the other his Piri. With that, Guru Sahib became the political leader as well as a religious guide of the Sikhs.
2. Guru Sahib also erected a new building near Sri Harmandir Sahib. The new building is called Akal Takht. Guru Sahib imparted the training in arms to the Sikhs.
3. Jahangir imprisoned Guru Hargobind Ji in the fort of Gwalior. Soon after, he learnt that he had taken a wrong decision. He released Guru Sahib. However, Guru Sahib persuaded Jahangir to release all the Rajput kings imprisoned in the Gwalior fort.
4. Guru Sahib also fought battles with the Mughals.- The Mughal emperor Shahjahan sent army against Guru Sahib three times. Guru Sahib fought against them very bravely. The Mughal army lost all the three battles.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Describe the origin, development and merits of the Masand System.
Answer:
Origin of the Masand System : Guru Ram Das Ji, the fourth Guru of the Sikhs, started the Masand System. He felt the need for more money when he was looking after the work of digging of Amritsar Sarovar and Santokhsar Sarovar. Guru Ram Das Ji did not have enough resources. Therefore, Guru Sahib deputed his trusted followers in different directions of the country to collect funds from his Sikh devotees. They were called the Masands or Ram Dasis. These followers were the close confidants of Guru Ram Das Ji. Wherever those followers or Masands went, they collected the donations and spread the message of Sikh religion.
Progress of the Masand System : Guru Arjan Dev Ji made improvements in the Masand system and made it an institution that was more effective. Before the period of Guru Arjan Dev Ji, the donations to earlier Guru Sahiban were not fixed and were irregular. Guru Arjan Dev Ji had started construction work of many buildings and Sarovars for which he required a fixed and regular inflow of cash. Apart from this, it had become difficult to collect the donations from numerous Sikh followers whose number had increased manifold. Guru Arjan Dev Ji gave a proof of his superior managing skill by providing the solution for the existing problems of organization of the Sikh religion.
Guru Sahib improved the organization of Masand system by taking the following measures :
1. Guru Sahib fixed the amount of donation to be made by his Sikh devotees to him. Guru Sahib enjoined upon his devotees to donate one-tenth of their annual income for the maintenance of Langar.
2. Guru Sahib appointed his representatives, who were called the Masands for the collection of Daswandh from his Sikh devotees. The Masands deposited the collections in the treasury of Guru Sahib (Guru Ki Golak) at Amritsar on Baisakhi day every year. The receipts were issued to the Masands for the donations received at Amritsar.
3. The Masands had appointed their representatives who were called the Sangtias, to collect the Daswandh. The Sangtias collected the Daswandhs from far off places and deposited them in the treasury of the Guru.
4. The Sangtias and Masands considered it a sin to use even a single penny out of the donations for personal use. Guru Sahib had already ordained on this issue that whosoever embezzled the money of Daswandh, would become the victim of physical sufferings.
5. The Masands did not confine their activities only to the collection of Daswandhs, they also employed their energies for spreading the message of the Sikh religion. Guru Sahib ensured at the time of appointment of a Sikh as a Masand that, he had a high moral character and deep faith in the Sikh religion.;
Importance and Benefits of the Masand System : The Masand system played an important role in building and consolidation of the Sikh religion. The importance of Masand System for the Sikh religion can be given as follows :
1. The donations to Guru Gaddi became fixed and regular. It helped Guru Sahib to continue with his construction work. Guru Sahib founded not only the Sarovars at Amritsar and Santokhsar but also built many cities, ponds, wells etc with the regular donations. The constructive work of Guru Sahib contributed in a significant way to the spread and popularity of Sikh religion.
2. On the one hand, the Masand System ensured a regular income to the Guru Ji and on the other, it popularised the Sikh religion in an effective manner. Earlier, Manji System carried out the work of spread of the Sikh religion. The Manji system had confined its activities to the Punjab region. Guru Sahib appointed Masands even outside Punjab. It resulted in the spread of Sikh religion in other parts of the country because the Masands collected not only the Daswandh but also devoted their energies for spreading the message of Sikh religion.
3. Guru Sahib started holding his own court with the regular donations received in the form of Daswandh. The Masands and devoted Sikhs brought donations and gifts to the court of Guru Arjan Dev Ji on every Baisakhi and bowed their heads before him to seek his blessings.
![]()
Question 2.
Describe the ‘New Policy’ of Guru Hargobind Ji.
Answer:
Guru Hargobind Ji, the son of Guru Arjan Dev Ji, became the sixth Guru of the Sikhs after the martyrdom of Guru Arjan Dev Ji. Guru Hargobind Ji adopted a ‘New Policy’. The main feature of his new policy was to make the Sikhs peace loving as well as courageous and fearless.
The main features of the ‘New Policy’ of Guru Hargobind Ji are the following :
1. The Royal Insignias and the title of ‘Sachcha Padshah’: Guru Hargobind Ji adopted the title of ‘Sachcha Padshah’ and put on a number of royal insignias in line with his ‘New Policy1. Guru Sahib started wearing princely dress and discontinued using the saintly headgear and woollen beads (sayli) which were the symbols of saints and fakirs. Guru Sahib put on two swords and a crest (Kalgi) in place of woollen beads (sayli) and saintly headgear. Guru Sahib also kept bodyguards for self-defence just like the princes of the contemporary times.
2. Miri and Piri : Guru Hargobind Ji had become the military leader of the Sikhs besides being their spiritual leader. From then onwards, Guru Sahib was ‘Mir’ (Military Commander) and ‘Pir’ (Religious Leader) of the Sikhs. Guru Sahib put on two swords to represent his new role as ‘Mir’ and ‘Pir’ of his Sikhs. Guru Sahib named one sword as ‘Piri’ and the second as ‘Miri’. Guru Sahib gave special attention to the physical fitness of the Sikhs. Guru Sahib encouraged his Sikh followers to take exercise regularly, to participate in wrestling bouts, to go on hunting and to receive training in horse riding. Guru Sahib thus transformed his saintly followers into saint soldiers by adopting his ‘New Policy’.
3. Construction of Akal Takht : Guru Hargobind Ji took upon himself the responsibility of guiding the worldly activities of his Sikh followers apart from his role of being their true Guru in the sphere of spiritual life. Guru Sahib imparted spiritual knowledge at Sri Harmandir Sahib. In order to guide the Sikhs in their worldly affairs, Guru Sahib built Akal Takht (Throne of Supreme God—The Timeless) near Sri Harmandir Sahib. Guru Sahib listened to the military and political problems of the Sikhs while sitting on a raised platform 12 feet high at the Akal Takht.
4. Raising of Army : Guru Hargobind Ji raised an army for self-defence of the Sikhs. There were numerous professional soldiers and volunteers in his army. The fearless and courageous Jats of Majha region volunteered to join his army. According to one estimate, Guru Sahib had 800 horses, 300 horse riders, and 60 musketeers. Guru Sahib was served by a contingent of 500 such volunteers who did not seek any salary. Besides this army, Guru Sahib was also served by a separate contingent of Afghan (Pathan) soldiers headed by Painda Khan.
5. Keeping of Horses and Arms : Guru Hargobind Ji took special measures to make his ‘New Policy’ successful. Guru Sahib advised his Sikh followers to make donations of horses and arms as far as possible. Consequently, Guru Sahib collected many horses and a large number of arms.
6. Fortification of Amritsar : Guru Hargobind Ji raised a thick wall around the city of Ramdaspur (Amritsar) for its defence and security. The fort of Lohgarh was built and stocked with armaments and other military provisions.
7. New Daily Routine : Guru Hargobind Ji also made changes in his daily routine. According to his ‘New Policy’ his new daily routine was that after taking his bath early in the morning, Guru Sahib visited Sri Harmandir Sahib to give religious instruction. After the discourse, the Langar was served every day under his supervision. After the Langar, Guru Sahib used to take rest for some time before leaving for hunting. Guru Hargobind Ji had instructed Abdul and Nathamal to sing songs of heroism (songs of vir rasa) on high notes in order to infuse courage in the Sikh Sangat. Guru Sahib organised special troupes of singers (Dhadis). In this manner, Guru Sahib raised a new awareness among the Sikhs and made them brave and fearless.
8. Inculcated the spirit of Self-Defence : The core of the ‘New Policy’ was to inculcate the spirit of self-defence among his Sikh followers. Therefore, the aim of raising the army was neither to grab the land of others nor to intimidate any one. No doubt, Guru Sahib valiantly fought battles against the Mughals, but in no way, those battles were motivated by any lust for territory. Rather they were’genuine efforts for self-defence and survival.
Question 3.
Besides adopting the New Policy what other measures were taken by Guru Hargobind Ji for the development of Sikhism?
Answer:
Guru Hargobind Ji was the only son of Guru Arjan Dev Ji, the fifth Guru Sahib. Guru Hargobind Ji was bom on June, 1595 in village Wadali in District Amritsar. Guru Sahib was a precocious child. Guru Sahib became the sixth Guru of the Sikhs after the martyrdom of his father, the fifth gum, Gum Arjan Dev Ji in 1606 and successfully guided the course of Sikh religion upto 1645. Gum Sahib made significant contribution to the development of Sikh religion by adopting the ‘New Policy’ and winning battles against the Mughals.
A brief survey of the contribution of Gum Hargobind Ji to Sikhism is given as under :
1. Stay at Kiratpur : The king of Kahlur, Raja Kalyan Chand, was a follower of Guru Sahib. The Raja had given land to Guru Gaddi. Guru Sahib built a city called Kiratpur on that land. Guru Sahib made the city his abode in 1635. Guru Sahib lived the last ten years of his life at Kiratpur and spent his time in spreading the message of Sikh religion.
2. Conversion of Hill Chiefs to Sikhism. Guru Hargobind Ji converted many people from hilly regions to Sikh religion. Many hill chiefs had accepted Sikhism under his influence. However, the people of hilly region did not continue.to follow the Sikh religion for a long period. The royal families reverted to their old practices of idol worship and other related ceremonies. Such practices were not permitted by Sikh religion.
3. The Religious Tours of Guru Hargobind Ji. Jahangir, the Mughal Emperor, became a friend of Guru Hargobind Ji when he released Guru Sahib from his confinement in Gwalior fort after realising his mistake. Guru Sahib undertook religious tours during that period of peace. Guru Sahib first visited Amritsar and then Lahore. At Lahore, Guru Sahib raised Gurudwara Dera Sahib in the memory of Guru Arjan Dev Ji. From Lahore, Guru Sahib went to Kashmir passing through Gujranwala and Bhimbar (Gujarat). Guru Sahib had made many followers in Kashmir. Guru Sahib inaugurated ‘Sangat’ in Kashmir. Bhai Sewa Das was deputed as representative of Guru Sahib in the ‘Sangat’.
Guru Sahib visited Nankana Sahib also. On his return journey from there, Guru Sahib spent some time at Amritsar. Guru Sahib also visited Nanakmatta (Gorakhmatta) in Uttar Pardesh. The yogis at Nanakmatta ran away from the city on seeing the grandeur of the entourage of Guru Hargobind Ji. Guru Sahib stayed there for some time to propagate the message of Sikh religion and reactivated the Sangat system. On his way back to Punjab, Guru Sahib also toured Malwa region of Punjab. Guru Sahib returned to Amritsar after staying for sometime at Dharauli Bhai (Ferozepur).
4. Deputed Religious Preachers : Guru Hargobind Ji remained involved in the battles upto 1635. Due to his pre-occupation, Guru Sahib deputed his eldest brother Bhai Gurditta (a saintly person with a big following) for preaching and spreading Sikh religion. Bhai Gurditta sent his four representatives named Bhai Almast, Phul, Gauda, and Balu Hasan for this task. Almast spread the message of Sikh religion in Nanakmatta and Dacca; Gauda and Phul in Doab and Malwa and Balu Hasan in Kashmir, Hazara, and Pathohar. Guru Sahib also sent Bhai Bidhi Chand to Bengal, Bhai Gurdas to Kabul and then to Benaras for preaching the Sikh faith.
5. Appointment of Guru Har Rai Ji as Successor: Guru Hargobind appointed his grandson Har Rai (son of Bhai Gurditta) as his successor before joining the Divine Power.