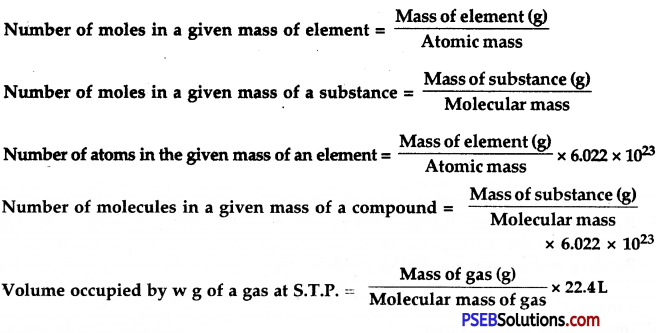This PSEB 9th Class Science Notes Chapter 3 Atoms and Molecules will help you in revision during exams.
PSEB 9th Class Science Notes Chapter 3 Atoms and Molecules
→ The idea of divisibility of matter was considered long back in India around 500 R.C.
→ Another Indian Philosopher, Pabuda Katyayama said these particles normally exist in a combined form which gives us various forms of matter.
→ Greek Philosophers-Democritus and Leucippus suggested that if we go on the dividing matter, a stage will come when particles obtained cannot be divided further.
→ Democritus called these indivisible particles atoms.

→ By the end of the 18th century, scientists recognized the difference between elements and compounds and how and why elements combine, and what happens when they combine.
→ Antoine L.Lavoisier gave two important laws of chemical combination given below.
→ According to the law of conservation of mass, mass can neither be created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction.
→ John Dalton provided the basic theory about the nature of matter.
→ Dalton picked up the idea of divisibility of matter and it was based upon laws of chemical combination.
→ Dalton gave Dalton’s atomic theory.
→ According to Dalton’s atomic theory, all matter, whether an element, a compound, or a mixture is composed of small particles called atoms, which are indivisible.
→ Dalton’s theory provided an explanation for the law of conservation of mass and the law of definite proportions.
→ All matter is made up of very tiny particles called atoms which cannot be seen with the naked eye.
→ The elements are represented with the help of symbols.
→ The symbol represents one atom of the element.
→ Berzelius suggested that the symbols of elements be made up from one or two letters of the name of the element.
→ The atomic mass of an element is the average relative mass of one atom of the element as compared to the mass of one atom of carbon-12, taken as 12 a.m.u. (atomic mass unit).

→ According to the latest IUPAC recommendations, a.m.u. has now been replaced by U (uniformed mass).
→ A molecule is in general a group of two or more atoms that are chemically bonded together.
→ A molecule can be defined as the smallest particle of an element or a compound that can exist independently and shows all the properties of that substance.
→ The molecules of an element are constituted by the same type of atoms.
→ The number of atoms constituting a molecule is known as its atomicity.
→ Atoms of different elements join together in definite proportions to form molecules of compounds.
→ Compounds composed of metals and non-metals contain charged species called ions. An ion is a charged particle and can be negatively or positively charged.
→ A negatively charged ion is called an anion and the positively charged ion is called a cation.
→ A group of atoms carrying a charge is known as a polyatomic ion.
→ The chemical formula of a compound is a symbolic representation of its composition.
→ The chemical formulae of different compounds are based upon their valencies.
→ The combining capacity of an element is known as its valency.

→ The molecular mass of a substance is the sum of the atomic masses of all the atoms in a molecule of the substance.
→ The formula unit mass of a substance is a sum of the atomic masses of all the atoms in a formula unit of a substance.
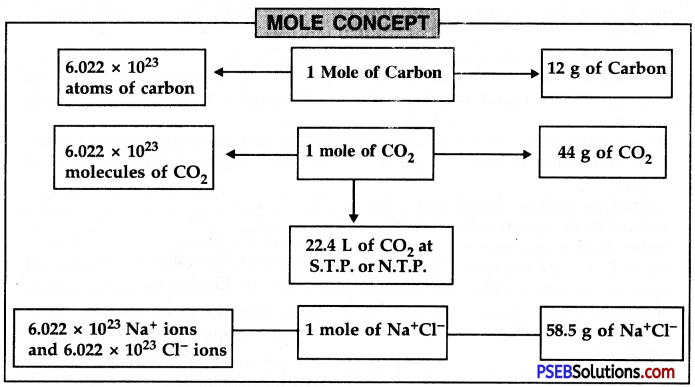
→ One mole of any species (atoms, molecules, ions, or particles) is that quantity in number having mass equal to its atomic or molecular mass in grams.
→ One mole of any substance represents 6.022 × 1023 particles (atoms, molecules, or ions) of it.
→ This number is an experimentally obtained value and is called Avogadro’s number or constant.
→ The mass of 1 mole of a substance is equal to its relative atomic or molecular mass in grams.
- 1 mole = 6.022 × 1023 particle = Relative mass in grams.
→ An Indian philosopher Maharishi Kanad, postulated that if we go on dividing matter (padarth), we shall get smaller and smaller particles.
→ Ultimately, a stage will reach when further division will not be possible. He named these particles ‘Parmanu’.
→ The radius of an atom is expressed in nanometres (nm)
- 1 nm = 10-9 m.
- 109 nm = 1 m.
→ Atom: It is the smallest or ultimate particle of an element that takes part in chemical reactions. It may or may not exist independently.
→ Molecule: It is the smallest or ultimate particle of a substance (element or compound) that can exist freely. It shows all the properties of a substance.
→ Law of conservation of mass: It states that matter (or mass) can neither be created nor destroyed during any known physical or chemical change.

→ Law of definite proportions (or Law of constant compositions): It states that a pure chemical compound is always found to be made up of the same elements combined together in the same fixed ratio by mass.
→ Symbol: It is the shorthand representation of an element. It is made up of one or two letters from the name of the element.
→ Relative atomic mass (RAM) or Atomic mass: It is the average relative mass of one atom of the element as compared to one atom of carbon-12 taken at 12 a.m.u.
→ Relative molecular mass (RMM) or Molecular mass: It is the average relative mass of one molecule of a substance as compared to one atom of carbon-12 taken at 12 a.m.u.
→ Ion: It is an atom or group of atoms carrying some charge and can exist freely in solution.
→ Polyatomic ion: It is an ion having more than one atom.
→ The chemical formula of a molecular compound is determined by the valency of each element.
→ The chemical formula of an ionic compound is determined by the charge on each ion.
→ Mole: It is the amount of substance that contains the same number of particles (atoms/ions/molecules/formula units.) etc. as there are atoms in 12 g of carbon-12.
→ Avogadro’s number or constant is the number of atoms in 12 g of carbon-12. It is denoted by N0 and its value is 6.022 × 1023, N0 = 6.022 × 1023.
→ The molar mass of a substance is the mass of one mole of a substance.
→ Variable valency: When an element shows more than one valency, it is said to have variable valency.
→ Radical: It is an atom or group of atoms having positive or negative charges and behaving as a single unit in chemical reactions. e.g. Na+, \(\mathrm{SO}_{4}^{2-}, \mathrm{NO}_{3}^{-}, \mathrm{NH}_{4}^{+}\) etc.

→ Simple radical: A radical which is made up of only one kind of atom is called a simple radical, e.g. Na+, Cl– etc.
→ Compound radical: A radical which is made up of more than one kind of atom is called a compound radical, e.g. \(\mathrm{NH}_{4}^{+}, \mathrm{SO}_{4}^{2-}, \mathrm{CO}_{3}^{2-}\), etc.
→ Atomic mass unit (AMU or u): It is 1/12th of the mass of one atom of carbon (C12- isotope).
→ S.T.P. stands for standard temperature (0°C or 273K) and pressure (1 atmosphere).
→ Molar volume: It is the volume occupied by one mole of a gas and its value at S.T.P./ N.T.P. is 22.4 litres.
→ Valency: It is the combining capacity of an atom of an element and is numerically equal to the number of hydrogen atoms or number of chlorine atoms or double the number of oxygen atoms with which one atom of the element can combine.
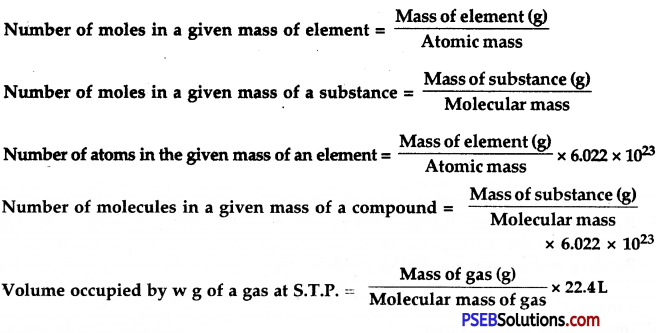
Atomic masses of some common elements in a.m.u. or u.
| Element |
Symbol |
Atomic Mass |
Element |
Symbol |
Atomic Mass |
| Aluminium |
A1 |
27 |
Lead |
Pb |
208 |
| Argon |
Ar |
40 |
Lithium |
Li |
7 |
| Beryllium |
Be |
9 |
Magnesium |
Mg |
24 |
| Boron |
B |
10.8 |
Neon |
Ne |
20 |
| Bromine |
Br |
80 |
Mercury |
Hg |
201 |
| Calcium |
Ca |
40 |
Nitrogen |
N |
14 |
| Carbon |
C |
12 |
Oxygen |
O |
16 |
| Chlorine |
Cl |
35.5 |
Phosphorus |
P |
31 |
| Copper |
Cu |
63.5 |
Potassium |
K |
39 |
| Fluorine |
F |
19 |
Silicon |
Si |
28 |
| Helium |
He |
4 |
Silver |
Ag |
108 |
| Hydrogen |
H |
1 |
Sodium |
Na |
23 |
| Iodine |
I |
127 |
Sulphur |
S |
32 |
| Iron |
Fe |
56 |
Zinc |
Zn |
65 |

Formulae of a few common compounds
| Name of the compound |
Formula |
Elements Present |
| Hydrogen |
H2 |
Hydrogen |
| Nitrogen |
N2 |
Nitrogen |
| Ammonia |
NH3 |
Nitrogen, Hydrogen |
| Carbon dioxide |
CO2 |
Carbon, Oxygen |
| Water |
H2O |
Hydrogen, Oxygen |
| Sulphur dioxide |
SO2 |
Sulphur, Oxygen |
| Nitric acid |
HNO3 |
Hydrogen, Nitrogen, Oxygen |
| Hydrochloric acid |
HCl |
Hydrogen, Chlorine |
| Sulphuric acid |
H2SO4 |
Hydrogen, Sulphur, Oxygen |
| Calcium carbonate |
CaC03 |
Calcium, Carbon, Oxygen |
| Silver nitrate |
AgN03 |
Silver, Nitrogen, Oxygen |
| Caustic soda |
NaOH |
Sodium, Oxygen, Hydrogen |
| Caustic potash |
KOH |
Potassium, Oxygen, Hydrogen |
| Baking soda |
NaHC03 |
Sodium, Hydrogen, Carbon, Oxygen |
| Phosphoric acid |
H3PO4 |
Hydrogen, Phosphorus, Oxygen |
| Carbonic add |
H2CO3 |
Hydrogen, Carbon, Oxygen |
| Nitrous acid |
HNO2 |
Hydrogen, Nitrogen, Oxygen |
| Marble |
CaC03 |
Calcium, Carbon, Oxygen |
| Phosphine |
PH3 |
Phosphorus, Hydrogen |
| Hydrogen sulphide |
H2S |
Hydrogen, Sulphur |
| Urea |
NH2CONH2 |
Nitrogen, Hydrogen, Carbon, Oxygen |
| Butane |
C4H10 |
Carbon, Hydrogen |
| Benzene |
C6H6 |
Carbon, Hydrogen |
| Acetic acid |
CH3COOH |
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen |
| Methane |
CH4 |
Carbon, Hydrogen |
| Soda ash |
Na2C03 |
Sodium, Carbon, and Oxygen |
Symbols or formulae of some common ions or radicals.
(A) Positive ions or Cations or Electropositive radicals:
(a) Cations having 1+ charges:
| Name |
Symbol or Formula |
| Hydrogen |
H+ |
| Lithium |
Li+ |
| Sodium |
Na+ |
| Potassium |
K+ |
| Ammonium |
NH4+ |
| Silver |
Ag+ |
| Cuprous |
Cu+ |
| Aurous |
Au+ |
| Mercurous |
Hg+ |
(b) Cations having 2+ charges:
| Name |
Symbol or Formula |
| Magnesium |
Mg2+ |
| Barium |
Ba2+ |
| Calcium |
Ca2+ |
| Strontium |
Sr2+ |
| Cobalt |
Co2+ |
| Nickel |
Ni2+ |
| Manganous |
Mn2+ |
| Zinc |
Zn2+ |
| Cadmium |
Cd2+ |
| Ferrous |
Fe2+ |
| Cupric |
Cu2+ |
| Mercuric |
Hg2+ |
| Plumbous |
Pb2+ |
| Stannous |
Sn2+ |
| Platinous |
Pt2+ |

(c) Cations having 3+ charges:
| Name |
Symbol or Formula |
| Ferric |
Fe3+ |
| Chromium |
Cr3+ |
| Aluminium |
Al3+ |
| Auric |
Au3+ |
(d) Cations having 4+ charges:
| Name |
Symbol or Formula |
| Plumbic |
Pb4+ |
| Stannic |
Sn4+ |
| Platinic |
Pt4+ |
| Manganic |
Mn4+ |
(B) Negative ions or Anions or Electronegative radicals:
(a) Anions having 1- charges
| Name |
Symbol or Formula |
| Flydride |
H– |
| Fluoride |
F– |
| Chloride |
Cl– |
| Bromide |
Br– |
| Iodide |
I– |
| Cyanide |
CN– |
| Hypochlorite |
CIO– |
| Chlorate |
ClO3– |
| Perchlorate |
ClO3– |
| Bicarbonate |
HCO3– |
| Name |
Symbol or Formula |
| Bisulphite |
HSO3– |
| Bisulphate |
HSO4– |
| Bisphide |
HS– |
| Hydroxide |
OH– |
| Meta-aluminate |
AlO2– |
| Nitrite |
NO2– |
| Nitrate |
NO3– |
| Acetate |
CH3COO– |
| Permanganate |
MnO4– |
| Sulphocyanide |
SCN– |

(b) Anions having 2- charges:
| Name |
Symbol or Formula |
| Carbonate |
CO32- |
| Sulphite |
SO32- |
| Sulphide |
S2- |
| Sulphate |
SO42- |
| Zincate |
ZnO22- |
| Oxide |
O2- |
| Manganate |
MnO42- |
| Chromate |
CrO42- |
| Dichromate |
Cr2O72- |
| Oxalate |
Cr2O42- |
| Peroxide |
O22- |
| Silicate |
SiO32- |
(c) Anions having 3- charges:
| Name |
Symbol or Formula |
| Nitride |
N3- |
| Phosphide |
P3- |
| Phosphite |
PO33- |
| Phosphate |
PO43- |
| Arsenite |
AsO33- |
| Arsenate |
AsO43- |
| Ferricyanide |
[Fe(CN)6]3- |
| Borate |
BO33- |
(d) Anions having 4- charges:
| Name |
Symbol or Formula |
| Carbide |
C4- |
| Ferrocyanide |
[Fe(CN)6]3- |
| Pyrophosphate |
P2O74- |
![]()
![]()
![]()