Punjab State Board PSEB 10th Class Science Book Solutions Chapter 7 Control and Coordination Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
PSEB Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 7 Control and Coordination
PSEB 10th Class Science Guide Control and Coordination Textbook Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Which of the following is plant hormone?
(A) Insulin
(B) Thyroxin
(C) Oestrogen
(D) Cytokinin.
Answer:
(D) Cytokinin.
Question 2.
The gap between two neurons is called :
(A) Dendrite
(B) Synapse
(C) Axon
(D) Impulse.
Answer:
(B) Synapse.
Question 3.
The brain is responsible for :
(A) Thinking
(B) Regulating the heart beat
(C) Balancing
(D) All of above.
Answer:
(D) All of above.
Question 4.
What is the function of receptors in the body? Think of situations where receptors do not work properly. What problems are likely to arise?
Answer:
Receptors. They are meant for receiving and detecting the information from environment. They are located in sense organs. They receive the information detected by tips of dendrites and convey them as electrical impulses.
If receptors do not detect the information, there will not be any co-ordination. It may lead to accidents. Body response will not be there.
Question 5.
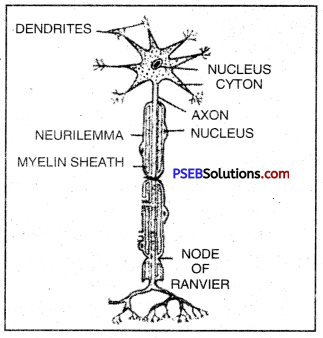
Draw a labelled diagram of neuron and explain its function.
Or
Draw the structure of neuron and label the following on it.
Nucleus, Dendrite, Cell body and Axon.
Answer:
Functions of Neuron (Nerve cell).
- Nerve cells are specialised for conducting information via electrical impulses from one part of the body to another part.
- Dendrites acquire the information.
- Axon conducts information as electrical impulse.
- Terminal arborization pass the information as chemical stimulus at synapse for onward transmission.
A Nerve Cell
![]()
Question 6.
How does phototropism Occur in planes?
Answer:
Phototropism.
It is an established fact that plants bend towards light when they are exposed to it from one side of long axis. The aerial parts are positively phototropic and the roots and other underground parts bend away from light. These movements are due to interaction of light and auxins. The unilateral growth causes bending of stem as tip grows more rapidly.
Question 7.
Which signals will get disrupted in case of spinal cord injury?
Answer:
- Spinal cord mainly controls reflex actions in the body. Spinal cord is made up of nerves which supply information to think about. Thus these actions will get disrupted in case of injury to spinal cord.
- Sensation and movement are restricted.
Question 8.
How does chemical co-ordination occur in plants?
Answer:
Chemical coordination in plants
- Plants do’not have well organised nervous and muscular system, still they respond to stimuli and co-ordinate in the best possible way.
- Different kinds of stimuli trigger the release of chemicals called plant hormones or phytohormones.
- These phytohormones help to coordinate growth development and responses to the environment.
- Auxins stimulate the cells to grow longer on one side of shoot in response to light thus it bends way.
- Gibberellins help in growth of stem.
- Cytokinins promote cell division.
- Abscisic acid inhibits growth. Its effects include wilting of leaves.
Question 9.
What is the need for a system of control and co-ordination in an organism?
Answer:
Control and Co-ordination in the body is of two types i.e. nervous control and hormonal control. Nervous control is rapid. It takes place through electrical signals called nerve impulses. The hormonal control is through chemical messengers called hormones secreted by endocrine (ductless) glands and carried by blood to the target organs.
Question 10.
How are involuntary actions different from reflex action?
Answer:
Reflex action is sudden and quick response to input (stimulus). It saves from many accidents. It is controlled by spiral cord. The involuntary actions are controlled by midbrain and hind brain. These are the actions in which thinking does not have any control. These actions are blood pressure, salivation and cycling.
Question 11.
Compare and contrast the nervous and hormonal mechanism for control and coordination in animals.
Answer:
Differences between endocrine system and nervous system
| Endocrine System | Nervous System |
| 1. The action of endocrine system is often very diverse, affecting many cells and sometimes several organs found in different parts of the body. | 1. The action of nervous system is limited to a few muscle fibres or gland cells of an organ or organ system. |
| 2. The system is not directly connected to organs or tissues under its control. | 2. The system is directly connected to tissues or organs under its control. |
| 3. It exerts its control through hormones or chemical regulators poured into circulatory system. | 3. Nervous system exerts its control through chemical stimulants poured directly over the tissues or organs. |
| 4. The information is transmitted slowly. | 4. The information is transmitted almost instantaneously. |
| 5. The system takes time to produce response. It, therefore, regulates those processes where the response is not immediately required. | 5. It controls process where an immediate response is required. |
| 6. The effect is long lasting. | 6. The effect is short lived. |
Question 12.
What is the difference between the manner is which movement takes place in a sensitive plant and the movement in our leg.
Answer:
Movement of human leg is under the control of nervous system. It is under the
direction of motor area which, controls voluntary muscles of leg. The sensitive plant “Touch me not,” moves its leaves in response to touch but without any regulation by nervous tissue.
Science Guide for Class 10 PSEB Control and Coordination InText Questions and Answers
Question 1.
What is the difference between reflex action and walking?
Answer:
Differences between reflex action and walking:
| Reflex Action | Walking |
| 1. It is an inborn action and present in an individual right from birth. | 1. Walking is acquired through learning. |
| 2. It is controlled by spinal cord. | 2. It is controlled by hind brain. |
| 3. It cannot be changed. | 3. It can be changed. |
| 4. It is involuntary action. | 4. To start with it is voluntary and later on it becomes involuntary. |
| 5. Response is given by muscles and glands. | 5. Response is given by muscles. |
Question 2.
What happens at the synapse between two neurons?
Answer:
Synapse is a junction between terminal ends of one axon and dendrites of adjacent neuron. There is a gap between the two called synaptic cleft. As the electrical impulse reaches the terminal knobs, they release chemicals called neurotransmitters. These chemicals cross the gap and start a similar electrical impulse in the dendrite of next neuron. Synapse ensures that nerve impulse travels in one direction only.
Question 3.
Which part of the brain maintains posture and equilibrium of the body?
Answer:
Cerebellum part of hind brain maintains posture and equilibrium.
Question 4.
How do we detect the smell of an agarbatti (Incense stick)?
Answer:
Sensory information regarding smell is received by olfactory lobes of brain. As the air passes through the nasal chambers, the olfactory epithelial cells get stimulated and convey the information as electrical impulses to brain which have the power of interpretation.
![]()
Question 5.
What is the role of the brain in reflex action?
Answer:
Thinking centres are located in brain. Brain is the co-ordinating centre. Brain and spinal cord in coordination with each other control all voluntary and involuntary actions. The spinal reflexes are produced in the spinal cord but the message of reflex action taken also goes to brain where the thinking process occurs. Some reflex arcs involve the brain rather than the spinal cord only.
Question 6.
WTiat are plant hormones? Name any two.
Answer:
Plant hormones. These are chemical compounds secreted by plants which diffuse all around the other cells and regulate the activities. Plant hormones help to co-ordinate growth, development and responses to the environment.
Examples : Auxins and Cytokinin.
Question 7.
How is the movement of leaves of the sensitive plant different from the movement of a shoot towards light?
Answer:
Sensitive plant show seismonastic movements. It is due to turgidity of cells. The movement of a shoot is a tropic movement.
| Movement of the leaves of sensitive plant | Movement of shoot towards light |
| 1. It is a nastic movement which does not depend on the direction of stimulus. | 1. It is a tropic movement. |
| 2. The stimulus is touch. | 2. The stimulus is light. |
| 3. It is caused by sudden loss of water from the swelling present at the base of the leaves. | 3. It is caused by the unequal growth on the two sides of the shoot. |
| 4. It is not a growth movement. | 4. It is a growth movement. |
Question 8.
Give an example of a plant hormone that promotes growth.
Answer:
IAA = Indole-3-Acetic Acid.
Question 9.
How do auxins promote the growth of a tendril around a support?
Answer:
Auxins synthesised in the tip helps the cells to grow longer. Some plants like the pea plant climb up other plants or support by means of tendrils. These tendrils are sensitive to touch. When they come in contact with any support, the part of the tendril in contact with the object does not grow as rapidly as the part of the tendril away from the object. This causes the tendril to circle around the object and thus cling to it. It is due to accumulation of auxins.
Question 10.
Design an experiment to demonstrate hydrotropism.
Answer:
Experiment to demonstrate hydrotropism
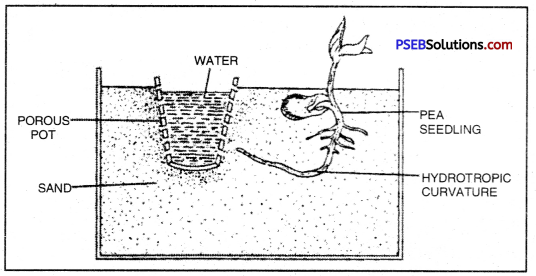
Demonstration of hydrotropism
- Take a porous pot and fill it with water.
- Keep a few freshly germinated pea seedlings in a dried sand.
- As the water is not available in sand the root growing will bend towards porous pot filled with water.
- You wall observe a hydrotropic curvature of the root as it grows towards water.
- This bending of root show the movement as a response towards water.
Question 11.
How does chemical coordination take place in animals?
Answer:
Chemical coordination. It is brought about by chemical messengers called hormones. They are secreted by endocrine glands (ductless glands). The hormones are carried by the blood to the site of action (target organs). The hormones are consumed during their action. Hormones provide wide ranging changes.
Question 12.
Why is the use of iodised salt advisable?
Answer:
Iodine is necessary for the thyroid gland to make thyroxine hormone. Thyroxine regulates carbohydrate, protein and fat metabolism. It is required for growth. In case of deficiency of thyroxine, a disorder called goitre is caused. Thus, the use of iodised salt is advisable .to prevent iodine deficiency disorders in the body.
Question 13.
How does our body respond when adrenaline is secreted into blood?
Answer:
Adrenaline is secreted by the adrenal gland during emergencies. It prepares the body to respond effectively. Following actions occur :
- Heartbeats faster so as to pump the blood to muscles that need more energy.
- The blood supply to the digestive system and skin is reduced due to the contraction of muscles around these organs. This helps in diverting blood supply to muscles.
- Breathing becomes fast.
![]()
Question 14.
Why are some patients with diabetes treated by giving injections of insulin?
Answer:
Insulin hormone is secreted by Islets of Langerhans of the pancreas. This hormone helps in regulating sugar levels in the blood. Its deficiency results in high sugar levels and causes many harmful effects. To bring the sugar level to normal in such diabetic patients, insulin injections are given.
