Punjab State Board PSEB 11th Class Chemistry Important Questions Chapter 13 Hydrocarbons Important Questions and Answers.
PSEB 11th Class Chemistry Important Questions Chapter 13 Hydrocarbons
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Why do hydrocarbon molecules with an odd number of carbon atoms have lower melting points than those with an even number of carbon atoms?
Answer:
Molecules with odd number of carbon atoms have lower melting points because they do not fit into crystal lattice easily whereas, hydrocarbons with even number of carbon atoms can fit into crystal lattice easily.
Question 2.
Why do the C—C bonds rather than C—H bonds break during cracking of alkanes?
Since, the bond dissociation energy of C—C bonds (348 kJ mol-1) is lower than bond dissociation energy of C—H bonds (414 kJ mol-1), therefore, during cracking of alkanes, C—C bonds break more easily than C—H bonds.
![]()
Question 3.
Which of the two frans-but-2-ene or trans-2-ene is non-polar?
Answer:
In frans-but-2-ene, the dipole moments of the two C—CH3 bonds are equal and opposite and therefore, they cancel out each other. Hence, trans-2-butene is non-polar.
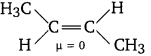
Question 4.
Explain why alkynes are less reactive than alkenes toward addition of Br2.
Answer:
The three-membered ring bromonium ion formed from the alkyne (A) has a full double bond causing it to be more strained and less stable than the one from the alkene (B),

Also, the carbon’s of (A) that are part of the bromonium ion have more s-character than (B), further making (A) less stable than (B).
Question 5.
Explain the reason for extra ordinary stability of benzene in spite of presence of three double bonds in it.
Answer:
It is due to resonance, 6 π-electrons are delocalised.
Question 6.
How will you demonstrate that double bonds of benzene are somewhat different from that of olefines?
Answer:
The double bonds of olefines decolourise Br2 in CCl4 and discharge the pink colour of Baeyer’s reagent with simultaneous formation of a brown ppt. of MnO2 while those of benzene do not.
Question 7.
n-propylmagnesium bromide on hydrolysis gives propane. Is there any other Grignard reagent which also gives propane? If so, give its name, structure and equation for the reaction.
Answer:
Iso-propylmagnesium bromide, (CH3)2CHMgBr,
(CH3)2CHMgBr + H2O → CH3CH2CH3 + Mg(OH)Br
![]()
Question 8.
How would you distinguish between
(i) But-l-yne and but-2-yne
(ii) Propene and propyne
Answer:
(i) Upon treatment with ammoniacal solution of AgNO3, but-l-yne would give white ppt. whereas but-2-yne does not react.
(ii) Upon treatment with ammoniacal solution of AgNO3, propyne would give white ppt. whereas propene does not react.
Question 9.
Give the structure of the alkene (C4H8) which adds on HBr in the presence and in absence of peroxide to give the same product, C4H9Br.
Answer:
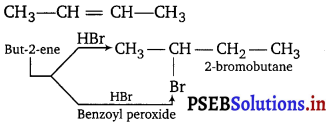
Question 10.
Convert 1-bromopropane to 2-bromopropane.
Answer:

Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Write hydrocarbon radicals that can be formed as intermediates during monochlorination of 2-methylpropane. Which of them is more stable? Give reasons.
Answer:
2-methylpropane gives two types of radicals
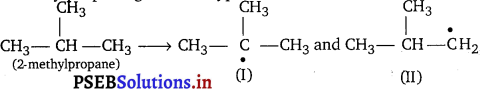
Radical (I) is more stable because it is 3° and stabilised by nine hyperconjugative structures (as it has 9 a-hydrogens). Radical (II) is less stable because it is 1° and stabilised by only one hyperconjugative structure (as it has only 1 a-hydrogen).
Question 2.
Rotation around carbon-carbon single bond of ethane is not completely free. Justify the statement.
Answer:
Rotation around C—C single bond is not completely free and it is restricted due to repulsions between the electron clouds of C—H bonds in the adjacent carbon atoms. Therefore, ethane exists in infinite number of conformations. Out of these, two extreme conformations are staggered and eclipsed.
![]()
Question 3.
List the following alkenes in decreasing order of reactivity towards electrophilic addition. ‘
(i) ClCH2CH = CH2 (ii) (CH3)2C = CH2 (iii) CH3CH = CH2 (iv) CH2 = CHCl
Explain your order.
Answer:
Electron donating alkyl groups make the rt-bond more electron rich and more reactive. Conversely, electron withdrawing groups such as Cl make the rc-bond more electron deficient and less reactive. The order is
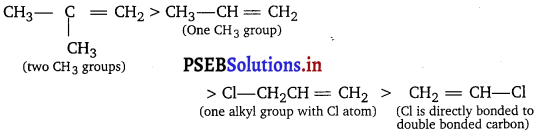
Question 4.
The intermediate carbocation formed in the reactions of HI, HBr and HCl with propene is the same and the bond energy of HC1, HBr and HI is 430.5 kJ mol-1, 363.7 kJ mol1 and 296.8 kJ mol-1 respectively. What will be the order of reactivity of these halogen acids?
Answer:
Addition of halogen acids to an alkene is an electrophilic addition reaction.
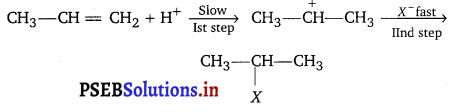
First step is slow so, it is rate determining step. The rate of this step depends on the availability of proton. This in turn depends upon the bond dissociation enthalpy of the H—X molecule. Lower the bond dissociation enthalpy of H—X molecule, greater the reactivity of halogen halide. Since, the bond dissociation energy decreases in the order; HI (296.8 kJ mol-1) < HBr (363.7 kJ mol-1) < HCl (430.5 kJ mol-1)
Therefore the reactivity of the halogen acids decreases from HI to HCl i.e., HI > HBr > HCl.
Question 5.
An alkyl halide (X) of formula C6H13Cl on treatment with alcoholic KOH or potassium terf-butoxide gives two isometric alkenes Y and Z(C6H12). Both alkenes on hydrogenation give 2, 3-dimethylbutane. Predict the structure of X, Y and Z.
Answer:
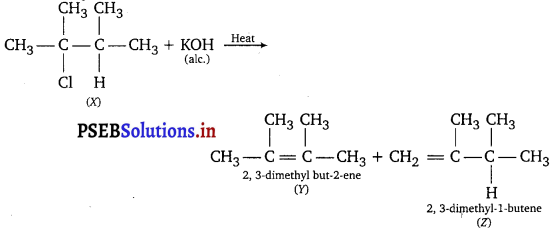
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Assign structures to the following:
(i) An alkyne (X) has molecular formula CsHg. It reacts neither with sodamide nor with ammoniacal cuprous chloride.
(ii) A hydrocarbon ‘Y’ decolourises bromine water. On ozonolysis it gives 3-methyl butanal and formaldehyde. Give the name of the compound.
(iii) A hydrocarbon (Z) has molecular formula C8H10. It does not decolourise bromine water and is oxidised to benzoic acid on heating with K2Cr2O7. It can also have three other isomers A, B and C. Write the structures of Z, A, B and C.
Ans. (i) Alkyne X is CsHg. Since, it does not react with sodamide or ammoniacal, cuprous chloride, the triple bond cannot be terminal. ∴ X is CH3CH2C = CCH3 (Pent-2-yne)
(ii) Hydrocarbon ‘Y’ is alkene because it decolourises bromine water. From the products of ozonolysis, the structure of alkene can be predicted.
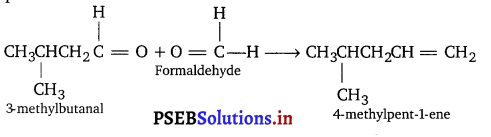
(iii) Since, it does not decolourise bromine water, it is arene. Its formula is
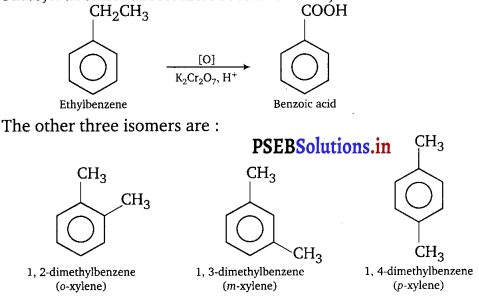
![]()
Question 2.
(i) Arrange the three isomeric pentanes in order of increasing stability at room temperature.
(ii) Give a method of preparation of propane from (a) an alkene (b) an alkyl halide.
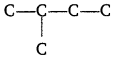
(iii) Write the structure of all the alkenes that can be hydrogenated to form 2-methyl butane.
(iv) Why is light or heat necessary to initiate the chlorination reaction?
Answer:
(i) The stability of structural isomers generally increases with increasing branching. Thus,
Pentane, [CH3(CH2)3CH3] iso-pentane, [(CH3)2CHCH2CH3] < neo-pentane, [(CH3)4C]
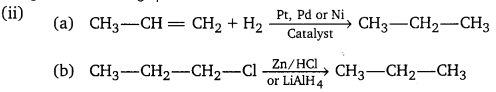
(iii) The alkenes must have the same carbon skeleton as 2-methyl butane.
There are three different positions for the double bond; hence the three different alkenes are :
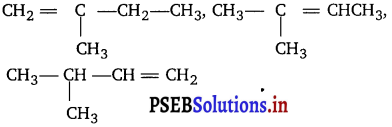
(iv) The Cl—Cl bond must be broken to form Cl radical before the reaction with methane. This homolysis requires energy, which is supplied either by heat or light.
