Punjab State Board PSEB 11th Class Maths Book Solutions Chapter 13 Limits and Derivatives Ex 13.1 Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
PSEB Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 13 Limits and Derivatives Ex 13.1
Question 1.
Evaluate the given limit: \(\lim _{x \rightarrow 3}\) x + 3.
Answer.
\(\lim _{x \rightarrow 3}\) x + 3 = 3 + 3 = 6.
Question 2.
Evaluate the given limit: \(\lim _{x \rightarrow \pi}\) (x – \(\frac{22}{7}\)).
Answer.
\(\lim _{x \rightarrow \pi}\) (x – \(\frac{22}{7}\)) = (π – \(\frac{22}{7}\)).
![]()
Question 3.
Evaluate the given limit : \(\lim _{x \rightarrow 1}\) πr2.
Answer.
\(\lim _{x \rightarrow 1}\) πr2 = π (1)2 = π.
Question 4.
Evaluate the given limit : \(\lim _{x \rightarrow 4} \frac{4 x+3}{x-2}\).
Answer.
\(\lim _{x \rightarrow 4} \frac{4 x+3}{x-2}=\frac{4(4)+3}{4-2}=\frac{16+3}{2}=\frac{19}{2}\)
Question 5.
Evaluate the given limit: \(\lim _{x \rightarrow-1} \frac{x^{10}+x^{5}+1}{x-1}\)
Answer.
\(\lim _{x \rightarrow-1} \frac{x^{10}+x^{5}+1}{x-1}=\frac{(-1)^{10}+(-1)^{5}+1}{-1-1}\)
= \(\frac{1-1+1}{-2}=-\frac{1}{2}\)
![]()
Question 6.
Evaluate the given limit : \(\lim _{x \rightarrow 0} \frac{(x+1)^{5}-1}{x}\).
Answer.

Question 7.
Evaluate the given limit : \(\lim _{x \rightarrow 2} \frac{3 x^{2}-x-10}{x^{2}-4}\).
Answer.
At x = 2, the value of the given rational function takes the form \(\frac{0}{0}\).
∴ \(\lim _{x \rightarrow 2} \frac{3 x^{2}-x-10}{x^{2}-4}=\lim _{x \rightarrow 2} \frac{(x-2)(3 x+5)}{(x-2)(x+2)}\)
Question 8.
Evaluate the given limit: \(\lim _{x \rightarrow 3} \frac{x^{4}-81}{2 x^{2}-5 x-3}\).
Answer.
At x = 3, the value of the given rational function takes the form \(\frac{0}{0}\).
∴ \(\lim _{x \rightarrow 3} \frac{x^{4}-81}{2 x^{2}-5 x-3}\) = \(\lim _{x \rightarrow 3} \frac{(x-3)(x+3)\left(x^{2}+9\right)}{(x-3)(2 x+1)}\)
\(\lim _{x \rightarrow 3} \frac{(x+3)\left(x^{2}+9\right)}{2 x+1}\) = \(\frac{(3+3)\left(3^{2}+9\right)}{2(3)+1}\)
= \(\frac{6 \times 18}{7}=\frac{108}{7}\)
![]()
Question 9.
Evaluate the given limit; \(\lim _{x \rightarrow 0} \frac{a x+b}{c x+1}\).
Answer.
\(\lim _{x \rightarrow 0} \frac{a x+b}{c x+1}=\frac{a(0)+b}{c(0)+1}\) = .
Question 10.
Evaluate the given limit: \(\lim _{z \rightarrow 1} \frac{z^{\frac{1}{3}}-1}{z^{\frac{1}{6}}-1}\).
Answer.
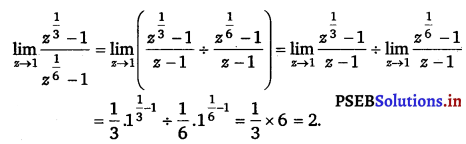
Question 11.
Evaluate the given limit: \(\lim _{x \rightarrow 1} \frac{a x^{2}+b x+c}{c x^{2}+b x+a}\), a + b + c ≠ 0.
Answer.
\(\lim _{x \rightarrow 1} \frac{a x^{2}+b x+c}{c x^{2}+b x+a}=\frac{a(1)^{2}+b(1)+c}{c(1)^{2}+b(1)+a}\)
= \(\frac{a+b+c}{a+b+c}\) = 1. [a + b + c ≠ 0]
Question 12.
Evaluate the given limit: \(\lim _{x \rightarrow-2} \frac{\frac{1}{x}+\frac{1}{2}}{x+2}\)
Answer.
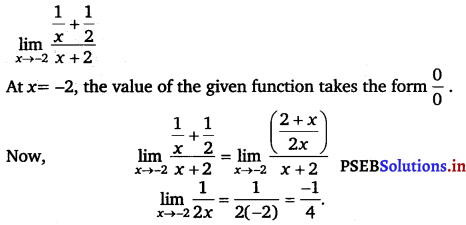
![]()
Question 13.
Evaluate the given limit: \(\lim _{x \rightarrow 0} \frac{\sin a x}{b x}\).
Answer.
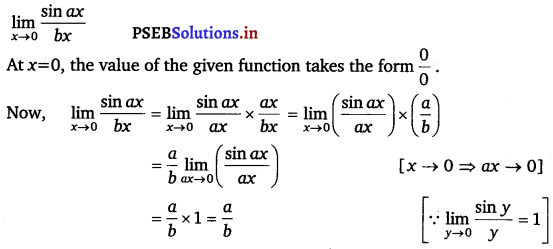
Question 14.
Evaluate the given limit: \(\lim _{x \rightarrow 0} \frac{\sin a x}{\sin b x}\), a, b ≠ 0.
Answer.
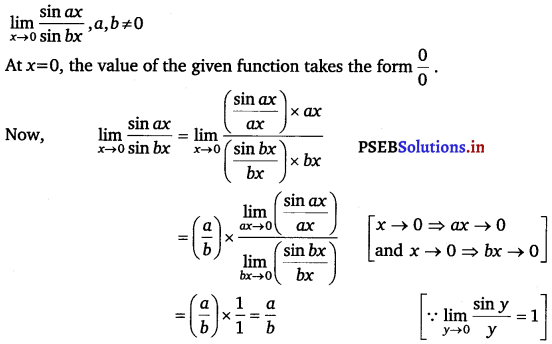
![]()
Question 15.
Evaluate the given limit: \(\lim _{x \rightarrow \pi} \frac{\sin (\pi-x)}{\pi(\pi-x)}\)
Answer.
\(\lim _{x \rightarrow \pi} \frac{\sin (\pi-x)}{\pi(\pi-x)}\)
put π – x = θ, As x → π, θ → 0 (zero)
\(\lim _{\theta \rightarrow 0} \frac{\sin \theta}{\pi \theta}=\lim _{\theta \rightarrow 0} \frac{1}{\pi} \frac{(\sin \theta)}{\theta}=\frac{1}{\pi}\)
Question 16.
Evaluate the given limit: \(\lim _{x \rightarrow 0} \frac{\cos x}{\pi-x}\).
Answer.
\(\lim _{x \rightarrow 0} \frac{\cos x}{\pi-x}=\frac{\cos 0}{\pi-0}=\frac{1}{\pi}\)
Question 17.
Evaluate the given limit: \(\lim _{x \rightarrow 0} \frac{\cos 2 x-1}{\cos x-1}\).
Answer.
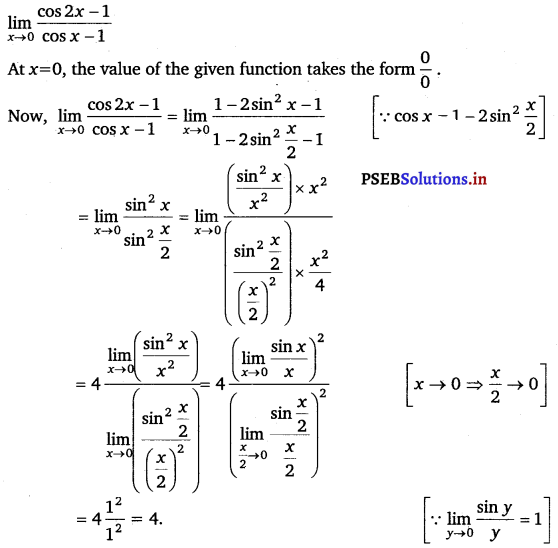
![]()
Question 18.
Evaluate the given limit: \(\lim _{x \rightarrow 0} \frac{a x+x \cos x}{b \sin x}\)
Answer.
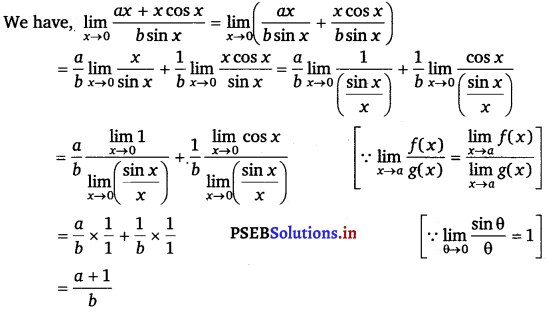
Question 19.
Evaluate the given limit: \(\lim _{x \rightarrow 0}\) x sec x.
Answer.
\(\lim _{x \rightarrow 0}\) x sec x = \(\lim _{x \rightarrow 0} \frac{x}{\cos x}=\frac{0}{\cos 0}=\frac{0}{1}\) = 0.
Question 20.
Evaluate the given limit: \(\) a, b, a + b ≠ 0.
Answer.
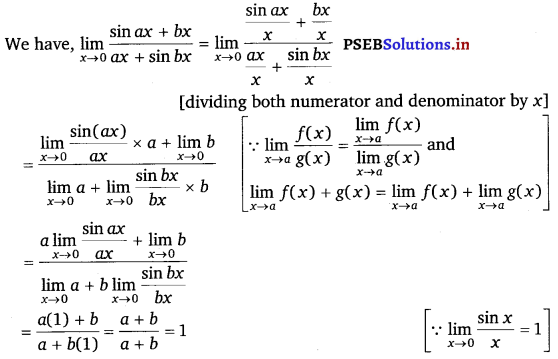
![]()
Question 21.
Evaluate the given limit: \(\lim _{x \rightarrow 0}\) (cosec x – cot x).
Answer.
\(\lim _{x \rightarrow 0}\) (cosec x – cot x)
At x = 0, the value of the given function takes the form ∞ – ∞.
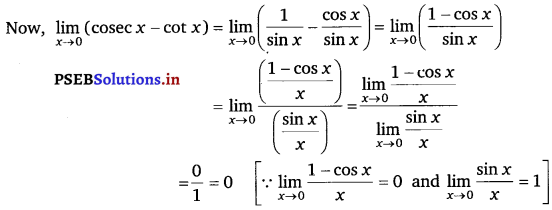
Question 22.
Evaluate the given limit \(\lim _{x \rightarrow \frac{\pi}{2}} \frac{\tan 2 x}{x-\frac{\pi}{2}}\).
Answer.
\(\lim _{x \rightarrow \frac{\pi}{2}} \frac{\tan 2 x}{x-\frac{\pi}{2}}\)
At x = \(\frac{\pi}{2}\), the value of the given function takes the form \(\frac{0}{0}\).
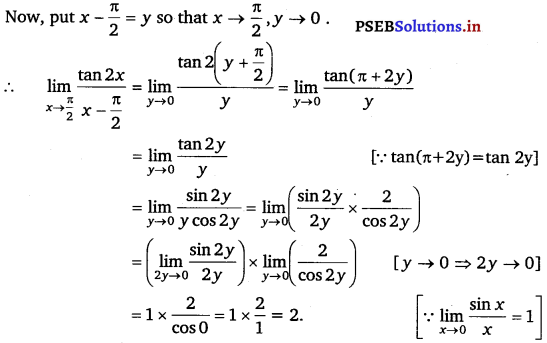
![]()
Question 23.
Find \(\lim _{x \rightarrow 0}\) f(x) and \(\lim _{x \rightarrow 1}\) f(x), where f(x) = 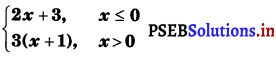 .
.
Answer.
Given, f(x) = 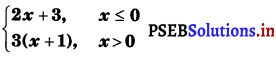
(i) Now, LHL = \(\lim _{x \rightarrow 0^{-}}\) f(x) = \(\lim _{x \rightarrow 0^{-}}\) (2x + 3)
= \(\lim _{h \rightarrow 0}\) [2 (0 – h) + 3] = 3
[putting x = 0 – h as x → 0, then h → 0]
RHL = \(\lim _{x \rightarrow 0^{+}}\) f(x) = \(\lim _{x \rightarrow 0^{+}}\) 3(x + 1)
= \(\lim _{h \rightarrow 0}\) [3(0 + h) + 1] = 3
[putting x = 0 + h as x → 0,then h → 0]J
Here, LHL = RHL
∴ \(\lim _{x \rightarrow 0}\) f(x) = 3
(ii) We have to find \(\lim _{x \rightarrow 1}\) f(x)
\(\lim _{x \rightarrow 1}\) f(x) = \(\lim _{x \rightarrow 1}\) 3 (x + 1)
= 3 (1 + 1) = 6
Question 24.
Find \(\lim _{x \rightarrow 1}\) f(x), where f(x) = 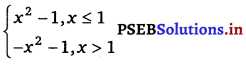
Answer.
Given, f(x) = 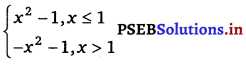
At x = 1,
RHL = \(\lim _{x \rightarrow 1^{+}}\) f(x) = \(\lim _{h \rightarrow 0}\) f(1 + h)
= \(\) (1 + h)2 – 1 [put x = 1 + h]
= – (1 + 0)2 – 1
= – 1 – 1 = – 2
LHL = \(\lim _{x \rightarrow 1^{-}}\) f(x) = \(\lim _{h \rightarrow 0}\) f(1 – h)
= \(\lim _{h \rightarrow 0}\) (1 – h)2 – 1 [put x = 1 – h]
= (1 – 0)2 – 1 = 1 – 1 = 0
RHL ≠ LHL
Hence, at x = 1 , limit does not exist.
![]()
Question 25.
Evaluate \(\lim _{x \rightarrow 0}\) f(x), where f(x) =  .
.
Answer.

Question 26.
Find \(\lim _{x \rightarrow 0}\) f(x), where f(x) =  .
.
Answer.
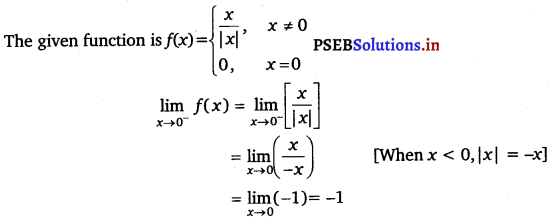
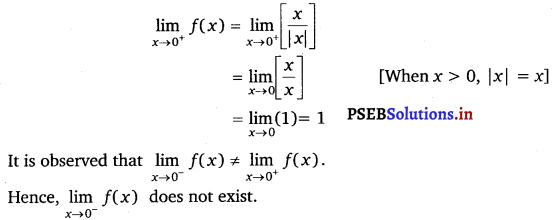
![]()
Question 27.
Find \(\lim _{h \rightarrow 5}\) f(x), where f(x) = |x| – 5.
Answer.
The given function is f(x) = |x| – 5
when x > 5, put x = 5 + h, where h is small
|x| = |5 + h| = 5 + h
∴ \(\lim _{x \rightarrow 5^{+}}\) f(x) = \(\lim _{h \rightarrow 0}\) [(5 + h) – 5] = \(\lim _{h \rightarrow 0}\) h = 0
when x < 5, put x = 5 – h, where h is small
∴ |5 – h| = 5 – h
∴ \(\lim _{x \rightarrow 5^{-}}\) f(x) = \(\lim _{h \rightarrow 0}\) (5 – h – 5) = \(\lim _{h \rightarrow 0}\) (- h) = 0
∴ \(\lim _{x \rightarrow 5^{-}}\) f(x) = \(\lim _{x \rightarrow 5^{+}}\) f(x) = 0
∴ \(\lim _{h \rightarrow 5}\) f(x) = 0
Question 28.
Suppose f(x) = 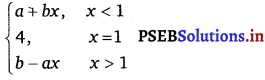 and if \(\lim _{h \rightarrow 1}\) f(x) = f(1) what are possible values of a and b ?
and if \(\lim _{h \rightarrow 1}\) f(x) = f(1) what are possible values of a and b ?
Answer.
The given function is f(x) = 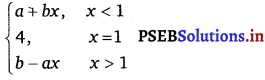
\(\lim _{x \rightarrow 1^{-}}\) f(x) = \(\lim _{x \rightarrow 1}\) (a + bx) = a + b
\(\lim _{x \rightarrow 1^{-}}\) f(x) = \(\lim _{x \rightarrow 1}\) (b – ax) = b – a
f(1) = 4
It is given that \(\lim _{x \rightarrow 1}\) f(x) = f(1).
∴ \(\lim _{x \rightarrow 1^{-}}\) f(x) = \(\lim _{x \rightarrow 1^{+}}\) f(x)
= \(\lim _{x \rightarrow 1}\) f(x) = f(1)
a + b = 4 and b – a = 4.
On solving these two equations, we obtain a = 0 and b = 4.
Thus, the respective possible values of a and b are 0 and 4.
![]()
Question 29.
Let a1, a2, ………. a, be fixed real numbers and define a function f(x) = (x – a1) (x – a2) ………….. (x – an). What is \(\lim _{x \rightarrow a_{1}}\) f(x)? For some a ≠ a1, a2, ………………. an compute \(\lim _{x \rightarrow a}\) f(x).
Answer.
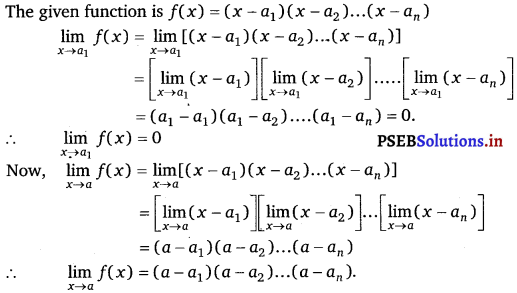
Question 30.
If f(x) = 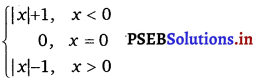 For what value(s) of a does f(x) exists?
For what value(s) of a does f(x) exists?
Answer.

![]()
Question 31.
If the function f(x) satisfies \(\lim _{x \rightarrow 1} \frac{f(x)-2}{x^{2}-1}\) = π, evaluate \(\lim _{x \rightarrow 1}\) f(x).
Answer.
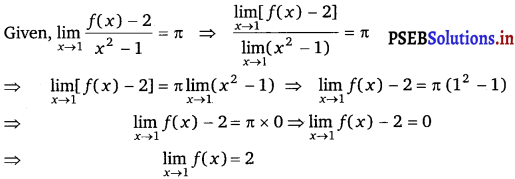
![]()
Question 32.
If f(x) = 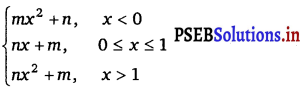 For what integers m and n does \(\lim _{x \rightarrow 0}\) f(x) and \(\lim _{x \rightarrow 1}\) f(x) exist?
For what integers m and n does \(\lim _{x \rightarrow 0}\) f(x) and \(\lim _{x \rightarrow 1}\) f(x) exist?
Answer.

