Punjab State Board PSEB 11th Class Maths Book Solutions Chapter 16 Probability Ex 16.1 Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
PSEB Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 16 Probability Ex 16.1
Question 1.
Describe the sample space for the indicated experiment: A coin is tossed three times.
Answer.
A coin has two faces : head (H) and tail (T).
When a coin is tossed three times, the total number of possible outcomes is 23 = 8
Thus, when a coin is tossed three times, the sample space is given by:
S = {HHH, HHT, HTH, HIT, THH, THT, TTH, TTT}.
Question 2.
Describe the sample space for the indicated experiment. A die is thrown two times.
Answer.
When a die is thrown, the possible outcomes are 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, or 6. When a die is thrown two times, the sample space is given by S={(x, y): x, y = 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}.
The number of elements in this sample space is 6 × 6 = 36, while the sample space is given by :
S = {(1, 1), (1, 2), (1, 3), (1, 4), (1, 5), (1, 6), (2, 1), (2, 2), (2, 3), (2, 4), (2, 5), (2, 6), (3, 1), (3, 2), (3, 3), (3, 4), (3, 5), (3, 6),
(4, 1), (4, 2), (4, 3), (4, 4), (4, 5), (4, 6), (5, 1), (5, 2), (5, 3), (5, 4), (5, 5), (5, 6), (6, 1), (6, 2), (6, 3), (6, 4), (6, 5), (6, 6)}.
![]()
Question 3.
Descibe the sample space for the indicated experiment: A coin is tossed four times.
Answer.
When a coin is tossed once, there are two possible outcomes: head (H) and tail (T).
When a coin is tossed four times, the total number of possible outcomes is 24 = 16
Thus, when a coin is tossed four times, the sample space is given by:
S = {HHHH, HHHT, HHTH, HHTT, HTHH, HTHT, HTTH, HTTT, THHH, THHT, THTH, THTT, TTHH, TTHT, TTTH, TTTT}.
Question 4.
Describe the sample space for the indicated experiment: A coin is tossed and a die is thrown.
Answer.
A coin has two faces: head (H) and tail (T).
A die has six faces that are numbered from 1 to 6, with one number on each face.
Thus, when a coin is tossed and a die is thrown, the sample space is given by:
S = {H1, H2, H3, H4, H5, H6, T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6}.
Question 5.
Describe the sample space for the indicated experiment: A coin is tossed and then a die is rolled only in case a head is shown on the coin.
Answer.
A coin has two faces: head (H) and tail (T).
A die has six faces that are numbered from 1 to 6, with one number on each face.
Thus, when a coin is tossed and then a die is rolled only in case a head is shown on the coin, the sample space is given by:
S = {H1, H2, H3, H4, H5, H6,T}.
![]()
Question 6.
2 boys and 2 girls are in Room X, and 1 boy and 3 girls in Room Y. Specify the sample space for the experiment in which a room is selected and then a person.
Answer.
Let us denote 2 boys and 2 girls in room X as B1 B2 and G1, G2 respectively.
Let us denote 1 boy and 3 girls in room Y as B3 and G3, G4, G5 respectively. Accordingly, the required sample space is given by
S = {XB1, XB2, XG1, XG2, YB3, YG3, YG4, YG5}.
Question 7.
One die of red colour, one of white colour and one of blue colour are placed in a bag. One die is selected at random and rolled, its colour and the number on its uppermost face is noted. Describe the sample space,
Answer.
A die has six faces that are numbered from 1 to 6, with one number on each face.
Let us denote the red, white, and blue dices as R, W, and B respectively. Accordingly, when a die is selected and then rolled, the sample space is given by
S = {R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6, W1, W2, W3, W4, W5, W6, B1, B2, B3, B4, B5, B6}.
Question 8.
An experiment consists of recording boy-girl composition of families with 2 children.
(i) What is the sample space if we are interested in knowing whether it is a boy Or girl in the order of their births?
(ii) What is the sample space if we are interested in the number of girls in the family?
Answer.
(i) When the order of the birth of a girl or a boy is considered, the sample space is given by S = {GG, GB, BG, BB}.
(ii) Since the maximum number of children in each family is 2, a family can either have 2 girls or 1 girl or no girl.
Hence, the required sample space is S = {0, 1, 2}.
![]()
Question 9.
A box contains 1 red and 3 identical white balls. Two balls are drawn at random in succession without replacement. Write the sample space for this experiment.
Answer.
It is given that the box contains 1 red ball and 3 identical white balls. Let us denote the red ball with R and a white ball with W.
When two balls are drawn at random in succession without replacememt, the sample space is given by
S = {RW, WR, WW}.
Question 10.
An experiment consists of tossing a coin and then throwing it second time if a head occurs. If a tail occurs on the first toss, then a die is rolled once. Find the sample space.
Answer.
It is a two stage experiment. First stage results is either ‘head’ or ‘tail’ when the coin shows up head, then it is tossed again showing up either a head or a tail. If the first toss shows up a tail, then a die is rolled once which may show up any one of the six numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6.
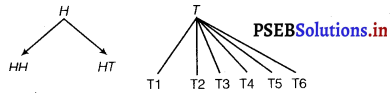
∴ S = {(H, H), (H, T), (T, 1), (T, 2), (T, 3), (T, 4), (T, 5), (T, 6)}.
![]()
Question 11.
Suppose 3 bulbs are selected at random from a lot. Each bulh is tested and classified as defective (D) or non-defective (N). Write the sample space of this experiment?
Answer.
Let we denote defective bulb by D and non-defective bulb by N.
There are 23 = 8 possible outcomes.
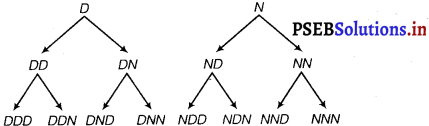
Question 12.
A coin is tossed. If the out come is a head, a die is thrown. If the die shows up an even number, the die is thrown again. What is the sample space for the experiment?
Answer.
When a coin is tossed, the possible outcomes are head (H) and tail (T).
When a die is thrown, the possible outcomes are 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, or 6.
Thus, the sample space of this experiment is given by:
S = {T, H1, H3, H5, H21, H22, H23, H24, H25, H26, H41, H42, H43, H44, H45, H46, H61, H62, H63, H64, H65, H66}.
![]()
Question 13.
The numbers 1, 2, 3 and 4 are written separately on four slips of paper. The slips are put in a box and mixed thoroughly. A person draws two slips from the box, one after the other, without replacement. Describe the sample space for the experiment.
Answer.
If 1 appears on the first drawn slip, then the possibilities that the number appears on the second drawn slip are 2, 3, or 4. Similarly, if 2 appears on the first drawn slip, then the possibilities that the number appears on the second drawn slip are 1, 3, or 4. The same holds true for the remaining numbers too.
Thus, the sample space of this experiment is given by:
S = {(1, 2), (1, 3), (1, 4), (2, 1), (2, 3), (2, 4), (3, 1), (3, 2), (3, 4), (4, 1), (4, 2), (4, 3)}.
Question 14.
An experiment consists of rolling a die and then tossing a coin once if the number on the die is even. If the number on the die is odd, the coin is tossed twice. Write the sample space for this experiment.
Answer.
A die has six faces that are numbered from 1 to 6, with one number on each face. Among these numbers, 2, 4, and 6 are even numbers, while 1, 3, and 5 are odd numbers. ‘
A coin has two faces: head (H) and tail (T).
Hence, the sample space of this experiment is given by:
S = {2H, 2T, 4H, 4T, 6H, 6T, 1HH, 1HT, 1TH, ITT, 3HH, 3HT, 3TH, 3TT, 5HH, 5HT, 5TH, 5TT}.
![]()
Question 15.
A coin is tossed. If it shows a tail, we draw a ball from a box which contains 2 red and 3 black balls. If it shows head, we throw a die. Find the sample space for this experiment.
Answer.
The box contains 2 red balls and 3 black balls. Let us denote the 2 red balls as Rj R2 and the 3 black balls as B1 B2 and B3.
The sample space of this experiment is given by
S = {TR1, TR2, TB1, TB2, TB3, H1, H2, H3, H4, H5, H6}.
Question 16.
A die is thrown repeatedly until a six comes up. What is the sample space for this experiment?
Answer.
In this experiment, six may come up on the first throw, the second throw, the third throw and so on till six is obtained.
Hence, the sample space of this experiment is given by
S = {6, (1, 6), (2, 6), (3, 6), (4, 6), (5, 6), (1, 1, 6), (1, 2, 6), (1, 5, 6), (2,1, 6,), (2, 2, 6), (2, 5, 6), (5, 1, 6), (5, 2, 6)}.
