Punjab State Board PSEB 11th Class Sociology Book Solutions Chapter 9 Social Structure Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
PSEB Solutions for Class 11 Sociology Chapter 9 Social Structure
Sociology Guide for Class 11 PSEB Social Structure Textbook Questions and Answers
Answer the following very short answer questions in 1-15 words each:
Question 1.
Give the meaning of the term social structure.
Answer:
Systematic form of interrelated parts of society is known as social structure.
Question 2.
From which word the word ‘structure’ is derived ?
Answer:
The word ‘structure’ is derived from the Latin word ‘Staruere’ whose meaning is ‘building’.
Question 3.
Who was the first sociologist to use the term social structure ?
Answer:
Herbert Spencer was the first sociologist to use the term social structure,
![]()
Question 4.
Name the elements of social structure.
Answer:
Status and role are the elements of social structure.
Question 5.
Who wrote the book ‘The Principles of Sociology’?
Answer:
This book was written by Herbert Spencer.
Question 6.
What is Status ?
Answer:
Status is a position given to a person while living in society.
Question 7.
Name two types of social statuses.
Answer:
Ascribed status and Achieved status are the two types of social statuses.
Question 8.
Who gave the terms ascribed and achieved status?
Answer:
These terms are given by Ralph Linton.
![]()
Question 9.
Give two examples of ascribed status.
Answer:
Status of father and brahmin are the examples of ascribed status.
Question 10.
Give two example of achieved status.
Answer:
The status of Prime Minister and Deputy Commissioner are the examples of achieved status.
Question 11.
Define Role.
Answer:
According to Ogburn and Nimkoff, “Role is a set of socially expected and approved behaviour patterns consisting of both duties and privileges, associated with a particular position in a group.
Question 12.
Mention any two characteristics of Role.
Answer:
(i) Role is the functional aspect of status.
(iii) Role is always having social sanction.
Answer the following short answer questions in 30-35 words each:
Question 1.
Define social structure.
Answer:
According to Talcott Parsons, “ The term social structure applies to the particular arrangement of the interrelated institutions, agencies, social patterns, as well as the statuses and roles which each person assumes in the group.”
![]()
Question 2.
Give two points of similarities between status and role.
Answer:
- Status and role are the two sides of same coin.
- Status is the position of an individual in society and role is the functional aspect of status.
- Both status and role change with time and circumstances.
Question 3.
Give the diagrammatic representation of structure of family.
Answer:
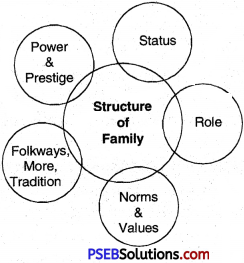
Question 4.
Distinguish between ascribed and achieved status.
Answer:
- One gets ascribed status according to his birth but one gets achieved status according to his ability.
- There are many bases of ascribed status but the only base of achieved status is one’s hard work.
Question 5.
In what ways are roles learned behaviour ?
Answer:
It is true that roles are learned behaviour as they are the collection of rules which are learned either through socialization or observation. After learning, whatever meaning man gives to it is a social role.
![]()
Question 6.
Write a short note on status and role.
Answer:
status:
Status is a position given to a person while living in society.
Role:
According to Ogburn and Nimkoff, “Role is a set of socially expected and approved behaviour patterns consisting of both duties and privileges, associated with a particular position in a group.
Question 7.
What is Status ?
Answer:
The position in a group, given to an individual, is known as social status. It is the position which one gets through his gender, age, birth, occupation, activities, patterns of work etc. For example an officer is respected by every one due to his post. Specific patterns related with his activities are known as status.
Question 8.
What is role set?
Answer:
While living in society, an individual gets many statuses. The collection of roles related with all such statuses is known as role set. For example students of 11th class of any school need to meet many persons in their daily routine and have to behave differently with them. Collection of roles related with all is known as role set.
![]()
Question 9.
What do you mean by role conflict ? Give its example.
Answer:
Every individual has many a status and a particular role is attached with each status. One has to fulfill all the roles attached with him. When he is unable to maintain balance with all of them and is not in a position to do justice with all of them, it is known as role conflict.
Answer the following short answer questions in 75-85 words each:
Question 1.
State the three characteristics of social structure.
Answer:
(i) Different social structures of different societies : Social structure of each society is different because the social life of different parts of a society is different. Every society has its different institutionalised rules. That’s why structures of all the societies are different.
(ii) Social structure is abstract : Social structure is abstract because the units with which this structure is formed like institution, association, norms etc. all are abstract. They don’t have any concrete form, we can only feel them. That’s why they are abstract.
(iii) Formed due to interactions : No proper planning is made to keep all the social units in a system. It is developed due to human interactions. That’s why no conscious efforts are required for its formation etc.
![]()
Question 2.
What is ascribed status ? Give its example.
Answer:
Ascribed status is the status which a person gets without doing any effort or hard work. Like, Brahmans have the higher status in caste system of Hindu society. Person gets social status according to his caste in which he was born. Sex, caste, birth, age, kinship all are ascribed status which a person gets without any effort.
Question 3.
Role is an element of social structure. Discuss in brief.
Answer:
Sub groups are the units of social structure and in these groups, members are given roles according to definite rules. Interactions take place among humans and to clarify them, roles are given to individual. Role is the behaviour of an individual in a particular situation which is associated with his status. If any change comes in social structure, change often comes in the status and role of an individual. Due to these roles, people establish contacts with each other and consequently social structure is maintained.
Question 4.
Status is an element of social structure. Discuss.
Answer:
There is no denying the fact that status is an element of social structure. Sub-groups are the units of social structure and every one gets many a status in these groups. People mutually interact and to clarify them, many status and roles are given to the people. When one gets any status, he needs to behave differently in different circumstances. If any change comes in social structure, change also comes in the status of people. Due to these statuses, people establish mutual relations and social structure is maintained.
Question 5.
Discuss how status and role are interrelated ?
Answer:
It is true that status and role are intererelated. Actually they are two sides of the same coin. If out of these two only one is given, other is of no importance. It means rights are given but not responsibility or vice versa. In the absence of one, other cannot work properly. If any one is given the status of an officer but he is not given any responsibility, the officer is of no advantage for people. If any one is given responsibility but no status is given, he will not be able to fulfill his role. So, they both are deeply related.
![]()
Answer the following short answer questions in 250-300 words each:
Question 1.
Define social structure and discuss its characteristics.
Answer:
Society is not an unbreakable system. Society is made up of many parts. These parts of society are interrelated with each other by doing their respective functions and they produce one type of balance. In the words of Sociology this balance is known as social system. On contrary to that when these different interrelated parts join each other and make a structure then this structure is known as social structure. In short the meaning of structure is the collection of those units or parts of society which are interrelated with each other.
(i) According to Maclver, “Social structure is abstract and many groups like family, class, caste and community come in this.–MacIver has accepted the stability and changing nature of social structure. According-to Maclver, “For a while the social structure itself is unstable and changeful, it has a definite character at every stage and many of its major elements have shown greater persistence of type through change.”
![]()
(ii) According to Morris Ginsberg, “Ginsberg has not differentiated between social structure and organization. He used the word social structure for systematic relations. According to him humans combine themselves with groups, institutions, associations etc. to achieve any purpose with which social structure is formulated.
According to Ginsberg, “The study of social structure is concerned with the principal forms of social organization i.e. types of groups, associations and institutions and the complex of these which constitute societies…full account of social structure would involve a review of the whole field of comparative institutions.”
(iii) According to Harry M. Johnson, “The structure of anything consists of relatively stable inter-relationship among its parts, moreover the part itself implies a certaip degree of stability since a social system is composed of the inter-related acts of people, its structure must be sought in some degree of regularity or recurrence in these acts.”
1. Different societies have different social structure. Every society has its own different rules because the relations which exist in different units of society have different place in social life. Except this social structure in different times is different. This difference is so because the relations which exist in units of society are different in different societies. It is related with specific society. That’s why social structure is related with specific society. Its different units like family institution, group, caste etc. have different forms.
![]()
2. It refers to the external aspect of society. Social structure is not related to internal system of society but is related with external aspect of soceity. For example the way in which different parts of human body make the full body and make the external structure of body, in that same way different parts of society combine and form the external structure of society. Hands, legs, head, nose etc. only show the external parts of body.
3. Social structure is abstract. Social structure is the sequence of interrelations of different units of society. Groups, castes, institutions, categories etc. are these units. This sequence of social structure doesn’t have any concrete form. That’s why it cannot be touched and seen. It can be felt only. Different relations which exist in different units are without any form and that’s why structure is abstract.
4. Social structure is changeable. Brown was of the view that mobility and continuity exist in social structure. It is not static. The way in which physical body changes in the same way change comes in structure of society but it doesn’t mean that the basic elements of structure also change.
5. Hierarchy of sub-structure in a structure. Our physical body is made up of many small structures, like backbone, neck, hands, feet etc.All these small structures form a big structure. In the same way we can take structure of educational institution. Staff, Principal office etc. are sub-structures which form the complete structure of educational institutions. In the same way in society, different categories and layers are there which jointly make a social structure.
![]()
6. Every unit of social structure has a definite position. Our social structure is made up of various units. Their position is definite and limited. No unit can take place of the other and cannot go beyond its limits. For example religion, school, family, caste etc. are different units of social structure. All of these have different place in social structure.
Religion never does function of school, school never does function of family etc. because every unit works in its limited area. If any unit comes out of its limits and works in the area of other unit then it will not be accepted by society. Every unit has different and definite place in society in different times. That’s why social structure is maintained.
7. Social structure is the product of social interactions. Development of social structure in every society is the product of social interactions. Different units of social structure are interrelated with each other. That’s why single unit is of no importance. Social interactions are very helpful in giving sequence to family, group, institution, association etc.
![]()
Question 2.
Which system helps in the maintenance of social structure ?
Answer:
In social structure, all the human beings have organised themselves into different associations to pursue some common goals. Such goals can be achieved if the social structure is based upon operational systems which help in its maintenance. Few of such systems are given below :
1. Normative System : Normative system presents some ideals and values in front of members of society. Members of society attach emotional importance to these values and ideas. Different groups, associations, institutions, communities etc. are interrelated according to norms and values. Different members of society perform their roles according to these norms. .
2. Position System : Position system refers to status and roles given to different individuals. Every one has unlimited and multiple aspirations and expectations. Different individuals in different societies have different status. For example, an individual in a family is a father, son, brother, uncle, husband etc. When he is in conversation with his wife, he acts as her husband and he forgets about other status. In the same way, while interacting with his son, he acts like a father. In other words, for the smooth functioning of social structure it is a must to properly allocate status and roles in society.
3. Sanction System: For the proper implementation of rules, society also provides a sanction system. To maintain balance between different parts, it is necessary to properly implement norms and values. Sanction can be negative as well as positive. Those who follow norms and values are rewarded by society and those who do not follow them are punished. Stability of social structure depends upon the effectiveness of sanction system. ‘
4. System of Anticipated Responses : A system of anticipated responses expects the individuals to participate in the social system. With their participation, social structure sets in metiori. The successful working of social structure depends upon the realisation of duties by the individuals. Members of society internalise the sanctioned behaviour with the help of socialisation with which they anticipate the experted behaviour of others in different situations. So the system of anticipated responses becomes one of the reason of stability-of a social structure.
5. Action System : Talcott Parsons gave special-stress on the concept of social action. He was of the view that society (web of social relationships) has emerged out of the action and interactions of the individual. Thus, the action system becemes one of the important elements that makes society active and sets the social structure in motion.
![]()
Question 3.
What is social structure ? What are the elements of social structure ?
Answer:
Our society is the web of social relationships. It has different units which are related with each other. They cannot do anything without each other’s help. It means they have the sense of cooperation These units are groups, institutions, associations, organizations etc. These units don’t have any independent existence, in fact when they relate with each other then they take the form of one structure. One sequence is there in their relations. With this sequence our society works properly.
We clarify the words sequence and arrangement pattern in an easy way with another example. If desk, bench, black-board, teacher, principal, peon, student and building can be kept at one place then it cannot be called as school. It can be called as school at that time when these different units will work in proper sequence with a proper arrangement pattern and on their definite place. Then only it can be called a school. We can take another example that we buy cloth for the shirt then it cannot be called as shirt until it doesn’t have any shape.
![]()
In this way every society has different social structure because there is always some difference in the units of the structure which makes the social structure. Our society is changeable. Time to time change comes in this due to natural forces or due to inventions by humans. That’s why social structure also changes. Its units are not concrete because we cannot touch them.
Yet these units of social structure like family, religion, institution, association, economy etc. are like each other but their types are different. Like any society is Patriarchal and any society is Matriarchal. It means that except some similarity its types are different. In short we can say that social structure it that systematic arragngement through which social relations can be tied in one thread.
Elements of Social Structure:
According to Harry M. Johnson and Talcot Parsons, there are four main elements of social structure which are given below :
1. Sub-Groups. According to Johnson and Parsons, every social structure is made up of units or sub-groups. Bigger group is made up of some sub-groups.
For example under educational group, school, college, university, family, religion etc. all these sub-groups are included which are related with educational group in one way or the other. Humans are getting roles and status through these groups and sub-groups. Place of every status and role is definite in the society.
Humans get birth and dying in society but these roles and status are definite. Humans get them after birth and after their death, other humans get their place. For example if principal of any school dies then other person takes his responsibilities by taking his status and role by becoming principal of that school. It means that sub-groups are short and permanent. They never come to an end. Their members are changing due to birth and death. Family, school, college etc. remain at their same place as they were 50 years ago but the members working in it are changing with time.
2. Roles. In sub-groups of social structure, humans are related to their roles through definite patterns. Society is the web of social relationships. Interactions take place between humans and groups to develop these relations. To clarify the activeness of these interactions, status and roles are defined.
Role is related with that behaviour of person which humans perform in specific condition and whichever function person has to perform related with specific status, are determined by social sanctions. Roles and status of members of society are changed when changes come in social structure. Social structure is maintained with these roles and definite social relations.
3. Social Norms. Roles and sub-groups are related with social norms because functions of humans are determined by these norms. That’s why roles and sub-groups become static. Social norms have many rules and sub-rules. These are those sanctioned ways of individual behaviour with which social structure is being formulated. Social ideals are related with these norms.
![]()
Humans would not be able to know about their responsiblities in the absence of these norms and our social structure cannot be maintained in its absence. For example, humans which are getting roles of father- son, mother-daughter, brother-sister, teacher-student etc.
are told about their responsibilities through these social norms. That’s why these are very important for social structure. Behaviour of humans is being regulated and directed by social norms in specific conditions with which roles and sub-groups are maintained. It is the third important element of social structure.
4. Social Values. According to Harry M. Johnson, “Value may be defined as a conception or standard cultural or merely personal, by which things are compared and approved or disapproved relative to one another held to be relatively desirable or undeiable, more meritorious or less, more or less correct. All kinds of things may be evaluated, feelings, ideas, actions, qualities, objects, persons, groups, goals and means.”
According to Johnson, values are measured because through them social norms are being evaluated. They appeal to the feelings of the members of society. Whenever person decides about any thing then he is definitely under the effect of his feelings. According to Johnson, everything is evaluated through values.”
![]()
The word ‘norm’ is used for specific behaviour pattern but values are simple measurements. These can be called as the norms of higher level. Social values are very important for social system and to stop social disorganization. Feelings of group are also related with these values. They also have functional relation between them because of which web of social relationship never breaks up.
With this our social structure and social system are maintained. With them balance is generally established between the feelings of human and group with which values are used as measures for the selection of behaviour. Human functions are divided in good or bad, high or low classes through these social values.
Question 4.
Define Status. Write its characteristics in detail.
Answer:
Society is the web of social relationships. The system of society is maintained through relations. No society can live without system. So to maintain this social system, every person in society is given one specific position. It is necessary for the maintenence of social system and organization that different persons should work according to their status in an efficient way and society expects from them that they should perform their duties in a proper way.
In this way every person has a position or status in society. Some persons are at higher posts and some persons are at lower posts. Status is the social position of a person which a person gets while living in society. Every person is related with some status.
All these statuses are the part of social position of a person because of which all these are the basis of social system. We can come to know about importance of status by comparing it with other status. Society has been divided into different parts due to status and as a result identity of person establishes in society.
![]()
In simple words, word ‘status’ is taken as social prestige. Higher status leads to more prestige. Social position of a person depends upon the evolution done by society. In sociology, meaning of status is taken by the position of person in society. There are many statuses in society and person gets some of them. Number of status, which a person gets, depends upon his membership of different groups.
In this way we can say that status is the position of a person which is given to him by organisation of group. Person gets status due to his age, gender, equality, birth, duty and his relations with other members. Every person has got some status like status of father, son, uncle, peon, officer etc. Person has to do some work according to his status. In this way we come to know about status by its functions. Person gets different status in different situations.
Definitions of Status:
- According to Secard and Berkman, “Status is the worth of a person as estimated by a group or a class of persons.”
- According to Kingsley Davis, “Status is a position in the general institutional system recognized and adopted by the entire society, spontaneously evolved rather than deliberately created, rooted in the folk ways and customs.”
- According to Linton, “The place in a particular system which a certain individual occupies at a particular time will be referred to as his status with respect to that system The role is what the individual has to do in order to validate his occupation of the status.”
- According to Maclver and Page, “Status is the social position that determines for its possessor apart from his personal attribute or social service, a degree of respect, prestige and influence.”
In this way on the basis of these definitions we can say that whichever position a person gets in specific group is his status. Because status is in group, that’s why number of status depends upon the number of groups of which a person is the member. In this way status is the social position of a person which a person gets due to his abilities, birth, gender, age, qualities etc. Person has to do a number of works related with his status. Person has to obey the orders of person of higher status than him. It maintains the social system and social discipline. Social prestige is also related with every status.
Characteristics of Social Status:
1. Every status has a place in society : Every status is known by the related rights, duties, norms and prestige of the group because a person has to do functions related to that. Like status of high ranked officer and low ranked officer is different in an office and this status can be known on the basis of group.
![]()
2. Status is determined by the culture of the society : Status is determined by the specific cultural values of a specific society that which status should be given to which person and what would be the related rights and duties. Person has to do functions according to social status. Like an elder member of the house father gets status and related roles automatically. All in all we can say that the status of every person is determined by the culture of that society.
3. Status is always comparable : Status is always comparable because we can come to know about our status by comparing it with the status of another person. If there would be no comparison of two status then how can we come to know that which status is higher or lower. For example, the status of owner of a factory is definitely higher than the status of a manager and we can come to know about this only by comparing it.
4. Every status has psychological base : Person always does hard work to get higher status because of which feelings also come in person. Respect and disrespect are also related with every status and these are related with psychological sector of person. When person achieves that social status with hard work then he gets mental satisfaction. In this way status has a psychological base.
5. Sthtus is of two types : Two types of status are there for every person. First one is Ascribed Status which a person gets without any effort and hard work. For example son, elder brother, elder sister etc. Second type of status is Achieved Status and this type of status person achieves with his hard work while living in society like officer, clerk etc.
![]()
6. Role is determined by status : Any role is definitely related to every status and this role is determined on the basis of social values. Person performs his role according to his status. Some statuses in society are very important and the roles of these statuses are also very important which the relative person has to perform. For example D.C. or S.S.P.
7. Similarity of status but not of functions : Many times it happens that many statuses in society are equal but their functions are different, for example, professors of any college. Status of all of them is same but their function, means subject of teaching is different. They teach different subjects or do different functions but their status is same. There are many engineers in a factory but their functions may be different.
Question 5.
Define role. Write its characteristics in detail.
Answer:
Every person has definitely any status in the society and some demands and responsibilities are also related to that status. These demands tell us that what a person has to do. Person achieves many status on the basis of ability, age, caste, sex etc. and person has to do a number of functions on the basis of tradition of that status. In this way it is expected from the person that what specific function he has to do in specific condition and this function is his role.
Importance of social role is at that time when person performs relative role. In this way status and role are the two sides of the same coin. Humans are differentiated on the basis of their functions. For example doctor, teacher, engineer etc.
It means functions of person are divided on the basis of different sectors. In this way person is given any function in social status on the basis of rules, laws or traditions. This function is role. Role is related with every status.
![]()
In this way we can say that every status has a set of relative functions. This set of functions is known as role. Person is always there on any status and some responsibilities are also there related with those status. The collection of those responsibilities is known as role.
Role of every one is different. In this way roles tell the person about that behaviour which is expected from the person who has that status. Role and status cannot be differentiated. Role is related with status. To know the more clear meaning of status now we will see the definitions of role.
Definitions:
1. According to Ogburn and Nimkoff, “A role is a set of socially expected and approved behaviour patterns, consisting of both duties and privileges, associated with a particular position in a group.”
2. According to Ginsberg, “Status is a position and a role is the manner in which that position is supposed to be filled.” .
3. According to Fitcher, “When a number of interrelated behaviour patterns are clustered around a social function we call this combination a social role.”
4. According to Kingsley Davis, “Role is the manner in which a person actually carries out the requirements of the position.”
In this way on the basis of these definitions we can say that the meaning of role is related with the specific behaviour of a person which he does in specific conditions.
Role is the way with which person fulfils his responsibilities or functions related with his status. For the maintenance of our social system it is necessary because society cannot run without doing work. In this way role is the accepted way in which a person performs his duties related with his status and uses rights of his status.
![]()
Characteristics of Role:
1. One person has many roles. A person gets many statuses while living in society and automatically gets many roles related with those status because he is able to perform those responsibilities or roles. For example, role of father and husband in family, role of clerk or officer in office, role of chairman in club etc. In this way one person performs many roles.
2. Role is determined by our culture. Because a person has many statuses, that’s why he needs to perform roles related with status according to the relative rules, laws, values and traditions. These laws, rules, traditions and values are the part of our culture. That’s why role is regulated by our culture.
3. Role is functional. Role always has one functional aspect. The meaning of functional aspect is that to do work related with that status. Person has to do work related to the status which he has and this is the functional aspect of role.
4. Role is determined by the social sanctions. The nature of humans is not same. If the members of the society will be allowed to work according to their wish then no work would be done in an efficient way. It is so because some will not be able to do that work and some will work against the values of society. That’s why only those roles are accepted by society which have social sanctions. These are determined by our culture that which role would be performgd by which person.
5. Different importance of different roles. S.ome roles in society are very important because they are related with any specific aspect and for them, person needs special training. That’s why they have more importance. In the same way some roles are of less importance because their status is of less importance and there is no need of special training for them. For example, there is a great difference between the role of the I.A.S. officer and a clerk.
6. Importance of ability in Role. Individual’s ability is of great importance in performing any role. It is so because it is not necessary that he can perform his role in proper way. One person performs one role successfully and in another he fails. It means that person can perform his role in right or wrong way according to his ability.
