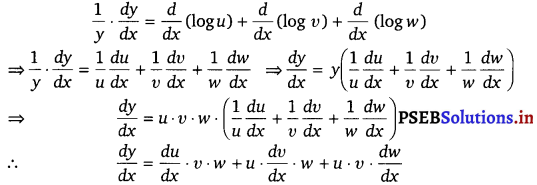Punjab State Board PSEB 12th Class Maths Book Solutions Chapter 5 Continuity and Differentiability Ex 5.5 Textook Exercise Questions and Answers.
PSEB Solutions for Class 12 Maths Chapter 5 Continuity and Differentiability Ex 5.5
DirectIon (1 – 11): Differentiate the following functions w.r.t. x:
Question 1.
cos x . cos 2x . cos 3x
Solution.
Let y = cos x . cos 2x . cos 3x
Taking logarithm on othsides, we get
log y = log(cos x . cos 2x . cos 3x)
⇒ log y = log (cos x) + log (cos 2x) + log (cos 3x)
On differentiating bothsides w.r.t x, we get
\(\frac{1}{y}\) . \(\frac{d y}{d x}\) = \(\frac{1}{\cos x}\) \(\frac{d}{d x}\) (cos x) + \(\frac{1}{\cos 2 x}\) . \(\frac{d}{d x}\) (cos 2x) + \(\frac{1}{\cos 3 x}\) . \(\frac{d}{d x}\) (cos 3x)
⇒ \(\frac{d y}{d x}\) = y \(\left[-\frac{\sin x}{\cos x}-\frac{\sin 2 x}{\cos 2 x} \cdot \frac{d}{d x}(2 x)-\frac{\sin 3 x}{\cos 3 x} \cdot \frac{d}{d x}(3 x)\right]\)
∴ \(\frac{d y}{d x}\) = – cos x . cos 2x . cos 3x [tan x + 2 tan 2x + 3 tan 3x]
![]()
Question 2.
\(\sqrt{\frac{(x-1)(x-2)}{(x-3)(x-4)(x-5)}}\)
Solution.
Let y = \(\sqrt{\frac{(x-1)(x-2)}{(x-3)(x-4)(x-5)}}\)
Taking logarithm on othsides, we get
log y = log \(\sqrt{\frac{(x-1)(x-2)}{(x-3)(x-4)(x-5)}}\)
⇒ log y = \(\frac{1}{2}\) log \(\sqrt{\frac{(x-1)(x-2)}{(x-3)(x-4)(x-5)}}\)
⇒ log y = \(\frac{1}{2}\) – [log {(x – 1) (x – 2)} – log {(x – 3) (x – 4) (x – 5)}]
⇒ log y = \(\frac{1}{2}\) [log (x – 1) + log (x – 2) – log (x – 3) – log (x – 4) – log (x – 5)]
On differentiating bothsides w.r.t x, we get
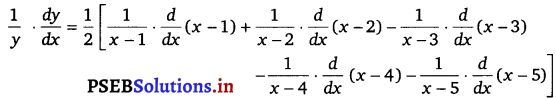
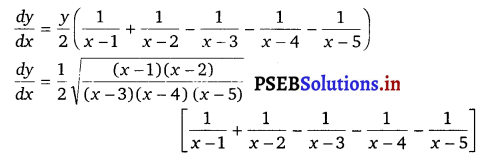
![]()
Question 3.
(log x)cos x
Solution.
Let y = (log x)cos x
On differentiating bothsides w.r.t x, we get
\(\frac{1}{y}\) . \(\frac{d y}{d x}\) = \(\frac{d}{d x}\) (cos x) × log(log x) + cos x × \(\frac{d}{d x}\) [log (log x)]
⇒ \(\frac{1}{y}\) . \(\frac{d y}{d x}\) = – sin x log (log x) + cos x × \(\frac{1}{\log x}\) . \(\frac{d}{d x}\) (log x)
⇒ \(\frac{d y}{d x}\) = y [- sin x log (log x) + \(\frac{\cos x}{\log x} \times \frac{1}{x}\)]
∴ \(\frac{d y}{d x}\) = (log x)cos x [\(\frac{\cos x}{x \log x}\) – sin x log (log x)]
Question 4.
xx – 2sin x
Solution.
Let y = xx – 2sin x
Also, let xx = u and 2sin x = v
∴ y = u – v
⇒ \(\frac{d y}{d x}\) = \(\frac{d u}{d x}\) – \(\frac{d v}{d x}\)
Now, u = xx
Taking lagarithm on bothsides, we get
log u = x log x
On differentiating bothsides w.r.t x, we get
\(\frac{1}{u}\) . \(\frac{d u}{d x}\) = [\(\frac{d}{d x}\) (x) × log x + x × \(\frac{d}{d x}\) (log x)]
⇒ \(\frac{d u}{d x}\) = u [1 × log x + x × \(\frac{1}{x}\)]
⇒ \(\frac{d u}{d x}\) = xx (log x + 1)
⇒ \(\frac{d u}{d x}\) = xx (1 + log x)
And, v = 2sin x
Taking lagarithm on bothsides, we get
log v = sin x log 2
On differentiating bothsides w.r.t x, we get
\(\frac{1}{v}\) . \(\frac{d v}{d x}\) = log 2 . [\(\frac{d}{d x}\) (sin x)
⇒ \(\frac{d v}{d x}\) = v log 2 cos x
⇒ \(\frac{d v}{d x}\) = 2sin x cos x log 2
⇒ \(\frac{d y}{d x}\) = xx (1 + log x) – 2sin x cos x log 2.
![]()
Question 5.
(x + 3)2 . (x + 4)3 . (x + 5)4
Solution.
Let y = (x + 3)2 . (x + 4)3 . (x + 5)4
Taking lagarithm on bothsides, we get
log y = log (x + 3)2 + log (x + 4)3 + log (x + 5)4
log y = 2 log (x + 3) + 3 log (x + 4) + 4 log (x + 5)
On differentiating bothsides w.r.t x, we get
\(\frac{1}{y}\) . \(\frac{d y}{d x}\) = 2 . \(\frac{1}{x+3}\) . \(\frac{d}{d x}\) (x + 3) + 3 . \(\frac{1}{x+4}\) . \(\frac{d}{d x}\) (x + 4) + 4 . \(\frac{1}{x +5}\) \(\frac{d}{d x}\) (x + 5)
⇒ \(\frac{d y}{d x}\) = y \(\left[\frac{2}{x+3}+\frac{3}{x+4}+\frac{4}{x+5}\right]\)
⇒ \(\frac{d y}{d x}\) = (x + 3)2 . (x + 4)3 . (x + 5)4 \(\left[\frac{2}{x+3}+\frac{3}{x+4}+\frac{4}{x+5}\right]\)
⇒ \(\frac{d y}{d x}\) = (x + 3)2 + (x + 4)3 + (x + 5)4 . \(\left[\frac{2(x+4)(x+5)+3(x+3)(x+5)+4(x+3)(x+4)}{(x+3)(x+4)(x+5)}\right]\)
⇒ \(\frac{d y}{d x}\) = (x + 3) (x + 4)2 (x + 5)3 . [2 (x2 + 9x + 20) + 3 (x2 + 8x + 15 + 4 (x2 + 7x + 12)]
⇒ \(\frac{d y}{d x}\) = (x + 3) (x + 4)2 (x + 5)3 . [2x2 + 18x + 40 + 3x2 + 24x + 45 + 4x2 + 28x + 48]
∴ \(\frac{d y}{d x}\) = (x + 3) (x + 4)2 (x + 5)3 (9x2 + 70x + 133)
![]()
Question 6.
\(\left(x+\frac{1}{x}\right)^{x}+x^{\left(1+\frac{1}{x}\right)}\)
Solution.
Let y = \(\left(x+\frac{1}{x}\right)^{x}+x^{\left(1+\frac{1}{x}\right)}\)
Also, let u = \(\left(x+\frac{1}{x}\right)^{x}\) and v = \(x^{\left(x+\frac{1}{x}\right)}\)
∴ y = u + v
⇒ \(\frac{d y}{d x}\) = \(\frac{d u}{d x}\) + \(\frac{d v}{d x}\)
Then, u = \(\left(x+\frac{1}{x}\right)^{x}\)
⇒ log u = log \(\left(x+\frac{1}{x}\right)^{x}\)
⇒ log u = x log (x + \(\frac{1}{x}\)) (Taking log on bothsides)
On differentiating bothsides w.r.t x, we get
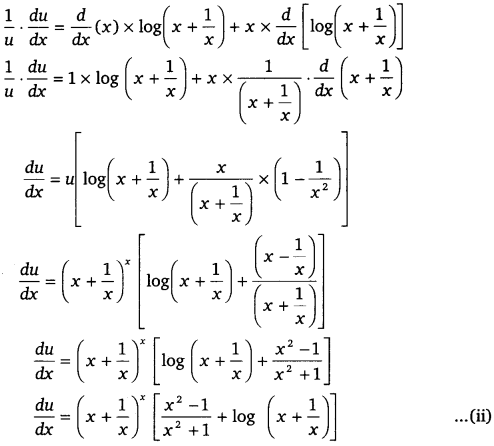
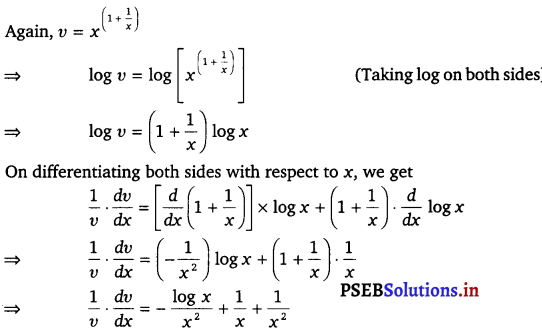
\(\frac{d y}{d x}\) = v \(\left(\frac{-\log x+x+1}{x^{2}}\right)\)
\(\frac{d y}{d x}\) = \(x^{\left(1+\frac{1}{x}\right)}\left(\frac{x+1-\log x}{x^{2}}\right)\) ………….(iii)
Therefore from eqs. (i), (ii) and (iii), we get
\(\frac{d y}{d x}\) = \(\left(x+\frac{1}{x}\right)^{x}\left[\frac{x^{2}-1}{x^{2}+1}+\log \left(x+\frac{1}{x}\right)\right]+x^{\left(1+\frac{1}{x}\right)}\left(\frac{x+1-\log x}{x^{2}}\right)\)
![]()
Question 7.
(log x)x + xlog x
Solution.
Let y = (log x)x + xlog x
Also, let u = (log x)x and v = xlog x
∴ y = u + v
⇒ \(\frac{d y}{d x}\) = \(\frac{d u}{d x}\) + \(\frac{d v}{d x}\) ………….(i)
Then, u = (log x)x
⇒ log u = log [(log x)x]
(Taking log on bothsides)
⇒ log u = x log (log x)
On differentiating bothsides w.r.t x, we get

Again, v = xlog x
⇒ log v = log (xlog x) (Taking log on bothsides)
⇒ log v = log x log x
= (log x)2
On differentiating bothsides w.r.t x, we get
\(\frac{1}{v}\) \(\frac{d v}{d x}\) = \(\frac{d}{d x}\) [(log x)2]
⇒ \(\frac{1}{v}\) \(\frac{d v}{d x}\) = 2 (log x) . \(\frac{d}{d x}\) (log x)
⇒ \(\frac{d v}{d x}\) = 2v (log x) . \(\frac{1}{x}\)
⇒ \(\frac{d v}{d x}\) = 2xlog x \(\frac{\log x}{x}\)
⇒ \(\frac{d v}{d x}\) = 2xlog x – 1 . log x
Therefore, from Eqs. (i), (ii) and (iii), we get
\(\frac{d y}{d x}\) = (log x)log x – 1 [1 + log x . log (log x)] + 2xlog x – 1 . log x
![]()
Question 8.
(sin x)x + sin-1 √x
Solution.
Let y = (sin x)x + sin-1 √x
Also, let u = (sin x)x and v = sin-1 √x
⇒ y = u + v
⇒ \(\frac{d y}{d x}\) = \(\frac{d u}{d x}\) + \(\frac{d v}{d x}\) ………….(i)
Then, u = (sin x)x
⇒ log u = log (sin x)x (Taking log on bothsides)
log u = x log (sin x)
On differentiating bothsides w.r.t x, we get

![]()
Question 9.
xsin x + (sin x)cos x
Solution.
Let y = xsin x + (sin x)cos x
also, let u = xsin x and v = (sin x)cos x
⇒ y = u + v
⇒ \(\frac{d y}{d x}\) = \(\frac{d u}{d x}\) + \(\frac{d v}{d x}\)
Then, u = xsin x
⇒ log u = log (xsin x) (Taking log on bothsides)
⇒ log u = sin x log x
On differentiating bothsides w.r.t x, we get
\(\frac{1}{u}\) . \(\frac{d u}{d x}\) = \(\frac{d}{d x}\) (sin x) . log x + sin x . \(\frac{d}{d x}\) (log x)
⇒ \(\frac{d u}{d x}\) = u [cos x log x + sin x . \(\frac{1}{x}\)]
⇒ \(\frac{d u}{d x}\) = xsin x [cos x log x + \(\frac{\sin x}{x}\)] …………..(ii)
Again, v = (sin x)cos x
⇒ log v = log (sin x)cos x
⇒ log v = cos x log (sin x)
On differentiating bothsides w.r.t x, we get
\(\frac{1}{v}\) . \(\frac{d v}{d x}\) = \(\frac{d}{d x}\) (cos x) × log(sin x) + cos x × \(\frac{d}{d x}\) [log(sin x)]
⇒ \(\frac{d v}{d x}\) = v[- sin x . log(sin x) + cos x . \(\frac{1}{\sin x} \cdot \frac{d}{d x}\) (sin x)]
⇒ \(\frac{d v}{d x}\) = (sin x)cos x [- sin x log sin x + \(\frac{\cos x}{\sin x}\) cos x]
⇒ \(\frac{d v}{d x}\) = (sin x)cos x [- sin x log . sin x + cot x cos x]
⇒ \(\frac{d v}{d x}\) = (sin x)cos x [cot x cos x – sin x log sin x] ……………(iii)
Therefore, from Eqs. (i), (ii) and (iii), we get
\(\frac{d v}{d x}\) = xsin x [cos x log x + \(\frac{\sin x}{x}\)] + (sin x)cos x [cot x cos x – sin x log sin x]
![]()
Question 10.
xx cos x + \(\frac{x^{2}+1}{x^{2}-1}\)
Solution.
Let y = xx cos x + \(\frac{x^{2}+1}{x^{2}-1}\)
Also, let u = xcos x and v = \(\frac{x^{2}+1}{x^{2}-1}\)
⇒ y = u + v
⇒ \(\frac{d y}{d x}\) = \(\frac{d u}{d x}\) + \(\frac{d v}{d x}\) …………..(i)
Then, u = xx cos x
⇒ log u = log (x)x cos x (Taking log on bothsides)
⇒ log u = x cos x log x
On differentiating bothsides w.r.t x, we get
\(\frac{1}{u}\) . \(\frac{d u}{d x}\) = \(\frac{d}{d x}\) (x) . cos x . log x + x . \(\frac{d}{d x}\) (cos x) . log x + x cos x . \(\frac{d}{d x}\) (log x)
⇒ \(\frac{d u}{d x}\) = u [1 . cos x . log x + x . (- sin x) log x + x cos x . \(\frac{1}{x}\)]
⇒ \(\frac{d u}{d x}\) = xx cos x (cos x log x – x sin x log x + cos x)
\(\frac{d u}{d x}\) = xx cos x [cos x (1 + log x) – x sin x log x] …………..(ii)
Again, v = \(\frac{x^{2}+1}{x^{2}-1}\)
⇒ log v = log(x2 + 1) – log (x – 1) (Taking log on both sides)
On differentiating both sides w.r.t x, we get
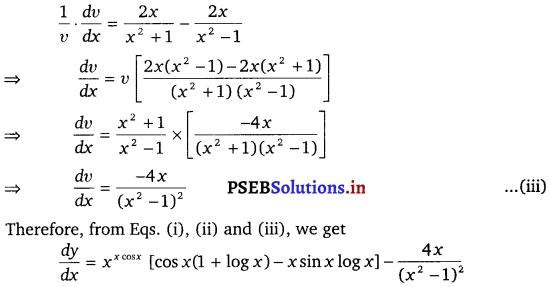
![]()
Question 11.
(x cos x)x + (x sin x)\(\frac{1}{x}\)
Solution.
Let y = (x cos x)x + (x sin x)\(\frac{1}{x}\)
Also, let u = (x cos x)x and v = (x sin x)\(\frac{1}{x}\)
⇒ y = u + v
⇒ \(\frac{d y}{d x}\) = \(\frac{d u}{d x}\) + \(\frac{d v}{d x}\)
Then, u = (x cos x)x
⇒ log u = log (x cos x)x (Taking log on both sides)
⇒ log u = x log (x cos x)
⇒ log u = x[log x + log cos x]
⇒ log u = x log x + x log cos x
On differentiating both sides w.r.t x, we get
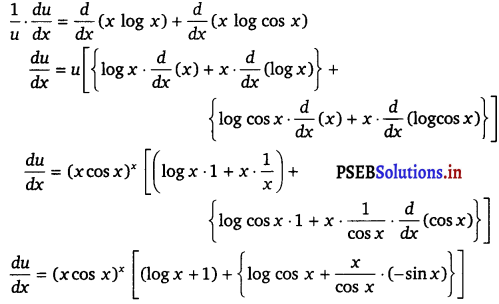
⇒ \(\frac{d u}{d x}\) = (x cos x)x [(1 + log x) + (log cos x – x tan x)]
⇒ \(\frac{d u}{d x}\) = (x cos x)x [1 – x tan x + (log x + log cos x)]
⇒ \(\frac{d u}{d x}\) = (x cos x)x [1 – x tan x + log (x cos x)] …………..(ii)
Again, v = (x sin x)\(\frac{1}{x}\)
⇒ log v = log (x sin x)\(\frac{1}{x}\) (Taking log on both sides)
⇒ log v = \(\frac{1}{x}\) log (x sin x)
⇒ log v = \(\frac{1}{x}\) (log x + log sin x)
⇒ log v = \(\frac{1}{x}\) log x + \(\frac{1}{x}\) log sin x
On differentiating both sides w.r.t x, we get
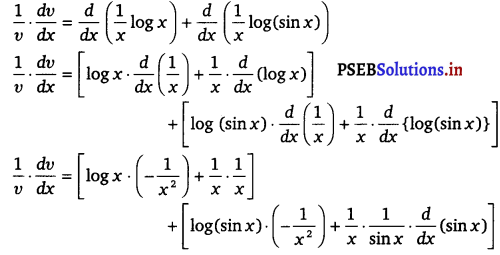
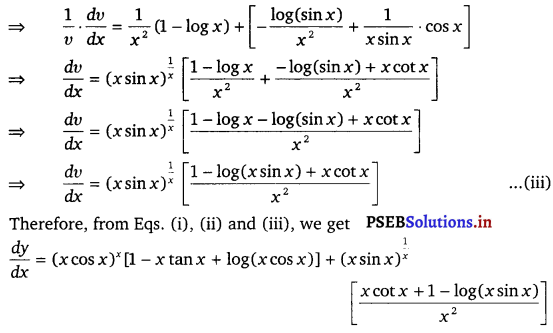
![]()
DIrectIon (12 – 15) : Find of the following functions:
Question 12.
xy + yx = 1
Solution.
Given, xy + yx = 1
Let xy = u and yx = v
Then, the function becomes u + v = 1
∴ \(\frac{d u}{d x}\) + \(\frac{d v}{d x}\) = 0
Now, u = xy
⇒ log u = log(xy) (Taking log on both sides)
⇒ log u = y log x
On differentiating both sides w.r.t. x, we get
\(\frac{1}{u}\) . \(\frac{d u}{d x}\) = log x \(\frac{d y}{d x}\) + y . \(\frac{d}{d x}\) (log x)
⇒ \(\frac{d u}{d x}\) = xy [log x \(\frac{d y}{d x}\) + y . \(\frac{1}{x}\)]
⇒ \(\frac{d u}{d x}\) = xy (log x \(\frac{d y}{d x}\) + \(\frac{y}{x}\)) …………(ii)
Again, v = yx
⇒ log v = log yx
⇒ log v = x log y
On differentiating both sides w.r.t. x, we get
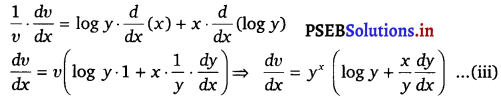
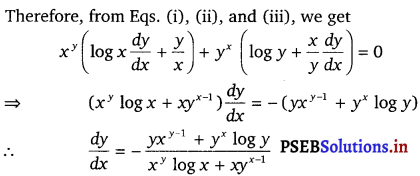
![]()
Question 13.
yx = xy
Solution.
Given, yx = xy
Taking logarithm on both sides , we get
log yx = log xy
⇒ x log y = y log x
On differentiating both sides w.r.t. x, we get
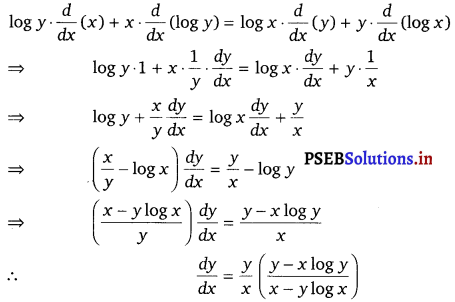
Question 14.
(cos x)y = (cos y)x
Solution.
Given, (cos x)y = (cos y)x
Taking logarithm on both sides , we get
⇒ log (cos x)y = log (cos y)x
⇒ y log (cos x) = x log (cos y)
On differentiating both sides w.r.t. x, we get
log cos x . \(\frac{d y}{d x}\) + y . \(\frac{d}{d x}\) (log cos x) = log cos y . \(\frac{d}{d x}\) (x) + x . \(\frac{d}{d x}\) (log cos y)
⇒ log cos x . \(\frac{d y}{d x}\) + \(\frac{y}{\cos x}\) (- sin x) = log cos y + \(\frac{x}{\cos y}\) (- sin y) . \(\frac{d y}{d x}\)
⇒ log cos x \(\frac{d y}{d x}\) – y tan x = log cos y – x tan y \(\frac{d y}{d x}\)
⇒ (log cos x + x tan y) \(\frac{d y}{d x}\) = y tan x + log cos y
∴ \(\frac{d y}{d x}=\frac{y \tan x+\log \cos y}{x \tan y+\log \cos x}\).
![]()
Question 15.
xy = e(x – y)
Solution.
Given, xy = e(x – y)
Taking logarithm on bothsides, we get
⇒ log (xy) = log (e(x – y))
⇒ log x + log y = (x – y) log e
⇒ log x + log y = (x – y) × 1
⇒ log x + log y = x – y
On differentiating both sides w.r.t. x, we get
\(\frac{d}{d x}\) (log x) + \(\frac{d}{d x}\) (log y) = \(\frac{d}{d x}\) (x) – \(\frac{d y}{d x}\)
⇒ \(\frac{1}{x}\) + \(\frac{1}{y}\) . \(\frac{d y}{d x}\) = 1 – \(\frac{d y}{d x}\)
⇒ (1 + \(\frac{1}{y}\)) \(\frac{d y}{d x}\) = 1 – \(\frac{1}{x}\)
⇒ \(\left(\frac{y+1}{y}\right) \frac{d y}{d x}=\frac{x-1}{x}\)
⇒ \(\frac{d y}{d x}=\frac{y(x-1)}{x(y+1)}\)
Question 16.
Find the derivative of the function given by f(x) = (1 + x) (1 + x2) (1 + x4) (1 + x8) and hence find f(1).
Solution.
Given f(x) = (1 + x) (1 + x2) (1 + x4) (1 + x8)
Taking logarithm on both sides, we get
log f(x) = log (1 + x) + log (1 + x2) + log(1 + x4) + log (1 + x8)
On differentiating both sides w.r.t. x, we get
\(\) . \(\frac{d}{d x}\) [f(x)] = \(\frac{d}{d x}\) log (1 + x) + \(\frac{d}{d x}\) log (1 + x2) + log (1 + x4) + log (1 + x8)
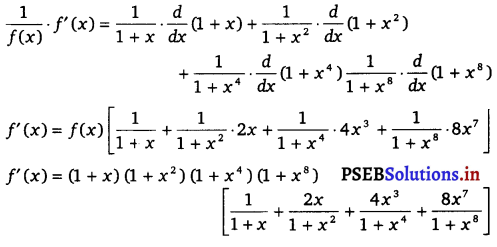
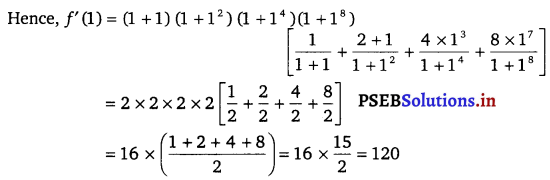
![]()
Question 17.
Differentiate(x2 – 5x + 8) (x3 + 7x +9) in three ways mentioned below:
(i) By using product rule.
(ii) By expanding the product to obtain a single polynomial.
(iii) By logarithmic differentiation.
Do they all give the same answer?
Solution.
(i) Let y = (x2 – 5x + 8) (x3 + 7x + 9)
Let x2 – 5x + 8 = u and x3 + 7x + 9 = v
∴ y = uv
⇒ \(\frac{d y}{d x}\) = \(\frac{d u}{d x}\) . v + u . \(\frac{d v}{d x}\)
⇒ \(\frac{d y}{d x}\) = \(\frac{d}{d x}\) (x2 – 5x + 8) . (x3 + 7x + 9) + (x2 – 5x + 8) . \(\frac{d}{d x}\) (x3 + 7x + 9)
⇒ \(\frac{d y}{d x}\) = (2x – 5) (x3 + 7x + 9) + (x2 – 5x + 8) (3x2 + 7)
⇒ \(\frac{d y}{d x}\) = 2x (x3 + 7x + 9) – 5 (x3 + 7x + 9) + x2 (3x2 + 7) – 5x (3x2 + 7) + 8 (3x2 + 7)
⇒ \(\frac{d y}{d x}\) = (2x4 + 14x2 + 18x) – 5x3 – 35x – 45 + (3x4 + 7x2) – 15x3 – 35x + 24x2 + 56
∴ \(\frac{d y}{d x}\) = 5x4 – 20x3 + 45x2 – 52x + 11
(ii) y = (x2 – 5x + 8) (x3 + 7x + 9)
= x2 (x3 +7x + 9) – 5x (x3 + 7x + 9) + 8(x3 + 7x + 9)
= x5 + 7x3 + 9x2 – 5x4 – 35x2 – 45x + 8x3 56x + 72
= x5 – 5x4 + 15x3 – 26x2 + 11x + 72
∴ \(\frac{d y}{d x}\) = \(\frac{d}{d x}\) (x5 – 5x4 + 15x3 – 26x2 + 11x + 72)
= \(\frac{d}{d x}\) (x5 – \(\frac{d}{d x}\) (5x4) + 15 \(\frac{d}{d x}\) (x3 – 26 \(\frac{d}{d x}\) (x2) + 11 \(\frac{d}{d x}\) (x) + \(\frac{d}{d x}\) (72)
= 5x4 – 5 × 4x3 + 15 × 3x2 – 26 × 2x + 11 × 1 + 0
= 5x4 – 20x3 + 45x2 – 52x + 11
(iii) y = (x2 – 5x + 8) (x3 + 7x + 9)
Taking logarithm on both sides, we get
log y = log (x2 – 5x + 8) + log (x3 + 7x + 9)
On differentiating both sides w.r.t x, we get
\(\frac{1}{y}\) . \(\frac{d y}{d x}\) = \(\frac{d}{d x}\) log (x2 – 5x + 8) + \(\frac{d}{d x}\) log (x3 + 7x + 9)
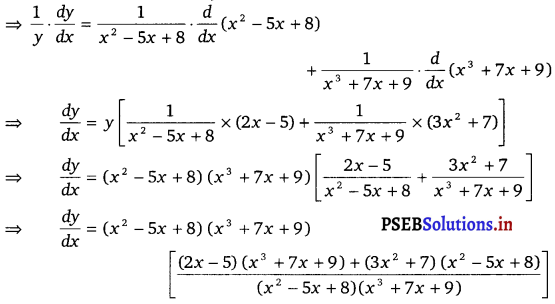
⇒ \(\frac{d y}{d x}\) = 2x (x3 + 7x + 9) -5 (x3 + 7x + 9) + 3x2 (x2 – 5x + 8) + 7 (x2 – 5x + 8)
⇒ \(\frac{d y}{d x}\) = (2x4 + 14x2 + 18x) – 5x3 – 35x – 45 + (3x4 – 15x3 + 24x2) + (7x2 – 35x + 56)
⇒ \(\frac{d y}{d x}\) = 5x4 – 20x3 + 45x2 – 52x + 11
From the above three observations, it can be concluded that all the results of \(\frac{d y}{d x}\) are same.
![]()
Question 18.
If u, v and w are functions of x, then show that
\(\frac{d}{d x}\) (u . v . w) = \(\frac{d u}{d x}\) v . w + u . \(\frac{d v}{d x}\) . w + u . v . \(\frac{d w}{d x}\)
in two ways-first by repeated application of product rule, second by logarithmic differentiation.
Solution.
Let y = u . v . w = u(v . w)
By applying product rule, we get
\(\frac{d y}{d x}\) = \(\frac{d u}{d x}\) (v . w) + u . \(\frac{d}{d x}\) (v . w)
\(\frac{d y}{d x}\) = \(\frac{d u}{d x}\) v . w + u [\(\frac{d v}{d x}\) . w + v . \(\frac{d w}{d x}\)] (Again, applying product rule)
\(\frac{d y}{d x}\) = \(\frac{d u}{d x}\) . v . w + u . \(\frac{d v}{d x}\) . w + u . v . \(\frac{d w}{d x}\)
By taking logarithm on both sides of the equation y = u u w, we get
log y = log u + log u + log w
On differentiating both sides w.r.t. x, we get