Punjab State Board PSEB 12th Class Maths Book Solutions Chapter 7 Integrals Ex 7.1 Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
PSEB Solutions for Class 12 Maths Chapter 7 Integrals Ex 7.1
Direcflon (1 – 5):
Find the anti-derivative (or integral) of the following by the method of inspection.
Question 1.
sin 2x
Solution.
The anti-derivative of sin 2x is a function of x whose derivative is sin 2x.
It is known that,
\(\frac{d}{d x}\) (cos 2x) = – 2 sin 2x
⇒ sin 2x = – \(\frac{1}{2} \frac{d}{d x}\) (cos 2x)
sin 2x = \(\frac{d}{d x}\) (- \(\frac{1}{2}\) cos 2x)
Therefore, the anti-derivative of sin 2x is – \(\frac{1}{2}\) cos 2x + C.
Question 2.
cos 3x
Solution.
The anti-derivative of cos 3x is a function of x whose derivative is cos 3x.
It is known that,
\(\frac{d}{d x}\) (sin 3x) = 3 cos 3x
⇒ cos 3x = \(\frac{1}{3}\) \(\frac{d}{d x}\) (sin 3x)
∴ cos 3x = \(\frac{d}{d x}\) (\(\frac{1}{3}\) sin 3x)
Therefore, the anti-derivative of cos 3x is \(\frac{1}{3}\) sin 3x + C.
![]()
Question 3.
e2x
Solution.
The anti-derivative of e2x is the function of x whose derivative is e2x.
It is known that,
\(\frac{d}{d x}\) (e2x) = 2e2x
⇒ e2x = \(\frac{1}{2}\) \(\frac{d}{d x}\) (e2x)
∴ e2x = \(\frac{d}{d x}\) (\(\frac{1}{2}\) e2x)
Therefore, the anti-derivative of e2x is \(\frac{1}{2}\) e2x + C.
Question 4.
(ax + b)2
Solution.
The anti-derivative of (ax + b)2 is the function of x whose derivative is (ax + b)2.
It is known that,
\(\frac{d}{d x}\) (ax + b)2 = 3a (ax + b)2
⇒ (ax + b)2 = \(\frac{1}{3 a}\) \(\frac{d}{d x}\) (ax + b)3
∴ (ax + b)2 = \(\frac{d}{d x}\) (\(\frac{1}{3 a}\) (ax + b)3))
Therefore, the anti-derivative of (ax + b)2 is \(\frac{1}{3 a}\) (ax + b)3) + C.
![]()
Question 5.
sin 2x – 4 e3x
Solution.
The anti-derivative of (sin 2x – 4 e3x) is the function of x whose derivative is (sin 2x – 4 e3x).
It is known that,
\(\frac{d}{d x}\) (- \(\frac{1}{2}\) cos 2x – \(\frac{4}{3}\) e3x) = sin 2x – 4 e3x
Therefore, the anti-derivative of (sin 2x – 4 e3x) is (- \(\frac{1}{2}\) cos 2x – \(\frac{4}{3}\) e3x) + C.
Direction (6 – 20): Find the following integrals:
Question 6.
∫ (4 e3x + 1) dx
Solution.
∫ (4 e3x + 1) dx = 4 ∫ e3x dx + ∫ 1 dx
= 4 \(\left(\frac{e^{3 x}}{3}\right)\) + x + C
= \(\frac{4}{3}\) e3x + x + C {∵ ∫ enx dx = \(\frac{e^{n x}}{x}\)}
Question 7.
∫ x2 (1 – \(\frac{1}{x^{2}}\)) dx
Solution.
∫ x2 (1 – \(\frac{1}{x^{2}}\)) dx = ∫ (x2 – 1) dx
= ∫ x2 dx – ∫ 1 dx
= \(\frac{x^{3}}{3}\) – x + C.
![]()
Q.8.
∫ (ax2 + bx + c) dx
Solution.
∫ (ax2 + bx + c) dx = a ∫ x2 dx + b ∫ x dx + c ∫ 1 dx
= \(\frac{a x^{2+1}}{2+1}+\frac{b x^{1+1}}{1+1}\) + cx + C
= \(a\left(\frac{x^{3}}{3}\right)+b\left(\frac{x^{2}}{2}\right)\) + cx + C
= \(\frac{a x^{3}}{3}+\frac{b x^{2}}{2}\) + cx + C
Question 9.
∫ (2x2 + ex) dx
Solution.
∫ (2x2 + ex) dx = 2 ∫ x2 dx + ∫ ex dx
= 2 \(\left(\frac{x^{2+1}}{2+1}\right)\) + ex + C
= 2 \(\left(\frac{x^{3}}{3}\right)\) + ex + C
= \(\frac{2}{3}\) x3 + ex + C
Question 10.
∫ (√x – \(\frac{1}{\sqrt{x}}\))2 dx
Solution.
∫ (√x – \(\frac{1}{\sqrt{x}}\))2 dx = ∫ [(√x)2 – 2 √x × \(\frac{1}{\sqrt{x}}\)] dx
= ∫ (x + \(\frac{1}{x}\) – 2) dx = ∫ x dx + ∫ \(\frac{1}{x}\) dx – 2 ∫ 1 dx
= \(\frac{x^{2}}{2}\) + log |x| – 2x + C.
![]()
Question 11.
∫ \(\frac{x^{3}+5 x^{2}-4}{x^{2}}\) dx
Solution.
∫ \(\frac{x^{3}+5 x^{2}-4}{x^{2}}\) dx = ∫ \(\left(\frac{x^{3}}{x^{2}}+5 \frac{x^{2}}{x^{2}}-\frac{4}{x^{2}}\right)\) dx
= ∫ (x + 5 – 4 x-2) dx
= ∫ x dx + 5 ∫ 1 dx – 4 ∫ x-2 dx
= \(\frac{x^{2}}{2}\) + 5x – 4 \(\left(\frac{x^{-2+1}}{-2+1}\right)\) + C
= \(\frac{x^{2}}{2}\) + 5x – 4 \(\left(\frac{x^{-1}}{-1}\right)\) + C
= \(\frac{x^{2}}{2}\) + 5x + \(\frac{4}{4}\) + C
Question 12.
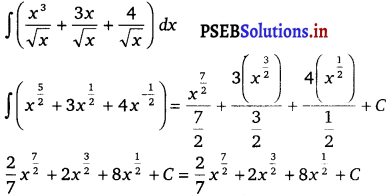
∫ \(\frac{x^{3}+3 x+4}{\sqrt{x}}\) dx
Solution.
∫ \(\frac{x^{3}+3 x+4}{\sqrt{x}}\) dx
= 
![]()
Question 13.
∫ \(\frac{x^{3}-x^{2}+x-1}{x-1}\) dx
Solution.
∫ \(\frac{x^{3}-x^{2}+x-1}{x-1}\) dx = ∫ \(\frac{x^{2}(x-1)+1(x-1)}{x-1}\) dx
= ∫ \(\frac{\left(x^{2}+1\right)(x-1)}{x-1}\) dx
= ∫ (x2 + 1) dx
= ∫ x2 dx + 1 dx
= \(\frac{x^{3}}{3}\) + x + C.
Question 14.
∫ (1 – x) √x dx
Solution.
∫ (1 – x) √x dx = ∫ \(\left(x^{\frac{1}{2}}-x^{\frac{3}{2}}\right)\) dx
= 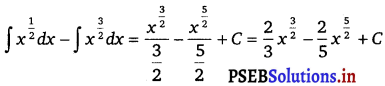
Question 15.
∫ √x (3x2 + 2x + 3) dx
Solution.
∫ √x (3x2 + 2x + 3) dx
= 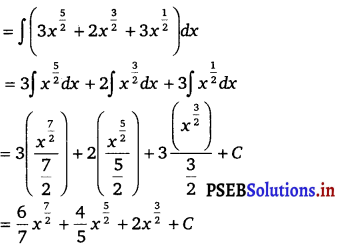
![]()
Question 16.
∫ (2x – 3 cos x + ex) dx
Solution.
∫ (2x – 3 cos x + ex) dx = 2 ∫ x dx – 3 ∫ cos x dx + ∫ ex dx
= \(\frac{2 x^{2}}{2}\) – 3 (sin x) + ex + C
= x2 – 3 sin x + ex + C
Question 17.
∫ (2x2 – 3 sin x + 5√x) dx
Solution.
∫ (2x2 – 3 sin x + 5√x) dx = 2 ∫ x2 dx – 3 ∫ sin x dx + 5 ∫ x\(\frac{1}{2}\) dx
= \(\frac{2 x^{3}}{3}\) – 3 (- cos x) + 5 \(\left(\frac{x^{3 / 2}}{\frac{3}{2}}\right)\) + C
= \(\frac{2}{3}\) x3 + 3 cos x + \(\frac{10}{3}\) x\(\frac{3}{2}\) + C.
![]()
Question 18.
∫ sec x (sec x + tan x) dx
Solution.
∫ sec x (sec x + tan x) dx = ∫ (sec2 x + sec x . tan x dx
= ∫ sec2 x dx + ∫ sec x . tan x dx
= tan x + sec x + C
Question 19.
∫ \(\frac{\sec ^{2} x}{\ {cosec}^{2} x}\) dx
Solution.
∫ \(\frac{\sec ^{2} x}{\ {cosec}^{2} x}\) dx = ∫ \(\frac{\frac{1}{\cos ^{2} x}}{\frac{1}{\sin ^{2} x}}\) dx
= ∫ \(\frac{\sin ^{2} x}{\cos ^{2} x}\) dx
= ∫ tan2 x dx
= ∫ (sec2 x – 1) dx
= ∫ sec2 x dx – ∫ 1 dx = tan x – x + C
Question 20.
∫ \(\int \frac{2-3 \sin x}{\cos ^{2} x} d x\)
Solution.
∫ \(\int \frac{2-3 \sin x}{\cos ^{2} x} d x\) = ∫ \(\left(\frac{2}{\cos ^{2} x}-\frac{3 \sin x}{\cos ^{2} x}\right)\) dx
= ∫ (2 sec2 x – 3 sec x . tan x) dx
= 2 ∫ sec2 x dx – ∫ tan x . sec x dx
= 2 tan x – 3 sec x + C.
![]()
Direction (21 – 22) : Choose the correct answer.
Question 21.
The anti-derivative of (√x + \(\frac{1}{\sqrt{x}}\)) equals.
(A) \(\frac{1}{3} x^{\frac{1}{3}}+2 x^{\frac{1}{2}}+C\)
(B) \(\frac{2}{3} x^{\frac{2}{3}}+\frac{1}{2} x^{2}+C\)
(C) \(\frac{2}{3} x^{\frac{3}{2}}+2 x^{\frac{1}{2}}+C\)
(D) \(\frac{3}{2} x^{\frac{3}{2}}+\frac{1}{2} x^{\frac{1}{2}}+C\)
Solution.
∫ (√x + \(\frac{1}{\sqrt{x}}\)) dx = ∫ \(x^{\frac{1}{2}}\) dx + ∫ \(x^{-\frac{1}{2}}\) dx
= \(\frac{x^{\frac{3}{2}}}{\frac{3}{2}}+\frac{x^{\frac{1}{2}}}{\frac{1}{2}}\) + C
= \(\frac{2}{3} x^{\frac{3}{2}}+2 x^{\frac{1}{2}}\) + C
Hence the correct answer is (C).
Question 22.
If \(\frac{d}{d x}\) f(x) = 4x3 – \(\frac{3}{x^{4}}\) such that f(2) = 0. Then, f(x) is
(A) x4 + \(\frac{1}{x^{3}}-\frac{129}{8}\)
(B) x4 + \(\frac{1}{x^{4}}+\frac{129}{8}\)
(C) x3 + \(\frac{1}{x^{3}}+\frac{129}{8}\)
(D) x3 + \(\frac{1}{x^{4}}-\frac{129}{8}\)
Solution.
It is given that,
\(\frac{d}{d x}\) f(x) = 4x3 – \(\frac{3}{x^{4}}\)
∴ Anti – derivative of 4x3 – \(\frac{3}{x^{4}}\) = f(x)
∴ f(x) = ∫ (4x3 – \(\frac{3}{x^{4}}\)) dx
⇒ f(x) = 4 ∫ x3 dx – 3 ∫ x-4 dx
f(x) = \(4\left(\frac{x^{4}}{4}\right)-3\left(\frac{x^{-3}}{-3}\right)+C\)
⇒ f(x) = x4 + \(\frac{1}{x^{3}}\) + C
Also, f(2) = 0
∴ f(2) = (2)4 + \(\frac{1}{(2)^{3}}\) + C
⇒ 16 + \(\frac{1}{8}\) + C = 0
⇒ C = – (16 + \(\frac{1}{8}\))
⇒ C = – \(\frac{129}{8}\)
⇒ f(x) = x4 + \(\frac{1}{x^{3}}-\frac{129}{8}\)
Hence, the correct answer is (A).
