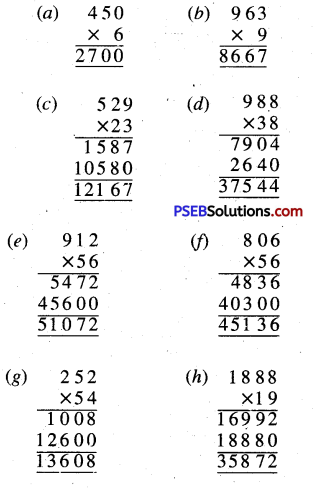
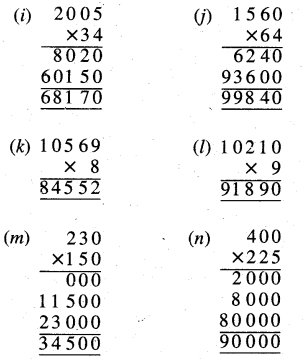
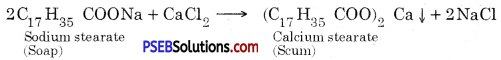
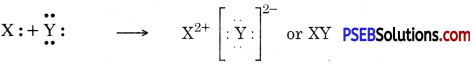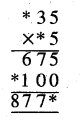Punjab State Board PSEB 10th Class Science Important Questions Chapter 6 Life Processes Important Questions and Answers.
PSEB 10th Class Science Important Questions Chapter 6 Life Processes
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What are the kinds of heterotrophic organisms on the basis of nutrition?
Answer:
Heterotrophic nutrition is a mode of nutrition in which organisms obtain readymade organic food from outside source. The organisms that depend upon outside sources for obtaining organic nutrients are called heterotrophs. It is a characteristic feature of all animals and non-green plants, that are unable to utilize carbon and synthesi s organic compounds necessary for life, but depends upon organic sources of carbon. They are thus dependent upon autotrophic organisms (Plants) and are called as heterotrophs.
It is of the following types :
- Saprophytic nutrition: In this type of nutrition, an organism lives upon dead organic sources such as dead plants and dead animals. These usually secrete dissolving and digesting enzymes and absorb the liquefied molecules so formed e.g. yeast, bread moulds and dung moulds etc.
- Parasitic nutrition: In this type of nutrition, an organism lives totally at the expense of others and derives its food material and shelter from the other .These organisms which derive food material are called parasites and the organism from which food is derived is called as host. This type of nutrition is termed as parasitic or holozoic nutrition: It is also known as parasite-host relationship e.g. Cuscuta, Ascaris etc.
- Holozoic nutrition. It is a mode of heterotrophic nutrition which involves intake of solid pieces of food. Since solid food is taken in, Holozoic nutrition is also called ingestive nutrition. Holozoic nutrition (GK. “Holo”-Whole; “Zoon”-Animal) is found in animals and protists. The food may consist of another animal, plant or its parts.
Depending upon the source of food, holozoic organisms are of three types :
- Herbivores: These organisms obtain their food from plants e.g. cow, rat, deer and goat etc.
- Carnivores: These organisms take the flesh of other organisms as their food e.g. tiger, cheetah, snake, eagle etc.
- Omnivores: These can feed on plants and flesh of other organisms e.g. human, cockroach, crow etc.
Question 2.
What is photosynthesis? Describe the significance of photo-synthesis.
Answer:
Photosynthesis (Photos-Light, Synthesis-putting together) may be defined as an anabolic process in which green plants manufacture complex organic food substances (carbohydrate) from simple inorganic compounds like carbon dioxide and wrater in presence of sunlight with the aid of chlorophyll and evolve out oxygen as a byproduct of the process. Thus photosynthesis is a process in which radiant energy is converted into chemical energy
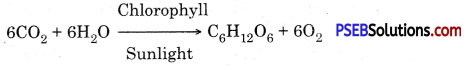
In other words photosynthesis is a series of oxidation- reduction reaction in which CO2 is reduced and H2O is oxidized to produce carbohydrates and oxygen.
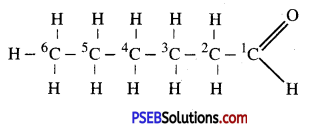
- Chloroplasts are the actual sites for photosynthesis.
- All green parts of a plant are involved in photosynthesis.
- Leaves are the most important organs of photosynthesis.
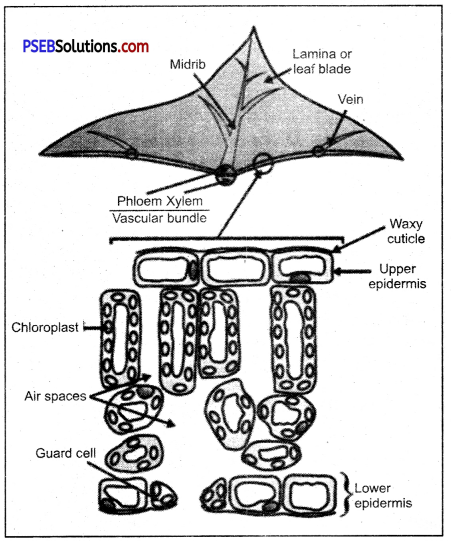
Section of Leaf showing site of photosynthesis
Significance of photosynthesis:
- Photosynthesis is a source of all our food and fuel. It is the only biological process that acts as the driving vital force for the whole animal kingdom and for the non-photosynthetic organisms.
- It drives all other processes of biological and abio- logical world. It is responsible for the growth and sustenance of our biosphere.
- It provides organic substances, which are used in the production of fats, proteins, nucleoproteins, pigments, enzymes, vitamins, cellulose, organic acids, etc. Some of them become structural parts of the organisms.
- It makes use of simple raw materials such as CO2, H2O and inexhaustible light energy for the synthesis of energetic organic compounds.
- It is significant because it provides energy in terms of fossil fuels like coal and petrol obtained from plants, which lived millions and millions of years ago.
- Plants, from great trees to microscopic algae, are engaged in converting light energy into chemical energy, while man with all his knowledge in chemistry and physics cannot imitate them.
Question 3.
Which organelle is responsible for photosynthesis? Describe the role of chlorophyll.
Answer:
Chloroplast is the organelle responsible for photosynthesis. Chloroplasts contain green pigment called as chlorophyll. Photosynthetic pigments occur in the granum. They constitute the pigment system called photosystem. About 250 to 400 pigment molecules are present in a photosystem.
The primary function of photosystems is to trap light energy and converts it to chemical energy.
- Chloroplast was discovered by Schimper.
- Number of chloroplasts is variable in different species of plants.
- In lower plants like algae they are 1 or 2 number.
- In higher plants their number varies from 40 -100 per palisade cell or more.
- Chloroplasts also have variable shapes, for example cup-shaped, ribbon-shaped etc. in algae while it is discoidal in higher plants.
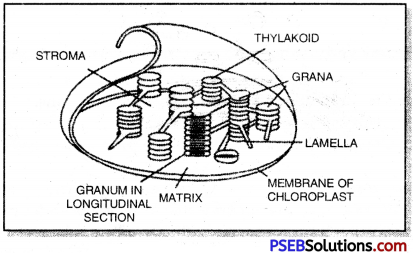
A typical structure of chloroplast is a double membranous structure having two parts.
- Grana: It is a lamellar system consisting of stacks of granum lamella each bounded by a membranous box called as thylakoid. They are 40 – 60 per cell. Number of thylakoids per grana is 50 or more. Chlorophyll molecules are found inside the thylakoid membrane where they trap solar energy in the form of small energy packets called ‘photon’ or ‘quanta’. Grana are interconnected to each other by a channel called as stroma lamellae or Fret’s channel.
- Stroma: It is a non-pigmented proteinaceous matrix in which grana remain embedded. It contains enzymes for dark reaction.
- Mechanism of Photosynthesis: Photosynthesis is formation of organic food from carbon dioxide and water with the help of sunlight inside chlorophyll containing cells. Oxygen is produced as by-products.
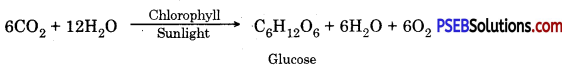
Oxygen comes from water. Hydrogen of water is used to reduce carbon dioxide to form carbohydrate.
Photosynthesis occurs in two main steps:
- The first step is dependent upon light and the second step is not dependent upon light. Hence, the former is called light reaction or photochemical phase while the latter, the dark reaction or biosynthetic phase of photosynthesis.
- Water is split up during photosynthesis by the process called photolysis. It provides reductant for carbon dioxide. Oxygen is liberated. All the liberated oxygen, therefore, comes from water.
- The photolysis of water in photosynthesis was discovered by Hill and hence it is also known as Hill reaction.
- The light reaction of photosynthesis is followed by the dark reaction. In this, CO2 is first fixed by ribulose diphosphate and from this fixed CO2 phosphoglyceric acid is formed. The phosphoglyceric acid thus formed ultimately forms carbohydrates.
- The basic organic compound formed in photosynthesis is often considered to be glucose. The storage product of plants is commonly starch.
- A chemical equation of photosynthesis is
![]()
In plants and most algae it occurs in the chloroplasts i.e., light reaction and dark reaction.
![]()
Question 4.
Discuss the steps of light reaction and dark reaction.
Answer:
Steps of light reaction.
Two main steps of light reaction are :
(a) Photolysis of water
(b) Conversion of fight energy into chemical energy.
- Light reaction takes places in the thylakoid membranes and the intergranal lamellae of the chloroplast in the presence of fight.
- Two photosystems (PSI and PSII) work in a coordinated manner.
- H2O splits into H+ and OH–.
- H+ is used to reduce NADP to NADPH2 which is used in dark reaction.
- Photophosphorylation takes place in two ways—cyclic and non-cyclic.
- Light energy is converted into chemical energy.
- The end-products are ATP and NADPH2.
- As a result of photolysis of water, oxygen is evolved as a by-product.
4H2O → 4 OH– + 4 H+
4 OH– + 4e– → 4 OH–
OH → 2H2O + O2
Summary of dark reaction :
- Dark reaction takes place in the stroma of the living chloroplast.
- Atmospheric CO2 is absorbed.
- The end products of fight reaction (ATP and NADPH2) are also used.
- All green plants operate C3 photosynthetic pathway. Some monocot plants like maize, sugarcane operate both C3 and C4 photosynthetic pathways.
- First end product of photosynthesis is sugar.
Question 5.
Explain process of nutrition in Amoeba.
Answer:
Nutrition in Amoeba. Amoeba is omnivorous, i.e. it feeds on smaller animals, plants, micro-organisms and fragments of larger organisms. Nutrition is holozoic. Ingestion can occur at any place on the surface since a regular mouth is absent. Ingestion occurs through phagocytosis or engulfing the food particle in an invagination of the body. The engulfed food particle comes to fie inside a food vacuole. The latter is surrounded by a membrane.
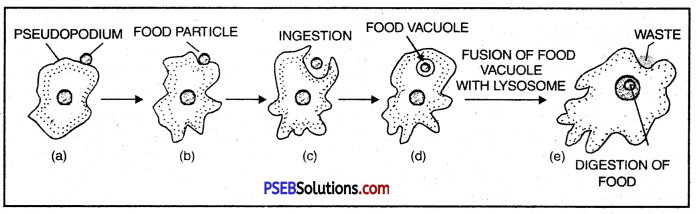
Digestion of food within food vacuole
Digestion: The digestion is intracellular and the food vacuoles act as temporary stomach for digestion.
Absorption: It occurs by diffusion and distribution takes place by cyclosis.
Assimilation: Assimilation of digested material occurs in a single cell.
Egestion: The undigested food is eliminated through the surface of the cell, where the food vacuole containing the undigested food bursts and discharges its contents to the outside.
Question 6.
Difference between the followings :
(i) Autotrophic and Heterotrophic nutrition
(ii) Herbivore and Carnivore.
Answer:
(i) Autotrophic and Heterotrophic nutrition :
| Autotrophic Nutrition | Heterotrophic Nutrition |
| 1. Food is self-manufactured. | 1. Food is obtained readymade from outside. |
| 2. An external source of energy is required for synthesis of food. | 2. An external source of energy is not required. The required energy is present in the food obtained from outside. |
| 3. Inorganic substances constitute the raw materials for manufacturing food. | 3. Inorganic substances are not much required. |
| 4. Chlorophyll is present for trapping light energy. | 4. Chlorophyll is absent |
| 5. Digestion is absent. | 5. An external or internal digestion is required for conversion of complex organic materials into simpler and soluble ones. |
| 6. Organisms performing autotrophic nutrition function as producers. Examples: Green plants, some bacteria, some protists. | 6. Organisms performing heterotrophic nutrition function as consumers. Animals, many protists and monerans. |
(ii) Herbivore and Carnivore
| Herbivore | Carnivore |
| Animals winch cat only plants. e.g. Cow, goat etc. | They feed on flesh of other animals, e.g. Lion, vulture etc. |
Question 7.
Describe human alimentary canal. Draw a labelled diagram of human alimentary canal.
Or
Describe the human alimentary canal with the help of a suitable diagram.
Answer:
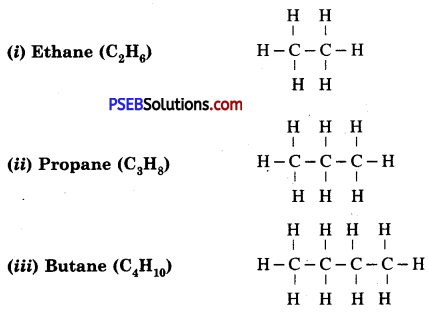
- Mammalian (human) alimentary canal comprises mouth, buccal cavity, pharynx, oesophagus, stomach, small intestine (duodenum, jejunum and ileum), large intestine (caecum, colon and rectum) and anus.
- The mouth, bounded by two lips open into oral cavity.
- Buccal cavity contains teeth and tongue, and receives saliva from 3 pairs of salivary glands. Teeth are meant for cutting and mastication of food.
- Pharynx: It is a vertical tube. It is a cross passage for food and air. It has uvula and epiglottis which closes the internal nares and glottis respectively during swallowing of food to ensure the passage of food into oesophagus (food pipe).
- Oesophagus: It is a 25 cm long narrow muscular straight tube. It opens into stomach. Oesophagus propels the swallowed food into stomach.
- Stomach: It is a sac-like structure situated in the upper part of abdominal cavity below the diaphragm. Large part of this sac is situated left of the median line.
- Small Intestine: It is the longest part of alimentary canal. It is thin-walled and highly coiled tubular structure. It is about 3-3.5 metres long and occupies most part of abdominal cavity. It is coiled upon itself. Its inner lining is thrown into numerous villi.
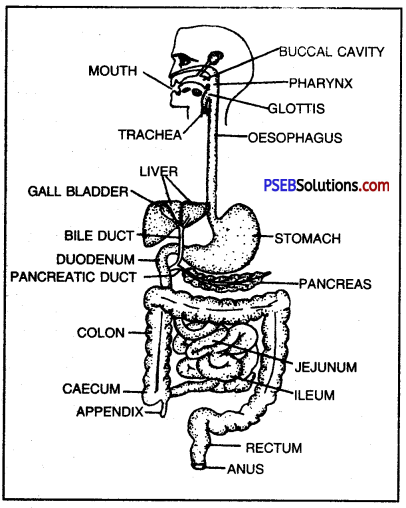
Human digestive system.
Large intestine: The large intestine is about 1.5 metres long. It is divided into following parts, i.e. the vermiform appendix, the colon and the rectum. Caecum is a blind tube and represented by vermiform appendix (5-8 cm) and is present below the junction of small and large intestine. Rectum is the last part and opens to the outside by anus guarded by anal sphincter.
![]()
Question 8.
Describe the process of digestion of food in man.
Answer:
Digestion: The process of conversion of non-diffusible form of food into the simple and diffusible form by chemical and mechanical processes in the alimentary canal is called digestion.
- The process of digestion starts in the mouth cavity and is completed in the intestine.
- In the mouth, food gets mixed up with saliva secreted by salivary glands.
- Saliva contains an enzyme ptyalin (salivary amylase) which breaks polysaccharide starch into disaccharide maltose.
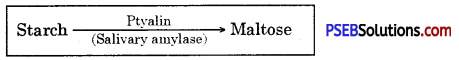
- The food from the mouth cavity called bolus passes into the stomach through the oesophagus.
- The gastric glands of the stomach secrete gastric juice which contains hydrochloric acid, protein digesting
- enzyme-pepsin Rennin, mucus and small amount of gastric lipase are also components of gastric juice.
- Pepsin breaks down proteins into peptones and proteoses in acidic medium of stomach.
- Rennin undies the milk.
- Muscles present on the wall of stomach churn and propel the food called chyme forward into duodenum.
- The digested food moves from stomach to duodenum of the small intestine.
- Duodenum receives bile from juices from liver and pancreatic juice from pancreas.
- The pancreatic juice contains trypsin, amylase and lipase.
- The proteins, fats and carbohydrates are further digested into diffusible form amino acids, glycerol and fatty acids, glucose and fructose.
- The intetinal juice consists of amylolytic, proteolytic and lipolytic enzymes.
- Finally, the digestion is completed in the ileum with the secretion of the intestinal juice by intestinal glands.
- Emulsion form of food called chyle is ready for absorption.
Question 9.
Name the constituents of blood and state the functions of each.
Answer:
| Constituents | Functions |
| 1. Plasma, (i) Serum | It contains proteins as well as organic and inorganic substances in solution. |
| (ii) Fibrinogen | It serves to carry the nutritive and waste materials, antibodies, enzymes and hormones. |
| 2. Red blood corpuscles (R.B.Cs.) | Clotting of blood. |
| (Erythrocytes) | They help to transport oxygen. |
| 3. White blood corpuscles (W.B.Cs) | They help to defend our body against bacteria, as well as the toxins which these organisms may produce. They also help to remove useless dead tissues from the blood. |
| 4. Blood Platelets or Thrombocytes | They play a vey important role in bringing about the coagulation of blood. |
Question 10.
State the functions of blood.
Answer:
Blood performs a number of functions in the body, the most important of which are as follows :
- Blood supplies nutrients and oxygen to various organs and cells of the body.
- It carries the waste matter formed in the cells to the excretory organs.
- It regulates the temperature of the body.
- It supplies hormones to different parts of the body.
- It prevents the body from various diseases by destroying the pathogenic germs.
- It prevents excessive loss of nutrients from cuts and wound by forming a clot.
Question 11.
Describe the structure of human heart.
Answer:
Heart.
- It is a highly efficient, pumping organ of body. Human heart consists of 4 chambers: upper smaller right and left atria (auricles) with thinner wall and lower larger right and left ventricles with thicker walls.
- Atria open into the respective ventricles by atrioventricular apertures guarded by atrioventricular valves.
- The two atria are separated from each other by interatrial septum, and the two ventricles are separated from each other by interventricular septum.
- The sinoatrial node (SAN) or the pacemaker is located in the upper wall of right atrium.
Valves of the heart.
Valves are muscular flaps which prevent the blood to flow back through it. Two types of heart valves are distinguished :
- The Atrioventicular valves: These valves separate the atria from the ventricles. The right side of the heart possesses the tricuspid valve or right atrioventricular valve and the left side of the heart possesses the bicuspid or mitral valve.
- Semilunar valves: These are located in the arteries leaving the heart. The pocket-shaped pulmonary semilunar valves lies in the opening where the pulmonary trunk leaves the right ventricle and aortic semilunar valve lies at the opening between the left ventricle and aorta.
Question 12.
Draw Human heart and label its parts.
Or
Draw a sectional view of the human heart and label on it, Aorta, Right Ventricle and Pulmonary veins.
Answer:
Human Heart
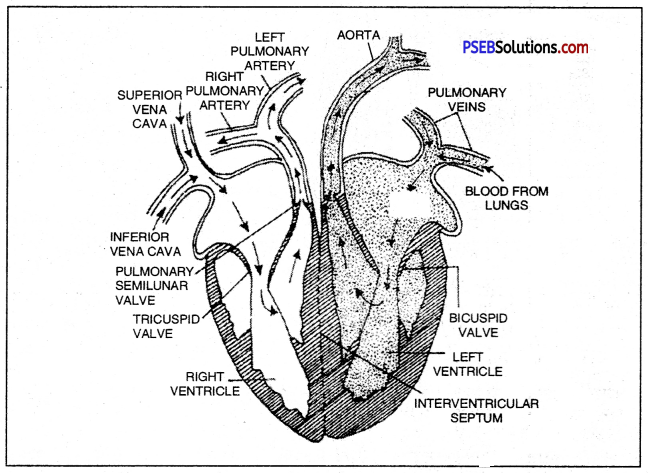
V.S. of Human heart.
Question 13.
Explain respiratory system of human.
Answer:
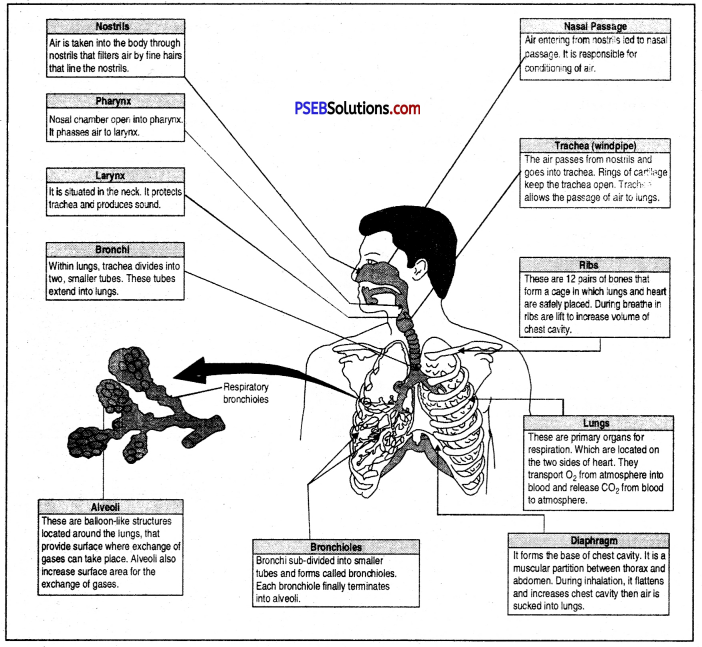
Human respiratory system
![]()
Question 14.
Describe the mechanism of breathing in human beings.
Answer:
Mechanism of breathing
Breathing. It is simply inhaling fresh air rich in oxygen and exhaling foul air rich in carbon dioxide. Respiratory system of man consists of :
- Respiratory tract.
- Respiratory organs (lungs).
Respiratory tract. It is the tract or the path through which fresh air enters the body reaches the lungs and foul air (rich in CO2) leaves the lungs to come out. It consists of Nasal cavity → Pharynx → Larynx → Trachea → Bronchi → Bronchioles → Alveoli (of Lungs).
Breathing is accomplished through changes in size and air pressure of chest cavity. It involves Inspiration and Expiration.
Inspiration:
Intake of fresh air is called inspiration. It occurs when the chest cavity is increased in size and therefore decrease in pressure.
Expiration:
The expulsion of foul air (rich in CO2) from lungs is called expiration. It results when the chest cavity is reduced in size.
Question 15.
Draw a well labelled diagram of human excretory system.
Answer:
Human Excretory System.
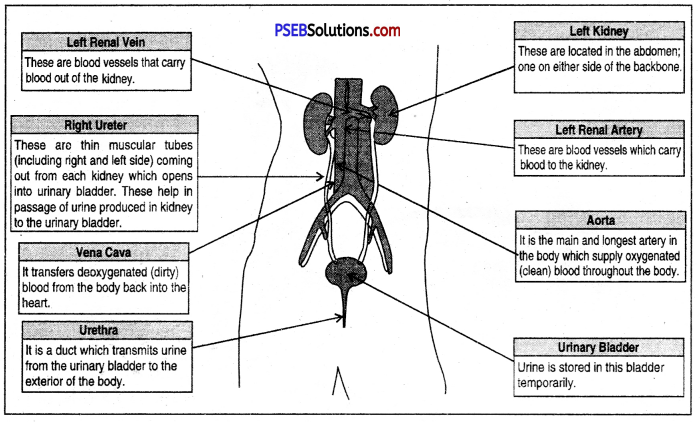
Human excretory system.
Question 16.
Describe the structure of human urinary system.
Answer:
The urinary system consists of the following :
- Kidneys
- Ureters
- Urinary bladder
- Urethra.
1. Kidneys: The kidneys are a pair of bean-shaped delicate organs. They are situated one on each side of the mid-dorsal line of the abdominal cavity, just below the level of the stomach.
2. Ureters: They are two tubes about 30 cm long, emerging from each kidney with the pelvis of which they are continuous. The ureters run downwards and inwards and open into the urinary bladder.
3. Urinary bladder: It serves as a reservoir for the urine. It is a hollow muscular organ lined by stratified epithelium. Its average capacity for storage is about 500 mm. It is situated in the cavity of the pelvis just behind the pubic symphysis.
4. Urethra: The urethra in two sexes differ. The male urethra is about 20 cm in length. The female urethra is a short duct of about 4 cm long and it extends from the urinary bladder to the external urethra orifice which is in the vestibule just above and anterior to the vaginal orifice.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What are life processes?
Answer:
Life processes: Every living organisms takes food, derives energy, removes wagte materials from their bodies and responds to changes in their environment. These activities are called life processes. In all living organisms there occur the basic life processes such as nutrition, respiration, transportation, excretion and reproduction, which are necessary for survival.
Question 2.
What is nutrition? Briefly explain the two major kinds of nutrition.
Or
Define autotrophic nutrition.
Answer:
Nutrition: All living organisms need matter to build up the body and energy to operate the metabolic reaction that sustains life. The materials which provide these two primary requirements of life are called nutrients or foods. The sum total of processes by which organisms obtain matter and energy is termed nutrition.
Modes of Nutrition:
1. Autotrophic or Holophytic nutrition: All green plants and certain protozoans (Euglena) have evolved a mechanism to directly use the energy7 of sunlight for preparing organic food in their own body from simple raw materials i.e. C02 and H20. These simple inorganic materials are transformed into glucose and oxygen is evolved.
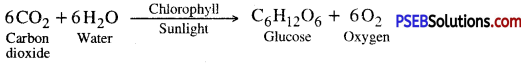
2. Heterotrophic Nutrition: Animal, fungi, (Amoeba) and many bacteria cannot utilize solar energy. They use chemical bond-energy of organic molecules synthesized by other organisms in building their own organic molecules. Such a mode of feeding is termed as heterotrophic nutrition, and the organisms having it are called heterotrophs.
It is of three types :
- Saprophytic
- Parasitic
- Holozoic.
Question 3.
Write a note on saprophytic nutrition.
Answer:
Saprophytic nutrition (Sapros = rotten; phyton = plant) It this organism releases some juices to soften or digest the food and then absorbs the nutrient. Thus they decompose the dead organic matter into simpler substance. Fungi (yeast, moulds, mushrooms) and many bacteria are saprophytic in nutrition.
The saprophytic mode of nutrition can best be exemplified by the common bread mould, Rhizopus. It converts the complex organic food materials of bread i.e. starch into soluble sugars with the help of starch digesting enzymes. These soluble sugars are then absorbed by the fungus.
Question 4.
Explain the two main steps of photosynthesis.
Answer:
Photosynthesis occurs in two main steps.
- The first step is dependent upon light and the second step is not dependent upon light. Hence, the former is called light reaction or photochemical phase while the latter, the dark reaction or biosynthetic phase of photosynthesis.
- Water is split up during photosynthesis by the process called photolysis. It provides reductant for carbon dioxide. Oxygen is liberated. All the liberated oxygen, therefore, comes from water.
- The photolysis of water in photosynthesis was discovered by Hill and hence it is also known as Hill reaction.
- The light reaction of photosynthesis is followed by the dark reaction. In this, CO2 is first fixed by ribulose diphosphate and from this fixed CO2 phosphoglyceric acid is formed. The phosphoglyceric acid thus formed ultimately forms carbohydrates.
- The basic organic compound formed in photosynthesis is often considered to be glucose. The storage product of plants is commonly starch.
- A chemical equation of photosynthesis is
![]()
In plants and most algae it occurs in the chloroplasts i.e., light reaction and dark reaction.
Question 5.
Give a brief account of factors affecting the process of photosynthesis.
Answer:
Factors affecting the process of photosynthesis.
- Temperature: The rate of photosynthesis increases with increase in temperature upto a maximum of 35°C. However, the rate starts decreasing if the temperature rises beyond 30°C.
- Water: The rate of photosynthesis is slow in water-deficient conditions.
- Carbon dioxide: The rate of photosynthesis increases with an increase in carbon dioxide concentration upto a certain level, beyond which there is no effect on the rate of photosynthesis.
- Anatomy of leaf
- Chlorophyll contents.
![]()
Question 6.
What are stomata? Explain role in respiration.
Or
How respiration takes place in roots and stems in plants?
Answer:
Respiration in plants. Plants, during the process of photosynthesis, give off oxygen which is utilized during respiration.
Plant respiration occurs at slower rate.
- In the leaves Stomata are the openings located on the surface of the leaves which are guarded by two kidney-shaped guard cells. Through stomatal opening, air can pass into or out of leaves.
- In woody stems. Lenticelo are the breathing pores located on the surface of the woody stems through which air can pass. Plants do not have any specialised ventilation mechanism.
- In roots. Roots take up oxygen present in between particles through root hairs by diffusion. Root hairs are simple extensions of epidermal cells of root in contact with soil.
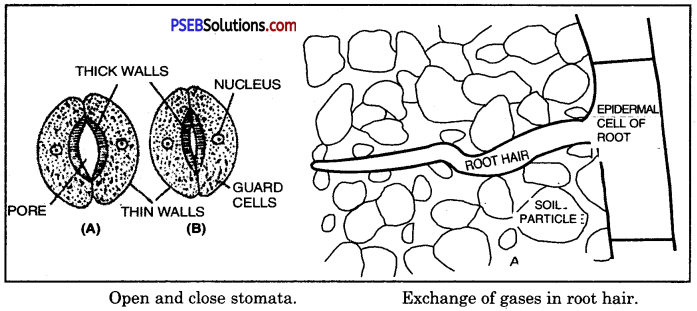
In the older parts of roots: Older portions of root hairs lacks root hairs. They are covered with protective layer of dead cells having very small openings called lenticels through which gaseous exchange take place between soil and inner living cell.
Question 7.
Demonstrate with experiment that O2 is evolved during photosynthesis.
Answer:
Take a beaker filled with water. Add a pinch of baking soda (NaHCO3) to it and put a Hydrilla plant (Aquatic plant) in it. Cover the plant with a funnel. Invert a test tube containing water over the stem of the funnel. Keep this apparatus in the bright sunlight. After some time bubbles start emerging out from the plant, which gets collected in the upper part of the test tube. Remove the test tube and test the gas with a lighted splinter, it keeps on glowing showing that the gas is a supporter of combustion. Thus, the experiment clearly shows that O2 is evolved during photosynthesis.

Question 8.
To demonstrate that photosynthesis take place in the presence of chlorophyll
Procedure :
- Take a potted plant with variegated leaves-for example, money plant or crotons.
- Keep the plant in a dark room for three days so that all the starch gets used up.
- Now keep the plant in the sunlight for about six hours.
- Pluck a leaf from the plant. Mark the green areas in it and trace them on a sheet of paper.
- Dip the leaf in boiling water for a few minutes.
- After this immerse it in a beaker containing alcohol.
- Carefully place the above beaker in a water-bath and heat till the alcohol begins to boil.
- What happens to the colour of the leaf? What is the colour of the solution?
- Now dip the leaf in a dilute solution of iodine for a few minutes.
- Take out the leaf and rinse off the iodine solution.
- Observe the colour of the leaf and compare this with the tracing of the leaf done in the beginning (Fig.).
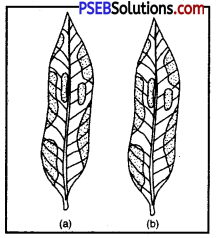
What can you conclude about the presence of starch in various areas of the leaf?
- Observation and Conclusion: Only green patches of variegated leaf take on blue colour. Other parts remain unchanged.
- Photosynthesis take place only in chlorophyll-containing patches of leaf.
Question 9.
To demonstrate that CO2 necessary for photosynthesis.
Answer:
Procedure:
- Take two healthy potted plants which are nearly of the same size.
- Keep them in a dark room for three days.
- Now place each plant on separate glass plates. Place a watch-glass containing potassium hydroxide by the side of one of the plants.
The potassium hydroxide is used to absorb carbon dioxide.
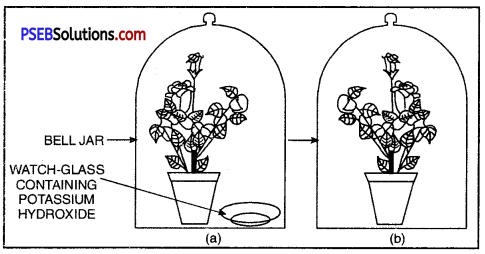
Experimetal set-up (a) with potassium hydroxide (b) without potassium hydroxide
- Cover both the plants with separate bell-jars as shown in Figure.
- Use vaseline to seal the bottom of the jars to the glass plates so that the set-up is air-tight.
- Keep the plants in sunlight for about two hours.
- Pluck a leaf from each plant and check for the presence of starch as in the above activity.
- Do both the leaves show the presence of the same amount of starch?
What can you conclude from this activity?
Observation and Conclusion. The plant containing CO2 in the surrounding carry out photosynthesis. Other plant does not. It proves that CO2 is essential for photosynthesis.
Question 10.
Demonstrate with experiment that light is essential for photosynthesis.
Answer:
Take a de-starched potted plant, which has been kept in dark for 3 to 4 days. Cover one of its leaves completely with a carbon paper so that no light falls on it. Keep the plant in light for 4 to 6 hours. Test the covered leaf and uncovered leaf for starch with iodine test. The covered leaf will show negligible amount of starch, while the uncovered leaf will give positive test for starch. The process clearly shows that light is necessary for photosynthesis.
Question 11.
How is respiration different from breathing?
Answer:
Differences between Breathing and Respiration
| Breathing | Respiration |
| 1. It is ventilation or bringing in of oxygenated air and giving out deoxygenated air. | 1. Respiration of animals includes breathing, gaseous exchange and catabolic breakdown of food. |
| 2. It is a physical process. | 2. Respiration is both a physical and physiological process. |
| 3. Breathing does not liberate energy. | 3. It liberates energy. |
| 4. It is restricted to organs where gaseous exchange occurs between blood and atmospheric air. | 4. Respiration involves every living ceil of the body. |
![]()
Question 12.
List three differences between respiration in plants and respiration in animals.
Answer:
Differences in respiration in plants and animals
| Respiration in plants | Respiration in animals |
| 1. All the cells of plant parts (root, stem, leaves) perform the respiration individually. | 1. It is performed by specific respiratory organs for all the cells of body. |
| 2. There is little transport of gases from one part to the other. | 2. Transport of gases is maximum. |
| 3. Rate of respiration is low. | 3. Rate of respiration is high. |
Question 13.
What is the function of epiglottis?
Answer:
Epiglottis is a flap like structure present at the top of glottis. It closes glottis during swallowing of food thus checks the entry of food into respiratory passage.
Question 14.
Why is food necessary for living organisms?
Answer:
Food provide energy to raw materials for growth and maintenance.
Utility of components of food.
- Carbohydrates are mainly used for producing energy.
- Fats serve as stored concentrated fuel for energy production.
- Proteins are mainly used to build up tissues.
- Mineral salts and vitamins regulate metabolic processes and growth.
- Water is essential for all biological activities.
Question 15.
Explain the mechanism of breathing in human.
Answer:
Inhalation or Inspiration
- The entry of air from outside into alveoli of lungs through respiratory tract is called inhalation.
- The air enters when thoracic cavity expands due to contraction of intercostal muscles attached to ribs and peripheral muscles of the diaphragm.
- Thus the thorax moves upward, outward and forward.
- It increases the volume of thoracic cavity and the pressure decreases.
- Thus air from outside rushes into alveoli of lungs through nostrils, nasal chambers, trachea, bronchi and bronchioles.
- The alveolar sac gets filled with oxygen rich air.
Exhalation or Expiration is concerned with the expelling of carbon dioxide from lungs.
- It takes place when the volume of the thoracic cavity decreases and the pressure of the contained air in the thoracic cavity increases.
- Air passes out through the respiratory tract from the lungs.
Question 16.
What is the effect of sternuos exercise on rate of breathing and why?
Answer:
Normally man breathes about 15-18 times per minute but during hard exercise the breathing rate increases to 20 to 25 times per minute. It is due to the fact that body needs more of energy thus requires more of oxygen.
Question 17.
Give an outline of Calvin-Benson Cycle.
Answer:
Melvin Calvin and Andy Benson discovered this cycle, hence it is called Calvin cycle.
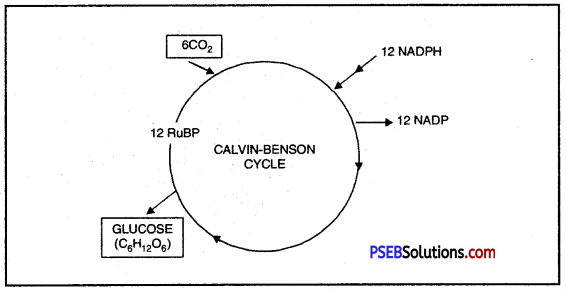
Calvin-Benson Cycle
Question 18.
Label the parts in the figure.
Answer:
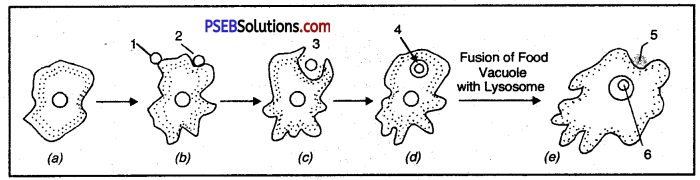
Answer:
- Pseudopodium
- Food particle
- Ingestion
- Food Vacuole
- Waste
- Digestion of food.
Question 19.
Describe the role of intestinal juice.
Answer:
Intestinal juice too is alkaline (pH 8.3).
It has many enzymes :
- Intestinal amylase hydrolyses the remaining starch and glycogen to maltose.
- Maltase changes maltose to glucose.
- Sucrase converts sucrose into glucose and fructose.
- Lactase hydrolyses lactose to glucose and fructose.
- Dipeptidases hydrolyse dipeptides to amino acids.
- Intestinal lipase splits emulsified fats into fatty acids and glycerol.
- Alkaline emulsion of digestion products formed in the small intestine is called chyle.
Question 20.
Explain absorption of food in the small intestine.
Answer:
Absorption. The process of diffusion of digested food into blood present in the blood capillaries of smail intestine is called absorption. Inner lining is thrown in fold called villi. They increase surface area for absorption of food.
Glucose, amino acid, vitamins, mineral salts and water diffuses into blood present in blood capillaries of numerous villi of the small intestine. The fatty acids and glycerol diffuses into lymph present in lymph vessels called lacteals. The digested food is carried to the liver by the hepatic portal vein. The fatty acid and glycerol unite in lymph to form fat. Most of the fat passes as a milky emulsion. After absorption, the undigested- food passes into large intestine.
Question 21.
State the functions of stomach and large intestine.
Functions of Stomach
Answer:
- Storage of food.
- Mechanical breakdown of food.
- Partial digestion of food.
Functions of large intestine
Colon:
- Its wall absorbs the water from undigested food.
- Absorption of digested food also takes place in this region which has not been absorbed by ileum.
![]()
Question 22.
Differentiate the following :
Respiration and Photosynthesis
Answer:
Differences between Respiration and Photosynthesis
| Respiration | Photosynthesis |
| 1. It is a catabolic process in which food substrates are broken down. | 1. It is an anabolic process in which food substrates are synthesized. |
| 2. It takes place in all living cells. | 2. It is carried out only by the chlorophyll containing cells of plants. |
| 3. CO2 and H2O are produced. | 3. CO2 and H2O are used. |
| 4. CO2 is given out. | 4. O2 is released as a byproduct. |
| 5. Chemical energy is converted into ATP and some energy is lost as heat. | 5. Radiant energy’of light is converted into 1 chemical energy. |
Question 23.
What is fermentation? How is it important?
Answer:
The slow decomposition of organic matter into simpler substances in the presence of enzymes is known as fermentation. It is a type of anaerobic respiration. Fermentation literally means a chemical change accompanied by effervescence. The anaerobic breakdown of glucose to carbon dioxide and ethanol is a form of respiration referred to fermentation. It is normally carried by yeast cells and accounts for the production of alcohol in alcoholic bevefages. In fermentation process, if glucose is converted into ethanol then it is called ethanolic fermentation. When glucose is converted into organic acids such as lactic acid, then this type of fermentation is known as lactic acid fermentation. It is carried out by the bacterium Bacillus acidilacti.
Question 24.
Briefly explain the human respiratory system and also label the parts 1, 2, 3, 4, 3 and 6.
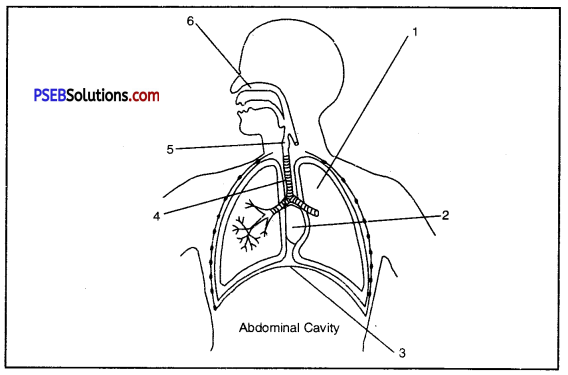
Answer:
Human Respiratory System. Respiratory system of human beings and other mammals consists of air passage or respiratory tract, a pair of lungs.
Respiratory tract is made up of nostrils nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx, trachea and bronchi.
- Left Lung
- Heart
- Diaphragm
- Trachea
- Larynx
- Nasal Cavity
The lungs are a pair of brownish grey coloured spongy structures situated in the thoracic cavity. The left lung consists of two lobes while the right lung consists of three lobes.
Each lobule of a lung consists of bronchioles which terminate into a bunch of spherical thin walled air sacs, called alveoli.
Each alveolus or air sac has a diameter of 75 to 300 microns and has a very thin wall. The walls of the alveoli are elastic and are supplied with capillaries. Gases are exchanged between the capillaries and the air sacs through these thin walls.
Question 25.
What are the different modes of respiration in animals?
Answer:
In animals such as earthworm, respiration is by skin.
- The insects have an elaborate tracheal system of respiration.
- Fishes respire through gills.
- Respiratory system of human beings and other mammals consists of air passage or Respiratory tract, and a pair of lungs.
- Respiratory tract is made up of nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx, trachea and bronchi. The lungs are a pair of brownish grey coloured spongy structures situated in the thoracic cavity.
- The left lung consists of two lobes while the right lung consists of three lobes.
- Each lobule of a lung consists of bronchioles which terminate into a bunch of spherical thin-walled air sacs, called alveoli.
Question 26.
Differentiate between respiration and combustion.
Answer:
Difference between respiration and combustion.
| Respiration | Combustion |
| 1. It occurs in living cells. | 1. It occurs in non living and dead cells. |
| 2. It is a complex biochemical process controlled by several enzymes. | 2. It is a chemical process. |
| 3. Heat produced is much less. | 3. A large amount of heat is produced. |
| 4. There is no flame or light produced. | 4. This process is usually accompanied with flame and light. |
Question 27.
What are parasitic nutrition?
Answer:
Parasitic nutrition (Para = besides ; sitos = food). In this an organism (parasite) depends upon the organism (host) for its nutritional requirements. Many bacteria, viruses, fungi, some non-green plants and many animals have this mode of nutrition.
For example, a fungus Puccinia is a parasite on wheat and barberry plants; Cuscuta or dodder plant grows as a parasite on many plants; tapeworms and round worms are parasites in the body of man etc.
Parasites are of two kinds :
- Ectoparasites and
- Endoparasites
Question 28.
Differentiate between Light reaction and Dark reaction in photosynthesis.
Answer:
Difference between light reaction and Dark reaction
| Light reaction | Dark reaction |
| 1. Light reaction is light induced chemical reaction. | 1. Dark reaction requires no light and is purely enzyme controlled reaction. |
| 2. Energy rich compounds like ATP and NADPH2 are synthesized. | 2. The energy rich compounds are used to produce the organic compounds. |
| 3. Oxygen is liberated. | 3. No liberation of oxygen. |
| 4. It takes place in the grana of the chloroplasts. | 4. It takes place in the stroma of chloroplasts. |
Question 29.
What are the functions of liver?
Answer:
Functions of liver
- Role in digestion. Bile produced by liver helps in the digestion of food as follows.
- It emulsifies the fats with its salts.
- It prevents decomposition of food by checking the growth of bacteria.
- It neutralizes the acid coming from the stomach along with food and provide alkaline medium in the intestine required for action of enzymes of pancreas and intestinal glands.
- Regulation of Blood Sugar: The liver separates the excess of sugar from the blood and stores it in its cells as glycogen (animals starch).
- Formation of Glycogen from non-carbohydrates Sources.
- Deamination: In the liver, the amino acids coming from the alimentary canal are sorted out, ammonia is formed. Ammonia is converted to less toxic urea.
- Excretion: Liver collects haemoglobin of the worn-out red blood corpuscles and changes it into bile pigments.
Question 30.
Differentiate between Saprophytic and Parasitic nutrition.
Answer:
| Saprotrophic Nutrition | Parasitic nutrition |
| Many organisms absorb fluid food through the body surface. This is called saprotrophic nutrition. Bacteria and fungi flourish on dead, decaying organic matter of both plant and animal origin. They secrete digestive enzymes onto this matter. The enzymes hydrolyze the organic matter into simple soluble products that are then absorbed. This method of taking up organic food is known as saprophytic nutrition. | The organisms obtain nutrients from a living host without helping it any way. Examples. Liver fluke lives in the bile duct of sheep and absorbs nutrient. Other examples include several fungi, bacteria and a few higher non-green plants such a cuscuta. |
![]()
Question 31.
Discuss the fate of food in the oral cavity of man.
Answer:
Fate of food in mouth cavity. The partial digestion of food occurs due to the action of Ptyalin enzyme. It acts on starches and forms maltose.
The sufficiently masticated, partially digested food forms bolus. It is swallowed into oesophagus through gullet by raising the throat aided by the muscles of pharynx.
Question 32.
What is a digestive gland? Name the various digestive glands of man and their secretions.
Answer:
Digestive gland. A gland that secretes digestive juice which is helpful in the digestion of food is called a digestive gland.
Digestive glands of Man
| Name of digestive gland | Name of digestive juice/Secretion |
| 1. Salivary gland | Saliva |
| 2. Gastric glands | Gastric juice |
| 3. Pancreas | Pancreatic juice |
| 4. Liver | Bile |
| 5. Intestinal glands | Intestinal juice |
Question 33.
Write the enzymes of the pancreatic juice, the substrates they digest and the products of their digestive action.
Answer:
Enzymes of the pancreatic juice
| Name of Enzyme | Substrate | Name of end products |
| 1. Amylase | Starch, glycogen | Maltose and Isomaltose |
| 2. Trypsin | Proteoses, Peptones and Proteins | Peptides and amino acid |
| 3. Lipase | Emulsified lipids | Glycerol and fatty acids |
Question 34.
What is meant by photosynthesis? What are the basic requirements for the process of photosynthesis?
Answer:
The manufacture of organic compounds from carbon dioxide and water in the presence of sunlight inside the chlorophyll containing cells of the plant is called photosynthesis. The overall reaction of photosynthesis is
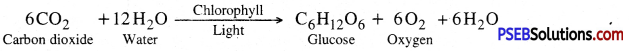
Basic requirements for photosynthesis. CO2, water, chlorophyll and solar energy. Photosynthesis is a photo-biochemical process in which energy rich compounds such as carbohydrates (glucose) are synthesized from simple inorganic compounds like CO2 and water in the presence of sunlight and chlorophyll. Oxygen is a by-product.
Question 35.
What are the different ways in which glucose is oxidized to provide energy in various organisms?
Answer:
Breaking down of glucose involves two step process. In the first step, it is broken into three carbon molecule called pyruvate. The pyruvate is further broken down into energy in following different ways in various organisms :
- Aerobic Respiration: In this case, pyruvate is broken down into water and carbon dioxide along with release of energy. It commonly occurs in mitochondria of cells.
- Anaerobic Respiration in Yeast: In yeast cells during fermentation pyruvate is converted into ethanol and carbon dioxide in the absence of oxygen.
- Anaerobic Respiration in Muscles: Due to lack of oxygen, e.g. during vigorous running or exercise, in human muscles, pyruvate is converted into lactic acid.
Question 36.
Explain how exchange of materials takes place between Blood and Tissues.
Answer:
Arteries supply fresh blood with 02 and food materials to different body organs. Inside the body organ the artery divides into smaller branches called arterioles. The arterioles further divide into extremely thin walled blood capillaries. The blood capillaries form an extensive network inside the body organ. They make their way through the tissue cells. Blood plasma along with the dissolved materials comes out of the thin walls of the blood capillaries and collects into the tissue. It is then called tissue fluid, which acts as an intermediate medium between blood and tissue cells.
The tissue fluid contains different materials such as oxygen, amino acids, glucose, mineral ions and proteins etc. which are needed by the body cells. The body cells take up the required materials from the tissue fluid and release their wastes such as C02 and nitrogenous wastes. These enter through the blood capillary wall and dissolve into the blood plasma or enter into the red blood cells and are carried away.
Question 37.
Outline inhalation-exhalation cycle.
Answer:
- Inhalation: Lowering of diaphragm → Rising of rib cage → Gas (O2) passes to Alveoli
- Exhalation: Air is forced out → Rising of diaphragm → Lowering of ribcage
Question 38.
Leaves of a healthy potted plant are coated with vaseline to block the stomata. Will this plant remain healthy for long? State three reasons to support your answer.
Answer:
No, the plant will not remain healthy because no exchange of gases will take place. It will lead to :
- low respiration
- no photosynthesis occurs
- no transpiration.
Hence plant will not remain healthy and may die eventually.
Question 39.
What are
(i) stomata and
Answer:
Stomata are tiny apertures found on the surface of the leaf, which regulate the exchange of respiratory gases and transpiration.
(ii) lenticels?
Answer:
Lenticels are the raised pores in the woody plants that allow the exchange of gases between the atmosphere and the internal tissues.
Question 40.
Briefly explain breathing, external resperation exchange of gases and tissue resperation.
Answer:
- Breathing involves inhaling of oxygen rich fresh air and exhaling of carbon dioxide rich foul air. The respiratory surface is richly supplied with blood for this purpose. Oxygen of the inhaled air is taken up by blood while carbon dioxide of the blood passes into the air for exhalation.
- The exchange of gases between the blood and the air at the respiratory surface is. known as external respiration.
- Oxygen absorbed by the blood at the respiratory surface is taken to various parts of the body through arteries. Blood loses the oxygen contained in it to tissue fluid, from where it picks up carbon dioxide. The latter is brought to the respiratory surface by blood.
- Tissue respiration, also called internal respiration, is the exchange of gases between the tissue cells and the blood involving uptake of oxygen by tissue cells, oxidation of respiratory substrate and elimination of carbon dioxide by the cells.
Question 41.
Why is mitochondria termed ‘power house’ of the cell?
Answer:
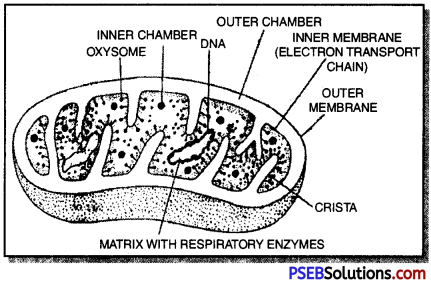
- Most of the aerobic respiration occurs inside the mitochondria and therefore, the latter are also called power houses of the cells.
- Mitochondria are site of synthesis, storage and transport of ATP.
- ATP (Adenosine triphosphate) is the energy currency of the living organisms.
- Adenosine triphosphate. The energy released during cellular respiration is immediately used to synthesise a molecule called ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate
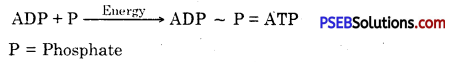
ATP is used to fuel all other activities in the cell. Therefore, it is said to be the energy currency for . most cellular processes.
Question 42.
The figure shows different ways in which glucose is oxidised to provide energy in various organisms?
Fill up the blanks : A _________ B _________ C _________, D. _________ E _________ F _________
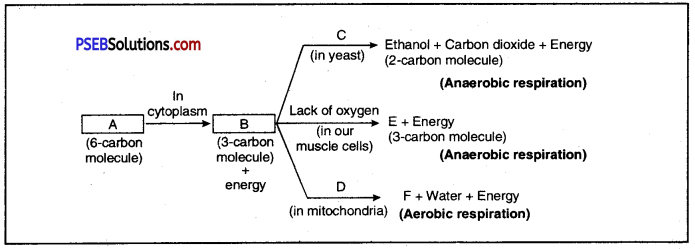
Answer:
Different pathways to provide energy from glucose
A. glucose
B. Pyruvate
C. Absence of Oxygen
D. Presence of oxygen
E. Lactic Acid F. Carbondioxide
Question 43.
Fill in the blanks 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 in the figure.
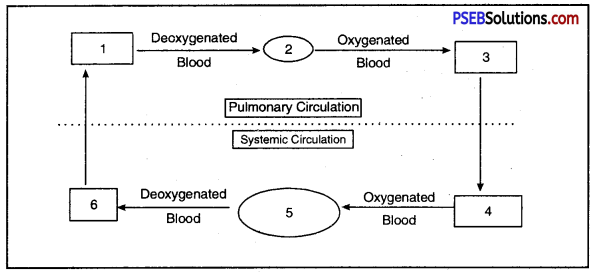
Double circulation of blood in birds and mammals.
Answer:
- Right vetricle
- Lungs
- Left Auricle
- Left Ventricle
- Body parts (except Lungs)
- Right Auricle
![]()
Question 44.
State differences between artery and vein.
Answer:
Differences between Artery and Vein
| Artery | Vein |
| 1. An artery carries blood from the heart to different organs of the body. | 1. A vein collects blood from different organs of the body and brings it back to the heart. |
| 2. Blood flows under great pressure. | 2. Blood flows under less pressure. |
| 3. It has a thick muscular wall. | 3. Wall is thin |
| 4. It is non collapsible. | 4. It is collapsible. |
| 5. It contains oxygenated blood (Exception pulmonary artery). | 5. It contains deoxygenated blood (Exception pulmonary vein) |
| 6. Valves are absent. | 6. Valves are present. |
| 7. Mostly deep seated. | 7. Mostly superficial. |
Question 45.
Why are WBCs called ‘soldiers of the body’?
Answer:
WBC (White Blood Corpuscles) or leucocytes engulf and destroy the foreign particles in the body. Hence they are called ‘soldiers of the body.’
Question 46.
What are hypertension and hypotension?
Answer:
Hypertension. It is the high blood pressure which is caused due to emotions such as worry, excitement, fear etc.
Hypotension. It is the low blood pressure when it falls below the normal level.
Question 47.
Name the three major types of blood vessels. Explain briefly.
Answer:
The three main types of blood vessels are :
- Arteries have thick elastic walls and their diameter may be even 1 cm. These blood vessels carry the blood from the heart to the various parts of the body.
- Capillaries. Arteries divide into thin arterioles and arterioles further ramify into capillaries (1 micron diameter). The wall of a capillary is made up of a single layer of cells. The muscles and elastic fibres are absent in the capillaries. The walls of these capillaries are so thin that the exchange of food materials, waste materials and gases takes place between the blood and protoplasm of cells (liver, lung etc.) through them.
- Veins. The capillaries again reunite to form venules and venules unite to form veins. These venules and veins return the blood to the heart.
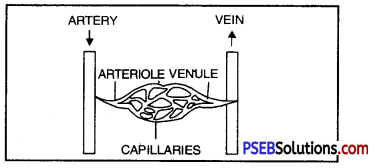
Diagram showing the relationship among blood vessels
Question 48.
Write a note on lymphatic system in human beings.
Answer:
Lymphatic system: The lymphatic system comprises colourless fluid, the lymph; a network of fine channels, the lymphatic capillaries; tubes of varied sizes, the lymphatic vessels; and the lymph nodes. Tissue or interstitial fluid present in the spaces between tissue cells is formed by filtration of protein-free fluid from the blood. Tissue fluid passes into lymphatic capillaries to form lymph. The latter is carried by lymphatic vessels to the veins. Lymphatic vessels have lymph nodes which filter lymph, removing microorganisms and cellular debris and adding lymphocytes.
Question 49.
Write functions of lymph.
Answer:
Functions of lymph
- It drains excess tissue fluid from the extracellular spaces back into the blood.
- Some of the fluid from the digestive tract is absorbed in the lymph. The lymphatic vessels store this fluid temporarily, and release it gradually so that the kidneys do not face a sudden pressure of urine excretion.
- It carries carbon dioxide and nitrogenous waste materials that diffuse into the tissue fluid to the blood.
- It takes lymphocytes and antibodies from the lymph nodes to the blood.
Question 50.
Give differences between blood and lymph.
Answer:
Differences between Blood and Lymph
| Blood | Lymph |
| 1. It consists of plasma, erythrocytes, leucocytes and platelets. | 1. It consists of plasma and leucocytes (lymphocytes most abundant). |
| 2. It is red in colour due to the presence of haemoglobin in erythrocytes. | 2. It is colourless as haemoglobin is absent, |
| 3. Its plasma has more proteins, calcium and phosphorus. | 3. Its plasma has fewer proteins and less calcium and phosphorus. |
| 4. It transports materials in the body. | 4. It acts as middle man between blood and body tissue. |
Question 51.
How are xylem and phloem well suited for transport of materials in plants? Explain.
Or
How are water and mineral transported in plants?
Answer:
Xylem and phloem are well suited to carry water, minerals and food in plants. Vessels in the xylem are cylindrical in shape with their ends open and are placed one above the other so as to form a continuous column stretching from roots to leaves. So, the water and minerals absorbed by the roots are carried upwards to the leaves. This is known as transportation.
Similarly, phloem has sieve tubes that are also cylindrical but the ends are not open instead covered with sieve (perforated) plate. These tubes are also placed one above the other, forming a continuous column from leaves to other parts of the plant body. The food synthesized in the leaves is carried to other paxts of the plant body through phloem. Sucrose is the main form in which carbohydrates are translocated in plants.
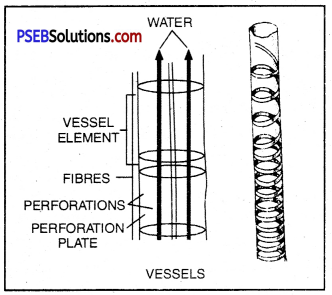
Xylem vessels that transport water and mineral sahs
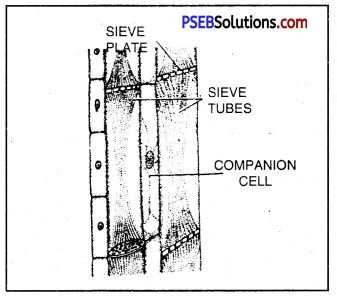
Phioem tubes that conduct prepared food.
Question 52.
Mention any three methods adopted by plants to minimise the transpiration rate.
Answer:
Three methods adopted by plants to minimise the rate of transpiration are :
- In some cases leaves are rolled to cover stomata (e.g. some grasses)
- The stomata may be sunken (e.g. Nerium)
- In some cases, leaves may be dropped or absent as in most cacti.
Question 53.
Write a short note on root pressure.
Answer:
Root pressure: During absorption, water is forced into the xylem vessels by the surrounding cortical cells with a certain force. This induces a pressure which is responsible for ascent of sap to many feet in xylem. This pressure which is developed due to the activity of root is called as root pressure.
Root pressure is a vital phenomenon and depends upon the activity of living root cells. The magnitude of root pressure varies from 2-8 atm.
Question 54.
How is transpiration useful to plants?
Answer:
Advantages of transpiration
- It has cooling effect on the plants as excess of sun’s energy is dissipated.
- It helps in the removal of excess of water from the plant.
- It causes ascent of sap.
- It helps to maintain water cycle.
- It increases the amount of sugar and mineral content in the fruit.
- It is needed to permit photosynthesis to take place.
Question 55.
What are the disadvantages of transpiration?
Answer:
- More plants die from excessive water loss by transpiration.
- Due to high rate of transpiration plants suffer from loss of turgidity.
![]()
Question 56.
What is translocation?
Answer:
Translocation: The long distance transport of the organic food from a source to a sink is known as translocation.
Question 57.
(a) What is blood pressure?
Answer:
Blood pressure is the force that blood exerts against the wall of a vessel. This pressure is much greater in arteries than in veins. The pressure of blood inside the artery during ventricular systole is called systolic pressure and pressure in artery during ventricular diastole is called diastolic pressure.
(b) What are normal value of systolic and diastolic blood pressure
Answer:
The normal systolic pressure is about 120 mm of Hg and diastolic pressure is 80 mm of Hg.
(c) How is it measured?
Answer:
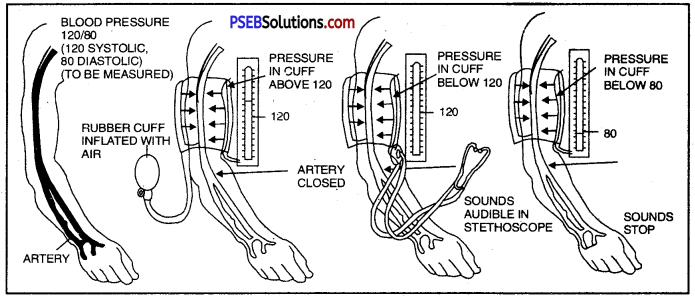
Measurement of blood pressure
(d) Name the instrument used to measure blood pressure.
Answer:
Blood pressure is measured with an instrument called sphygmomanometer.
High blood pressure is also called hypertension and is caused by the constriction of arterioles, which results in increased resistance to blood flow. It can lead to the rupture of an artery and internal bleeding.
Question 58.
Write a note on mechanism of blood clotting.
Answer:
Blood Clotting: At the site of injury, blood platelets disintegrate and release enzyme thromboplastin. Thromboplastin in the presence of calcium ions, transforms the inactive prothrombin into active thrombin. Thrombin converts soluble fibrinogen into insoluble fibrin. This forms a meshwork of fibrils which entangle blood corpuscle and transforms the liquid blood into a gel or clot.
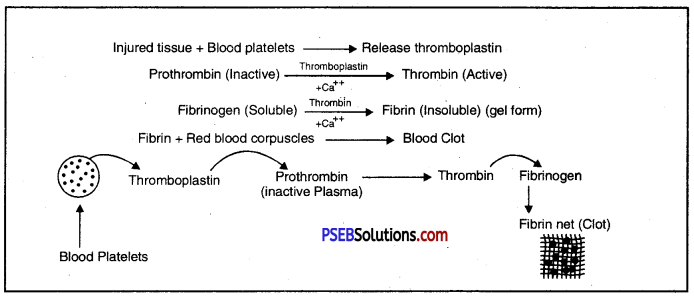
Mechanism of Blood Clotting
Unless the blood clots at the site of the injury, there will be loss of blood (blood haemorrhage).
Such a loss of blood will lead to death of the person.
Question 59.
Briefly describe excretory system.
Answer:
- Kidneys are a pair of bean-shaped reddish brown organs which lie in the lumbar part of abdomen along the dorsal wall, one on either side of the vertebral column.
- Each kidney receives a renal artery from dorsal aorta and sends a renal vein to inferior vena cava.
- The excretory waste products ,are filtered out in the kidney.
- Each kidney contains about 1.2 million excretory units called uriniferous tubules or nephrons.
- Uriniferous tubule is a long, twisted, narrow, tubular structure which consists of ‘ Bowman’s capsule, neck, proximal convoluted tubule, loop of Henle and distal convoluted tubule.
- Bowman’s capsule is a blind cup-shaped end of uriniferous tubule with a tuft of blood capillaries called glomerulus.
- Ureters are two distensible tubes which connect the kidneys with the urinary bladder.
- Urinary bladder is a median pear-shaped bag-like structure that occurs in she pelvic region of abdominal cavity.
- Urinary bladder can hold 300-800 ml of urine.
- Urethra is a tubular connection between the urinary bladder and the external Opening of urinary tract.
Question 60.
Label the parts of human excretory system.
Answer:
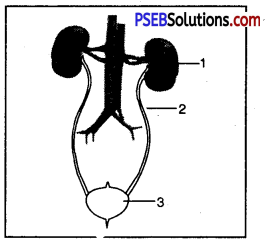
- Kidney
- Ureter
- Urinary Bladder.
Question 61.
How does the excretion take place in Amoeba?
Answer:
The excretory product of Amoeba is ammonia. Special excretory organelle is lacking in Amoeba. C02 and ammonia are excreted by diffusing in solution through plasma membrane. The concentration of ammonia is always higher in Amoeba than in the surrounding water. The water enters through plasma membrane by “endosmosis”. Ammonia is formed in cytoplasm by metabolism.
Surplus water enters contractile vacuole. This surplus water can rupture the animal’s body. Thus size of contractile vacuole increases, when the contractile vacuole is fully expanded with water, it moves towards the periphery. As the contractile vacuole comes in close contact with the plasma membrane, it bursts. Thus excess of water (surplus water) is discharged in the surrounding water. This phenomenon of controlling the amount of water in the body is called as “osmoregulation”.
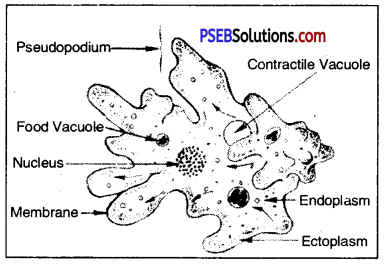
Excretion in Amoeba
Question 62.
State one main function of the following :
(i) Glomerulus
Answer:
The filtration of blood in the nephron takes place in the glomerulus.
(ii) Malpighian capsule
Answer:
Malpighian capsule is concerned with ultrafiltration.
(iii) Sweat gland
Answer:
Sweat glands produce sweat containing urea, uric acid and salts. Sweat evaporates to bring down the body temperature to normal.
(iv) Nephron of kidney tubule
Answer:
Through the kidney tubule or nephrons, filtration of urea, uric acid, water and some salts occur from the blood.
(v) Loop of Henle.
Answer:
Loop of Henle is useful in the absorption of water and secretion of urea.
Question 63.
Name the chief organs of excretion in man. Mention the waste products that they excrete.
Answer:
The chief excretory organs and the waste products removed by them are :
- Kidneys – Urea in the form of urine.
- Lungs – Carbon dioxide.
- Skin – Water and salts as sweat.
Question 64.
Name the following :
(i) A process by which the unwanted nitrogenous wastes are eliminated from the body.
Answer:
Excretion
(ii) Major excretory organs of man.
Answer:
Kidneys
(iii) The structural and functional units of kidney.
Answer:
Nephrons
(iv) A tuft of blood capillaries found in the Bowman’s capsule of nephron.
Answer:
Glomerulus
Question 65.
Name the following :
(i) The structure that brings urine from the kidney to the urinary bladder.
Answer:
Ureter
(ii) Thin membranous sac serving as the reservoir of urine.
Answer:
Urinary bladder
(iii) Any two organic constituents of normal human urine.
Answer:
Urea, creatinine
(iv) The chief nitrogenous waste product in the human urine and the organ which produces it.
Answer:
Urea, liver
(v) Name two excretory products formed by the liver.
Answer:
Bile pigments (Bilirubin, Biliverdin), urea.
Question 66.
What do you understand by artificial kidney? Name the principle on which it works.
Or
Write a note on haemodialysis.
Answer:
Artificial Kidney or Haemodialysis. In case of acute kidney failure, the poisonous materials may accumulate in the body fluids which will cause oedema and finally lead to death of the patient. In such cases, artificial kidney is used. It works on the principle of dialysis and separates wastes from the blood. The process is called haemodialysis.
Artificial kidney contains a number of tubes with a semipermeable lining.
Its functioning is similar to kidney, but it is different since there is no reabsorption involved.
In this, blood from an artery is diverted through a cellophane tube, having pores equal to those of glomerular capillaries, placed in a circulating bath. Concentration of bath-fluid is kept equal to that of normal plasma. The pores in the cellophane tube allow small sized wastes like urea, ammonium salts etc. to pass through but do not allow the passage of blood cells, proteins, fats etc. Diffusion of small and useful substances like glucose, amino acids etc is prevented by keeping their concentration in the dialysis fluid equal to the normal plasma. Blood from dialyser is returned to the body through a vein.
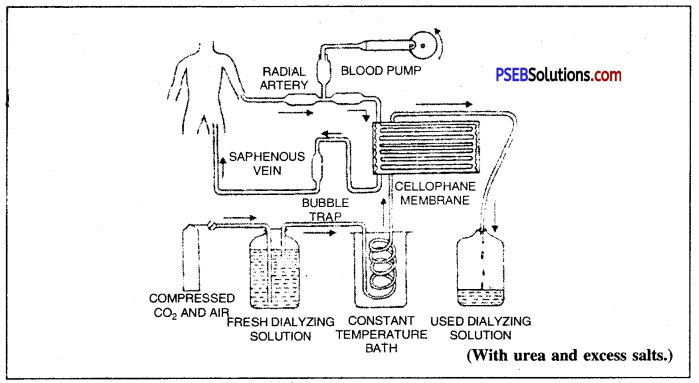
Flow of blood through an artificial kidney for haemodialysis.
Question 67.
What are the functions of tongue?
Answer:
Functions of tongue.
- It helps in mastication of food.
- It bears taste buds and helps in the sensation of taste of food.
- It takes part in the modification of sound production.
- It acts as a brush and cleans the teeth.
- It aids in deglutition of food.
![]()
Question 68.
(i) Label the part A-E
Answer:
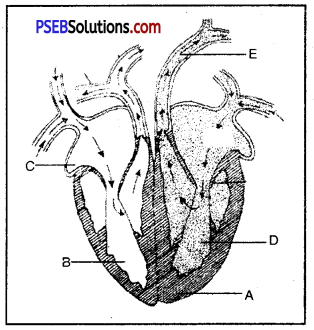
A. Interventricular System B. Right Ventricle C. Right Atrium D. Left Ventricle E. Aorta
(ii) Write Function of E.
Answer:
Function of E-Aorta carries blood to all parts of body.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Why are maintenance processes required?
Answer:
They are required to prevent breakdown.
Question 2.
List three characteristics of living organisms.
Answer:
- Growth
- Movements
- Repair and maintenance of their structures.
Question 3.
What are life processes?
Answer:
The processes which together perform the maintenance jobs are collectively termed as life processes.
Question 4.
What is the basic requirement of maintenance?
Answer:
Energy is needed by living organisms for maintenance.
Question 5.
What are sources of energy for living organisms?
Answer:
Carbon based molecules i.e. food obtained from environment.
Question 6.
List the common reactions required to obtain energy from carbon based molecules.
Answer:
Oxidising-reducing reactions.
Question 7.
Name any four life processes required for maintenance.
Answer:
- Nutrition
- Respiration
- Transportation
- Excretion.
Question 8.
What are nutrients?
Answer:
The substances which provide materials for growth, energy and maintenance are called nutrients.
Question 9.
What is nutrition? Why is it necessary?
Answer:
Nutrition. The sum total of processes by which living organisms obtain food materials and prepare them for use in the growth, repair and providing energy is termed nutrition.
Question 10.
What is food?
Answer:
Food provides energy. It Provides raw materials for growth and maintenance.
Question 11.
What is holozoic nutrition?
Answer:
Holozoic nutrition. When the nutrients are ingested as solid organic food matter, it is called holozoic nutrition.
![]()
Question 12.
What is the source of food for heterotrophs?
Answer:
All heterotrophs obtain food from autotrophs.
Question 13.
Name the process which prepares food is autotrophs.
Answer:
Photosynthesis.
Question 14.
Why are green plants called producers?
Answer:
Green plants prepare their food from CO2 and H2O in the presence of sunlight and chlorophyll. All other organisms obtain food from green plants, thus called as producers.
Question 16.
In which spectrum of light maximum photosynthesis occurs?
Answer:
Red light.
Question 17.
Where is chlorophyll present in cells of leaves?
Answer:
Chloroplast.
Question 18.
How does oxygen produced during photosynthesis enter the atmosphere?
Answer:
Oxygen passes out of green leaves through stomata and diffuses into the atmosphere.
Question 19.
Where does photolysis occur in plant?
Answer:
Photolysis occurs in chloroplasts present in the cell.
Question 20.
Write chemical reaction of photosynthesis.
Answer:
![]()
Question 21.
What are the advantages of cooked food?
Answer:
Human beings consume cooked food. Cooking makes it soft, palatable, tasty and easier to digest.
Question 22.
What is the role of CO2 during photosynthesis?
Answer:
CO2 provides carbon for synthesis of glucose (C6H12O8) during photosynthesis.
Question 23.
What is the role of stomata in green leaves?
Answer:
Stomata are minute pores through which exchange of gas occurs.
Question 24.
Name the minerals obtained from soil by plants.
Answer:
Nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, iron, magnesium and other minerals.
Question 25.
What is the role of nitrogen plants?
Answer:
Nitrogen is constituent of proteins and nitrogen bases of nucleic acids.
Question 26.
What is the food of Amoeba?
Answer:
Food of Amoeba consists of small protozoans, algae, rotifers, bacteria, and diatoms. It also feeds upon bits of organic matter.
Question 27.
Is food vacuole of Amoeba, temporary structure or a permanent one?
Answer:
Food vacuole is a temporary structure.
Question 28.
What is saliva?
Answer:
Saliva is a digestive juice secreted by salivary glands present in oral cavity.
Question 29.
Name the enzyme present in saliva.
Answer:
Salivary amylase.
Question 30.
Name the organ through which blood passes into stomach from oral cavity.
Answer:
Pharynx and oesophagus.
Question 31.
Name the largest part of alimentary canal.
Answer:
Small intestine.
Question 32.
Which of the animals need long large intestine?
Answer:
Animals eating grasses need large intestine for digestion of cellulose.
Question 33.
What is the nature of food entering small intestine from stomach?
Answer:
Acidic in nature.
Question 34.
Name the juices which convert acidic food into alkaline in small intestine.
Answer:
Bile and pancreatic juice.
Question 35.
Name the digestive juice secreted by liver.
Answer:
Bile juice.
Question 36.
Name the digestive juice secreted by pancreas.
Answer:
Pancreatic juice.
![]()
Question 37.
List the enzymes which help in the digestion of proteins.
Answer:
- Pepsin
- Trypsin
- Chymotryposin
- Peptidases.
Question 38.
What is approximate length of human alimentary canal?
Answer:
9 to 10 metres.
Question 39.
Name the largest gland present in human body.
Answer:
Liver.
Question 40.
Name the gland which is exocrine as well as endocrine in nature.
Answer:
Pancreas.
Question 41.
What are three parts of small intestine?
Answer:
- Duodenum
- Jejunum
- Ileum.
Question 42.
Differentiate between chyme and chyle.
Answer:
- Chyme is a semisolid, semidigested acidic food which passes from stomach into duodenum.
- Chyle is emulsion form, completely digested, alkaline food present is small intestine ready for absorption.
Question 43.
Name the four enzymes present in pancreatic juice.
Answer:
- Pancreatic amylase
- Pancreatic lipase
- Trypsin
- Chymotrypsin.
Question 44.
Maximum water is absorbed in which part of alimentary canal.
Answer:
Large intestine.
Question 45.
What is digestion?
Answer:
Digestion. Chemical and mechanical break down of complex, non-diffusible form of food into simple diffusible form of food by action of enzyme.
Question 46.
What is assimilation?
Answer:
The absorption and digestion of food or nutrients by the body or any biological system.
Question 47.
What is egestion?
Answer:
The act or process of discharging undigested food as faeces from a cell in case of unicellular organisms.
Question 48.
What are villi present is small intestine and not in stomach?
Answer:
Small intestine is site of absorption of digested food, villi increase the surface area for absorption of food. No absorption of food occurs in stomach thus villi are absent.
Question 49.
What happens to pyrnvate produced during anaerobic respiration?
Answer:
Pyruvate produced at the end of glycolysis is converted to C02 and ethanol.
Question 50.
What is aerobic respiration?
Answer:
Aerobic respiration is the process of producing cellular energy involving oxygen cells break down food in the mitochondria in a long, multistep process that produces roughly 36 ATP.
Question 51.
What is anaerobic res-piration?
Answer:
A form of incomplete intracellular breakdown of sugar or other organic compounds in the absence of oxygen that releases energy.
Question 52.
What is ATP?
Answer:
ATP is Adenosine triphosphate. It is the energy currency of life. ATP is a high- energy molecule found in every cell. Its job is to store and supply the cell with needed energy.
Question 53.
Expand NADP.
Answer:
NADP. Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide.
Question 54.
Name three animals which respire through skin.
Answer:
- Earthworm
- Leech
- Frog.
Question 55.
Where does Krebs cycle occur in the body?
Answer:
Krebs cycle is completed in mitochondria of cells.
Question 56.
What is hypoxia?
Answer:
Hypoxia is a condition of shortage of oxygen in the body due to strangulation on cyanide poisoning.
Question 57.
Name the respiratory sub-strate.
Answer:
Glucose.
Question 58.
What is the end product of aerobic respiration?
Answer:
Carbon dioxide and water.
Question 59.
What is fermentation?
Answer:
Incomplete breakdown of glucose in the absence of oxygen in microbes such as bacteria and yeast. It forms CO22, ethanol and energy is released in small amount.
Question 60.
Man breaths how many times per minute?
Answer:
12-15 times.
Question 61.
What are the functions of ATP?
Answer:
ATP provide energy for all metabolic reactions in the body such as movements, synthesis, cell division.
![]()
Question 62.
What is bark?
Answer:
The tissue ontside the outer most covering of the stem or root is called bark.
Question 63.
Name the tissue which transport food in plants.
Answer:
Phloem.
Question 64.
What is xylem?
Answer:
Xylem is a complex tissue which transport water and minerals from roots to other parts of the plant.
Question 65.
Name two substances which enter the root through the root hairs.
Answer:
- Water
- Soluble minerals from soil.
Question 66.
What is ascent of sap?
Answer:
The process by which water absorbed by the root is carried to aerial parts of plant is called ascent of sap.
Question 67.
Name the transport tissue of body.
Answer:
Blood and lymph.
Question 68.
Name the three types of blood vessels.
Answer:
- Arteries
- Veins
- Capillaries.
Question 69.
List types of circulation in human body.
Answer:
Double circulation involving pulmonary circulation and systemic circulation.
Question 70.
Name the fluid medium of blood.
Answer:
Plasma.
Question 71.
Why is the S-A node called pace-maker of the heart?
Answer:
S-A node, being self-excitatory, initiates a wave of contraction in the heart.
Question 72.
Name the organs which play role in circulation of blood.
Answer:
Heart. It is a muscular, pumping organ. It pumps the blood in the body.
Question 73.
Name the types of cells which destroy harmful bacteria in the body.
Answer:
White blood corpuscles (W.B.C.)
Question 74.
Name the instrument used to measure blood pressure.
Answer:
Sphigmomanometer.
Question 75.
Name the artery which carry impure (deoxygenated) blood from heart to lungs.
Answer:
Pulmonary artery.
Question 76.
Expand ECG.
Answer:
Electrocardiogram.
Question 77.
Write normal blood pressure in human body.
Answer:
120/80 → Systolic = 120 and Diastolic = 80
Question 78.
Name the largest artery.
Answer:
Aorta.
Question 79.
What is excretion?
Answer:
Excretion. Elimination of nitrogenous waste materials from body is called excretion.
Question 80.
How many nephrons are present in each kidney?
Answer:
About 10 lakhs.
Question 81.
What are the excretory structures of amoeba?
Answer:
Contractile vacuole.
Question 82.
What is a malpighian body (renal corpuscle)?
Answer:
Bowman’s capsule and glomerulus.
Question 83.
Name the reservoir of urine in the body.
Answer:
Urinary bladder.
Question 84.
What is micturition?
Answer:
Act of passing out of urine from urinary bladder is called micturition.
Question 85.
Name the structures which store wastes in plants.
Answer:
Central vacuoles.
Question 86.
What are resins and gums?
Answer:
These are storage wastes of plants.
Question 87.
Define autotrophic nutrition.
Answer:
The organisms prepare their own food from raw materials like C02 and H20 in the presence of sunlight. It takes place in green plants containing chlorophyll.
Question 88.
Define heterotrophic nutrition.
Answer:
The mode of taking readymade organic food material is called heterotrophic nutrition. It may be holozoic (ingestive) or saprophytic and parasitic (absorptive).
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Among the following which is a parasitic plant?
(A) Plasmodium
(B) Cuscuta
(C) Amoeba
(D) Rhizobium.
Answer:
(B) Cuscuta
Question 2.
Dark reaction and light reaction of photosynthesis takes place is:
(A) stroma and grana of chioroplast respectively
(B) grana and stroma of chioroplast respectively
(C) grana only
(D) stroma only.
Answer:
(A)stroma and grana of chioroplast respectively
![]()
Question 3.
Chemical reaction takes place during dark reaction of photosynthesis is:
(A) photo1ysi
(B) hydrolysis
(C) carbon dioxide is bonded with RUBP
(D) nitrogen fixation.
Answer:
(C) carbon dioxide is bonded with RUBP
Question 4.
Plants are green in colour because:
(A) they absorb green light only
(B) they reflect green light
(C) they absorb green light but reflect all other lights
(D) none of the above are correct.
Answer:
(B) they reflect green light.
Question 5.
The nutrition in Mucor is:
(A) parasitic
(B) autotrophic
(C) saprophytic
(D) holozoic.
Answer:
(C) saprophytic
Question 6.
In amoeba the digestion is intracellular because :
(A) amoeba is unicellular
(B) amoeba is multicellular ‘
(C) amoeba is found in pond
(D) amoeba is microscopic animal.
Answer:
(A) amoeba is unicellular
Question 7.
Which of the following has no digestive enzyme?
(A) Saliva
(B) Bile
(C) Gastric juice
(D) Intestinal juice.
Answer:
(B) Bile
Question 8.
C02 acceptor during dark reaction of photosynthesis is :
(A) RUBP
(B) PEP
(C) NADPH
(D) ATP.
Answer:
(A) RUBP
Fill in the blanks:
Question 1.
Viruses show _________ movements.
Answer:
Molecular.
Question 2.
Growth, _________ and repair and _________ are characteristics of life.
Answer:
movements, maintenance.
Question 3.
_________ is needed by living organisms for movements and maintenance.
Answer:
Energy.
![]()
Question 4.
_________ is the largest gland of body.
Answer:
Liver
Question 5.
_________ and are the raw materials for photosynthesis.
Answer:
C02 and H20.
Question 6.
RBC transport _________ in the body.
Answer:
Oxygen.
Question 7.
Xylem and _________ are the main conducting tissues in plants.
Answer:
Phloem.
Question 8.
Translocation of food takes place through _________ of phloem.
Answer:
Sieve tubes.