Punjab State Board PSEB 10th Class Hindi Book Solutions Hindi Grammar anek shabdon ke liye ek shabd अनेक शब्दों के लिए एक शब्द Exercise Questions and Answers, Notes.
PSEB 10th Class Hindi Grammar अनेक शब्दों के लिए एक शब्द
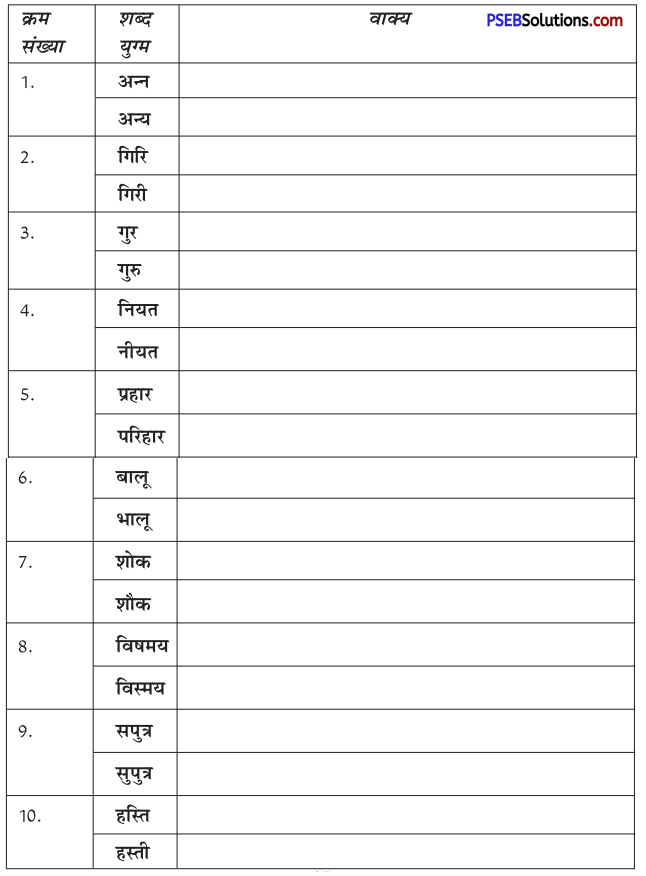
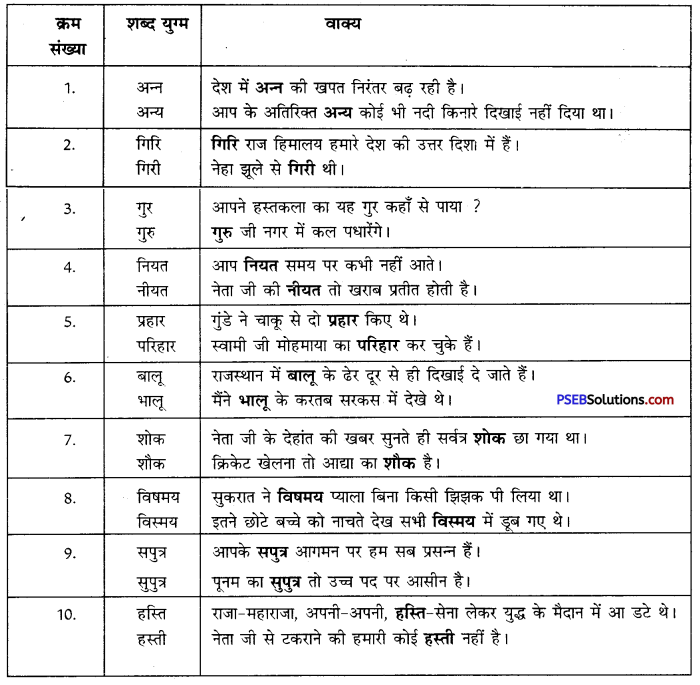
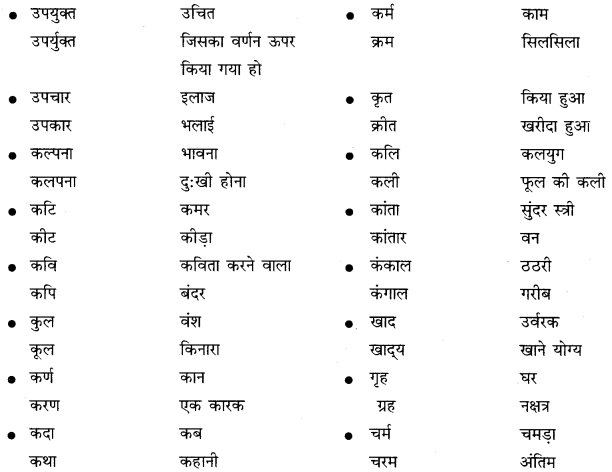
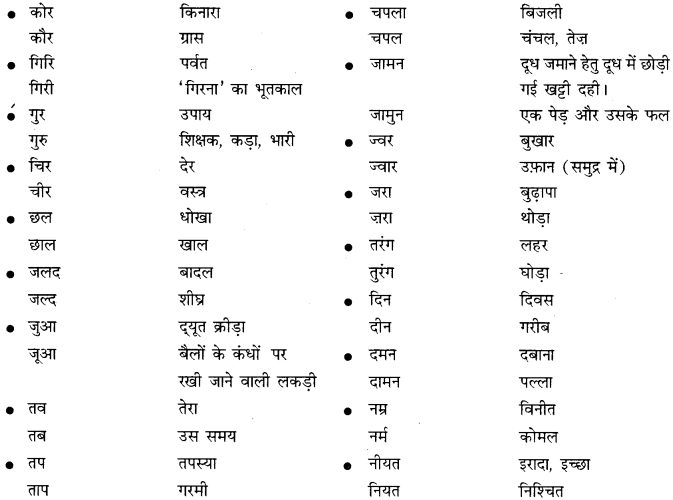
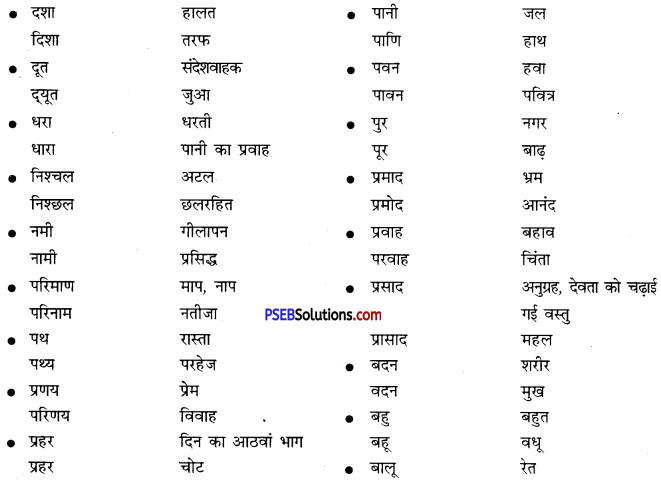
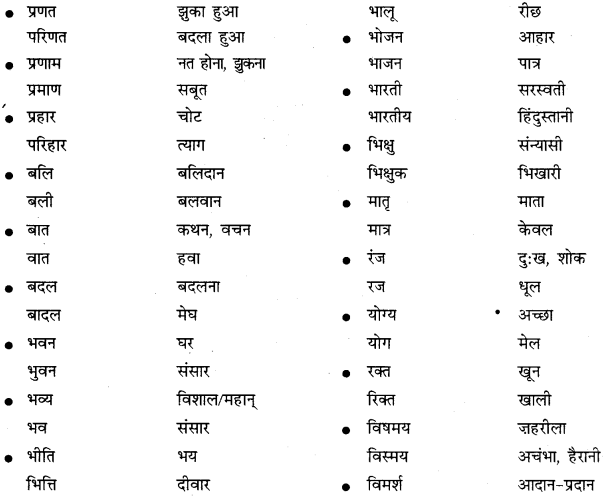
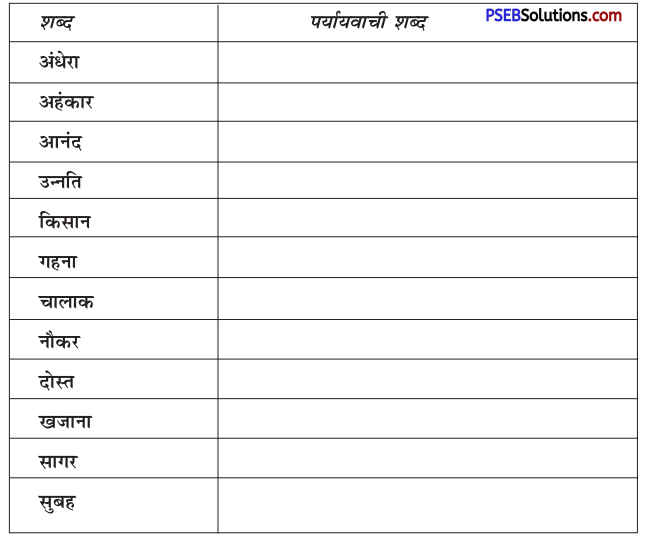
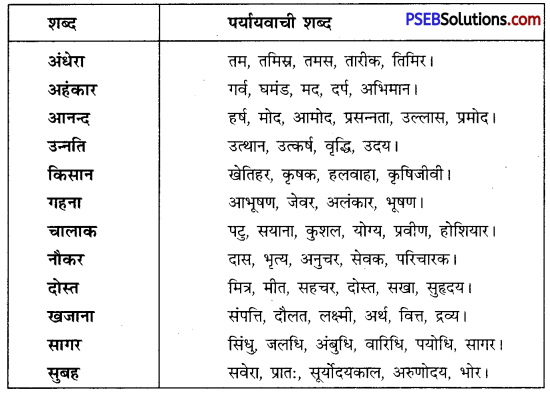
निम्नलिखित वाक्यांशों के लिए एक शब्द लिखिए
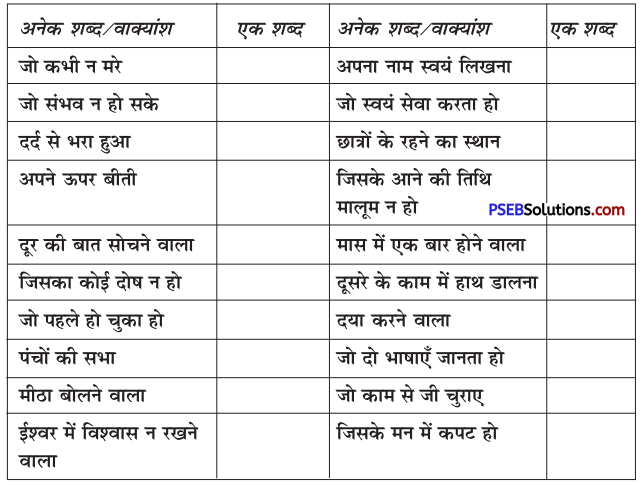
उत्तर:
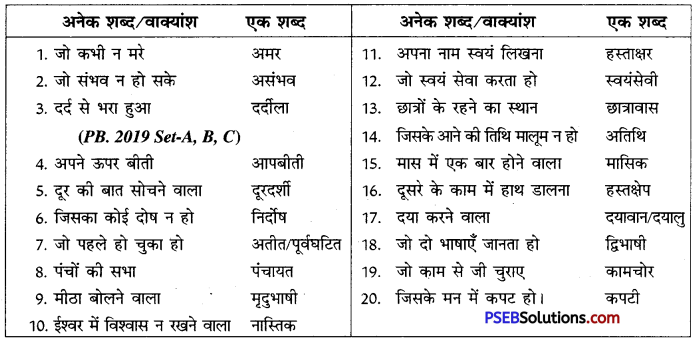
![]()
निम्नलिखित बहुविकल्पी प्रश्नों के उत्तर एक सही विकल्प चुनकर लिखें
प्रश्न 1.
जो कहा न जा सके के लिए एक शब्द है-
(क) अकथ
(ख) अकहानीय
(ग) अगोचर
(घ) अनंत।
उत्तर:
(क) अकथ
प्रश्न 2.
जो देखा न जा सके के लिए एक शब्द है
(क) अमूर्त
(ख) अदृश्य
(ग) निराकार
(घ) निरंजन।
उत्तर:
(ख) अदृश्य
प्रश्न 3.
जो कभी न मरता हो के लिए एक शब्द है-
(क) अवध्य
(ख) अगम
(ग) अमर
(घ) अधोरी।
उत्तर:
(ग) अमर
प्रश्न 4.
जिसका आकार हो के लिए एक शब्द है,
(क) आर्कारी
(ख) साकार
(ग) सार्कारी
(घ) आर्कारीय।
उत्तर:
(ख) साकार
प्रश्न 5.
जो सब कुछ जानता हो के लिए एक शब्द है, अज्ञानी (हाँ या नहीं में उत्तर दीजिए)
उत्तर:
नहीं
प्रश्न 6.
जो ईश्वर को न मानता हो के लिए एक शब्द है, नास्तिक (सही या गलत लिखकर उत्तर दें)
उत्तर:
सही
![]()
प्रश्न 7.
जो प्रतिदिन होता हो के लिए एक शब्द है, दैनिक (सही या गलत लिखकर उत्तर दें)
उत्तर:
सही
प्रश्न 8.
जो आकाश में उड़ते हों के लिए एक शब्द है, नभीय (हाँ या नहीं में उत्तर दीजिए)
उत्तर:
नहीं
प्रश्न 9.
जिसके माता-पिता न हो के लिए एक शब्द है, अनादि (सही या ग़लत लिखकर उत्तर दें)
उत्तर:
गलत
प्रश्न 10.
पीछे-पीछे चलने वाला के लिए एक शब्द है, अनुगामी (हाँ या नहीं में उत्तर लिखें)
उत्तर:
हाँ।
बोर्ड परीक्षा में पूछे गए प्रश्न निम्नलिखित में से किसी एक वाक्यांश (अनेक शब्दों) के लिए एक शब्द लिखिए
वर्ष
डाक बाँटने वाला, आलोचना करने वाला।
उत्तर:
डाक बाँटने वाला = डाकिया
आलोचना करने वाला = आलोचक।
ईश्वर में विश्वास रखने वाला, वर्ष में एक बार होने वाला।
उत्तर:
ईश्वर में विश्वास रखने वाला = आस्तिक
वर्ष में एक बार होने वाला = वार्षिक।
उपकार को मानने वाला, कम खाने वाला।
उत्तर:
उपकार को मानने वाला = कृतज्ञ
कम खाने वाला = अल्पाहारी, मिताहारी।
वर्ष
समाज से संबंधित, देश से द्रोह करने वाला
उत्तर:
समाज से संबंधित = सामाजिक
देश से द्रोह करने वाला = देशद्रोही।
जिसका पार न हो, डाक बाँटने वाला।
उत्तर:
जिसका पार न हो = अपार
डाक बाँटने वाला = डाकिया।
![]()
गाँव में रहने वाला, कृषि कर्म करने वाला।
उत्तर:
गाँव में रहने वाला = ग्रामीण
कृषि कर्म करने वाला = कृषक।
वर्ष
पूर्वजों से प्राप्त हुई सम्पत्ति, जो नीति का ज्ञाता हो।
उत्तर:
पूर्वजों से प्राप्त हुई सम्पत्ति = पैतृक सम्पत्ति,
जो नीति का ज्ञाता हो = नीतिज्ञ।
प्रश्न 1.
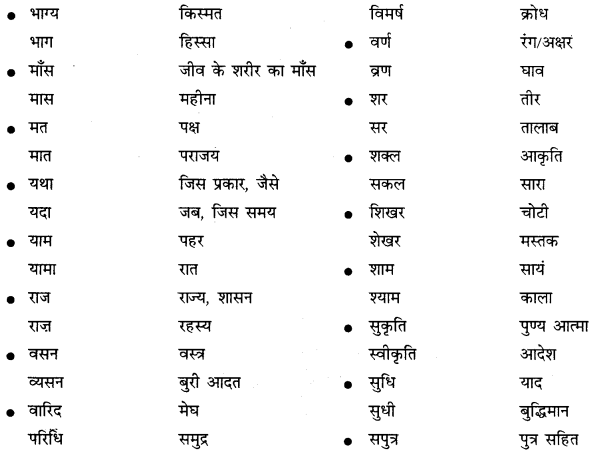
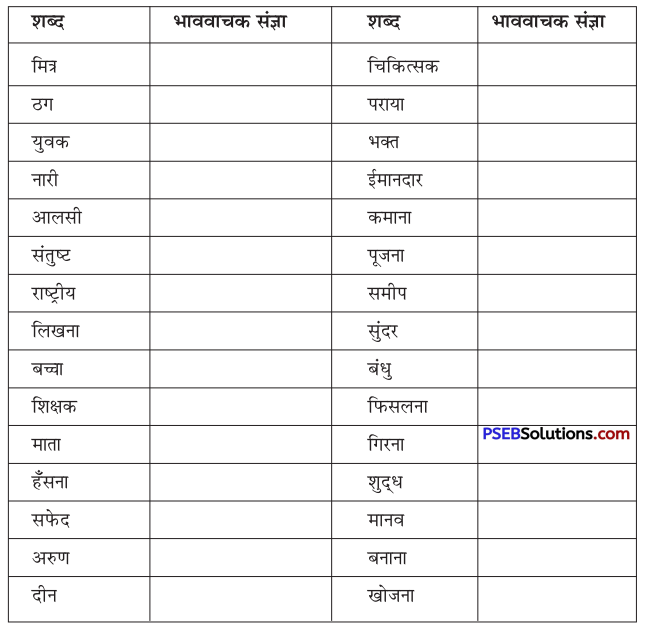
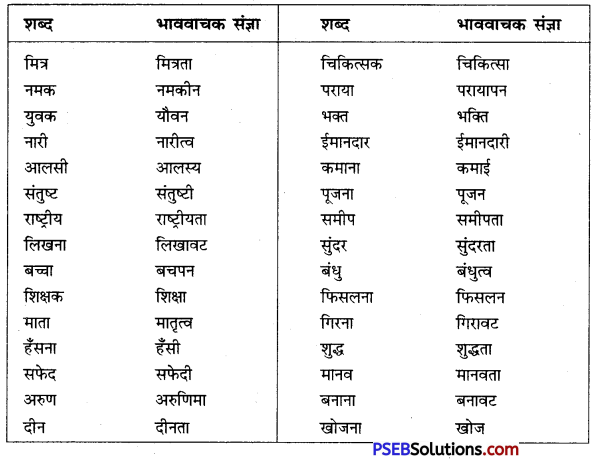
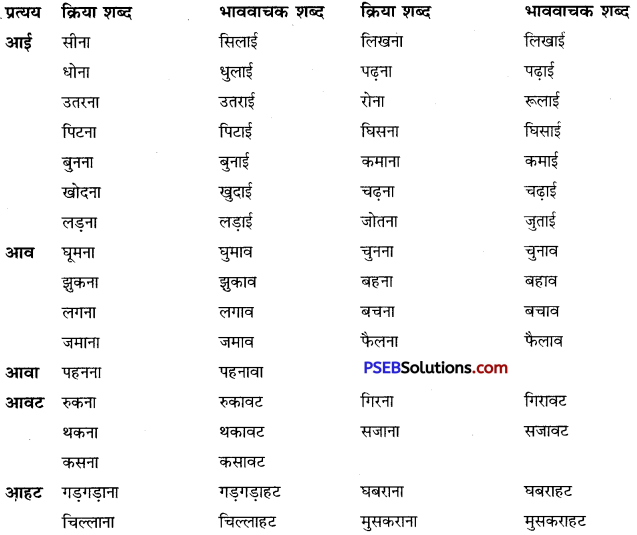
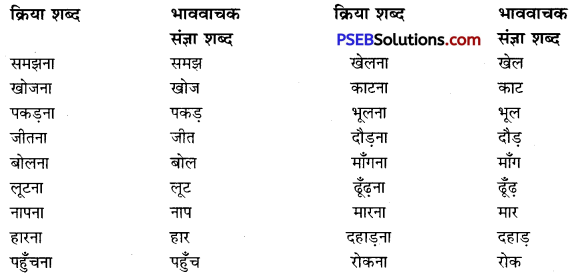
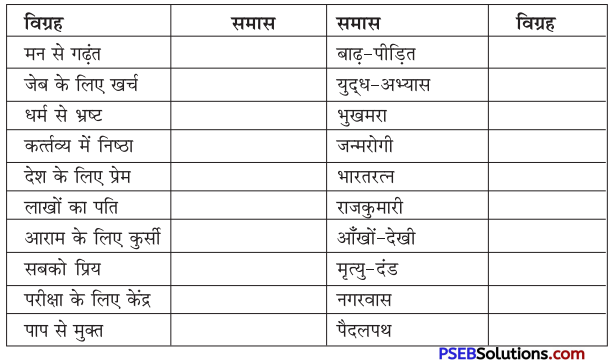
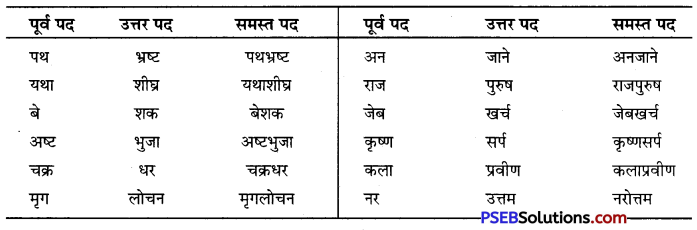
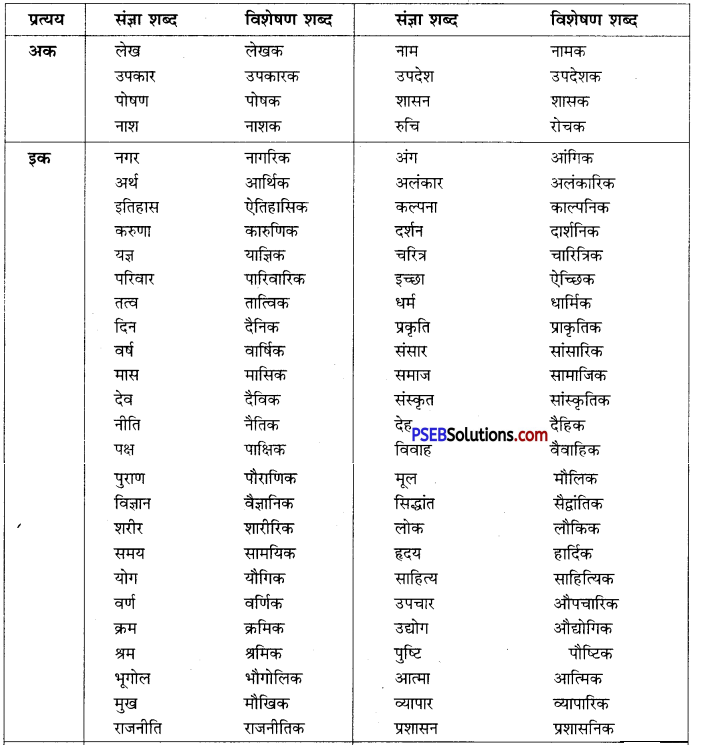
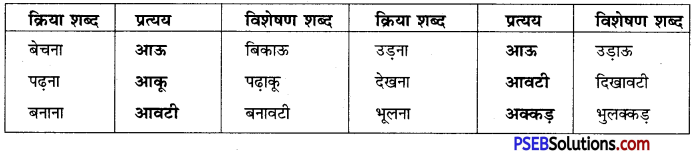
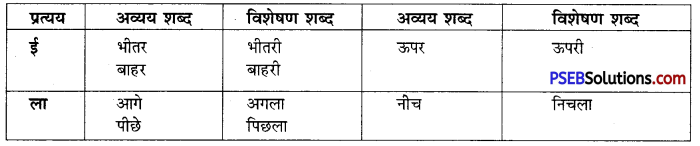
वाक्यांश बोधक शब्द किसे कहते हैं?
उत्तर:
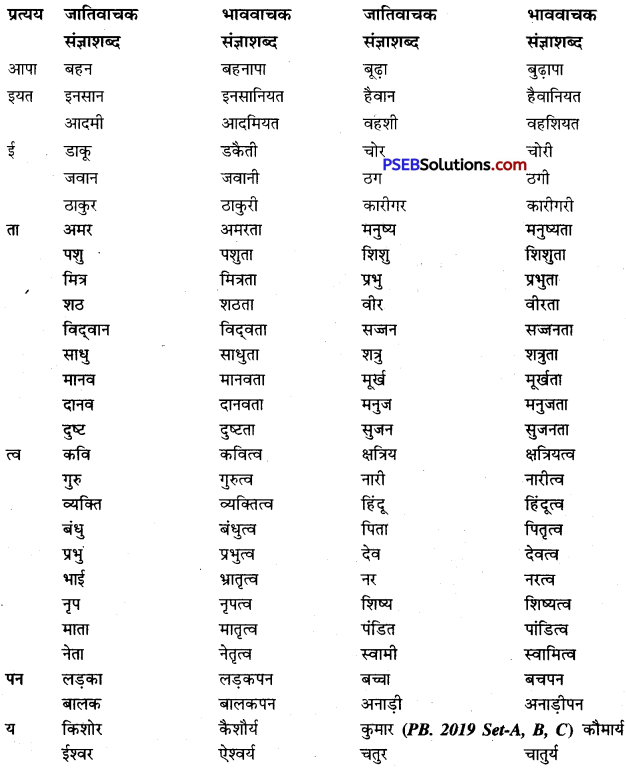
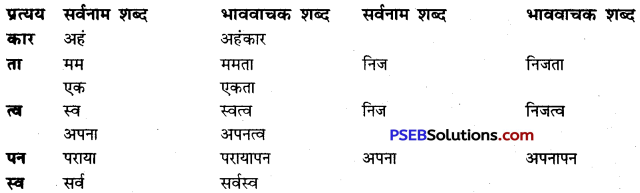
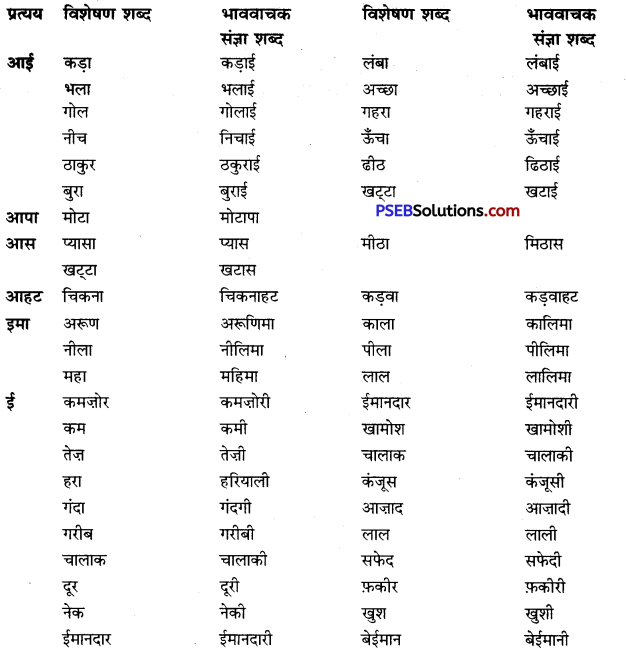
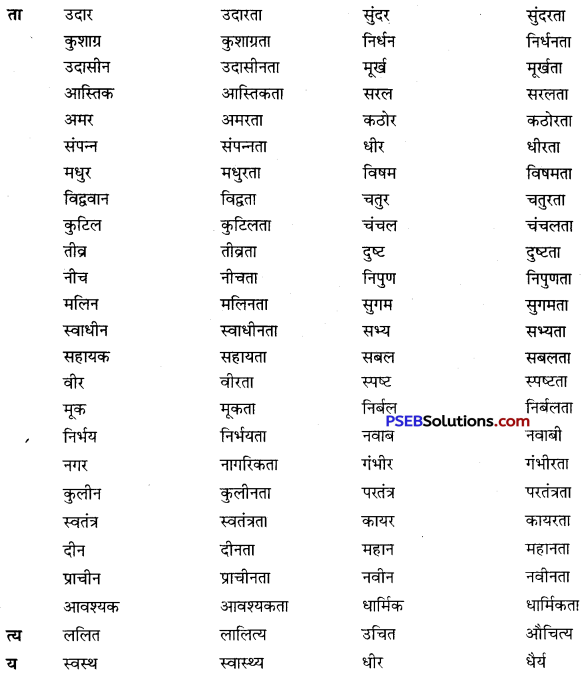
जो शब्द अनेक शब्दों के स्थान पर अकेले ही बोलने या लिखने के लिए प्रयोग में लाए जाते हैं उन्हें वाक्यांश बोधक शब्द कहते हैं, जैसे- कृतघ्न, सदाचारी, अवसरवादी, नास्तिक आदि।
प्रश्न 2.
अनेक शब्दों के लिए एक ही शब्द/वाक्यांश का प्रयोग भाषा में क्यों किया जाता है?
उत्तर:
अनेक शब्दों के लिए केवल एक ही शब्द/वाक्यांश का प्रयोग भाषा की सहजता, सुंदरता, संक्षिप्तता और प्रभावात्मकता को बढ़ाने के लिए किया जाता है। इससे कम-से-कम शब्दों में अधिक-से-अधिक भाव अभिव्यक्त किए जा सकते हैं। इसमें एक ही शब्द संपूर्ण वाक्य को अपने भीतर समेटे रहता है। उदाहरण-
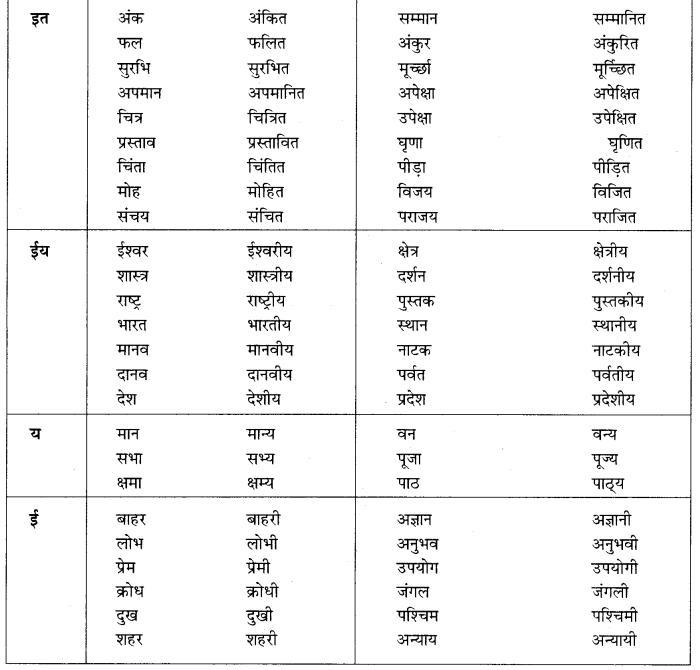
जिसका जन्म न हो सके – अजन्मा
जिसके समान कोई दूसरा न हो – अद्वितीय
जिसका कोई शत्रु न हो – अजातशत्रु
बिना वेतन के काम करने वाला – अवैतनिक
विद्या ग्रहण करने वाला – विद्यार्थी’
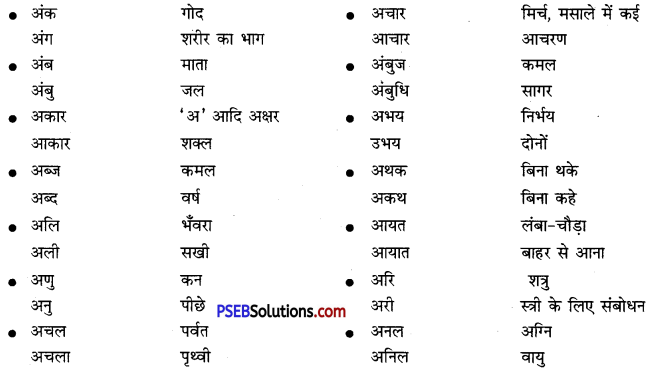
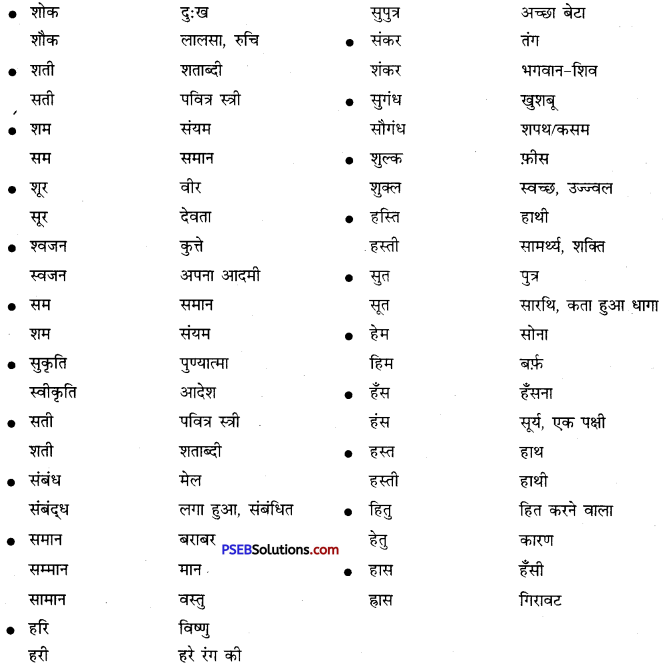
अनेक शब्द/वाक्यांश के लिए एक शब्द के उदाहरण-
अनेक शब्द/वाक्यांश – एक शब्द
जहाँ पहुँचा न जा सके – अगम्य
अचानक होने वाली बात या घटना – आकस्मिक
अवसर के अनुसार बदल जाने वाला – अवसरवादी
अपना मतलब निकालने वाले – स्वार्थी, मतलबी
दूसरे के पीछे चलने वाला – ‘अनुयायी, अनुचर, अनुगामी
न करने योग्य – अकरणीय
आँखों के सामने होने वाला – प्रत्यक्ष
बिना वेतन काम करने वाला – अवैतनिक
आँखों के सामने न होने वाला – परोक्ष
कम जानने वाला – अल्पज्ञ
आलोचना करने वाला – आलोचक
तेज बुद्धि वाला – कुशाग्र बुद्धि
आगे या भविष्य की सोचने वाला – दूरदर्शी
बरे मार्ग पर चलने वाला – कुमार्गी
ईश्वर में विश्वास रखने वाला – आस्तिक
हानि को पूरा करना – क्षतिपूर्ति
ईश्वर में विश्वास न रखने वाला – नास्तिक
बड़ी इमारत के टूटे-फूटे भाग – खंडहर
उपकार को न मानने वाला – कृतज्ञ
चारों वेदों को जानने वाला – चतुर्वेदी
उपकार को न मानने वाला – कृतघ्न
बहुत समय तक बना रहने वाला – चिरस्थायी
ऊपर कहा गया – उपर्युक्त
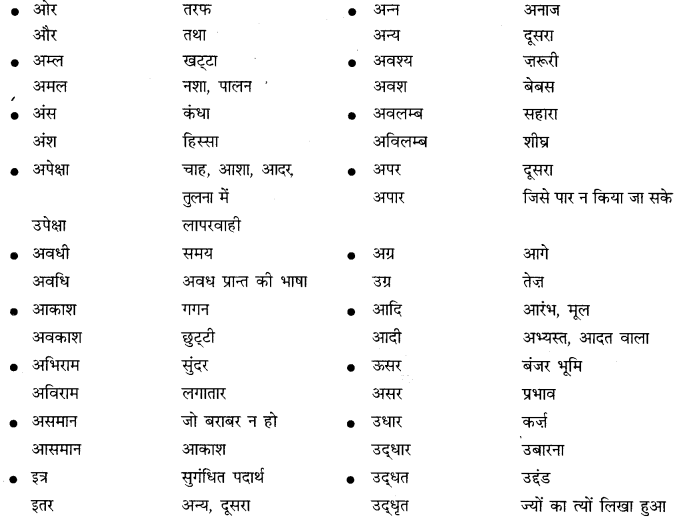
![]()
जल में रहने वाला – जलचर
कम खाने वाला – अल्पाहारी, मिताहारी
जानने की इच्छा रखने वाला – जिज्ञासु
किसी विषय का विशेष ज्ञान रखने वाला – विशेषज्ञ
छोटा भाई – अनुज
कुछ जानने की इच्छा रखने वाला – जिज्ञासु
दूसरे देश से मँगाया जाना – आयात
जिसका आदि न हो – अनादि
उपजाऊ भूमि – उर्वरा
जिसका आचरण अच्छा हो – सदाचारी
उद्योग से संबंधित – औद्योगिक
किए हुए उपकार को मानने वाला – कृतघ्न
संध्या और रात्रि के बीच का समय – गोधूलि
आकाश को छूने वाला – गगनचुंबी
रोगी का इलाज करने वाला – चिकित्सक
जनता द्वारा चलाया जाने वाला राज – जनतंत्र
तीन मास में एक बार होने वाला – त्रैमासिक
बच्चों के लिए उपयोगी – बालोपयोगी
दूसरे के काम में हाथ डालना – हस्तक्षेप
अपना नाम स्वयं लिखना – हस्ताक्षर
जिसके हाथ में वीणा हो – वीणापति
जिसके पास लाखों रुपये हों – लखपति
जिसका इलाज न हो – लाइलाज
जिसका आचरण अच्छा हो – सदाचारी
जिसका आचरण बुरा हो – दुराचारी
जिसकी आत्मा महान् हो – महात्मा
जिसका कोई अर्थ हो। – सार्थक
जिसका मूल्य न आँका जा सके – अमूल्य
जिसका कोई अर्थ न हो – निरर्थक
जिसके हाथ में चक्र हो – चक्रपाणि
जिसका आकार न हो – निराकार
जिस पर उपकार किया गया हो – उपकृत
जिसका पार न हो – अपार
जिसका कोई स्वामी या नाथ न हो – अनाथ
जिसका भाग्य अच्छा न हो – अभागा, भाग्यहीन
जिसका जन्म न हो सके – अजन्मा
जिसकी परीक्षा ली जा रही हो – परीक्षार्थी
जिसका इलाज न हो सके – असाध्य
जिसकी आयु बड़ी लम्बी हो – दीर्घायु
जिसका विश्वास न किया जा सके – अविश्वसनीय
जिसकी बहुत अधिक चर्चा हो – बहुचर्चित
जिसका मन और ध्यान दूसरी तरफ़ हो – अन्यमनस्क
जिसकी कोई फीस न ली जाए – निःशुल्क
जिसका मूल्य न आँका जा सके – अमूल्य
जिसकी गिनती न की जा सके – अगणनीय
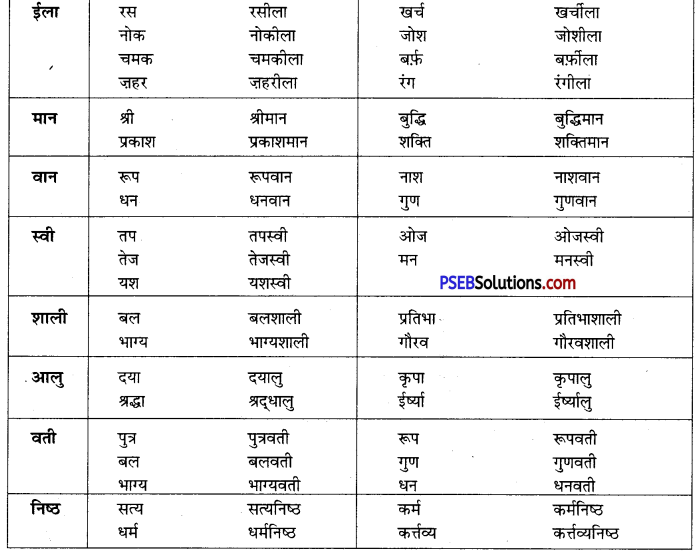
जिसका पति मर गया हो – विधवा
जिसका कोई शत्रु न हो – अजातशत्रु
जिसकी पत्नी मर गई हो – विधुर
जिसका पति जीवित हो – सधवा/सुहागिन
जिसे क्षमा न किया जा सके – अक्षम्य
जिसने ऋण चुका दिया हो – उऋण
जिसने अपनी इन्द्रियों पर विजय पा ली हो – जितेन्द्रिय
जिस पर अभियोग लगाया गया हो – अभियुक्त/प्रतिवादी
जो हाथ से लिखित हो – हस्तलिखित
जो कुछ न करता हो – अकर्मण्य
जो लोगों में प्रिय हो। – लोकप्रिय
जो सबसे आगे रहता हो – अग्रणी, अग्रगामी, अगग्रण्य
जो शरण में आया हो – शरणागत
जो अनुकरण करने योग्य हो – अनुकरणीय
जो सरलता से प्राप्त हो – सुलभ
जो धन का अपव्यय करता है – अपव्ययी
जो स्वयं सेवा करता हो – स्वयंसेवक
जो थोड़ा बोलता हो – अल्पभाषी/मितभाषी
जो वेतन के बिना काम करे – अवैतनिक
जो सदा रहे/जो कभी मरता न हो – अमर
जो देखा न जा सके – अदृश्य
जो कानून के विरुद्ध हो – अवैध
![]()
जो साथ-साथ पढ़ते हों – सहपाठी
जो सहन न किया जा सके – असह्य
जो थोड़ी देर पहले पैदा हुआ हो – नवजात
जो पहले न पढ़ा हो – अपठित
जो थोड़ा बोलता हो – मितभाषी
जो आँखों के सामने न हो – अप्रत्यक्ष
जो कम व्यय करता हो – मितव्ययी
जो परिचित न हो – अपरिचित
जो नियम के अनुसार न हो – अनियमित
जो केवल कहने और दिखाने के लिए हो – औपचारिक
जो बात कही ना सके – अकथनीय
जो कल्पना से परे हो – कल्पनातीत
जो पहले न पढ़ा हो – अपठित क
जो व्यक्ति अपनी बुराई के लिए प्रसिद्ध हो – ुख्यात
जो परिचित न हो – अपरिचित
जो निरंतर प्रत्यनशील रहे – कर्मठ
जो कभी तृप्त न हो – अतृप्त
जो पढ़ा-लिखा न हो – अनपढ़/निरक्षर
जो बात न कही गई हो – अनकही
जो उच्च कुल में पैदा हुआ हो – कुलीन
जो कार्य कष्ट से साध्य हो – कष्ट साध्य/दुःसाध्य
जो कड़वा बोलता हो – कटुभाषी
जो क्षमा करने योग्य हो। – क्षम्य
जो टुकड़े-टुकड़े हो गया हो – खंडित
जो छिपाने योग्य हो – गोपनीय
जो जन्म से अंधा हो – जन्मांध
जिसकी मीन/मछली जैसी आँखें हों – मीनाक्षी
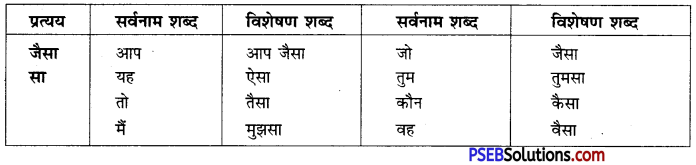
जिसने यश प्राप्त किया है – यशस्वी
दूसरे लोक से संबंधित – पारलौकिक
मांस खाने वाला – मांसाहारी/समिषभोजी
युद्ध में स्थिर रहने वाला – युधिष्ठर
शक्ति के अनुसार – यथाशक्ति
अत्यंत सुंदर स्त्री – रूपसी
पत्तों से बनी कुटिया – पर्णकुटी
दिन में होने वाला – दैनिक
सप्ताह में एक बार होने वाला – साप्ताहिक
पंद्रह दिन में एक बार होने वाला – पाक्षिक
तीन मास में एक बार होने वाला – त्रैमासिक
वर्ष में एक बार होने वाला – वार्षिक
घूमने फिरने वाला – घुम्मकड़
देश से द्रोह करने वाला – देशद्रोही
छात्रों के रहने का स्थान – छात्रावास
दो कामों में से करने योग्य एक कार्य – वैकल्पिक
चारों वेदों को जानने वाला – चतुर्वेदी
नई चीज़ की खोज करने वाला – आविष्कारक
एक ही जाति के – सजातीय
परदेश में जाकर बस जाने वाला – प्रवासी
हिंसा करने वाला – हिंसक
पश्चिम से सम्बन्ध रखने वाला – पाश्चात्य
शक्ति का उपासक – शाक्त
पूर्वजों से प्राप्त हुई सम्पत्ति – पैतृक
संकट से ग्रस्त – संकटग्रस्त/विपन्न
प्रशंसा करने योग्य – प्रशंसनीय
समान अवस्था का – समवयस्क
बिना विचार किया हुआ विश्वास – अंधविश्वास
युगों से चला आने वाला – सनातन
समाज से संबंधित – सामाजिक
अच्छे चरित्र वाला – सच्चरित्र
सदा रहने वाला – शाश्वत
![]()
अपना मतलब निकालने वाला – स्वार्थी
सौ वर्षों का समूह – शताब्दी
साफ़-साफ़ कहने वाला – स्पष्टवादी
हित चाहने वाला – हितैषी, शुभेच्छु
सौतेली माँ – विमाता
जिसमें संदेह हो – संदिग्ध