Punjab State Board PSEB 6th Class Maths Book Solutions Chapter 10 Practical Geometry Ex 10.2 Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
PSEB Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 10 Practical Geometry Ex 10.2
1. With the help of a ruler, construct line segments of given lengths:
Question (i)
5 cm
Solution:
Steps of Construction.
1. Place the ruler on a paper and hold it firmly.
2. Mark a point A with the pencil against 0 of the ruler and the point B against 5 cm mark of the ruler.

3. Join the two points A and B by moving the pencil along the ruler.

Thus, AB = 5 cm is the required line segment.

Question (ii)
6.5 cm
Solution:
Steps of Construction.
1. Place the ruler on a paper and hold it firmly.
2. Mark a point A with the pencil against 0 of the ruler and another point B against 6.5 cm mark of the ruler.
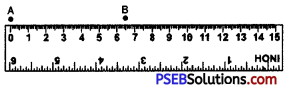
3. Join the two points A and B by moving the pencil along the ruler. Thus, AB = 6.5 cm is the required line segment.)

Question (iii)
5.2 cm
Solution:
Steps of Construction.
1. Place the ruler on a paper and hold it firmly.
2. Mark a point P with the pencil against 0 of the ruler and another point Q against 5.2 cm mark of the ruler.
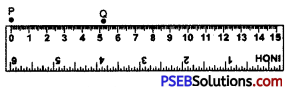
3. Join the two points P and Q by moving the pencil along the ruler. Thus, PQ = 5.2 cm is the required line segment.

Question (iv)
6.8 cm
Solution:
Steps of Construction.
1. Place the ruler on a paper and hold it firmly.
2. Mark a point C with the pencil against o of the ruler and another point D against 6.8 cm mark of the ruler.
3. Join the two points C and D by moving the pencil along the ruler.

Thus CD = 6.5 cm is the required line segment.

Question (v)
9.7 cm
Solution:
Steps of Construction.
1. Place the ruler on a paper and hold it firmly.
2. Mark a point L with the pencil against zero mark of the ruler and another point M against 9.7 cm mark of the ruler.

3. Join the two points L and M by moving the pencil along the ruler.

4. Thus, LM = 9.7 cm is the required line segment.
Question (vi)
8.4 cm.
Solution:
Steps of Construction.
1. Place the ruler on a paper and hold it firmly.
2. Mark a point X with the pencil against zero of the ruler and another point Y against 8.4 cm mark of the ruler.

3. Join the two points X and Y by moving the pencil along the ruler.

4. Thus XY = 8.4 cm is the required line segment.
2. Draw line segments given in Question by using a ruler and compasses.
Solution:
(i) Steps of Construction.
1. Draw a line l and mark a point A on it.

2. Place the compasses pointer on the zero mark of the ruler. Open it to place the pencil point upto the 5 cm mark.
3. Now without changing the opening of compasses, place the pointer on A and draw an arc to cut the line l at point B.

4. Thus AB = 5 cm is the required line segment.
(ii) Steps of Construction.
1. Draw a line l and mark a point A on it.
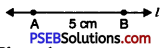
2. Place the compasses pointer on the zero mark of the ruler. Open it to place the pencil point upto the 6.5 cm mark.
3. Now without changing the opening of compasses, place the pointer on A and draw an arc to cut the line l at point B.
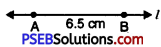
4. Thus AB = 6.5 cm is the required line segment.

(iii) Steps of Construction.
1. Draw a line l and mark a point A on it.

2. Place the compasses pointer on the zero mark of the ruler.
Open it to place the pencil point up to the 5.2 cm mark.
3. Now without changing the opening of compasses, place the pointer on A and draw an arc to cut the line l at point B.

4. Thus AB = 5.2 cm is the required line segment.
(iv) Steps of Construction.
1. Draw a line l and mark a point P on it.
2. Place the compasses pointer on the zero mark of the ruler. Open it to place the pencil point upto the 6.8 cm mark.
3. Now without changing the opening of compasses, place the pointer on P and draw an arc to cut the line l at point Q.

4. Thus PQ = 6.8 cm is the required line segment.
(v) Steps of Construction.
1. Draw a line l and mark a point L on it.

2. Place the compasses pointer on the zero mark of the ruler. Open it to place the pencil point upto the 9.7 cm mark.
3. Now without changing the opening of compasses, place the pointer on L and draw an arc to cut the line l at point M.
4. Thus LM = 9.7 cm is the required line segment.
(vi) Steps of Construction.
1. Draw a line l and mark a point X on it.

2. Place the compasses pointer on the zero mark of the ruler. Open it to place the pencil point upto the 8.4 cm mark.
3. Now without changing the opening of compasses, place the pointer on X and draw an arc to cut the line l at point Y.

4. Thus XY = 8.4 cm is the required line segment.
3. Construct AB of length 8.4 cm. From it cut off AC of length 5.3 cm. Measure BC.
Solution:
Steps of Construction.
1. Draw a line l and mark a point A on it.
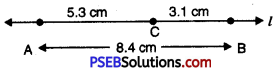
2. Place the compasses pointer on the zero mark of the ruler. Open it to place the pencil point upto the 8.4 cm mark.
3. Now without changing the opening of compasses, place the pointer on A and draw an arc to cut the line l at point B.
4. Thus AB = 8.4 cm.
5. Now open the compasses equal to AC = 5.3 cm.
6. Place the metal point of compasses on A. Then point with pencil point draw an arc, interecting the line l at C.
7. Now AC = 5.3 cm.
8. By measurement BC = 3.1 cm.

4. Draw two line segments AB and CD of lengths 8.4 cm and 4.5 cm respectively. Construct the line segments of the following lengths:
Question (i)
AB + CD
Solution:
AB + CD = 8.4 cm + 4.5 = 12.9 cm. We can construct a line segment AD of length 12.9 cm. Using a ruler and compasses.
Steps of Construction:
1. Draw line segment AB = 8.4 cm and segment CD = 4.5 cm line.
2. Draw a line l longer than combined length of AB and CD i. e. 12.9 cm. Mark a point A on it.

3. Take the compasses and measure AB. Without changing the opening of the compasses place its needle at A and draw an arc intersecting line l at B.

4. Again adjust the 8.4 cm compass and measure the line segment CD.
5. Without changing the opening of the compasses place the pointer at B on the line l and draw an arc cutting the line l at P.
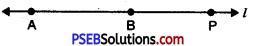
6. Then AP is the required line segment whose length is equal to the sum of lengths of line segments AB and CD.
7. On measurement AP = 12.9 cm.
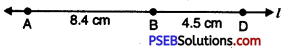
Verification:
AP= AB + BP
= AB + CD
= 8.4 cm + 4.5 cm
= 12.9 cm.

Question (ii)
AB – CD
Solution:
Steps of Construction:
1. Draw a line l and mark point A on it.
2. Take the compasses and measures AB. Without changing the opening of the compasses place its needle at A and draw an arc intersecting l at B.

3. Again adjust the compasses and measure the line segment CD.
4. Without changing the opening of the compasses place the pointer at B and draw an arc intersecting AB at Q.
5. AQ is the required line segment whose length is equal to difference of lengths of line segments AB and CD.
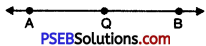
6. On measurement AQ = 3.9 cm.
Verification:
AQ = AB – OB
= AB – CD
= 8.4 cm – 4.5 cm
= 3.9 cm.
Question (iii)
2 CD.
Solution:
Steps of Construction.
1. Draw a line l and mark point P on it.

2. Open out the compasses and adjust measure CD without changing the opening of the compasses place the needle at point P and draw an arc intersecting line l at point X such that PX = CD.
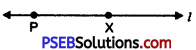
3. Now again without changing the opening of compasses place the needle at point X and draw an arc cutting the line l at Q. Such that XQ = CD.
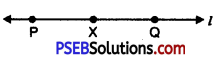
Thus, PQ is the required line segment which is equal to 2 CD.
4. Measure PQ, PQ = 9 cm.
Verification.
Now, PQ = PX + XQ
= CD + CD = 2CD
= 2 × 4.5 cm = 9 cm
Hence, PQ = 2 CD.

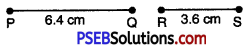
5. Draw two line segments PQ and RS of lengths 6.4 cm and 3.6 cm respectively. Construct the line segments of the following lengths:
Question (i)
PQ + RS
Solution:
Steps of Construction.
1. Draw line segment PQ = 6.4 cm and line segment RS = 3.6 cm.
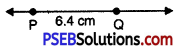
2. Draw a line l longer than combined length of PQ and RS i. e. 10 cm. Take a point P on it.

3. Take the compasses and measure PQ. Without changing the opening of the compasses place its needle at P and draw an arc cutting line l at Q.
4. Again adjust the compasses and measure the line segment RS.
5. Without changing the opening of the compasses place the pointer at Q on the line l and draw an arc cutting the line l at R.
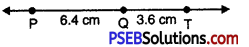
Thus PT is the required line segment whose length is equal to the sum of line segments PQ and RS.
7. Measure PT = 10 cm.
Verification:
PT = PQ + QT
= PQ + RS
= 6.4 cm + 3.6 cm
= 10 cm

Question (ii)
PQ – RS
Solution:
Steps of Construction:
1. Draw a line l and mark a point P on it.
2. Take the compasses and measure PQ. Without changing the opening of the compasses place its needle at P and draw an arc intersecting l at Q.
3. Again adjust the compasses and measure the line segment RS.
4. Without changing the opening of the compasses place the pointer at Q and draw an arc intersecting PQ at T.

5. PT is the required line segment whose length is equal to difference of lengths of line segments PQ and RS.
6. Measure PT, PT = 2.8 cm
Verification:
PT = PQ – QT
= PQ – RS
= 6.4 cm – 3.6 cm
= 2.8 cm.
Question (iii)
2 PQ
Solution:
Steps of Construction:
1. Draw a line l and mark a point A on it.

2. Take the compasses and measure PQ. Without changing the opening of the compasses place its needle at point A and draw an arc intersecting line l at point B such that AB = PQ.

3. Now again without changing the compasses, place the needle at point B and draw an arc cutting the line l at C such that BC = PQ.

4. Then AC is the required line segment whose length is equal to 2 PQ.
5. Measure AC, AC = 12.8 cm
Verification:
AC = AB + BC
= PQ + PQ
= 2PQ = 2 × 6.4 cm
= 12.8 cm.

Question (iv)
2 RS
Solution:
Steps of Construction
1. Draw a line l and mark a point A on it.
2. Take the compasses and measure RS. Without changing the compasses, place the needle at point A and draw an arc intersecting the line l at point B such that AB = RS.

3. Again without changing the opening of compasses, place the needle at point B and draw an arc cutting line l at C such that BC = RS.
4. Then AC is the required line segment whose length is equal to 2RS.
5. Measure AC, AC = 7.2 cm
Verification:
AC = AB + BC
= RS + RS
= 2 RS = 2 × 3.6 cm
= 7.2 cm.
Question (v)
3 RS.
Solution:
Steps of Construction.
1. Draw a line l and mark point A on it.
2. Take the compasses and measure RS. Without changing the compasses, place the needle at point A and draw an arc cutting the line l at point B such that AB = RS.

3. Again, without changing the opening of the compasses, place the needle at point B and draw an arc cutting line l at C such that BC = RS.

4. Once again, without changing the opening of the compasses, place the needle at point C and draw an arc cutting line l at D such that CD = RS. Then AD is the required line segment whose length is equal to 3 RS.
5. Measure AD, AD = 10.8 cm
Verification:
AD = AB + BC + CD
= RS + RS + RS
= 3RS = 3 × 3.6 cm
= 10.8 cm

6. Draw a line segment PQ of any length. Now without measuring it draw a copy of PQ.
Solution:
Steps of Construction.
1. Draw given line segment PQ

2. Draw a line l and mark a point A on it.

3. Take the compass and measure PQ. Without disturbing the compasses, place the needle of the compasses at point A on l and draw an arc, which intersect the line l at point B.

4. Then AB is the required line segment which is equal to the length of PQ. Thus AB = PQ
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()








