Punjab State Board PSEB 6th Class Maths Book Solutions Chapter 8 Basic Geometrical Concepts Ex 8.1 Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
PSEB Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 8 Basic Geometrical Concepts Ex 8.1
1. Give the examples of:
Question (i)
A point
Solution:
A point. Point A •
Examples:
(i) A small dot marked by a sharp pencil on a sheet of paper.
(ii) A tiny prick made by a fine needle or pin on a paper.
(iii) Bindi.
(iv) A star in the sky.
![]()
Question (ii)
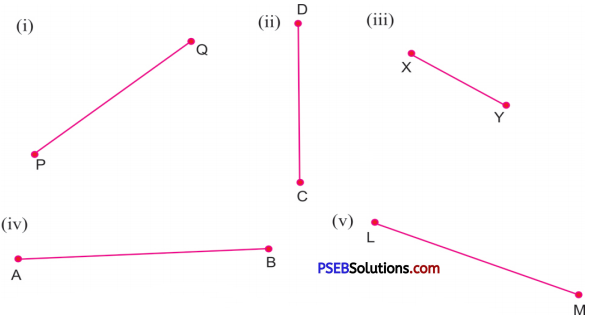
A line segment
Solution:
A line segment
Examples:
(i) An edge of a box.
(ii) A tube light.
(iii) The edge of a postcard.
(iii) Parallel lines.
Question (iii)
Parallel lines
Solution:
Examples:
(i) The opposite edges of ruler (scale).
(ii) The crossbars of window.
(iii) The opposite edges of blackboard.
(iv) Rail lines.
(iv) Interescting lines.
Question (iv)
Intersecting lines
Solution:
Examples:
(i) Two adjacent edges of your notebook.
(ii) The letter X of the English alphabet.
(iii) Crossing roads.
Question (v)
Concurrent lines.
Solution:
Concurrent lines.
(i) Three angle bisectors of a triangle.
(ii) Three medians of a triangle.
(iii) Three perpendiculars of a triangle.
(iv) The intersection of the three walls of a room.
![]()
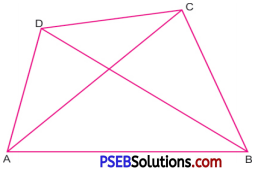
2. Name the lines segments in given lines.
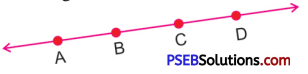
Solution:
AB, AC, AD, BC, BD, CD are line segments.
3. How many lines can pass through a point?
Solution:
Infinite lines can pass through a point.
4. How many points lie on line?
Solution:
Infinite points lie on a line.
5. How many lines pass through two points?
Solution:
One and only one line passes through two points.
6. Use the figure to name:
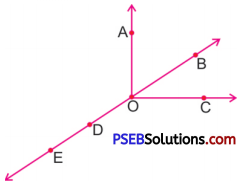
Question (i)
Five Points
Solution:
Five Points are :
O, A, B, C, D, or E
Question (ii)
A line
Solution:
BE is the line.
Question (iii)
Four rays
Solution:
Four rays are :
\(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{OA}}, \overrightarrow{\mathrm{OB}}, \overrightarrow{\mathrm{OC}}, \overrightarrow{\mathrm{OD}} \text { or } \overrightarrow{\mathrm{OE}}\)
![]()
Question (iv)
Five line segments.
Solution:
Five line segments are :
OA, OB, OC, OD, OE, DE.
7. Name the given ray in all possible ways.

Solution:
The possible rays are:
\(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{PQ}}, \overrightarrow{\mathrm{PR}}, \overrightarrow{\mathrm{QR}}\)
8. Use the figure to name :
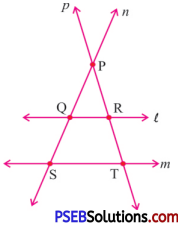
Question (i)
Pair of parallel lines.
Solution:
Pair of parallel lines are :
l and m.
![]()
Question (ii)
All pairs of intersecting lines.
Solution:
All pairs of intersecting lines are:
p and n, n and l, n and m, p and l, p and m.
Question (iii)
Lines whose point of intersection is S.
Solution:
Lines whose point of intersection is S :
m and n.
Question (iv)
Collinear points.
Solution:
Collinear points are :
P, Q, S and P, R, T.
9. Use the figure to name:
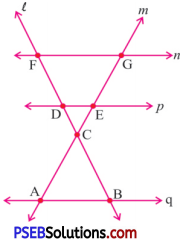
Question (i)
All pairs of parallel lines.
Solution:
All pairs of parallel lines are : n and p, q and p, n and q.
![]()
Question (ii)
All pairs of intersecting lines.
Solution:
All pairs of intersecting lines are :
m and l, m and n, m and p, m and q, l and n, l and p, l and q.
Question (iii)
Lines whose point of intersection is D.
Solution:
Lines whose point of intersection is D are :
p and l.
Question (iv)
Point of intersection of lines m and p.
Solution:
Point of intersection of lines m and p is E.
Question (v)
All sets of collinear points.
Solution:
All sets of collinear points are :
G, E, C, A and F, D, C, B.
10. Use the figure to name:
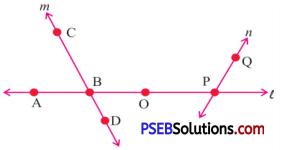
Question (i)
Line containing point P.
Solution:
Lines containing point are : l, n.
![]()
Question (ii)
Lines whose point of intersection is B.
Solution:
Lines whose point of intersection is B are : l and m.
Question (iii)
Point of intersection of lines m and l.
Solution:
Point of intersection of lines m and l is : B.
Question (iv)
All pairs of intersecting lines.
Solution:
All pairs of intersecting lines are : m and l, n and l.
11. State which of the following statements are True (T) or False (F):
Question (i)
Two lines in a plane, always intersect at a point
Solution:
False
Question (ii)
If four lines intersect at a point, those are called concurrent lines.
Solution:
True
![]()
Question (iii)
Point has a size because we can see it as a thick dot on the paper.
Solution:
False
Question (iv)
Through a given point, only one line can be drawn.
Solution:
False
Question (v)
Rectangle is a part of the plane.
Solution:
True.