Punjab State Board PSEB 6th Class Maths Book Solutions Chapter 3 Playing with Numbers Ex 3.2 Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
PSEB Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 3 Playing with Numbers Ex 3.2
1. Find the common factors of the followings:
Question (i)
16 and 24
Solution:
The factors of 16
= 1, 2, 4, 8, 16
The factors of 24
= 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 12, 24
Common factors of 16 and 24
= 1, 2, 4, 8

Question (ii)
25 and 40
Solution:
The factors of 25
= 1, 5, 25
The factors of 40
= 1, 2, 4, 5, 8, 10, 20, 40
Common factors of 25 and 40
= 1, 5
Question (iii)
24 and 36
Solution:
The factors of 24
= 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 12, 24
The factors of 36
= 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 12, 18, 36
Common factors of 24 and 36
= 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 12
Question (iv)
14, 35 and 42
Solution:
The factors of 14
= 1, 2, 7, 14
The factors of 35
= 1, 5, 7, 35
The factors of 42
= 1,2,3, 6, 7, 21, 42
Common factors of 14, 35 and 42
= 1, 7
Question (v)
15, 24 and 35.
Solution:
The factors of 15
= 1, 3, 5, 15
The factors of 24
= 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 12, 24
The factors of 35
= 1, 5, 7, 35
Common factors of 15, 24 and 35.
= 1

2. Find first three common multiples of the followings:
Question (i)
3 and 5
Solution:
The multiples of 3
= 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21, 24, 27, 30, 33, 36, 39, 42, 45
The multiples of 5
= 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35, 40,45
First three common multiples of 3 and 5
= 15, 30 and 45
Question (ii)
6 and 8
Solution:
The multiples of 6
= 6, 12, 18, 24, 30, 36, 42, 48 54, 60, 66, 72
The multiples of 8
= 8, 16, 24, 32, 40, 48, 56, 64, 72
First three common multiples of 6 and 8
= 24, 48 and 72
Question (iii)
2, 3 and 4.
Solution:
The multiples of 2
= 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20, 22, 24, 26, 28, 30, 32, 34, 36
The multiples of 3
= 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21, 24, 27, 30, 33, 36
The multiples of 4
= 4, 8, 12, 16, 20, 24, 28, 32, 36
First three common multiples of 2, 3 and 4
= 12, 24 and 36
3. Which of the following numbers are divisible by 2 or 4?
Question (i)
52314
Solution:
52314 is divisible by 2 as it is even number.
52314 is not divisible by 4 because the last two digits i.e. 14 which is not divisible by 4

Question (ii)
678913
Solution:
678913 is not divisible by 2. As it is an odd number.
678913 is not divisible by 4 because the last two digits i.e. 13 is not divisible by 4.
Question (iii)
4056784
Solution:
4056784 is divisible by 2. As it is an even number.
4056784 is also divisible by 4 because the last two digits i.e. 84 which is divisible by 4.
Question (iv)
21536
Solution:
21536 is divisible by 2. As it is an even number.
21536 is divisible by 4. As number formed by their last two digits is divisible by 4.
Question (v)
412318.
Solution:
412318 is divisible by 2. As it is an even number.
412318. is not divisible by 4. As number formed by their last two digits is not divisible by 4.
4. Which of the following numbers are divisible by 3 or 9?
Question (i)
654312
Solution:
654312 is divisible by 3.
As sum of its digits = 6 + 5 + 4 + 3 + 1 + 2 = 21, which is divisible by 3.
654312 is not divisible by 9.
As sum of its digits = 21, which is not divisible by 9.

Question (ii)
516735
Solution:
516735 is divisible by 3.
As sum of its digits = 5 + 1 + 6 + 7 + 3 + 5 = 27, which is divisible by 3.
516735 is also divisible by 9.
As sum of its digits = 27, which is divisible by 3.
Question (iii)
423152
Solution:
423152 is divisible by 3.
As sum of its digits = 4 + 2 + 3 + 1 + 5 + 2=17, which is not divisible by 3.
423152 is also not divisible by 9.
As sum of its digits = 17, which is not divisible by 9.
Question (iv)
704355
Solution:
704355 is divisible by 3.
As sum of its digits = 7 + 0 + 4 + 3 + 5 + 5 = 24, which is divisible by 3.
704355 is not divisible by 9.
As sum of its digits = 24, which is not divisible by 9.
Question (v)
215478.
Solution:
215478 is divisible by 3.
As sum of its digits = 2 + 1 + 5 + 4 + 7 + 8 = 27, which is divisible by 3.
215478 is divisible by 9.
As sum of its digits = 27, which is divisible by 9.
5. Which of the following numbers are divisible by 5 or 10?
Question (i)
456803
Solution:
456803 is not divisible by 5
As its last digit is not 0 or 5.
456803 is not divisible by 10
As its last digit is not 0.

Question (ii)
654130
Solution:
654130 is divisible by both 5 and 10
As its last digit is 0.
Question (iii)
256785
Solution:
256785 is divisible by 5
As its last digit is 5.
256785 is not divisible by 10
As its last digit is not 0.
Question (iv)
412508
Solution:
412508 is not divisible by 5
As its last digit is not 0 or 5.
412508 is not divisible by 10
As its last digit is not 0.
Question (v)
872565.
Solution:
872565 is divisible by 5
As its last digit is 5.
872565 is not divisible by 10
As its last digit is not 0.
6. Which of the following numbers are divisible by 8?
Question (i)
457432
Solution:
457432 is divisible by 8, because its last three digits are 432, which is divisible by 8.

Question (ii)
5134214
Solution:
5134214 is not divisible by 8, because its last three digits are 214, which is not divisible by 8.
Question (iii)
7232000
Solution:
7232000 is divisible by 8, because its last three digits are 000, which is divisible by 8.
Question (iv)
5124328
Solution:
5124328 is divisible by 8, because its last three digits are 328, which is divisible by 8.
Question (v)
642516.
Solution:
642516 is not divisible by 8, because its last three digits are 516, which is not divisible by 8.
7. Which of the following numbers are divisible by 6?
Question (i)
425424
Solution:
425424 is divisible by 2 because, it has 4 in its units place.
Sum of digits = 4 + 2 + 5+4 + 2 + 4 = 21
Sum of digits of 425424 is divisible by 3.
∴ 425424 is divisible by 2 as well as 3
Hence, 425424 is divisible by 6.
Question (ii)
617415
Solution:
617415 is not divisible by 2 because, it has 5 in its units place.
∴ 617415 is not divisible by 6.

Question (iii)
3415026
Solution:
3415026 is divisible by 2 because, it has 6 in its units place.
Sum of digits = 3 + 4 + 1 + 5 + 0 + 2 + 6 = 21
Sum of digits of 3415026 is divisible by 3
So, 3415026 is divisible by 3
∴ 3415026 is divisible by 2 as well as 3
Hence, 3415026 is divisible by 6.
Question (iv)
4065842
Solution:
4065842 is divisible by 2 because, it has 2 in its units place.
Sum of digits = 4 + 0 + 6 + 5 + 8 + 4 + 2 = 29
Sum of digits of 4065842 is not divisible by 3.
So, 4065842 is not divisible by 3.
∴ 4065842 is divisible by 2 but not by 3.
Hence, 4065842 is not divisible by 6.
Question (v)
725436.
Solution:
725436 is divisible by 2 because, it has 6 in its units place.
Sum of digits = 7 + 2 + 5 + 4 + 3 + 6 = 27
Sum of digits of 725436 is divisible by 3.
So, 725436 is divisible by 3.
∴ 725436 is divisible by 2 as well as 3
Hence, 725436 is divisible by 6.
8. Which of the following numbers are divisible by 11?
Question (i)
4281970
Solution:
4281970 is divisible by 11.
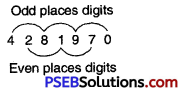
Since sum of its digits in odd places = 4 + 8 + 9 + 0 = 21 and
sum of its digits in even places = 2 + 1 + 7 = 10
Their difference = 21 – 10=11, which is odd places digits divisible by 11.

Question (ii)
8049536
Solution:
8049536 is divisible by 11.
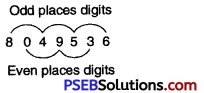
Since sum of its digits in odd places = 8 + 4 + 5 + 6 = 23
and sum of its digits in even places = 0 + 9 + 3 = 12
Difference = 23 – 12 = 11, which is divisible by 11.
Question (iii)
1234321
Solution:
1234321 is divisible by 11.

Since sum of its digits in odd places = 1 + 3 + 3 + 1 = 8
and sum of its digits in even places = 2 + 4 + 2 = 8
Difference = 8 – 8 = 0.
Question (iv)
6450828
Solution:
6450828 is not divisible by 11.

Since sum of its digits in odd places = 6 + 5 + 8 + 8 = 27
and sum of its digits in even places = 4 + 0 + 2 = 6
Difference = 27 – 6 = 21, which is not divisible by 11.
Question (v)
5648346.
Solution:
5648346 is divisible by 11.

Since sum of its digits in odd places = 5 + 4 + 3 + 6 = 18 and
sum of its digits in even places = 6 + 8 + 4 = 18.
Difference = 18 – 18 = 0.
9. State True or False:
Question (i)
If a number is divisible by 24, then it is also divisible by 3 and 8.
Solution:
True

Question (ii)
60 and 90 both are divisible by 10 then their sum is not divisible by 10.
Solution:
False
Question (iii)
If a number is divisible by 8 then it is also divisible by 16.
Solution:
False
Question (iv)
If a number is divisible by 15 then it is also divisible by 3.
Solution:
True
Question (v)
144 and 72 are divisible by 12 then their difference is also divisible by 12.
Solution:
True
10. If a number is divisible by 5 and 9 then by which other numbers will that number be always divisible?
Solution:
If a number is divisible by 5 and 9. Then the number is also divisible by their product i.e. 5 × 9 = 45.
11. Which of the following pairs are co-prime?
Question (i)
25, 35
Solution:
Two numbers are said to be co-prime if they do not have a common factor other than 1.
Given numbers are 25 and 35 Factors of 25 = 1, 5, 25
Factors of 35 = 1, 5, 7, 35
Since 25 and 35 have 1 and 5 two common factors
∴ 25 and 33 are not co-prime.
Question (ii)
16,21
Solution:
Given numbers are 16 and 21
Factors of 16 = 1, 2, 4, 8, 16
Factors of 21 = 3, 7, 21
There is only 1 common factors 16 and 21 are co-prime
∴ 16 and 21 are co-prime.

Question (iii)
24, 41
Solution:
Given numbers are 24 and 41
Factors of 24 = 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 12, 24
Factors of 41 = 1, 41
There is only one (1) common factors.
∴ 24 and 41 are co-prime.
Question (iv)
48,33
Solution:
Given numbers are 48 and 33
Factors of 48 = 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 12, 16, 24, 48
Factors of 33 = 1, 3, 11
There are two common factors 1 and 3.
∴ 48 and 33 are not co-prime.
Question (v)
20, 57.
Solution:
Given numbers are 20 and 57
Factors of 20 = 1, 2, 4, 5, 10, 20
Factors of 57 = 1, 3, 19, 57
There is only only one (1) common factors.
∴ 20 and 57 are co-prime.
![]()
![]()
![]()