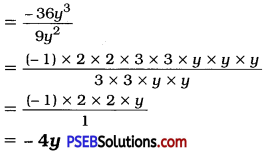
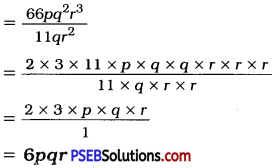
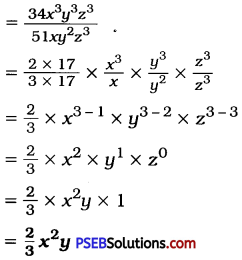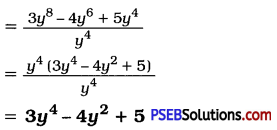Punjab State Board PSEB 8th Class Maths Book Solutions Chapter 14 Factorization Ex 14.2 Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
PSEB Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 14 Factorization Ex 14.2
1. Factorise the following expressions:
Question (i)
a2 + 8a + 16
Solution:
= (a)2 + 2 (a)(4) + (4)2
= (a + 4)2

Question (ii)
p2 – 10p + 25
Solution:
= (p)2 – 2 (p)(5) + (5)2
= (P – 5)2
Question (iii)
25m2 + 30m + 9
Solution:
= (5m)2 + 2 (5m) (3) + (3)2
= (5m + 3)2
Question (iv)
49y2 + 84yz + 36z2
Solution:
= (7y)2 + 2 (7y)(6z) + (6z)2
= (7y + 6z)2

Question (v)
4x2 – 8x + 4
Solution:
= 4(x2 – 2x + 1)
= 4 [(x)2 – 2 (x)(1) + (1)2]
= 4 (x – 1)2
Question (vi)
121b2 – 88bc + 16c2
Solution:
= (11b)2 – 2 (11b)(4c) + (4c)2
= (11b – 4c)2
Question (vii)
(l + m)2 – 4lm [Hint: Expand (1 + m)2 first]
Solution:
= l2 + 2lm + m2 – 4lm
= l2 + 2lm – 4lm + m2
= l2 – 2lm + m2
= (l)2 – 2 (l) (m) + (m)2
= (l – m)2
Question (viii)
a4 + 2a2b2 + b4
Solution:
= (a2)2 + 2 (a2)(b2) + (b2)2
= (a2 + b2)2

2. Factorise:
Question (i)
4p2 – 9q2
Solution:
= (2p)2 – (3q)2
= (2p – 3q) (2p + 3q)
Question (ii)
63a2 – 112b2
Solution:
= 7 (9a2 – 16b2)
= 7 [(3a)2 -(4b)2]
= 7 (3a – 4b) (3a + 4b)
Question (iii)
49x2 – 36
Solution:
= (7x)2 – (6)2
= (7x – 6) (7x + 6)
Question (iv)
16x5 – 144x3
Solution:
= 16x3(x2 – 9)
= 16x3 [(x)2 – (3)2]
= 16x3 (x-3) (x + 3)

Question (v)
(l + m)2 – (l – m)2
Solution:
=[(l + m) + (l – m)] [(l + m) – (l – m)]
= [l + m + l – m] [l + m – l + m]
= (2l) (2m)
= 4lm
Question (vi)
9x2y2 – 16
Solution:
= (3xy)2 – (4)2
= (3xy – 4) (3xy + 4)
Question (vii)
(x2 – 2xy + y2) – z2
Solution:
= (x – y)2 – (z)2
= [(x – y) – z] [(x – y) + z]
= (x – y – z) (x – y + z)
Question (viii)
25a2 – 4b2 + 28bc – 49c2
Solution:
= (25a2) – (4b2 – 28bc + 49c2)
= (5a)2 – (2b – 7c)2
= [(5a) – (2b – 7c)] [(5a) + (2b – 7c)]
= (5a – 2b + 7c) (5a + 2b – 7c)

3. Factorise the expressions:
Question (i)
ax2 + bx
Solution:
= x (ax + b)
Question (ii)
7p2 + 21q2
Solution:
= 7 (p2 + 3q2)
Question (iii)
2x3 + 2xy2 + 2xz2
Solution:
= 2x(x2 + y2 + z2)
Question (iv)
am2 + bm2 + bn2 + an2
Solution:
= am2 + bm2 + an2 + bn2
= m2 (a + b) + n2(a + b)
= (a + b) (m2 + n2)

Question (v)
(lm + l) + m + 1
Solution:
= l (m + 1) + 1 (m + 1)
= (m + 1) (l + 1)
Question (vi)
y(y + z) + 9(y + z)
Solution:
= (y + z)(y + 9)
Question (vii)
5y2 – 20y – 8z + 2yz
Solution:
= 5y2 – 20y + 2yz – 8z
= 5y (y – 4) + 2z (y – 4)
= (y- 4) (5y + 2z)
Question (viii)
10ab + 4a + 5b + 2
Solution:
= 2a (5b + 2) + 1 (5b + 2)
= (5b + 2) (2a + 1)

Question (ix)
6xy – 4y + 6 – 9x
Solution:
= 6xy – 4y – 9x + 6
= 2y (3x-2)-3(3x-2)
= (3x-2) (2y – 3)
4. Factorise:
Question (i)
a4 – b4
Solution:
= (a2)2 – (b2)2
= (a2 – b2) (a2 + b2)
= ((a)2 – (b2)] (a2 + b2)
= (a – b) (a + b) (a2 + b2)
Question (ii)
p4 – 81
Solution:
= (p2)2 – (9)2
= (p2 – 9) (p2 + 9)
= ((p)2 – (3)2] (p2 + 9)
= (p – 3)(p + 3)(p2 + 9)

Question (iii)
x4 – (y + z)4
Solution:
= (x2)2 – (a2)2 (∵ y + z = a)
= (x2 – a2) (x2 + a2)
= (x – a) (x + a) (x2 + a2)
= [x – (y + z)] [x + (y + z)] [x2 + (y + z)2] (∵ a = y + z)
= (x – y – z) (x + y + z) [x2 + (y + z)2]
Question (iv)
x4 – (x – z)4
Solution:
= (x2)2 – [(x – z)2]2
= [x2 – (x – z)2] [x2 + (x – z)2]
= [x2 – (x2 – 2xz + z2)] [x2 + (x2 – 2xz + z2)]
= (x2 – x2 + 2xz – z2) (x2 + x2 – 2xz + z2)
= (2xz – z2) (2x2 – 2xz + z2)
= z (2x – z) (2x2 – 2xz + z2)
Question (v)
a4 – 2a2b2 + b4
Solution:
= (a2)2 – 2(a2)(b2) + (b2)2
= (a2 – b2)2
= (a2 – b2) (a2 – b2)
= (a – b) (a + b) (a – b) (a + b)

5. Factorise the following expressions:
Question (i)
p2 + 6p + 8
Solution:
= p2 + 6p + 9 – 1
= (p2 + 6p + 9) – (1)
= (p + 3)2 – (1)2
= (p + 3 + 1) (p + 3 – 1)
= (P + 4) (p + 2)
Here, last term is 8.
∴ 9 – 1 = 8.
OR
p2 + 6p + 8
Here, ab = 8 and a + b = 6
On solving equations, a = 4, b = 2
Now, p2 + 6p + 8
= p2 + 4p + 2p + 8
= p (p + 4) + 2 (p + 4)
= (p + 4) (p + 2)
Question (ii)
q2 – 10q + 21
Solution:
= q2 – 10q + 25 – 4
= (q2 – 10q + 25) – (4)
= (q – 5)2 – (2)2
= (q – 5 + 2) (q – 5 – 2)
= (q – 3) (q – 7)
Here, last term is 21.
∴ 25 – 4 = 21.
OR
q2 – 10q + 21
Here, ab = 21 and a + b = (- 10)
Possible values of a = 7 or (-7)
b = 3 or (- 3)
Let us check, 7 + 3 = 10 ≠ (- 10)
∴ a = – 7, b = – 3
Now, q2 – 10q + 21
= q2 – 7q – 3q + 21
= q (q – 7) – 3 (q – 7)
= (q – 7) (q – 3)

Question (iii)
p2 + 6p – 16
Solution:
= p2 + 6p + 9 – 25
= (P2 + 6p + 9) – (25)
= (p + 3)2 – (5)2
= (p + 3 – 5) (p + 3 + 5)
= (p – 2) (p + 8)
Here, last term is (-16).
∴ (-25) + 9 = (-16)
OR
p2 + 6p – 16
Here, ab = – 16 and a + b = 6
Possible values of a = 8 or (-8) b = 2 or (-2)
Let us check, 8 + 2 = 10 ≠ 6
(- 8) + 2 = (-6) ≠ 6
8 + (-2) = 8 – 2 = 6
Now, p2 + 6p – 16
= p2 + 8p – 2p – 16
= P (P + 8) – 2 (p + 8)
= (p + 8) (p – 2)
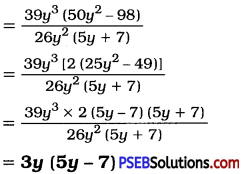
![]()
![]()