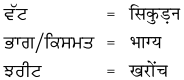Punjab State Board PSEB 8th Class Punjabi Book Solutions Chapter 2 ਪੇਮੀ ਦੇ ਨਿਆਣੇ Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
PSEB Solutions for Class 8 Punjabi Chapter 2 ਪੇਮੀ ਦੇ ਨਿਆਣੇ (1st Language)
Punjabi Guide for Class 8 PSEB ਪੇਮੀ ਦੇ ਨਿਆਣੇ Textbook Questions and Answers
ਪੇਮੀ ਦੇ ਨਿਆਣੇ ਪਾਠ – ਅਭਿਆਸ
1. ਦੱਸੋ :
(ਉ) ਲੇਖਕ ਅਤੇ ਉਸ ਦੀ ਭੈਣ ਨੂੰ ਬਚਪਨ ਵਿੱਚ ਹਰ ਰੋਜ਼ ਕਿੱਥੇ ਜਾਣਾ ਪੈਂਦਾ ਸੀ ਅਤੇ ਕਿਉਂ ?
ਉੱਤਰ :
ਲੇਖਕ ਅਤੇ ਉਸ ਦੀ ਭੈਣ ਨੂੰ ਹਰ ਰੋਜ਼ ਇਕ ਵਾਰੀ ਡਰਾਉਣੀ ਜਰਨੈਲੀ ਸੜਕ ਪਾਰ ਕਰ ਕੇ ਖੇਤ ਵਿਚ ਜਾਣਾ ਪੈਂਦਾ ਸੀ, ਕਿਉਂਕਿ ਉੱਥੇ ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਨੇ ਕੰਮ ਕਰਦੇ ਬਾਪੁ ਅਤੇ ਕਾਮੇ ਨੂੰ ਰੋਟੀ ਫੜਾਉਣੀ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਸੀ !
(ਅ) ਬੱਚਿਆਂ ਨੂੰ ਕਿਹੜੀ ਗੱਲ ਭੈ – ਸਾਗਰ ਲੱਗਦੀ ਸੀ ਅਤੇ ਕਿਉਂ ?
ਉੱਤਰ :
ਬੱਚਿਆਂ ਨੂੰ ਜਰਨੈਲੀ ਸੜਕ ਨੂੰ ਪਾਰ ਕਰਨਾ ਭੈ – ਸਾਗਰ ਲਗਦਾ ਸੀ, ਕਿਉਂਕਿ ਉਸ ਉੱਤੋਂ ਜਾਂਗਲੀਆਂ, ਪਠਾਣਾਂ, ਰਾਸ਼ਿਆਂ ਤੇ ਹੋਰਨਾਂ ਪਰਦੇਸੀਆਂ ਦਾ ਕਾਫ਼ੀ ਲਾਂਘਾ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਸੀ ਅਤੇ ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਰਾਸ਼ਿਆਂ ਤੋਂ ਘਰ ਬੈਠਿਆਂ ਹੀ ਡਰ ਆਉਂਦਾ ਰਹਿੰਦਾ ਸੀ।
![]()
(ੲ) ਲੇਖਕ ਕਿਹੜੀਆਂ ਗੱਲਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਨਰਕ ਤੇ ਕਿਹੜੀਆਂ ਨੂੰ ਸੁਰਗ ਆਖਦਾ ਹੈ ?
ਉੱਤਰ :
ਲੇਖਕ ਖੇਡ ਨੂੰ ਸੁਰਗ ਆਖਦਾ ਹੈ, ਜਿਸ ਤੋਂ ਬਿਨਾਂ ਹੋਰ ਕਿਸੇ ਚੀਜ਼ ਵਿਚ ਉਸ ਨੂੰ ਸੁਰਗ ਨਹੀਂ ਸੀ ਦਿਸਦਾ, ਪਰੰਤੂ ਨਰਕ ਦੇ ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਖੁੱਲ੍ਹੇ ਗੱਫੇ ਮਿਲਦੇ ਸਨ। ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਆਪਣੇ ਅੰਦਾਣੇ ਰਾਹ ਦੇ ਹਰ ਮੋੜ ਉੱਤੇ ਨਰਕ ਘਾਤ ਲਾਈ ਖੜਾ ਦਿਸਦਾ। ਸਭ ਤੋਂ ਵੱਡਾ ਨਰਕ ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਲਈ ਮਦਰੱਸਾ (ਸਕੂਲੀ ਸੀ। ਜੇ ਉਹ ਇਸ ਤੋਂ ਕਦੀ ਛੁੱਟ ਜਾਂਦੇ, ਤਾਂ ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਖੇਤ ਰੋਟੀ ਦੇਣ ਜਾਣ ਲਈ ਨਰਕ ਵਿਚੋਂ ਲੰਘਣਾ ਪੈਂਦਾ। ਉੱਬ ਲੇਖਕ ਸਪੱਸ਼ਟ ਕਰਦਾ ਹੈ। ਕਿ ਖੇਤ ਤਾਂ ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਲਈ ਸੁਰਗ ਸੀ, ਪਰੰਤੂ ਉੱਥੇ ਰੋਟੀ ਲੈ ਕੇ ਜਾਣ ਦੀ ਖੇਚਲ ਨਰਕ।
(ਸ) ਲੇਖਕ ਅਤੇ ਉਸ ਦੀ ਭੈਣ ਨੇ ਸੜਕ ਪਾਰ ਕਰਨ ਦੇ ਡਰ ਨੂੰ ਦਬਾਉਣ ਲਈ ਕਿਹੜਾ ਤਰੀਕਾ ਸੋਚਿਆ ?
ਉੱਤਰ :
ਲੇਖਕ ਤੇ ਉਸ ਦੀ ਭੈਣ ਨੇ ਸੜਕ ਪਾਰ ਕਰਨ ਦੇ ਡਰ ਨੂੰ ਦਬਾਉਣ ਲਈ ਪਹਿਲਾਂ ਤਾਂ ਇਕ ਆਮ ਜਿਹਾ ਤਰੀਕਾ ਵਰਤਣਾ ਚਾਹਿਆ ਭੈਣ – ਭਰਾ ਨੂੰ ਇਕ ਰਾਜੇ ਤੇ ਰਾਣੀ ਦੀ ਕਹਾਣੀ ਸੁਣਾਉਣ ਲੱਗ ਪਈ ! ਪਰ ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਦੇ ਅਚੇਤ ਮਨ ਵਿਚ ਸੜਕ ਦਾ ਡਰ ਕਾਇਮ ਰਿਹਾ ਤੇ ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਪਿੱਛੋਂ ਆਉਂਦੇ ਇਕ ਆਦਮੀ ਨੂੰ ਦੇਖ ਕੇ ਸੁਖ ਦਾ ਸਾਹ ਲਿਆ, ਪਰ ਜਦੋਂ ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਉਸ ਨੂੰ ਹੋਰ ਪਾਸੇ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਦੇਖਿਆ ਤੇ ਸੜਕ ਘੁਮਾਓਂ ਕੁ ਦੂਰ ਰਹਿ ਗਈ, ਤਾਂ ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਦੀ ਕਹਾਣੀ ਵੀ ਠਠੰਬਰ ਕੇ ਖਲੋ ਗਈ ਤੇ ਉਹ ਵੀ ਸਹਿਮ ਗਏ।
ਫਿਰ ਜਦੋਂ ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਸੜਕ ਉੱਤੇ ਇਕ ਕਾਲੇ ਸੂਫ਼ ਦੀ ਵਾਸਕਟ ਤੇ ਪਠਾਣਾਂ ਵਰਗੀ ਖੁੱਲੀ ਸਲਵਾਰ ਵਾਲਾ ਆਦਮੀ ਲੰਮਾ ਪਿਆ ਦੇਖਿਆ, ਤਾਂ ਕਹਾਣੀਕਾਰ ਨੇ ਆਪਣੀ ਭੈਣ ਨੂੰ “ਵਾਹਿਗੁਰੂ ਵਾਹਿਗੁਰੂ ਕਰਨ ਦੀ ਸਲਾਹ ਦਿੱਤੀ ਕਿਉਂਕਿ ਉਸਨੇ ਸੁਣਿਆ ਹੋਇਆ ਸੀ ਕਿ ਵਾਹਿਗੁਰੂ ਦਾ ਨਾਂ ਲੈਣ ਨਾਲ ਡਰ ਹਟ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ। ਪਰ ਜਦੋਂ ਉਸਦੀ ਭੈਣ ਨੇ ਕਿਹਾ ਕਿ ਵਾਹਿਗੁਰੂ ਤੋਂ ਭੂਤ – ਪ੍ਰੇਤ ਡਰਦੇ ਹਨ, ਆਦਮੀ ਨਹੀਂ, ਤਾਂ ਦੋਹਾਂ ਦਾ ਡਰ ਫਿਰ ਉਸੇ ਤਰ੍ਹਾਂ ਹੀ ਕਾਇਮ ਰਿਹਾ।
(ਹ) ਭੈਣ – ਭਰਾ ਸੜਕ ਪਾਰ ਕਰਨ ਵਿੱਚ ਸਫਲ ਕਿਵੇਂ ਹੋਏ?
ਉੱਤਰ :
ਅੰਤ ਜਦੋਂ ਭੈਣ – ਭਰਾ ਨੂੰ ਸੜਕ ਪਾਰ ਕਰਨ ਵਿਚ ਸਾਥ ਦੇਣ ਵਾਲਾ ਕੋਈ ਬੰਦਾ ਨਾ ਮਿਲਿਆ ਤੇ ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਦੇ ਡਰ ਨੂੰ ਦਬਾਉਣ ਦੇ ਤਰੀਕੇ ਵੀ ਫੇਲ੍ਹ ਹੋ ਗਏ, ਤਾਂ ਰੋਂਦੇ ਭਰਾ ਦੇ ਅੱਥਰੂ ਪੂੰਝਦਿਆਂ ਉਸ ਦੀ ਭੈਣ ਨੇ ਉਸ ਨੂੰ ਕਿਹਾ ਕਿ ਉਹ ਕਹਿਣਗੇ ਕਿ ਉਹ ਪੇਮੀ ਦੇ ਨਿਆਣੇ ਹਨ, ਉਹ (ਰਾਸ਼ਾ) ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਨਾ ਫੜੇ। ਇਹ ਸੁਣ ਕੇ ਭਰਾ ਦੇ ਮਨ ਨੂੰ ਢਾਰਸ ਬੱਝ ਗਈ ਤੇ ਉਹ ਪੇਮੀ ਦਾ ਨਾਂ ਲੈ ਕੇ ਸੜਕ ਪਾਰ ਹੋ ਗਏ।
2. ਔਖੇ ਸ਼ਬਦਾਂ ਦੇ ਅਰਥ :
- ਬੀਰ : ਵੀਰ, ਭਰਾ
- ਪਠੋਰੇ : ਮੇਮਣੇ, ਲੇਲੇ, ਛੇਲੇ
- ਵਾਰ : ਵਾਂਗ
- ਭੈ – ਸਾਗਰ : ਭਵ – ਸਾਗਰ, ਸੰਸਾਰ
- ਮਦਰਸਾ : ਸਕੂਲ, ਪਾਠਸ਼ਾਲਾ
- ਕਰਾਰ : ਇਕਰਾਰ, ਕੌਲ, ਪ੍ਰਣ, ਵਚਨ
- ਠਠੰਬਰ ਕੇ : ਡੌਰ – ਭੌਰ ਹੋ ਕੇ, ਡਰ ਕੇ
- ਘਮਾਉਂ ਕੁ : ਘੁਮਾਂ ਕੁ, ਅੱਠ ਕਨਾਲ ਥਾਂ
- ਸੂਫ : ਕਾਲੇ ਰੰਗ ਦਾ ਕੱਪੜਾ ਵਾਸਕਟ
- ਵਾਸਕਟ : ਫ਼ਤੂਹੀ, ਕੋਟੀ (ਬਿਨਾਂ ਬਾਹਾਂ ਤੋਂ)
- ਭਲੱਪਣ : ਭਲਿਆਈ, ਭਲਮਾਣਸੀ
- ਬੇਕਰਾਰ : ਬੇਚੈਨ, ਵਿਆਕਲ
- ਢਾਰਸ : ਦਿਲਾਸਾ, ਧੀਰਜ, ਤਸੱਲੀ
![]()
3. ਵਾਕਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਵਰਤੋ :
ਮੁਸ਼ਕਲ – ਘਾਟੀ, ਸ਼ਰਨ, ਮੰਤਵ, ਰੁਝੇਵੇਂ, ਗੁਸਤਾਖ਼ੀ, ਦਿਲਾਸਾ, ਠਠੰਬਰ ਕੇ, ਘਾਤ ਲਾਈ ਖਲੋਤਾ
ਵਿਆਕਰਨ : ਤੁਸੀਂ ਪਿਛਲੀ ਸ਼੍ਰੇਣੀ ਵਿੱਚ ਪੜ੍ਹ ਚੁੱਕੇ ਹੋ ਕਿ ਕਿਸੇ ਵਿਅਕਤੀ, ਵਸਤੂ, ਸਥਾਨ, ਗੁਣ, ਭਾਵ ਆਦਿ ਦਾ ਬੋਧ ਕਰਾਉਣ ਵਾਲੇ ਸ਼ਬਦਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਨਾਂਵ ਕਿਹਾ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ, ਜਿਵੇਂ ਏਕਮ, ਸੋਨਾ, ਐੱਸ ਏ ਐਸ, ਨਗਰ , ਫ਼ੌਜ, ਖ਼ੁਸ਼ੀ ਆਦਿ
ਉੱਤਰ :
- ਮੁਸ਼ਕਲ ਘਾਟੀ (ਔਖਾ ਕੰਮ) – ‘ਪੇਮੀ ਦੇ ਨਿਆਣੇ ਕਹਾਣੀ ਵਿਚਲੇ ਭੈਣ – ਭਰਾ ਨੂੰ ਡਰਾਉਣੀ ਜਰਨੈਲੀ ਸੜਕ ਨੂੰ ਪਾਰ ਕਰਨਾ ਇਕ ਮੁਸ਼ਕਲ ਘਾਟੀ ਪ੍ਰਤੀਤ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਸੀ !
- ਸ਼ਰਨ (ਸਹਾਰਾ, ਆਸਰਾ) – ਪਿੰਗਲਵਾੜੇ ਵਿਚ ਲੂਲ੍ਹਿਆਂ – ਲੰਝੜਿਆਂ ਤੇ ਕੋਹੜੀਆਂ ਨੂੰ ਸ਼ਰਨ ਮਿਲਦੀ ਹੈ।
- ਮੰਤਵ (ਉਦੇਸ਼) – ਇਸ ਕਹਾਣੀ ਦਾ ਮੰਤਵ ਦਾਜ ਦੀ ਰਸਮ ਵਿਰੁੱਧ ਅਵਾਜ਼ ਬੁਲੰਦ ਕਰਨਾ ਹੈ।
- ਰੁਝੇਵੇਂ ਕੰਮੀ – ਜ਼ਨਾਨੀਆਂ ਭਾਵੇਂ ਘਰ ਵਿਚ ਹੀ ਰਹਿਣ ਪਰੰਤੂ ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਦੇ ਰੁਝੇਵੇਂ ਨਹੀਂ ਮੁੱਕਦੇ।
- ਗੁਸਤਾਖੀ (ਢੀਠਤਾਈ, ਸ਼ਰਾਰਤ) – ਜਿਸ ਵੀ ਵਿਦਿਆਰਥੀ ਨੇ ਸਕੂਲ ਵਿਚ ਨਿਯਮਾਂ ਦਾ ਉਲੰਘਣ ਕਰਨ ਦੀ ਗੁਸਤਾਖੀ ਕੀਤੀ, ਉਸ ਨੂੰ ਸਜ਼ਾ ਮਿਲੇਗੀ।
- ਦਿਲਾਸਾ (ਢਾਰਸ, ਧੀਰਜ) – ਮੈਂ ਪ੍ਰੀਖਿਆ ਵਿਚ ਫੇਲ੍ਹ ਹੋਣ ਕਾਰਨ ਹੋ ਰਹੇ ਵਿਦਿਆਰਥੀ ਨੂੰ ਦਿਲਾਸਾ ਦੇ ਕੇ ਅੱਗੋਂ ਮਿਹਨਤ ਕਰਨ ਦੀ ਪ੍ਰੇਰਨਾ ਦਿੱਤੀ।
- ਘਾਤ ਲਾਈ ਖਲੋਤਾ (ਹਮਲਾ ਕਰਨ ਲਈ ਓਹਲੇ ਵਿਚ ਬੈਠਣਾ) – ਬਿੱਲੀ ਚੂਹੇ ਨੂੰ ਫੜਨ ਲਈ ਘਾਤ ਲਾਈ ਬੈਠੀ ਸੀ।
- ਸਹਿਮ ਡਰ) – ਜੰਗਲ ਵਿਚ ਅਸੀਂ ਬਘਿਆੜ ਨੂੰ ਦੇਖ ਕੇ ਸਹਿਮ ਗਏ।
- ਠਠੰਬਰ ਕੇ ਡਰ ਕੇ) – ਬਘਿਆੜ ਨੂੰ ਦੇਖ ਕੇ ਅਸੀਂ ਠਠੰਬਰ ਕੇ ਖੜੇ ਹੋ ਗਏ।
- ਢਾਰਸ ਹੌਸਲਾ – ਮੈਂ ਪ੍ਰੀਖਿਆ ਵਿਚ ਫੇਲ੍ਹ ਹੋ ਕੇ ਰੋ ਰਹੇ ਵਿਦਿਆਰਥੀ ਨੂੰ ਢਾਰਸ ਦਿੱਤੀ ਤੇ ਅੱਗੋਂ ਮਿਹਨਤ ਕਰਨ ਲਈ ਪ੍ਰੇਰਿਆ।
- ਭ੍ਰਮਤ (ਇਸਤਰੀ) – ਗਲੀਆਂ ਦੀਆਂ ਤ੍ਰੀਮਤਾਂ ਬੱਚਿਆਂ ਪਿੱਛੇ ਇਕ – ਦੂਜੀ ਨਾਲ ਲੜ ਪਈਆਂ।
ਨਾਂਵ ਪੰਜ ਪ੍ਰਕਾਰ ਦੇ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ :
(ੳ) ਆਮ ਨਾਂਵ ਜਾਂ ਜਾਤੀ ਵਾਚਕ ਨਾਂਵ
(ਅ) ਖ਼ਾਸ ਨਾਂਵ ਜਾਂ ਨਿੱਜ ਵਾਚਕ ਨਾਂਵ
(ੲ) ਵਸਤੂ – ਵਾਚਕ ਨਾਂਵ ਜਾਂ ਪਦਾਰਥ ਵਾਚਕ ਨਾਂਵ
(ਸ) ਇਕੱਠ – ਵਾਚਕ ਨਾਂਵ ਜਾਂ ਸਮੂਹ ਵਾਚਕ ਨਾਂਵ
(ਹ) ਭਾਵਵਾਚਕ ਨਾਂਵ
ਉੱਤਰ :
(ੳ) ਆਮ ਨਾਂਵ ਜਾਂ ਜਾਤੀਵਾਚਕ ਨਾਂਵ : ਜਿਹੜੇ ਸ਼ਬਦ ਕਿਸੇ ਚੀਜ਼, ਜੀਵ ਜਾਂ ਸਥਾਨ ਆਦਿ ਦੀ ਪੂਰੀ ਜਾਤੀ ਜਾਂ ਸ਼੍ਰੇਣੀ ਦਾ ਬੋਧ ਕਰਾਉਣ, ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਆਮ ਨਾਂਵ ਜਾਂ ਜਾਤੀਵਾਚਕ ਨਾਂਵ ਆਖਿਆ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ; ਜਿਵੇਂ – ਸੜਕ, ਪਠਾਣ, ਰਾਸ਼ਾ, ਆਦਮੀ, ਵਾਸਕਟ, ਮਦਰੱਸਾ ਆਦਿ।
(ਅ) ਖ਼ਾਸ ਨਾਂਵ ਜਾਂ ਨਿੱਜਵਾਚਕ ਨਾਂਵ : ਜਿਹੜੇ ਸ਼ਬਦ ਕਿਸੇ ਖ਼ਾਸ ਵਿਅਕਤੀ, ਖ਼ਾਸ ਚੀਜ਼ ਜਾਂ ਖ਼ਾਸ ਸਥਾਨ ਦੇ ਨਾਂ ਦਾ ਬੋਧ ਕਰਾਉਣ, ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਖ਼ਾਸ ਨਾਂਵ ਜਾਂ ਨਿੱਜਵਾਚਕ ਨਾਂਵ ਆਖਿਆ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ; ਜਿਵੇਂ – ਗੁਰਨਾਮ ਸਿੰਘ, ਸੀ ਗੁਰੂ ਨਾਨਕ ਦੇਵ ਜੀ, ਸ੍ਰੀ ਅੰਮ੍ਰਿਤਸਰ ਸਾਹਿਬ, ਸ੍ਰੀ ਅਨੰਦਪੁਰ ਸਾਹਿਬ, ਹਿਮਾਲਾ, ਮਾਊਂਟ ਐਵਰੈਸਟ, ਸਤਲੁਜ, ਬਿਆਸ, ਰਾਵੀ ਆਦਿ।
![]()
(ਈ) ਵਸਤਵਾਚਕ ਨਾਂਵ : ਜਿਹੜੇ ਸ਼ਬਦਾਂ ਤੋਂ ਤੋਲਣ, ਮਿਣਨ ਜਾਂ ਮਾਪੀਆਂ ਜਾਣ ਵਾਲੀਆਂ ਵਸਤੂਆਂ ਦੇ ਨਾਂ ਦਾ ਬੋਧ ਹੋਵੇ, ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਵਸਤਵਾਚਕ ਨਾਂਵ ਆਖਿਆ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ; ਜਿਵੇਂ: ਪਾਣੀ, ਦੁੱਧ, ਤੇਲ, ਸੋਨਾ, ਚਾਂਦੀ, ਲੋਹਾ, ਕੱਪੜਾ, ਪੱਗ, ਚੁੰਨੀ, ਮਿੱਟੀ ਆਦਿ।
(ਸ) ਇਕੱਠਵਾਚਕ ਨਾਂਵ : ਜਿਹੜੇ ਸ਼ਬਦ ਮਨੁੱਖਾਂ, ਜੀਵਾਂ ਜਾਂ ਵਸਤਾਂ ਦੇ ਗਿਣਨਯੋਗ ਇਕੱਠ ਜਾਂ ਸਮੂਹ ਦਾ ਗਿਆਨ ਕਰਵਾਉਣ, ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਇਕੱਠਵਾਚਕ ਨਾਂਵ ਆਖਦੇ ਹਨ; ਜਿਵੇਂ – ਜੰਬ, ਜਮਾਤ, ਮੇਲਾ, ਕਮੇਟੀ, ਟੋਲੀ, ਢਾਣੀ, ਹੇੜ੍ਹ, ਸੰਗਤ, ਡਾਰ, ਫ਼ੌਜ, ਇੱਜੜ ਆਦਿ।
(ਹ) ਭਾਵਵਾਚਕ ਨਾਂਵ : ਜਿਹੜੇ ਸ਼ਬਦਾਂ ਤੋਂ ਕਿਸੇ ਭਾਵ, ਗੁਣ ਜਾਂ ਹਾਲਤ ਆਦਿ ਦਾ ਗਿਆਨ ਹੋਵੇ, ‘ਭਾਵਵਾਚਕ ਨਾਂਵ’ ਆਖਿਆ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ; ਜਿਵੇਂ – ਹਾਸਾ, ਰੋਣਾ, ਸ਼ਰਧਾ, ਰੌਣਕ, ਝੂਠ, ਸੱਚ, ਖ਼ੁਸ਼ੀ, ਗ਼ਮੀ, ਮਕਬੂਲੀਅਤ, ਪਿਆਰ ਆਦਿ।
ਆਮ ਨਾਂਵ ਜਾਂ ਜਾਤੀਵਾਚਕ ਨਾਂਵ :
ਜਿਹੜੇ ਸ਼ਬਦ ਕਿਸੇ ਵਸਤੂ, ਜੀਵ ਜਾਂ ਸਥਾਨ ਆਦਿ ਦੀ ਪੂਰੀ ਜਾਤੀ ਜਾਂ ਸ਼੍ਰੇਣੀ ਦਾ ਬੋਧ ਕਰਾਉਣ, ਉਹਨਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਆਮ ਨਾਂਵ ਜਾਂ ਜਾਤੀਵਾਚਕ ਨਾਂਵ ਕਿਹਾ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ, ਜਿਵੇਂ : ਸੜਕ, ਪਠਾਣ, ਰਾਸ਼ਾ, ਆਦਮੀ, ਵਾਸਕਟ, ਮਦਰਸਾ ਆਦਿ।
ਖਾਸ ਨਾਂਵ ਜਾਂ ਨਿੱਜਵਾਚਕ ਨਾਂਵ :
ਜਿਹੜੇ ਸ਼ਬਦ ਤੋਂ ਕਿਸੇ ਖ਼ਾਸ ਵਿਅਕਤੀ, ਖ਼ਾਸ ਜੀਵ, ਖ਼ਾਸ ਵਸਤੂ ਜਾਂ ਖ਼ਾਸ ਸਥਾਨ ਦੇ ਨਾਂ ਦਾ ਬੋਧ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ, ਉਸ ਨੂੰ ਖ਼ਾਸ ਨਾਂਵ ਜਾਂ ਨਿੱਜਵਾਚਕ ਨਾਂਵ ਕਿਹਾ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ, ਜਿਵੇਂ : ਪੇਮੀ, ਹਿਮਾਲਾ, ਸ੍ਰੀ ਗੁਰੁ ਗੋਬਿੰਦ ਸਿੰਘ ਜੀ, ਸ੍ਰੀ ਅਨੰਦਪੁਰ ਸਾਹਿਬ, ਸਤਲੁਜ, ਬਿਆਸ, ਰਾਵੀ ਆਦਿ।
ਬੱਚਿਓ! ਆਪਣੇ ਨਾਲ ਵਾਪਰੀ ਕਿਸੇ ਅਜਿਹੀ ਦਿਲਚਸਪ ਘਟਨਾ ਨੂੰ ਆਪਣੇ ਸ਼ਬਦਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਲਿਖੋ।
PSEB 8th Class Punjabi Guide ਪੇਮੀ ਦੇ ਨਿਆਣੇ Important Questions and Answers
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 1.
“ਪੇਮੀ ਦੇ ਨਿਆਣੇ ਕਹਾਣੀ ਦਾ ਸਾਰ ਲਿਖੋ।
ਉੱਤਰ :
ਕਹਾਣੀਕਾਰ ਸੱਤ ਸਾਲਾਂ ਦਾ ਸੀ ਤੇ ਉਸ ਦੀ ਵੱਡੀ ਭੈਣ ਗਿਆਰਾਂ ਸਾਲਾਂ ਦੀ। ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਦਾ ਖੇਤ ਘਰੋਂ ਮੀਲ ਕੁ ਦੀ ਵਿੱਥ ‘ਤੇ ਸੀ। ਰਸਤੇ ਦੇ ਅੱਧ ਵਿਚੋਂ ਇਕ ਜਰਨੈਲੀ ਸੜਕ ਲੰਘਦੀ ਸੀ, ਜਿਸ ਉੱਤੋਂ ਜਾਂਗਲੀਆਂ, ਪਠਾਣਾਂ, ਰਾਸ਼ਿਆਂ ਤੇ ਹੋਰਨਾਂ ਪਰਦੇਸੀਆਂ ਦਾ ਬਹੁਤ ਲਾਂਘਾ ਸੀ। ਕਹਾਣੀਕਾਰ ਤੇ ਉਸ ਦੀ ਭੈਣ ਦੋਵੇਂ ਰਾਸ਼ਿਆਂ ਤੋਂ ਬਹੁਤ ਡਰਦੇ ਸਨ ਅਸਲ ਵਿਚ ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਦੀ ਪਾਲਣਾ – ਪੋਸਣਾ ਹੀ ਅਜਿਹੀ ਹੋਈ ਸੀ ਕਿ ਅਜਿਹੇ ਡਰ ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਦੇ ਸੁਭਾ ਦਾ ਅੰਗ ਬਣ ਚੁੱਕੇ ਸਨ।
ਸਿਆਣਿਆਂ ਤੋਂ ਨਰਕ – ਸਵਰਗ ਦੀਆਂ ਗੱਲਾਂ ਸੁਣ ਕੇ ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਸਿਵਾਏ ਖੇਡ ਤੋਂ ਬਾਕੀ ਹਰ ਸਮੇਂ ਨਰਕ ਘਾਤ ਲਈ ਖਲੋਤਾ ਦਿਸਦਾ ਸੀ ! ਰਾਸ਼ਿਆਂ ਤੋਂ ਡਰਦੇ ਕਹਾਣੀਕਾਰ ਤੇ ਉਸ ਦੀ ਭੈਣ ਕਿਸੇ ਸਾਥ ਨੂੰ ਲਏ ਬਗੈਰ ਸੜਕ ਤੋਂ ਲੰਘਣੋਂ ਡਰਦੇ ਸਨ, ਪਰ ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਹਰ ਰੋਜ਼ ਖੇਤ ਵਿਚ ਬਾਪੁ ਤੇ ਉਸ ਦੇ ਕਾਮੇ ਦੀ ਰੋਟੀ ਲੈ ਕੇ ਜਾਣਾ ਪੈਂਦਾ ਸੀ।
ਇਕ ਵਾਰ ਦੋਵੇਂ ਭੈਣ – ਭਰਾ ਦੁਪਹਿਰ ਦੀ ਰੋਟੀ ਲੈ ਕੇ ਖੇਤ ਨੂੰ ਚੱਲ ਪਏ ਸੜਕ ਤੋਂ ਲੰਘਣ ਦਾ ਡਰ ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਦੇ ਮਨ ਨੂੰ ਖਾ ਰਿਹਾ ਸੀ। ਕਹਾਣੀਕਾਰ ਦੀ ਭੈਣ ਨੇ ਡਰ ਨੂੰ ਦਬਾਉਣ ਲਈ ਰਾਜੇ – ਰਾਣੀ ਦੀ ਕਹਾਣੀ ਸ਼ੁਰੂ ਕਰ ਦਿੱਤੀ। ਕਹਾਣੀ ਸੁਣਦਿਆਂ – ਸੁਣਾਦਿਆਂ ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਪਿੰਡ ਵਲੋਂ ਆਉਂਦਾ ਇਕ ਆਦਮੀ ਦਿਸਿਆ। ਉਹ ਖੜੇ ਹੋ ਕੇ ਉਸ ਦੀ ਉਡੀਕ ਕਰਨ ਲੱਗੇ ਤੇ ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਦੀ ਕਹਾਣੀ ਵੀ ਨਾਲ ਹੀ ਖੜ੍ਹੀ ਹੋ ਗਈ, ਪਰ ਉਹ ਆਦਮੀ ਕਿਸੇ ਹੋਰ ਪਾਸੇ ਨੂੰ ਚਲਾ ਗਿਆ।
ਹੁਣ ਸੜਕ ਕੇਵਲ ਘੁਮਾ ਕੁ ਦੂਰ ਹੀ ਰਹਿ ਗਈ ਤੇ ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਦੀ ਕਹਾਣੀ ਵੀ ਠਠੰਬਰ ਕੇ ਖੜ੍ਹੀ ਹੋ ਗਈ। ਕੋਈ ਸਾਥੀ ਨਾ ਮਿਲਣ ਕਰਕੇ ਦੋਵੇਂ ਬੱਚੇ ਸਹਿਮੇ ਹੋਏ ਸਨ। ਦਸ – ਵੀਹ ਕਦਮ ਪੁੱਟ ਕੇ ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਕਾਲੇ ਸੂਫ਼ ਦੀ ਵਾਸਕਟ ਤੇ ਪਠਾਣਾਂ ਵਾਲੀ ਸਲਵਾਰ ਪਾਈ ਲੰਮਾ ਪਿਆ ਇਕ ਬੰਦਾ ਦੇਖਿਆ 1 ਦੋਵੇਂ ਇਸ ਖ਼ਿਆਲ ਨਾਲ ਡਰ ਗਏ ਕਿ ਉਹ ਰਾਸ਼ਾ ਹੈ ਤੇ ਉਹ ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਫੜ ਲਵੇਗਾ।
ਕਹਾਣੀਕਾਰ ਦੀ ਭੈਣ ਨੇ ਉਸ ਨੂੰ “ਵਾਹਿਗੁਰੂ ਦਾ ਨਾਂ ਲੈਣ ਲਈ ਕਿਹਾ, ਪਰ ਕਹਾਣੀਕਾਰ ਦਾ ਖ਼ਿਆਲ ਸੀ ਕਿ “ਵਾਹਿਗੁਰੂ` ਤੋਂ ਭੂਤ – ਪ੍ਰੇਤ ਡਰਦੇ ਹਨ, ਆਦਮੀ ਨਹੀਂ। ਦੋਵੇਂ ਪੰਜ – ਸੱਤ ਮਿੰਟ ਖਲੋਤੇ ਰਹੇ। ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਪਿੰਡ ਵਲੋਂ ਕੋਈ ਆਦਮੀ ਆਉਂਦਾ ਨਾ ਦਿਸਿਆ। ਕਹਾਣੀਕਾਰ ਦਾ ਰੋਣ ਨਿਕਲ ਗਿਆ। ਉਸ ਦੀ ਭੈਣ ਨੇ ਉਸ ਦੇ ਅੱਥਰੂ ਪੂੰਝ ਕੇ ਹੋਂਸਲਾ ਦਿੱਤਾ। ਫਿਰ ਉਸ ਨੇ ਕੁੱਝ ਵਿਚਾਰ ਤੋਂ ਮਗਰੋਂ ਕਹਾਣੀਕਾਰ ਨੂੰ ਕਿਹਾ ਕਿ ਅਸੀਂ ਕਹਾਂਗੇ, “ਅਸੀਂ ਤਾਂ ਪੇਮੀ ਦੇ ਨਿਆਣੇ ਹਾਂ, ਸਾਨੂੰ ਨਾ ਫੜ।’ ਕਹਾਣੀਕਾਰ ਨੂੰ ਭੈਣ ਦੇ ਮੂੰਹੋਂ ‘ਪੇਮੀ’ ਸ਼ਬਦ ਬਹੁਤ ਮਿੱਠਾ ਲੱਗਦਾ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਸੀ। ਇਹ ਗੱਲ ਉਸ ਦੇ ਵੀ ਮਨ ਲੱਗੀ। ਬੱਸ ਫਿਰ ਦੋਵੇਂ ਡਰਦੇ ਤੇ ਕੰਬਦੇ ਹੋਏ ‘ਪੇਮੀ ਦਾ ਨਾਂ ਲੈ ਕੇ ਸੜਕ ਪਾਰ ਹੋ ਗਏ ਤੇ ਰਾਸ਼ਾ ਉੱਥੇ ਹੀ ਪਿਆ ਰਿਹਾ।
![]()
1. ਵਾਰਤਕ – ਟੁਕੜੀ/ਪੈਰੇ ਦਾ ਬੋਧ
ਅਸਾਨੂੰ ਧਾਰਮਿਕ ਸਿੱਖਿਆ ਵੀ ਕੁੱਝ ਇਸ ਕਿਸਮ ਦੀ ਮਿਲ ਰਹੀ ਸੀ ਕਿ ਅਜਿਹੇ ਡਰ ਸਾਡੇ ਸੁਭਾਵਾਂ ਦਾ ਹਿੱਸਾ ਬਣ ਗਏ ਸਨ ਹਰ ਰੋਜ਼ ਸ਼ਾਮ ਨੂੰ ਅਸੀਂ ਘਰ ਸਿਆਣਿਆਂ ਕੋਲੋਂ ਨਰਕ – ਸੁਰਗ ਦੀਆਂ ਕਹਾਣੀਆਂ ਸੁਣਦੇ। ਸੁਰਗ ਤਾਂ ਸਾਨੂੰ ਖੇਡ ਤੋਂ ਬਾਹਰ ਕਿਤੇ ਘੱਟ ਹੀ ਪ੍ਰਾਪਤ ਹੁੰਦਾ, ਪਰ ਨਰਕ ਦੇ ਹਰ ਥਾਂ ਖੁੱਲ੍ਹੇ ਗੱਫੇ ਮਿਲਦੇ। ਸਭ ਤੋਂ ਵੱਡਾ ਨਰਕ ਮਦਰੱਸਾ ਸੀ ਤੇ ਜੇ ਉਸ ਤੋਂ ਕਿਸੇ ਦਿਨ ਛੁੱਟ ਜਾਂਦੇ, ਤਾਂ ਖੇਤ ਰੋਟੀ ਦੇਣ ਜਾਣ ਦਾ ਨਰਕ ਪੇਸ਼ ਆ ਜਾਂਦਾ। ਗੱਲ ਕੀ ਸਾਡੇ ਅੰਞਾਣੇ ਰਾਹ ਦੇ ਹਰ ਇੱਕ ਮੋੜ ’ਤੇ ਨਰਕ ਜਾਣੋਂ ਘਾਤ ਲਾਈ ਖਲੋਤਾ ਹੁੰਦਾ। ਖ਼ਬਰੇ ਇਸ ਸੜਕ ਦਾ ਭੈ – ਸਾਗਰ ਲੰਘਣ ਕਰਕੇ ਅਸਾਨੂੰ ਖੇਤ ਜਾਣਾ ਨਰਕ ਲਗਦਾ ਸੀ ਜਾਂ ਖੇਤ ਰੋਟੀ ਲੈ ਜਾਣ ਲੱਗੇ। ਇਸ ਸੜਕ ਨੂੰ ਲੰਘਣਾ ਪੈਣ ਕਰਕੇ, ਇਹ ਅਸਾਨੂੰ ਭੈ – ਸਾਗਰ ਦਿਖਾਈ ਦਿੰਦਾ ਸੀ, ਮੈਂ ਇਸ ਦੀ ਬਾਬਤ ਯਕੀਨ ਨਾਲ ਕੁੱਝ ਨਹੀਂ ਕਹਿ ਸਕਦਾ। ਇਹ ਮੈਨੂੰ ਪਤਾ ਹੈ ਕਿ ਖੇਤ ਸੁਰਗ ਸੀ ਤੇ ਰੋਟੀ ਲੈ ਕੇ ਜਾਣ ਦੀ ਖੇਚਲ ਨਰਕ ਅਤੇ ਉਹ ਜਰਨੈਲੀ ਸੜਕ, ਵਿਚਕਾਰਲਾ ਭੈ – ਸਾਗਰ।
ਉੱਪਰ ਦਿੱਤੇ ਪੈਰੇ ਨੂੰ ਪੜ੍ਹ ਕੇ ਹੇਠ ਲਿਖੇ ਬਹੁਵਿਕਲਪੀ ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨਾਂ ਦੇ ਸਹੀ ਉੱਤਰ ਚੁਣੋ –
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 1.
ਇਹ ਪੈਰਾ ਕਿਸ ਪਾਠ ਵਿਚੋਂ ਲਿਆ ਗਿਆ ਹੈ ?
(ਉ) ਪੇਮੀ ਦੇ ਨਿਆਣੇ
(ਅ) ਲੋਹੜੀ
(ਈ) ਧਰਤ
(ਸ) ਸਾਂਝੀ ਮਾਂ।
ਉੱਤਰ :
(ਉ) ਪੇਮੀ ਦੇ ਨਿਆਣੇ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 2.
ਜਿਸ ਪਾਠ ਵਿਚੋਂ ਇਹ ਪੈਰਾ ਲਿਆ ਹੈ, ਉਹ ਕਿਸਦੀ ਰਚਨਾ ਹੈ ?
(ਉ) ਸ਼ਿਵ ਕੁਮਾਰ ਬਟਾਲਵੀ
(ਅ) ਸੁਖਦੇਵ ਮਾਦਪੁਰੀ
(ਈ) ਅੰਮ੍ਰਿਤਾ ਪ੍ਰੀਤਮ
(ਸ) ਪਿੰ: ਸੰਤ ਸਿੰਘ ਸੇਖੋਂ।
ਉੱਤਰ :
(ਸ) ਪਿੰ: ਸੰਤ ਸਿੰਘ ਸੇਖੋਂ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 3.
ਕਿਹੜੀ ਸਿੱਖਿਆ ਕਰ ਕੇ ਸਾਡੇ ਡਰ (ਬੱਚਿਆਂ) ਸੁਭਾਵਾਂ ਦਾ ਅੰਗ ਬਣ ਗਏ ਸਨ ?
(ਉ) ਧਾਰਮਿਕ ਸਿੱਖਿਆ।
(ਅ) ਸਮਾਜਿਕ ਸਿੱਖਿਆ।
(ਈ) ਰਾਜਸੀ ਸਿੱਖਿਆ
(ਸ) ਪਰਿਵਾਰਕ ਸਿੱਖਿਆ।
ਉੱਤਰ :
(ਉ) ਧਾਰਮਿਕ ਸਿੱਖਿਆ।
![]()
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 4.
ਹਰ ਰੋਜ਼ ਸ਼ਾਮ ਨੂੰ ਸਿਆਣੇ ਕਿਹੋ ਜਿਹੀਆਂ ਕਹਾਣੀਆਂ ਸੁਣਾਉਂਦੇ ਸਨ ?
(ਉ) ਪਰੀਆਂ ਦੀਆਂ
(ਅ) ਪਸ਼ੂਆਂ ਦੀਆਂ
(ਈ) ਨਰਕ – ਸੁਰਗ ਦੀਆਂ
(ਸ) ਪੰਛੀਆਂ ਦੀਆਂ।
ਉੱਤਰ :
(ਈ) ਨਰਕ – ਸੁਰਗ ਦੀਆਂ
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 5.
ਬੱਚਿਆਂ ਨੂੰ ਖੇਤ ਵਿਚੋਂ ਕੀ ਪਾਪਤ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਸੀ ?
(ਉ) ਨਰਕ
(ਅ ਇਨਾਮ
(ਇ) ਸੁਰਗ
(ਸ) ਖੁੱਲ੍ਹ – ਡੁੱਲ੍ਹ।
ਉੱਤਰ :
(ਇ) ਸੁਰਗ
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 6.
ਸਭ ਤੋਂ ਵੱਡਾ ਨਰਕ ਕਿਹੜੀ ਥਾਂ ਸੀ ?
(ਉ) ਘਰ
(ਅ) ਮਦਰੱਸਾ
(ਈ) ਖੇਡ ਦਾ ਮੈਦਾਨ
(ਸ) ਗਲੀ – ਗੁਆਂਢ।
ਉੱਤਰ :
(ਅ) ਮਦਰੱਸਾ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 7.
ਸਾਡੇ ਅੰਞਾਣੇ ਰਾਹ ਉੱਤੇ ਕਿਹੜੀ ਚੀਜ਼ ਘਾਤ ਲਾਈ ਖਲੋਤੀ ਹੁੰਦੀ ?
(ੳ) ਭੂਤ
(ਅ) ਚੁੜੇਲ
(ਇ) ਨਰਕ
(ਸ) ਸੁਰਗ।
ਉੱਤਰ :
(ੲ) ਨਰਕ।
![]()
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 8.
ਸਾਨੂੰ ਬੱਚਿਆਂ ਨੂੰ ਭੈ – ਸਾਗਰ ਕਿਹੜੀ ਚੀਜ਼ ਪ੍ਰਤੀਤ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਸੀ ?
(ਉ) ਸੜਕ ਨੂੰ ਲੰਘਣਾ
(ਅ) ਮਦਰੱਸੇ ਜਾਣਾ
(ੲ) ਘਰ ਨੂੰ ਮੁੜਨਾ
(ਸ) ਖੇਤੋਂ ਮੁੜਨਾ।
ਉੱਤਰ :
(ੳ) ਸੜਕ ਨੂੰ ਲੰਘਣਾ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 9.
ਮੇਰੇ ਲਈ ਖੇਤ ਕੀ ਸੀ ?
(ਉ) ਨਰਕ
(ਅ) ਸੁਰਗ
(ੲ) ਭੈ – ਸਾਗਰ
(ਸ) ਖੇਡ ਦਾ ਮੈਦਾਨ
ਉੱਤਰ :
(ਅ) ਸੁਰਗ
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 10.
ਸਾਨੂੰ ਸੁਰਗ ਦੀ ਥਾਂ ਹਰ ਥਾਂ ਕੀ ਮਿਲਦਾ ਸੀ ?
(ਉ) ਪਿਆਰ
(ਅ) ਭੈ – ਸਾਗਰ
(ਈ) ਨਰਕ ਦੇ ਖੁੱਲ੍ਹੇ ਗੱਫੇ
(ਸ) ਖੁਸ਼ੀ।
ਉੱਤਰ :
(ਈ) ਨਰਕ ਦੇ ਖੁੱਲ੍ਹੇ ਗੱਫੇ।
![]()
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 11.
ਉਪਰੋਕਤ ਪੈਰੇ ਵਿਚੋਂ ਭਾਵਵਾਚਕ ਨਾਂਵ ਦੀ ਠੀਕ ਉਦਾਹਰਨ ਚੁਣੋ
(ਉ) ਸ਼ਾਮ
(ਅ ਮਦਰੱਸਾ
(ਈ) ਖੇਤ
(ਸ) ਸਿੱਖਿਆ/ਡਰ/ਨਰਕ/ਸੁਰਗ/ਭੈ – ਸਾਗਰ/ਸੁਭਾ/ਖੇਚਲ !
ਉੱਤਰ :
(ਸ) ਸਿੱਖਿਆ/ਡਰ/ਨਰਕ ਸੁਰਗ/ਭੈ – ਸਾਗਰ/ਸੁਭਾ/ਖੇਚਲ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 2.
ਉਪਰੋਕਤ ਪੈਰੇ ਵਿਚੋਂ ਆਮ ਨਾਂਵ ਦੀ ਠੀਕ ਉਦਾਹਰਨ ਚੁਣੋ
(ੳ) ਘਰ/ਖੇਡ/ਗੱਫੇ/ਮਦਰੱਸਾ/ਸੜਕ/ਰਾਹ/ਖੇਤ
(ਅ) ਨਰਕ
(ਈ) ਸਿੱਖਿਆ।
(ਸ) ਖੇਚਲ
ਉੱਤਰ :
(ੳ) ਘਰ/ਖੇਡ/ਗੱਫੇ/ਮਦਰੱਸਾ/ਸੜਕ/ਖੇਤਰਾਹ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 13.
ਉਪਰੋਕਤ ਪੈਰੇ ਵਿਚੋਂ ਠੀਕ ਪੜਨਾਂਵ ਚੁਣੋ
(ੳ) ਇਕ
(ਅ) ਮੋੜ
(ਈ) ਖੇਤ
(ਸ) ਅਸਾਨੂੰ ਸਾਡੇ/ਅਸੀਂ/ਉਸ/ਮੈਂ/ਉਹ/ਇਹ/ਮੈਨੂੰ ਕੁੱਝ ॥
ਉੱਤਰ :
(ਸ) ਅਸਾਨੂੰ ਸਾਡੇਅਸੀਂ/ਉਸ/ਮੈਂ/ਉਹ/ਇਹ/ਮੈਨੂੰ ਕੁੱਝ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 14.
ਉਪਰੋਕਤ ਪੈਰੇ ਵਿਚੋਂ ਵਿਸ਼ੇਸ਼ਣ ਦੀ ਠੀਕ ਉਦਾਹਰਨ ਚੁਣੋ
(ਉ) ਅਸਾਨੂੰ
(ਅ) ਸਿੱਖਿਆ
(ਈ) ਦਿਨ
(ਸ) ਧਾਰਮਿਕ/ਕੁੱਝ ਇਸ/ਅਜਿਹੇ/ਹਰ/ਖੁੱਲ੍ਹੇ ਸਭ ਤੋਂ ਵੱਡਾ/ਕਿਸੇ/ਅੰਞਾਣੇਹਰ ਇਕ/ਇਸ/ਜਰਨੈਲੀ/ਵਿਚਕਾਰਲਾ।
ਉੱਤਰ :
(ਸ) ਧਾਰਮਿਕ/ਕੁੱਝ ਇਸ/ਅਜਿਹੇ/ਹਰ/ਖੁੱਲੇ ਸਭ ਤੋਂ ਵੱਡਾ/ਕਿਸੇ ਅੰਞਾਣੇ ਹਰ ਇਕ/ਇਸ/ਜਰਨੈਲੀਵਿਚਕਾਰਲਾ।
![]()
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 15.
ਉਪਰੋਕਤ ਪੈਰੇ ਵਿਚੋਂ ਕਿਰਿਆ ਦੀ ਠੀਕ ਉਦਾਹਰਨ ਚੁਣੋ
(ਉ) ਨਰਕ
(ਅ) ਖੇਤ
(ਈ) ਘਾਤ
(ਸ) ਮਿਲ ਰਹੀ ਸੀ/ਬਣ ਗਏ ਸਨ/ਸੁਣਦੇ/ਹੁੰਦਾ/ਮਿਲਦੇ/ਸੀ/ਛੁੱਟ ਜਾਂਦੇਆ/ਜਾਂਦਾ/ਖਲੋਤਾ ਹੁੰਦਾ/ਲਗਦਾ ਸੀ/ਜਾਣ ਲੱਗੇ/ਦਿਖਾਈ ਦਿੰਦਾ ਸੀ/ਕਹਿ। ਸਕਦਾ/ਪਤਾ ਹੈ।
ਉੱਤਰ :
(ਸ) ਮਿਲ ਰਹੀ ਸੀ/ਬਣ ਗਏ ਸਨ/ਸੁਣਦੇ/ਹੁੰਦਾ/ਮਿਲਦੇ/ਸੀ/ਛੁੱਟ ਜਾਂਦੇ/ਆ ਜਾਂਦਾਖਲੋਤਾ ਹੁੰਦਾ/ਲਗਦਾ ਸੀਜਾਣ ਲੱਗੇ/ਦਿਖਾਈ ਦਿੰਦਾ ਸੀ ਕਹਿ ਸਕਦਾ/ਪਤਾ ਹੈ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 16.
‘ਸਿਆਣਿਆਂ ਦਾ ਲਿੰਗ ਬਦਲੋ
(ਉ) ਨਿਆਣਿਆਂ
(ਅ) ਨਿਆਣੀਆਂ
(ਈ) ਸਿਆਣੀਆਂ
(ਸ) ਸਿਆਨੀਆਂ।
ਉੱਤਰ :
(ੲ) ਸਿਆਣੀਆਂ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 17.
ਹੇਠ ਲਿਖਿਆਂ ਵਿਚੋਂ ਕਿਹੜਾ ਸ਼ਬਦ ਕਿਰਿਆ ਹੈ ?
(ਉ) ਕਿਸਮ
(ਅ) ਸੁਣਦੇ
(ਇ) ਨਰਕ
(ਸ) ਡਰ।
ਉੱਤਰ :
(ਅ) ਸੁਣਦੇ।
![]()
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 18.
ਉਪਰੋਕਤ ਪੈਰੇ ਵਿਚੋਂ ਕੋਈ ਦੋ ਪੜਨਾਂਵ ਲਿਖੋ।
ਉੱਤਰ :
ਅਸਾਨੂੰ, ਕੁੱਝ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 19.
ਉਪਰੋਕਤ ਪੈਰੇ ਵਿਚੋਂ ਹੇਠ ਲਿਖੇ ਵਿਸਰਾਮ ਚਿੰਨ੍ਹ ਚੁਣੋ
(ਉ) ਡੰਡੀ ( )
(ਅ) ਕਾਮਾ ( )
(ਈ) ਜੋੜਨੀ ( )
(ਸ) ਛੁੱਟ ਮਰੋੜੀ ( )
ਉੱਤਰ :
(ਉ) ਡੰਡੀ ( । )
(ਅ) ਕਾਮਾ ( , )
(ਈ) ਜੋੜਨੀ ( – )
(ਸ) ਛੁੱਟ ਮਰੋੜੀ ( ‘ )
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 20.
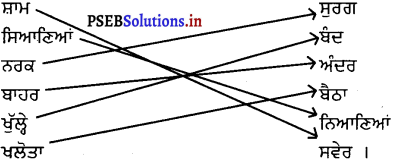
ਉਪਰੋਕਤ ਪੈਰੇ ਵਿਚੋਂ ਵਿਰੋਧੀ ਸ਼ਬਦਾਂ ਦਾ ਮਿਲਾਣ ਕਰੋ
ਸ਼ਾਮ – ਸੁਰਗ
ਸਿਆਣਿਆਂ – ਬੰਦ
ਨਰਕ – ਅੰਦਰ
ਬਾਹਰ – ਬੈਠਾ
ਖੁੱਲ੍ਹੇ – ਨਿਆਣਿਆਂ
ਖਲੋਤਾ – ਸਵੇਰ।
ਉੱਤਰ :
2. ਵਿਆਕਰਨ ਤੇ ਰਚਨਾਤਮਕ ਕਾਰਜ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 1.
ਨਾਂਵ ਕੀ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ ਅਤੇ ਇਸਦੀਆਂ ਕਿਸਮਾਂ ਬਾਰੇ ਜਾਣਕਾਰੀ ਦਿਓ।
ਉੱਤਰ :
ਕਿਸੇ ਵਿਅਕਤੀ, ਚੀਜ਼, ਸਥਾਨ, ਗੁਣ, ਭਾਵ, ਆਦਿ ਦਾ ਬੋਧ ਕਰਾਉਣ ਵਾਲੇ ਸ਼ਬਦਾਂ ਨੂੰ “ਨਾਂਵ” ਕਿਹਾ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ; ਜਿਵੇਂ – ਸੁਰਿੰਦਰ, ਪਿੰਡ, ਏਕਮ, ਜਲੰਧਰ, ਸੋਨਾ, ਜਮਾਤ, ਫ਼ੌਜ, ਰੇਤ, ਖ਼ੁਸ਼ੀ ਆਦਿ।
![]()
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 2.
ਕੀ ਤੁਹਾਡੇ ਨਾਲ ਕਦੇ ਕੋਈ ਅਜਿਹੀ ਘਟਨਾ ਵਾਪਰੀ ਹੈ, ਜਿਹੋ ਜਿਹੀ ਘਟਨਾ ਦਾ “ਪੇਮੀ ਦੇ ਨਿਆਣੇ ਕਹਾਣੀ ਵਿਚ ਬਿਆਨ ਹੈ, ਉਸ ਦਾ ਬਿਆਨ ਆਪਣੇ ਸ਼ਬਦਾਂ ਵਿਚ ਕਰੋ।
ਉੱਤਰ :
(ਨੋਟ – – ਵਿਦਿਆਰਥੀ ਆਪੇ ਲਿਖਣ ਦਾ ਅਭਿਆਸ ਕਰਨ)
3. ਔਖੇ ਸ਼ਬਦਾਂ ਦੇ ਅਰਥ
- ਵਿੱਥ – ਫ਼ਾਸਲਾ
- ਲਾਂਘਾ – ਆਉਣ – ਜਾਣ, ਆਵਾਜਾਈ
- ਅੰਞਾਣੇ – ਬੱਚੇ।
- ਭੈ – ਡਰ।
- ਟੰਟਾ – ਮੁਸ਼ਕਿਲ ਕੰਮ ਨੂੰ
- ਘੁਮਾਓਂ – ਅੱਠ ਕਨਾਲ ਦੀ ਥਾਂ ਜਾਂ ਖੇਤ।
- ਪਠੋਰੇ – ਮੇਮਣੇ, ਛੇਲੇ।
- ਵਾਕੁਰ – ਵਾਂਗਰ।
- ਭੈ – ਸਾਗਰ – ਭਵਸਾਗਰ, ਸੰਸਾਰ, ਡਰਾਉਣਾ ਰਸਤਾ।
- ਮਦਰੱਸਾ – ਸਕੂਲ।
- ਘਾਤ ਲਾਈ – ਲੁਕ ਕੇ ਵਾਰ ਕਰਨ ਲਈ ਤਿਆਰ
- ਕਰਾਰ – ਇਕਰਾਰ
- ਬੀਰ – ਵੀਰ, ਭਰਾ।
- ਗੁਸਤਾਖ਼ੀ – ਢੀਠਤਾਈ, ਸ਼ਰਾਰਤ, ਸ਼ੋਖ਼ੀ।
- ਸੀਰੀ – ਸਨ।
- ਭਾਸਦੇ – ਮਹਿਸੂਸ ਹੁੰਦੇ। ਅਚੇਤ ਜਿਸ ਬਾਰੇ ਸੁਚੇਤ ਨਾ ਹੋਵੋ !
- ਰਾਹਾਂ – ਅੱਗੇ !
- ਖਰੂਵੇ – ਰੁੱਖੇ।ਤੀਮਤ – ਇਸਤਰੀ। ਚਿਤਾਵਨੀ ਖ਼ਬਰਦਾਰੀ
- ਬਾਤ – ਕਹਾਣੀ ਠਠੰਬਰ
- ਕੇ – ਡਰ ਕੇ
- ਸਹਿਮ – ਡਰ।
- ਬੇਕਰਾਰ – ਬੇਚੈਨ।
- ਦਿਲਾਸਾ – ਹੌਸਲਾ, ਧੀਰਜ।
- ਬਾਰਸ – ਹੌਸਲਾ, ਧੀਰਜ।