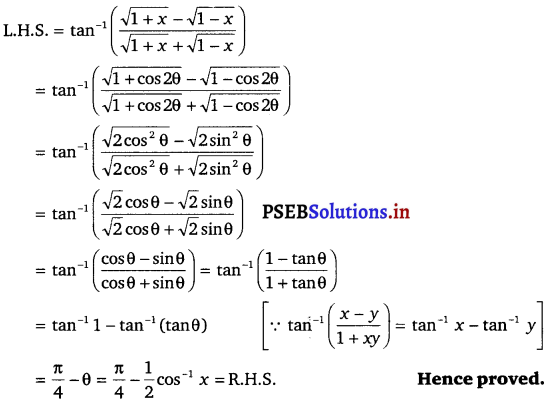
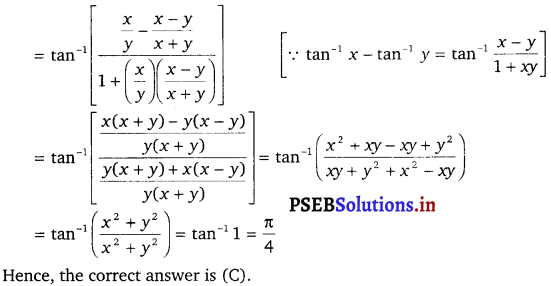
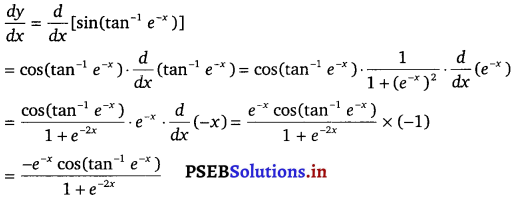
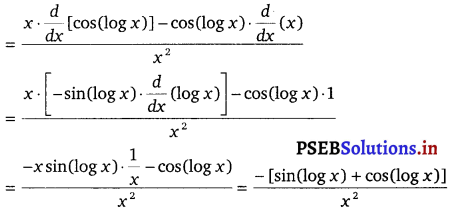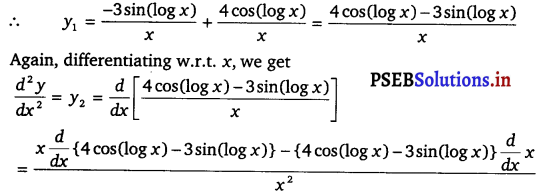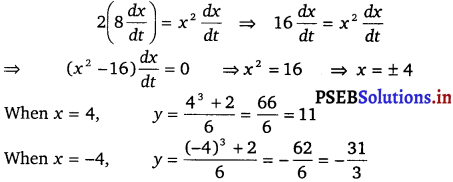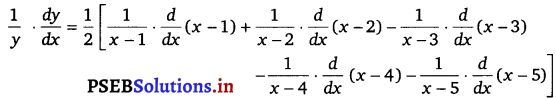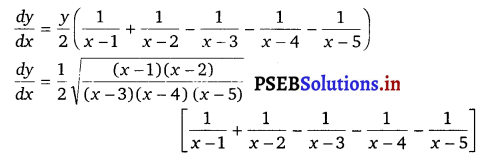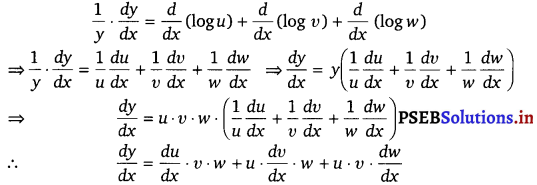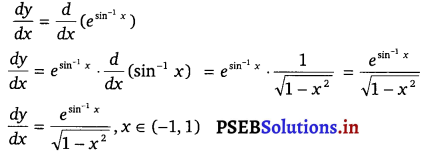Punjab State Board PSEB 12th Class Maths Book Solutions Chapter 6 Application of Derivatives Ex 6.2 Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
PSEB Solutions for Class 12 Maths Chapter 6 Application of Derivatives Ex 6.2
Question 1.
Show that the function given by f(x) = 3x +17 is strictly increasing on R.
Solution.
Let x1 and x2 by any two numbers in R, where x1 < x2 Then, we have
3x1 < 3x2
⇒ 31 + 17 < 3x2 +17
⇒ f(x1) < f(x2)
Hence, f is strictly increasing on R.
Alternate Method:
Given, f(x) = 3x +17
On differentiating w.r.t. x, we get f'(x) = 3 > 0, in every interval of R.
Thus, the function is strictly increasing on R.
![]()
Question 2.
Show that the function given by f(x) = e2x is strictly increasing on R.
Solution.
Let x1 and x2 be any two numbers in R, where x1 < x2 Given, f(x) = e2x Then, we have
x1 < x2
⇒ 2x1 < 2x2
⇒ e2x1 < e2x2
⇒ f(x1) < f(x2)
Hence, f is strictly increasing on R.
Question 3.
Show that the function given y f(x) = sin x is
(a) strictly increasing in (0, \(\frac{\pi}{2}\))
(b) strictly decreasing in (\(\frac{\pi}{2}\), π)
(c) neither increasing nor decreasing in (0, π)
Solution.
The given function is f(x) = sin x.
∴ f'(x) = cos x
(a) Since, for each x ∈ (0, \(\frac{\pi}{2}\)), cos x > 0, we have f'(x) > 0.
Hence, f is strictly increasing in (o, \(\frac{\pi}{2}\)).
(b) Since for each x ∈ (\(\frac{\pi}{2}\), π), cos x < 0, we have f'(x) < 0.
Hence, f is strictly decreasing in (\(\frac{\pi}{2}\), π)
(c) From the results obtained in (a) and (b), it is clear that f is neither increasing nor decreasing in (0, π).
![]()
Question 4.
Find the intervals in which the function f given by
f(x) = 2x2 – 3x is
(a) strictly increasing
(b) strictly decreasing
Solution.
The given function is f(x) = 2x2 – 3x.
Differentiating w.r.t. x, we get
∴ f'(x) = 4x – 3
On putting f'(x) = 0, we get
4x – 3 = 0
⇒ x = \(\frac{3}{4}\)
Now, the point \(\frac{3}{4}\) divides the real line into two disjoint intervals i.e., (- ∞, \(\frac{3}{4}\)) and (\(\frac{3}{4}\), ∞)
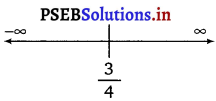
In Interval (- ∞, \(\frac{3}{4}\)),
f'(x) = 4x – 3 < 0 Hence, the given function (f) is strictly decreasing in interval (- ∞, \(\frac{3}{4}\)). In interval, (\(\frac{3}{4}\), ∞), f'(x) = 4x – 3 > 0.
Hence, the given function (f) is stricdy increasing in interval (\(\frac{3}{4}\), ∞).
Question 5.
Find the intervals in which the function f given by f(x) = 2x3 – 3x2 – 36x + 7 is
(a) strictly increasing
(b) strictly decreasing
Solution.
The given function is f(x) = 2x3 – 3x2 – 36x + 7
∴ f'(x) = 6x2 – 6x – 36
= 6(x2 – x – 6)
= 6(x + 2) (x – 3)
∴ f'(x) = 0
⇒ x = – 2, 3.
The points x = – 2 and x = 3 divide the real line into three disjoint intervals i.e., (- ∞, – 2), (- 2, 3) and (3, ∞).
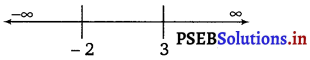
In intervals (- ∞, – 2) and (3, ∞), f'(x) is positive while in interval (- 2 , 3), f’ (x) is negative.
Hence, the given function (f) is strictly increasing in intervals (- ∞, – 2) and (3, ∞), while function (f) is strictly decreasing in interval (- 2, 3).
![]()
Question 6.
Find the intervals in which the following functions are strictly increasing or decreasing:
(a) x2 + 2x – 5
(b) 10 – 6x – 2x2
(c) -2x3 – 9x2 – 12x + 1
(d) 6 – 9x – x2
(e) (x + 1)3 (x – 3)3
Solution.
(a) we have f(x) = x2 + 2x – 5
∴ f'(x) = 2x + 2
= 2 (x + 1)
The function f(x) will be increasing if f'(x) > 0
i.e., if 2(x + 1) > 0
⇒ x + 1 > 0
⇒ x > – 1
The function f(x) will be decreasing if f'(x) < 0
i.e., 2(x + 1) < 0
⇒ (x + 1) < 0
⇒ x < – 1
Hence, f(x) is increasing on (- 1, ∞) and decreasing on (- ∞, – 1).
(b) We have, f(x) = 10 – 6x – 2x2
Differentiating w.r.t. x, we get
f'(x) = – 6 – 4x
= – 2 (3 + 2x)
Now, f(x) is increasing, if f'(x) > 0
i.e., – 6 – 4x > 0
i.e., – 4x > 6
⇒ x < \(-\frac{3}{2}\)
and f'(x) is decreasing if f'(x) < 0
i.e., if – 6 – 4x < 0
i.e., – 4x < 6 ⇒ x > \(-\frac{3}{2}\)
Hence, f(x) is increasing for x < \(-\frac{3}{2}\) i.e., in the interval (- ∞, \(-\frac{3}{2}\)) and decreasing on x > \(-\frac{3}{2}\) i.e., (\(-\frac{3}{2}\), ∞).
![]()
(c) Let f(x) = – 2x3 – 9x2 – 12x + 1
Differentiating w.r.t. x, we get
f'(x) = – 6x2 – 18x – 12
= – 6(x2 + 3x + 2)
= – 6 (x +1) (x + 2)
f'(x) = 0 gives x = – 1 or x = – 2
The points x = – 2 and x = – 1 (arranged in ascending order) divide the real line into three disjoint intervals namely, (- ∞, – 2), (- 2, – 1) and (- 1, ∞).
In the interval (- ∞, – 2) i.e., – ∞ < x < – 2 (x +1) and (x + 2) are negative
∴ f'(x) = (-) (-) (-) = – ve
⇒ f(x) is decreasing in (- ∞, – 2)
In the interval (- 2, – 1) i.e., – 2 < x < – 1 (x + 1) is -ve and (x + 2) is positive
∴ f'(x) = (-) (-) (+) = +ve
⇒ f(x) is increasing in (- 2, – 1)
In the interval (- 1, ∞) i.e., – 1 < x < ∞
(x + 1) and (x + 2) are both positive
∴ f'(x) = (-) (+) (+) = – ve
⇒ f{x) is decreasing in (- 1, ∞)
Hence, f(x) is increasing for – 2 < x < -1 and decreasing for x < – 2 and x > – 1.
(d) We have, f(x) = 6 – 9x – x2
Differentiating w.r.t. x, we get
f'(x) = – 9 – 2x
Now, f(x) is increasing if f'(x) > 0 i.e., if – 9 – 2x > 0
i.e., if – 2x > 9
⇒ x < \(-\frac{9}{2}\) and f(x) is decreasing if f'(x) > 0 i.e., if – 9 – 2x < 0
i.e., – 2x < 9 ⇒ x > \(-\frac{9}{2}\)
Hence, f(x) is increasing for x < \(-\frac{9}{2}\) and decreasing for x > \(-\frac{9}{2}\).
(e) We have, f(x) = (x + 1)3 (x – 3)3
Differentiating w.r.t x, we get
f'(x) = 3(x + 1)2 [\(\frac{d}{d x}\) (x + 1)] + (x – 3)3 + (x + 1)3 . 3 (x – 3)2 . \(\frac{d}{d x}\) (x – 3)
= 3(x + 1)2 (x – 3)3 + 3 (x + 1)3 (x – 3)2
= 3(x + 1)2 (x – 3)2 (x – 3 + x +1)
= 6(x + 1)2 (x – 3)2 (x – 1)
For f(x) to be increasing :
f'(x) > 0
⇒ 6(x + 1)2 (x – 3)2 (x – 1) > 0
⇒ (x – 1) > 0 [∵ 6(x + 1)2 (x – 3)2 > 0]
⇒ x > 1
But f'(x) = 0 at x = 3
⇒ f is increasing in (1, 3) and (3, 0)
∴ f(x) is increasing on (1, ∞).
For f(x) to be decreasing :
f'(x) < 0
⇒ 6(x + 1)2 (x – 3)2 (x – 1) < 0
(x – 1) < 0 [∵ 6 (x +1)2 (x – 3)2 > 0]
⇒ x < 1 But f'(x) = 0 at x = – 1 Hence, f(x) is strictly decreasing in (- ∞, 1), (- 1, 1).
![]()
Question 7.
Show that y = log (1 + x) – \(\frac{2 x}{(2+x)}\) , x > -1, is an increasing function of x throughout its domain.
Solution.
Given, y = log(1 + x) – \(\frac{2 x}{(2+x)}\)
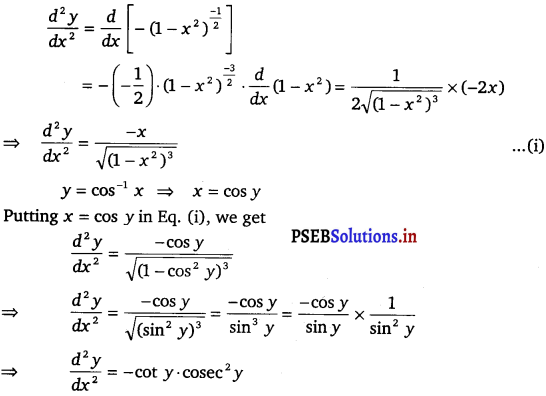
On differentiating, we get \(\frac{d y}{d x}\) = \(\frac{d}{d x}\) [log (1 + x) – \(\frac{2 x}{(2+x)}\)]
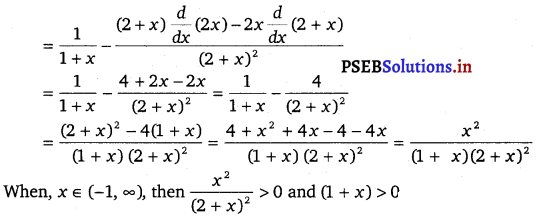
y’ > 0, when x > – 1
Hence, y is increasing function throughout (x > – 1) its domain.
Question 8.
Find the values of x for which y = [x(x – 2)]2 is an increasing function.
Solution.
We have, y = [x(x – 2)]2
= [x2 – 2x]2
∴ \(\frac{d y}{d x}\) = y’
= 2 (x2 – 2x) (2x – 2)
= 4x (x – 2) (x – 1)
∴ \(\frac{d y}{d x}\) = 0
⇒ x = 0, x = 2, x = 1
The points x = 0, x = 1 and x = 2 divide the real line into four disjoint intervals i.e., (- ∞, 0), (0, 1) (1, 2) and (2, ∞).
∴ In intervals (- ∞, 0) and (1, 2), \(\frac{d y}{d x}\) < 0. ∴ y is strictly decreasing in intervals (- ∞, 0) and (1, 2). However, in intervals (0, 1) and (2, ∞), \(\frac{d y}{d x}\) > 0.
∴ y is strictly increasing in intervals (0, 1) and (2, ∞).
∴ y is strictly increasing for 0 < x < 1 and x > 2.
![]()
Question 9.
Prove that y = \(\frac{4 \sin \theta}{(2+\cos \theta)}\) – θ is an increasing function of θ in [0,
\(\frac{\pi}{2}\)].
Solution.
We have, y = \(\frac{4 \sin \theta}{(2+\cos \theta)}\) – θ
Differentiating w.r.t θ, we get
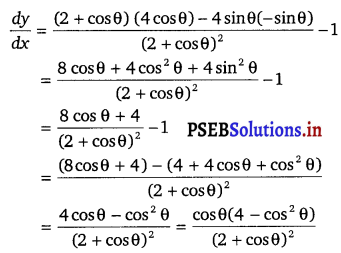
For the function to be increasing:
\(\frac{d y}{d \theta}\) > 0
⇒ \(\frac{\cos \theta\left(4-\cos ^{2} \theta\right)}{(2+\cos \theta)^{2}}\) > 0
⇒ cos θ (4 – cos2 θ) > 0
⇒ cos θ > 0, [(4 – cos2 θ) > 0 as cos2 θ is not > 1]
∴ θ ∈ (0, \(\frac{\pi}{2}\))
Hence, given function is increasing in interval [0, \(\frac{\pi}{2}\)].
Question 10.
Prove that the logarithmic function is strictly increasing on (0, ∞).
Solution.
The given function is f(x) = log x
Differentiating w.r.t. x, we get
f'(x) = \(\frac{1}{x}\)
It is clear that for x > 0, f’ (x) = \(\frac{1}{x}\) > 0.
Hence, f(x) = log x is strictly increasing in interval (0, ∞).
![]()
Question 11.
Prove that the function f given by f(x) = x2 – x + 1 is neither strictly increasing nor strictly decreasing on (- 1, 1).
Solution.
The given function is f(x) = x2 – x + 1
Differentiating w.r.t. x, we get f'(x) = 2x – 1
Now, f'(x) = 0
⇒ x = \(\frac{1}{2}\)
The point \(\frac{1}{2}\) divides the interval (- 1, 1) into two disjoint intervals i.e., (- 1, \(\frac{1}{2}\)) and (\(\frac{1}{2}\), 1)
Now, in interval (- 1, \(\frac{1}{2}\)), f'(x) = 2x – 1 < 0 Therefore, f is strictly decreasing in interval (- 1, \(\frac{1}{2}\)) However, in interval (\(\frac{1}{2}\), 1). f’(x) = 2x – 1 > 0.
Therefore, f is strictly increasing in interval (\(\frac{1}{2}\), 1)
Hence, f is neither strictly increasing nor strictly decreasing in interval (- 1, 1).
Question 12.
Which of the following functions are strictly decreasing on
(A) cos x
(B) cos 2x
(C) cos 3x
(D) tan x
Solution.
(A) Let, f(x) = cos x then f’(x) = – sin x
For 0 < x < \(\frac{\pi}{2}\), sin x > 0
∴ f’(x)= – sin x < 0 in (o, \(\frac{\pi}{2}\))
∴ f(x) is a decreasing function.
(B) Let, f(x) = cos 2x then f’(x) = – 2 sin 2x
For 0 < x < \(\frac{\pi}{2}\)
or 0 < 2x < π, sin 2x is positive
∴ f(x) is a decreasing function.
![]()
(C) Let, f(x) = cos 3x then f’(x) = – 3 sin 3x
For 0 < x < \(\frac{\pi}{2}\) ⇒ 0 < 3x < \(\frac{\pi}{2}\)
sin 3x is positive in 0 < 3x < π
∴ f’(x) < 0
⇒ f(x) is decreasing
And sin 3x is negative in π < 3x < \(3 \frac{\pi}{2}\) ∴ f’(x) > 0
⇒ f(x) is increasing
∴ f(x) is neither increasing nor decreasing in (o, \(\frac{\pi}{2}\))
Hence, f(x) is not a decreasing function in (o, \(\frac{\pi}{2}\)).
(D) Let, f(x) = tan x then f’(x) = sec2 x
In interval x ∈ (o, \(\frac{\pi}{2}\))f’(x) > 0
∴ f(x) is an increasing function.
Thus, (A) cos x (B) cos 2x are strictly decreasing functions on (o, \(\frac{\pi}{2}\)).
Question 13.
On which of the following intervals is the function f given by f(x) = x100 + sin x – 1 strictly decreasing?
(A) (0, 1)
(B) (\(\frac{\pi}{2}\), π)
(C) (0, \(\frac{\pi}{2}\))
(D) None of these
Solution.
Given, f(x) = x100 + sin x – 1
⇒ f'(x) = 100 x99 + cos x
In interval (0, 1), cos x > 0 and 100 x99 > 0.
f'(x) > 0
Thus, function f is strictly increasing in interval (0, 1).
In interval (\(\frac{\pi}{2}\), π), cos x < 0 and 100 x99 < 0.
also, 100 x99 > cos x
∴ f'(x) > 0 in (\(\frac{\pi}{2}\), π)
In interval (0, \(\frac{\pi}{2}\)), cos x > 0 and 100 x99 > 0
∴ 100 x99 + cos x > 0
⇒ f'(x) > 0 on (0, \(\frac{\pi}{2}\))
∴ f is strictly increasing in interval (0, \(\frac{\pi}{2}\))
Hence, function f is strictly decreasing in the given intervals.
The correct answer is (D).
![]()
Question 14.
Find the least value of a such that the function f given by fix) – x2 + ax + 1 is strictly increasing on (1, 2).
Solution.
Given, f(x) = x2 + ax +1
⇒ f'(x) = 2x + a
Now, function f will be increasing in (1, 2), if f'(x) > 0 in (1, 2).
∴ f'(x) > 0
⇒ 2x + a > 0
⇒ 2x > – a
⇒ x > – \(\frac{a}{2}\)
Therefore, we have to find the least value of a such that x > – \(\frac{a}{2}\), when x ∈ (1, 2).
⇒ x > – \(\frac{a}{2}\) (when 1 < x < 2)
Thus, the least value of a for f to be increasing on (1, 2) given by
– \(\frac{a}{2}\) = 1
⇒ a = – 2
Hence, the least value of a is – 2.
Question 15.
Let I be any interval disjoint from (- 1, 1). Prove that the function f given by f(x) = x + \(\frac{1}{x}\) is strictly increasing on I.
Solution.
Given, f(x) = x + \(\frac{1}{x}\)
∴ f'(x) = 1 – \(\frac{1}{x^{2}}\)
= \(\frac{x^{2}-1}{x^{2}}\)
Now, x ∈ I ⇒ x ∉ (- 1, 1)
⇒ x ≤ – 1 or x ≥ 1
⇒ x2 ≥ 1
⇒ x2 – 1 ≥ 0
⇒ \(\frac{x^{2}-1}{x^{2}}\) ≥ 0 [∵ x2 ≥ 1 > 0]
∴ f'(x) ≥ 0
Thus, f'(x) ≥ 0 for all x ∈ I.
Hence, f'(x) is strictly increasing on I.
![]()
Question 16.
Prove that the function f given hy f(x) = log sin x is strictly increasing on (0, \(\frac{\pi}{2}\)) and strictly decreasing on (\(\frac{\pi}{2}\), π).
Solution.
Given, f(x) = log sin x
∴ f'(x) = \(\frac{1}{\sin x}\) . cos x = cot x
In interval (0, \(\frac{\pi}{2}\)), f'(x) = cot x > 0
∴ f is strictly increasing in (0, \(\frac{\pi}{2}\))
In inerval (\(\frac{\pi}{2}\), π), f'(x) = cot x < 0 ∴ f is strictly increasing on (\(\frac{\pi}{2}\), π).
Question 17.
Prove that the function f given by f(x) = log (cos x) is strictly decreasing on (0, \(\frac{\pi}{2}\)) and strictly increasing on (\(\frac{\pi}{2}\), π). Solution. Given, f(x) = log (cos x) ⇒ f’(x) = \(\frac{1}{\cos x}\) (- sin x) = – tan x In interval (0, \(\frac{\pi}{2}\)), tan x > 0
⇒ – tan x < 0
∴ f’(x) < 0 on (0, \(\frac{\pi}{2}\))
∴ f is strictly decreasing on (o, \(\frac{\pi}{2}\))
In interval (\(\frac{\pi}{2}\), π) tan x < 0 ⇒ – tan x > 0.
∴ f’(x) > 0 on (\(\frac{\pi}{2}\), π)
∴ f is strictly increasing on (\(\frac{\pi}{2}\), π).
![]()
Question 18.
Prove that the function given by f(x) = x3 – 3x2 + 3x – 100 is increasing in R.
Solution.
Given, f(x) = x3 – 3x2 + 3x – 100
f'(x) = 3x2 – 6x + 3
= 3(x2 – 2x + 1)
= 3(x – 1)2
For any x ∈ R, (x – 1)2 > 0.
Thus, f(x) is always positive in R.
Hence, the given function (f) is increasing in R.
Question 19.
The interval in which y = x2 e-x is increasing, is
(A) (- ∞, ∞)
(B) (- 2, 0)
(C) (2, ∞)
(D) (0, 2)
Solution.
Given, y = x2 e-x
⇒ \(\frac{d y}{d x}\) = 2xe-x – x2e-x
= xe-x (2 – x)
Now, \(\frac{d y}{d x}\) = 0
⇒ x = 0 and x = 2
The points x = 0 and x = 2 divide the real line into three disjoint intervals
i.e., (- ∞, 0), (0, 2) and (2, ∞).
In intervals (- ∞, 0) and (2, ∞), f(x) < 0 and e~x is always positive. ∴ f is decreasing on (- ∞, 0) and (2, ∞). In interval (0, 2), f'(x) > 0
∴ f is strictly increasing on (0, 2).
Hence, f is strictly increasing in interval (0, 2).
The correct answer is (D).