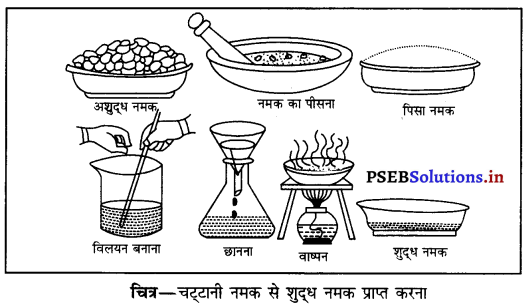
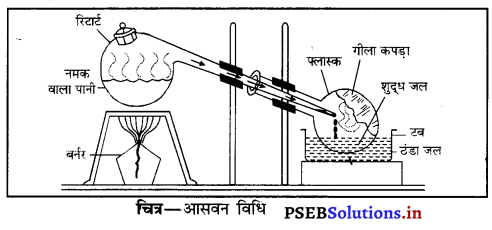
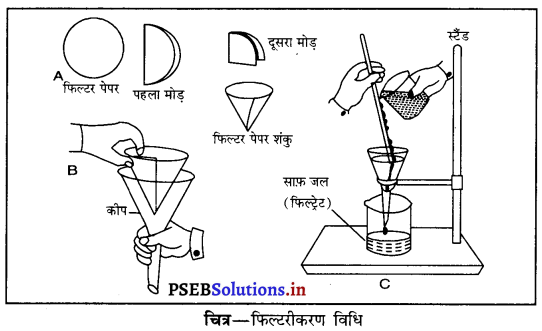
Punjab State Board PSEB 6th Class Science Book Solutions Chapter 6 हमारे चारों ओर के परिवर्तन Textbook Exercise Questions, and Answers.
PSEB Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 6 हमारे चारों ओर के परिवर्तन
PSEB 6th Class Science Guide हमारे चारों ओर के परिवर्तन Textbook Questions, and Answers
1. खाली स्थान भरें
(i) …………………. परिवर्तन में नया पदार्थ बनता है।
उत्तर-
रासायनिक
(ii) बर्फ का पिघलना …………………… तथा ………………… परिवर्तन है।
उत्तर-
भौतिक, प्रतिवर्ती
(iii) कागज़ का जलना ……………….. परिवर्तन है।
उत्तर-
रासायनिक/अपरिवर्तनीय
(iv) धातुएँ गर्म करने पर ………………… हैं।
उत्तर-
विस्तार
(v) वे परिवर्तन जो किसी आवर्त समय के बाद दोहराएं जाते हैं, ………………….. परिवर्तन कहलाते हैं।
उत्तर-
आवधिक परिवर्तन।
![]()
2. सही या ग़लत बताएं
(i) दूध से पनीर का बनना उत्क्रमित परिवर्तन है।
उत्तर-
ग़लत
(ii) लोहे को जंग लगना एक धीमा परिवर्तन है।
उत्तर-
सही
(iii) गर्म करने पर धातुएँ सिकुड़ती हैं।
उत्तर-
ग़लत
(iv) पहाड़ों पर बर्फ का पिघलना एक प्राकृतिक परिवर्तन है।
उत्तर-
सही
(v) पटाखों का जलना एक तेज़ परिवर्तन है।
उत्तर-
सही
3. कॉलम ‘क’ का कॉलम ‘ख’ से उचित मिलान करें
| कॉलम ‘क’ | कॉलम ‘ख’ |
| (i) पानी का जमना | (क) अनियमित |
| (ii) दूध से दही | (ख) भौतिक और उत्क्रमित |
| (iii) माचिस का जलना | (ग) नियमित |
| (iv) भूचाल | (घ) तेज |
| (v) मौसम का बदलना | (ङ) रासायनिक |
उत्तर-
| कॉलम ‘क’ | कॉलम ‘ख’ |
| (i) पानी का जमना | (ख) भौतिक और उत्क्रमित |
| (ii) दूध से दही | (ङ) रासायनिक |
| (iii) माचिस का जलना | (घ) तेज |
| (iv) भूचाल | (क) अनियमित |
| (v) मौसम का बदलना | (ग) नियमित |
![]()
4. सही विकल्प चुनें
प्रश्न (i)
भोजन का पकना कौन-सा परिवर्तन है?
(क) भौतिक
(ग) उत्क्रमित
(ख) तेज
(घ) अनुत्क्रमित।
उत्तर-
(घ) अपरिवर्तनीय ।
प्रश्न (ii)
कौन परिवर्तन अनियमित है?
(क) दिल का धड़कना
(ख) भूचाल
(ग) दिन और रात का बनना
(घ) पेंडुलम की गति।
उत्तर-
(ख) भूचाल ।
प्रश्न (iii)
गर्म करने पर क्या फैलता है?
(क) लकड़ी
(ख) पेपर
(ग) धातु
(घ) कपड़ा ।
उत्तर-
(ग) धातु।
प्रश्न (iv)
लोहे को जंग लगना किस प्रकार का परिवर्तन है?
(क) उत्क्रमित
(ख) धीमा
(ग) नियमित
(घ) तेज।
उत्तर-
(ख) धीमा ।
प्रश्न (v)
पौधों तथा जंतुओं में वृद्धि किस तरह का परिवर्तन है?
(क) धीमा
(ख) उत्क्रमित
(ग) रासायनिक
(घ) नियमित ।
उत्तर-
(क) धीमा।
![]()
5. अति लघूत्तर प्रश्न
प्रश्न (i)
परिवर्तन क्या है?
उत्तर-
परिवर्तन एक ऐसी क्रिया है जिसके द्वारा कोई वस्तु किसी अन्य रूप अथवा वस्तु में परिवर्तित हो जाती है।
प्रश्न (ii)
धीमे तथा तेज परिवर्तनों को उदाहरण सहित परिभाषित करें।
उत्तर-
धीमे परिवर्तन वे होते हैं जिन्हें होने में अधिक समय लगता है। उदाहरण के लिए, पेड़ का बढ़ना, बच्चे का वयस्क होना आदि। तेज परिवर्तन वे होते हैं जो बहुत तेजी से होते हैं। उदाहरण के लिए, माचिस की तीली जलाना, पटाखे फोड़ना आदि।
प्रश्न (iii)
उत्क्रमित परिवर्तन के दो उदाहरण लिखें।
उत्तर-
बर्फ का पिघलना और गर्म करने पर धातुओं का फैलना ।
प्रश्न (iv)
लोहे का रिम लकड़ी के पहिए से छोटा क्यों बनाया जाता है?
उत्तर-
प्रयुक्त धातु रिम पहियों की तुलना में व्यास में थोड़ा छोटा होता है क्योंकि गर्म करने पर रिम फैलता है और आसानी से पहियों पर पूरा आ सकता है। जब रिम ठंडा हो जाता है, तो यह सिकुड़ जाता है और पहिए पर कसकर फिट हो जाता है।
प्रश्न (v)
रासायनिक परिवर्तन के दो उदाहरण लिखें।
उत्तर-
दूध को पनीर और दही में बदलना, सब्जियों को पकाना।
6. लघूत्तर प्रश्न
प्रश्न (i)
नियमित तथा अनियमित परिवर्तनों का उदाहरण सहित अंतर लिखें।
उत्तर-
आवधिक परिवर्तन – जो परिवर्तन नियमित अंतराल के बाद दोहराए जाते हैं, उन्हें आवधिक परिवर्तन कहा जाता है। उदाहरण हैं-दिन और रात का परिवर्तन, घड़ी के लोलक का झूलना, हृदय की धड़कन, ऋतुओं का परिवर्तन।
गैर-आवधिक परिवर्तन – वे परिवर्तन जो नियमित अंतराल के बाद दोहराए नहीं जाते हैं, गैर-आवधिक परिवर्तन कहलाते हैं। उदाहरण हैं-भूकंप की घटना, बारिश की घटना आदि हैं।
![]()
प्रश्न (ii)
उत्क्रमित तथा अनुत्क्रमित परिवर्तनों का उदाहरण सहित अंतर लिखें।
उत्तर-
उत्क्रमणीय परिवर्तन – जब किसी पदार्थ में होने वाले परिवर्तन को परिस्थितियों में बदलाव करके उलटा किया जा सकता है तो इसे प्रतिवर्ती अथवा उत्क्रमणीय परिवर्तन कहा जाता है। उदाहरण हैं-बर्फ का पिघलना, पानी का वाष्पीकरण आदि।
अनुत्क्रमणीय परिवर्तन – यदि परिवर्तन के बाद किसी पदार्थ को उसकी मूल स्थिति में वापस नहीं लाया जा सकता है तो परिवर्तन को अनुत्क्रमणीय अथवा अपरिवर्तनीय परिवर्तन कहा जाता है। उदाहरण हैं- भोजन पकाना, दूध को पनीर और दही में बदलना आदि।
प्रश्न (iii)
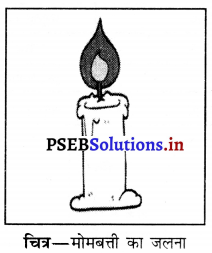
किसी मोसबत्ती को जलाने पर उसका आकार क्यों कम हो जाता है?
उत्तर-
जलने पर कुछ मोम पिघल जाता है और कुछ कार्बन डाइऑक्साइड और पानी में बदल जाता है। इन परिवर्तनों के कारण जलने पर मोमबत्ती का आकार कम हो जाता है।
प्रश्न (iv)
भौतिक तथा रासायनिक परिवर्तनों में अन्तर उदाहरण देकर स्पष्ट करें।
उत्तर-
भौतिक परिवर्तन – भौतिक परिवर्तन एक अस्थायी परिवर्तन है जिसमें कोई नया पदार्थ नहीं बनता है और मूल पदार्थ की रासायनिक संरचना समान रहती है। इस परिवर्तन के दौरान रंग, आकार, आयतन, अवस्था आदि बदल सकते हैं। यह एक प्रतिवर्ती अथवा उत्क्रमणीय परिवर्तन है। जैसे-बर्फ का पिघलना, गुब्बारे का उड़ना, रबर का खिंचना, कागज का फटना, कागज को मोड़ना आदि भौतिक परिवर्तनों के कुछ उदाहरण हैं।
रासायनिक परिवर्तन – कोई भी परिवर्तन जो स्थायी होता है, जिसमें ऐसे नए पदार्थ बनते हैं जिनके भौतिक और रासायनिक गुण मूल पदार्थ से पूरी तरह भिन्न होते हैं, रासायनिक परिवर्तन कहलाते हैं। रासायनिक परिवर्तन प्रकृति में अपरिवर्तनीय अथवा अनुत्क्रमणीय होते हैं। जैसे-आम का पकना, भोजन पकाना, दूध को पनीर में बदलना, पौधों की वृद्धि आदि रासायनिक परिवर्तनों के कुछ उदाहरण हैं।
7. निबंधात्मक प्रश्न
प्रश्न 1.
फैलाव की परिभाषा लिखें। ताप फैलाव क्या होता है? कोई दो उदाहरण देकर स्पष्ट करें।
उत्तर-
फैलाव – इसे उच्च तापमान और उच्च दबाव के अधीन शरीर के आयाम में वृद्धि के रूप में परिभाषित किया जा सकता है। उदाहरण के लिए गुब्बारा फुलाना, स्प्रिंग को खींचना।
जब फैलाव तापमान में वृद्धि के कारण होता है तो इसे ताप फैलाव कहा जाता है। इसे हम कई उदाहरणों की मदद से समझा सकते हैं।
- जब हम क्लीनिकल थर्मामीटर मुँह में डालते हैं तो पारे का स्तर बढ़ जाता है। ऐसा इसलिए है क्योंकि पारा एक धातु है और धातु गर्म करने पर फैलती है।
- एक धातु की गेंद जो गर्म करने पर एक रिंग से गुजर सकती है, आकार में बड़ी हो जाती है और उसी रिंग से नहीं गुजर सकती है।
Science Guide for Class 6 PSEB हमारे चारों ओर के परिवर्तन Intext Questions and Answers
सोचें और उत्तर दें (पेज 53)
प्रश्न 1.
आपकी माता जी रोटी बनाने से पहले गूंधे हुए आटे से लोई बनाती हैं। क्या लोई को पुनः आटे में परिवर्तित किया जा सकता है?
उत्तर-
हाँ, लोई को पलटकर आटे में पलटा जा सकता है।
![]()
प्रश्न 2.
कागज़ के टुकड़े से पेपर बोट (कागज़ की कश्ती) बनाई जाती है। क्या कागज़ की कश्ती को पुनः कागज़ में परिवर्तित किया जा सकता है ?
उत्तर-
हाँ, हम कागज़ को मूल रूप में वापस प्राप्त कर सकते हैं।
सोचें और उत्तर दें (पेज 54)
प्रश्न 1.
पाँचवीं श्रेणी तथा आठवीं श्रेणी के बच्चों की लंबाई को ध्यान से देखें। क्या लंबाई में वृद्धि उत्क्रमित परिवर्तन है या अनुत्क्रमित है?
उत्तर-
ऊंचाई में परिवर्तन एक अनुत्क्रमित परिवर्तन है।
प्रश्न 2.
क्या मोमबत्ती का जलना उत्क्रमित परिवर्तन है या अनुत्क्रमित परिवर्तन है?
उत्तर-
मोमबत्ती का जलना एक अनुत्क्रमित परिवर्तन है।
सोचें और उत्तर दें (पेज 55)
प्रश्न 1.
कागज़ को फाड़ना किस तरह का परिवर्तन है?
उत्तर-
भौतिक परिवर्तन।
प्रश्न 2.
बर्फ से पानी बनना किस तरह का परिवर्तन है?
उत्तर-
भौतिक परिवर्तन।
सोचें और उत्तर दें (पेज 56)
प्रश्न 1.
दूध से पनीर बनाना किस तरह का परिवर्तन है ?
उत्तर-
रसायनिक परिवर्तन।
प्रश्न 2.
जलती हुई मोमबत्ती से मोम का बनना किस तरह का परिवर्तन है?
उत्तर-
रसायनिक परिवर्तन।
![]()
सोचें और उत्तर दें (पेज 56)
प्रश्न 1.
क्या आपने कभी सुनार की दुकान पर बर्नर देखा है ? इसका क्या काम है?
उत्तर-
इसका उपयोग सोने को पिघलाने के लिए किया जाता है।
प्रश्न 2.
जब आप डॉक्टरी थर्मामीटर को मुँह में रखते हैं तो थर्मामीटर की नली में मर्करी ऊपर क्यों चढ़ जाता है तथा मुँह में से थर्मामीटर बाहर निकालकर तथा छिड़कने पर मर्करी नली में से यह क्यों नीचे गिर जाता है ? (नोट करें : मर्करी कमरे के तापमान पर तरल धातु है।)
उत्तर-
धातुएँ गर्म करने पर फैलती हैं और ठंडा करने पर सिकुड़ती हैं। जब हम क्लिनिकल थर्मामीटर को मुँह में डालते हैं तो मुँह के अंदर का तापमान अधिक होने के कारण थर्मामीटर में पारे का स्तर बढ़ जाता है। जब हम इसे मुँह से बाहर निकालते हैं तो पारे का स्तर गिर जाता है क्योंकि बाहर का तापमान मुँह के तापमान से कम होता है।
PSEB Solutions for Class 6 Science हमारे चारों ओर के परिवर्तन Important Questions and Answers
1. बहुविकल्पीय प्रश्न
प्रश्न (i)
खाना पकना एक …………….. परिवर्तन है।
(क) उत्क्रमित
(ख) अनुत्क्रमित
(ग) तीव्र
(घ) धीमा।
उत्तर-
(ख) अनुत्क्रमित।
प्रश्न (ii)
यह एक उत्क्रमित परिवर्तन है।
(क) बर्फ का पिघलना
(ख) मोमबत्ती का जलना
(ग) खाना पकाना
(घ) बीजों का अंकुरित होना।
उत्तर-
(क) बर्फ का पिघलना।
प्रश्न (iii)
दूध से दही बनाने के लिए दूध को …………………….. किया जाता है।
(क) गर्म
(ख) ठंडा
(ग) उबाला
(घ) कुछ नहीं।
उत्तर-
(क) गर्म।
प्रश्न (iv)
धूपबत्ती जलने में पैदा होती है।
(क) राख
(ख) गैस
(ग) खुशबू
(घ) उपरोक्त सभी विकल्प।
उत्तर-
(घ) उपरोक्त सभी विकल्प।
प्रश्न (v)
धातु के रिम को लकड़ी के पहिए से थोड़ा …………………….. रखा जाता है।
(क) छोटा
(ख) बड़ा
(ग) समान
(घ) इनमें से कोई नहीं।
उत्तर-
(क) छोटा।
![]()
प्रश्न (vi)
सड़क पर कोलतार (लुक) डालने से पहले …………………. की जाती है ताकि वह पिघल जाए।
(क) गर्म
(ख) ठंडी
(ग) उबाली
(घ) इनमें से कोई नहीं।
उत्तर-
(क) गर्म।
प्रश्न (vii)
जब पदार्थ किसी क्रिया-कलाप के बाद पुनः अपनी अवस्था में वापस आ जाए उस क्रिया को ……………………. कहते हैं।
(क) धीमी
(ख) उत्क्रमित
(ग) अनुत्क्रमित
(घ) इनमें से कोई नहीं।
उत्तर-
(ख) उत्क्रमित ।
प्रश्न (viii)
गुब्बारे को फुलाना एक …………………….. परिवर्तन है।
(क) तेज़
(ख) धीमा
(ग) उत्क्रमित
(घ) अनुत्क्रमित।
उत्तर-
(ग) उत्क्रमित।
प्रश्न (ix)
गूंथे हुए आटे से कई आकृतियाँ बनाई जा सकती हैं। इस परिवर्तन को ……………………. कहते हैं।
(क) तेज़
(ख) धीमा
(ग) उत्क्रमित
(घ) अनुत्क्रमित।
उत्तर-
(ग) उत्क्रमित।
प्रश्न (x)
मोमबत्ती का पिघलना कौन-सा परिवर्तन है?
(क) भौतिक
(ख) रासायनिक
(ग) भौतिक तथा रासायनिक
(घ) इनमें से कोई नहीं।
उत्तर-
(क) भौतिक।
![]()
2. खाली स्थान भरें
(i) बच्चे से बड़ा होना ………………….. है ।
उत्तर-
धीमा परिवर्तन
(ii) वर्षा एक ………………………. है ।
उत्तर-
अनियमित परिवर्तन
(iii) पेंसिल को तेज करना एक …………………….. परिवर्तन है ।
उत्तर-
अपरिवर्तनीय
(iv) लकड़ी के पहिये की परिधि से धातु का रिम थोड़ा ……………………. बना होता है।
उत्तर-
छोटा।
3. सही या ग़लत चुनें
(i) भौतिक परिवर्तन प्रतिवर्ती हैं।
उत्तर-
सही
(ii) मोमबत्ती का जलना एक भौतिक और रासायनिक परिवर्तन है।
उत्तर-
सही
(iii) विस्तार और संकुचन समान हैं।
उत्तर-
ग़लत
(iv) ठंडा होने पर वस्तु/धातु फैलती है।
उत्तर-
ग़लत
![]()
4. कॉलम ‘क’ और कॉलम ‘ख’ का उचित मिलान करें
| कॉलम ‘क’ | कॉलम ‘ख’ |
| (i) लोहे का संक्षारण | (a) भौतिक परिवर्तन |
| (ii) जल का जमना | (b) धीमा परिवर्तन |
| (iii) कोयला जलाना | (c) प्राकृतिक परिवर्तन |
| (iv) माचिस की तीली का जलना | (d) रासायनिक परिवर्तन |
| (v) सर्दियों में नारियल का तेल जम जाना | (e) तेज परिवर्तन |
उत्तर-
| कॉलम ‘क’ | कॉलम ‘ख’ |
| (i) लोहे का संक्षारण | (d) रासायनिक परिवर्तन |
| (ii) जल का जमना | (a) भौतिक परिवर्तन |
| (iii) कोयला जलाना | (b) धीमा परिवर्तन |
| (iv) माचिस की तीली का जलना | (e) तेज परिवर्तन |
| (v) सर्दियों में नारियल का तेल जम जाना | (c) प्राकृतिक परिवर्तन |
5. अति लघूत्तर प्रश्न
प्रश्न 1.
परिवर्तन किसे कहते हैं ? परिवर्तनों के उदाहरण दीजिए।
उत्तर-
परिवर्तन – किसी पदार्थ के आकार अथवा गुणों में आए बदलाव को परिवर्तन कहते हैं।
उदाहरण – नाखून का बढ़ना, बालों का बढ़ना, खेतों में फ़सलों का पकना और पत्तों का गिरना।
प्रश्न 2.
उत्क्रमणीय परिवर्तन किसे कहते हैं?
उत्तर-
उत्क्रमणीय परिवर्तन – ऐसा परिवर्तन जो होने के पश्चात् दोबारा अपनी पहली स्थिति में आ जाए उसे उत्क्रमणीय परिवर्तन कहते हैं।
प्रश्न 3.
कागज़ का जलना एक उत्क्रमणीय परिवर्तन है या अनुत्क्रमणीय।
उत्तर-
अनुत्क्रमणीय परिवर्तन।
प्रश्न 4.
क्या वनों की कटाई को एक उत्क्रमणीय परिवर्तन माना जा सकता है?
उत्तर-
हां, क्योंकि वृक्ष लगाने से वन पैदा हो सकता है।
प्रश्न 5.
छपाई एक उत्क्रमणीय परिवर्तन है या अनुत्क्रमणीय।
उत्तर-
छपाई एक अनुत्क्रमणीय परिवर्तन है।
![]()
प्रश्न 6.
मोमबत्ती के जलने में ऊर्जा का उत्सर्जन होता है अथवा अवशोषण।
उत्तर-
मोमबत्ती के जलने में ऊर्जा का उत्सर्जन होता है।
प्रश्न 7.
ऐसे परिवर्तन का उदाहरण दीजिए जिसमें ऊर्जा का अवशोषण होता हो।
उत्तर-
हरे पौधों द्वारा भोजन बनाने में ऊर्जा का अवशोषण होता है।
प्रश्न 8.
लोहे को जंग लगना कौन-सा परिवर्तन है ? अनुत्क्रमणीय अथवा उत्क्रमणीय और क्यों?
उत्तर-
लोहे को जंग लगना एक अनुत्क्रमणीय परिवर्तन है क्योंकि लोहे का जंग एक नए गुणों वाला नया पदार्थ है।
प्रश्न 9.
डिब्बे बनाने से पहले लोहे की चादर पर टिन का लेप क्यों चढ़ाते हैं ?
उत्तर-
डिब्बा बनाने से पहले लोहे पर टिन की परत चढ़ाई जाती है ताकि जंग न लगे। जंग लगना एक अनुत्क्रमणीय परिवर्तन है।
प्रश्न 10.
भौतिक परिवर्तन किस प्रकार का परिवर्तन है?
उत्तर-
भौतिक परिवर्तन उत्क्रमणीय परिवर्तन है।
प्रश्न 11.
मनुष्य का बूढ़ा होना किस प्रकार का परिवर्तन है ?
उत्तर-
मनुष्य का बूढ़ा होना अनुत्क्रमणीय परिवर्तन है।
![]()
प्रश्न 12.
दो उत्क्रमणीय परिवर्तन लिखिए।
उत्तर-
- ऊन के तागे से बुना हुआ स्वैटर।
- तार से कुंडली बनाना।
प्रश्न 13.
दो अनुत्क्रमणीय परिवर्तन लिखिए।
उत्तर-
- पत्तियों से कंपोस्ट खाद बनाना।
- गाय के गोबर से बायो-गैस बनाना।
प्रश्न 14.
जल से जल वाष्प बनना कौन-सा परिवर्तन है-उत्क्रमणीय या अनुत्क्रमणीय?
उत्तर-
जल से जल वाष्पों का बनना उत्क्रमणीय परिवर्तन है।
प्रश्न 15.
क्या तार को गर्म करना उत्क्रमणीय परिवर्तन है ?
उत्तर-
हाँ, तार (tar) को गर्म करना उत्क्रमणीय परिवर्तन है।
प्रश्न 16.
दूध से दही जमाना उत्क्रमणीय अथवा अनुत्क्रमणीय परिवर्तन है?
उत्तर-
दूध से दही जमाना अनुत्क्रमणीय परिवर्तन है।
प्रश्न 17.
बर्फ का पिघलना कौन-सा परिवर्तन है?
उत्तर-
उत्क्रमणीय परिवर्तन।
![]()
6. लघूत्तर प्रश्न
प्रश्न 1.
हमारे चारों ओर कौन-से परिवर्तन होते रहते हैं ?
उत्तर-
हमारे चारों ओर बहुत-से परिवर्तन होते रहते हैं, जैसे-खेतों में फ़सलें समयानुसार बदलती रहती हैं, पत्तियाँ रंग बदलती रहती हैं और सूख कर पेड़ों से गिर जाती हैं, फूल खिलते हैं और मुरझा जाते हैं।
प्रश्न 2.
हमारे शरीर में होने वाले परिवर्तन उत्क्रमणीय हैं अथवा अनुत्क्रमणीय।
उत्तर-
हमारे शरीर में होने वाले परिवर्तन अनुत्क्रमणीय हैं जैसे हमारे नाखून बढ़ते हैं। उनको दोबारा छोटा नहीं किया जा सकता। वे केवल काट कर ही छोटे किए जा सकते हैं। इसी प्रकार हमारे शरीर में होने वाले परिवर्तन अनुत्क्रमणीय हैं।
प्रश्न 3.
उत्क्रमणीय परिवर्तन किसे कहते हैं ? इनके दो उदाहरण दीजिए।
उत्तर-
उत्क्रमणीय परिवर्तन – ऐसा परिवर्तन जो एक बार होने के पश्चात् दोबारा अपनी पहली स्थिति में वापिस आ सकता है, उसे उत्क्रमणीय परिवर्तन कहते हैं।
उदाहरण-
- मोम का पिघलना।
- पानी का वाष्प बनना।
- पानी में चीनी घोलना।
प्रश्न 4.
अनुत्क्रमणीय परिवर्तन किसे कहते हैं ? उदाहरणे दीजिए।
उत्तर-
अनुत्क्रमणीय परिवर्तन – ऐसा परिवर्तन जो एक बार होने के पश्चात् दोबारा अपनी पहली स्थिति में वापिस न आ सके, उसे अनुत्क्रमणीय परिवर्तन कहते हैं।
उदाहरण-
- मोमबत्ती का जलना।
- दूध से दही बनना।
- फ़सलों का पकना।
प्रश्न 5.
निम्नलिखित को उत्क्रमणीय या अनुत्क्रमणीय परिवर्तनों में वर्गीकृत करें-
(i) पौधों में वृद्धि।
(ii) खेतों में हल चलाना।
(iii) मोम का पिघलना।
(iv) वर्षा का गिरना।
(v) रबड़ के बैंड को खींचना।
(vi) शीशे की छड़ को तोड़ना।
(vii) भोजन बनाना।
उत्तर-
(i) अनुत्क्रमणीय परिवर्तन
(ii) उत्क्रमणीय परिवर्तन
(iii) उत्क्रमणीय परिवर्तन
(iv) अनुत्क्रमणीय परिवर्तन
(v) उत्क्रमणीय परिवर्तन
(vi) अनुत्क्रमणीय परिवर्तन
(vii) अनुत्क्रमणीय परिवर्तन।
प्रश्न 6.
गुब्बारे में हवा भरने से उसके आमाप और आकार में हुआ परिवर्तन कौन-सा परिवर्तन है। उत्क्रमणीय अथवा अनुत्क्रमणीय और क्यों?
उत्तर-
गुब्बारे में हवा भरने से उसके आमाप और आकार में हुआ परिवर्तन उत्क्रमणीय है क्योंकि हवा निकालने से गुब्बारा पुनः अपनी अवस्था में आ जाएगा।
![]()
प्रश्न 7.
गूंथे हुए आटे की लोई से रोटी बेलकर तवे पर सेंकना कौन-सा परिवर्तन है ? उत्क्रमणीय अथवा अनुत्क्रमणीय और क्यों?
उत्तर-
गूंथे हुए आटे से रोटी बनाकर तवे पर सेंकना अनुत्क्रमणीय परिवर्तन है क्योंकि बनी हुई रोटी से पुनः आटे की लोई को पतली अवस्था में नहीं प्राप्त कर सकते और न ही आटा प्राप्त कर सकते हैं।
प्रश्न 8.
सारणी में दिए गए परिवर्तन को उत्क्रमणीय और अनुत्क्रमणीय परिवर्तनों में बाँटें।
| परिवर्तन |
परिवर्तन का वर्गीकरण उत्क्रमणीय / अनुत्क्रमणीय |
| कच्चे अंडे से उबला हुआ अंडा | |
| गाढ़े घोल से इडली | |
| साबुत सब्जियों से कटी हुई सब्जी | |
| ऊन के धागे से बुना हुआ स्वैटर | |
| अनाज से बनाया गया आटा | |
| गन्ने से गन्ने का रस | |
| तार से कुंडली | |
| कली से फूल | |
| पत्तियों से कंपोस्ट (खाद) | |
| गाय के गोबर से बायोगैस | |
| रबड़ बैंड को खींचना |
उत्तर-
| परिवर्तन |
परिवर्तन का वर्गीकरण उत्क्रमणीय / अनुत्क्रमणीय |
| कच्चे अंडे से उबला हुआ अंडा | अनुत्क्रमणीय परिवर्तन |
| गाढ़े घोल से इडली | अनुत्क्रमणीय परिवर्तन |
| साबुत सब्जियों से कटी हुई सब्जी | अनुक्रमणीय परिवर्तन |
| ऊन के धागे से बुना हुआ स्वैटर | उत्क्रमणीय परिवर्तन |
| अनाज से बनाया गया आटा | अनुक्रमणीय परिवर्तन |
| गन्ने से गन्ने का रस | अनुत्क्रमनीय परिवर्तन |
| तार से कुंडली | उत्क्रमणीय परिवर्तन |
| कली से फूल | अनुत्क्रमणीय परिवर्तन |
| पत्तियों से कंपोस्ट (खाद) | अनुत्क्रमणीय परिवर्तन |
| गाय के गोबर से बायोगैस | अनुत्क्रमणीय परिवर्तन |
| रबड़ बैंड को खींचना | उत्क्रमणीय परिवर्तन |
| लकड़ी के लट्टे से बुरादा | अनुत्क्रमणीय परिवर्तन |
प्रश्न 9.
मिट्टी खोदने वाले औज़ारों में लोहे के फलक में लकड़ी के हत्थे कैसे जड़े जाते हैं ?
उत्तर-

मिट्टी खोदने वाले औज़ारों में लोहे के फलक में एक वलय होता है जिसमें लकड़ी के हत्थे को फंसा दिया जाता है। साधारणतया इस वलय का आमाप लकड़ी के हत्थे के घेरे से थोड़ा छोटा होता है। हत्थे को वलय में फंसाने के लिए वलय को गर्म करते हैं जिससे उसका आकार बड़ा हो जाता है (फैल जाता है)। अब हत्था आसानी से इसमें जड़ दिया जाता है। जब वलय ठंडा होता है तो सिकुड़ जाता है जिससे यह हत्थे पर कस जाता है। यह बहुत उपयोगी उत्क्रमणीय परिवर्तन है।
प्रश्न 10.
बैलगाड़ी के पहिए पर लोहे का रिम किस प्रकार फिट किया जाता है ? इस प्रक्रिया में किस प्रकार के परिवर्तन का उपयोग होता है?
उत्तर-
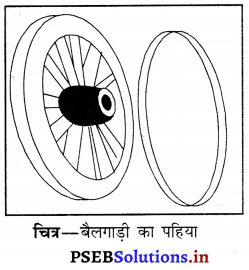
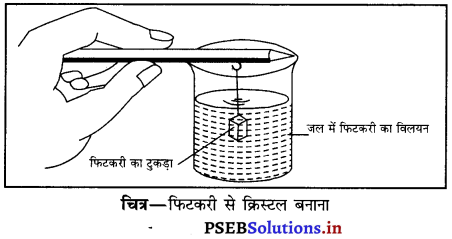
उत्क्रमणीय परिवर्तन का प्रयोग बैलगाड़ी के लकड़ी के पहिए पर लोहे के रिम को कसने के लिए किया जाता है, जैसा कि चित्र में दर्शाया गया है। धातु के रिम को लकड़ी के पहिए के घेरे से थोड़ा-सा छोटा बनाते हैं। गर्म करने पर रिम पहिए पर चढ़ जाता है। अब पहिए के किनारे के ऊपर ठंडा पानी डालते हैं जिससे रिम ठंडा हो जाता है तथा पहिए के ऊपर कस जाता है।
प्रश्न 11.
जब हम जल को गर्म करते हैं तो क्या होता है? क्या यह परिवर्तन उत्क्रमणीय है या अनुत्क्रमणीय और क्यों?
उत्तर-
जब हम जल को बर्तन में गर्म करते हैं तो कुछ समय के बाद यह उबलना शुरू हो जाता है। अगर हम इसे लगातार गर्म करते रहें तो जल की मात्रा बर्तन में कम होना शुरू हो जाती है। जल वाष्प में परिवर्तित हो रहा है। यह परिवर्तन उत्क्रमणीय परिवर्तन है क्योंकि जल वाष्पों को ठंडा करके हम जल को पुनः प्राप्त कर सकते हैं।
प्रश्न 12.
जब हम बर्फ के टुकड़े को गर्म करते हैं तो यह किसमें परिवर्तित होता है ? क्या हम पानी को पुनः बर्फ में बदल सकते हैं?
उत्तर-
जब हम बर्फ को गर्म करते हैं तो बर्फ पिघल कर जल में परिवर्तित हो जाती है। जब हम पानी को अधिक ठंडा करते हैं तो यह पुनः बर्फ में बदल जाता है। इस प्रकार बर्फ का पानी में बदलना और पुनः पानी का बर्फ में परिवर्तित होना उत्क्रमणीय परिवर्तन है।
![]()
प्रश्न 13.
आप मोमबत्ती के जलने के कारण हुए परिवर्तनों का उत्क्रमण क्यों नहीं कर सकते हैं?
उत्तर-
मोमबत्ती के जलने से नए गुणों वाले नए पदार्थ उत्पन्न होते हैं अर्थात् यह एक रासायनिक परिवर्तन है। इसलिए इन परिवर्तनों (बत्ती का जलकर गैस तथा राख बनना) को उत्क्रमित नहीं किया जा सकता है।
7. निबंधात्मक प्रश्न
प्रश्न 1.
निम्नलिखित दिए गए प्रत्येक जोड़े में दो परिवर्तन एक ही प्रकार के आभाषित होते हैं। दोनों में ठीक अंतर बताओ।
(i) गर्म करने पर पिन लाल गर्म हो जाता है। पिन जंग लगने पर लाल हो जाता है।
(ii) दुर्घटना में कार मुड़ जाती है। कार के शरीर की दोबारा आकृति लाना।
(iii) गुब्बारे में हवा भरना। गर्म चूल्हे में आटा फूल जाना।
उत्तर-
(i) जब पिन को लाट पर रखा जाता है, इसका ताप बढ़ जाता है तथा वह लाल गर्म हो जाती है। यह उत्क्रमणीय है। जब लोहे से बनी पिन ऑक्सीजन के साथ मिलती है तो पिन को जंग लग जाता है। जंग लगने से पिन लाल हो जाता है। यह अनुत्क्रमणीय है।
(ii) दुर्घटनाग्रस्त कार का शरीर हानिकारक तथा उत्क्रमणीय परिवर्तन है। कार के शरीर की आकृति वापिस लाना, उत्क्रमणीय परिवर्तन है।
(iii) गुब्बारे को फुलाना उत्क्रमणीय परिवर्तन है। गर्म चूल्हे पर आटे का फूल जाना अनुत्क्रमणीय परिवर्तन है।