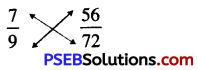
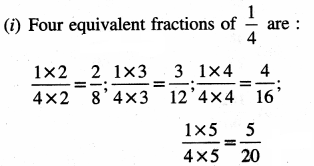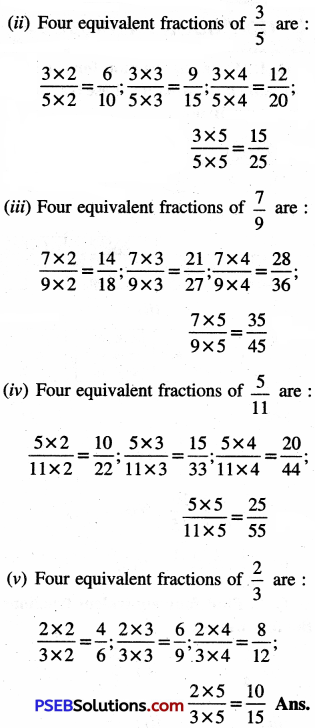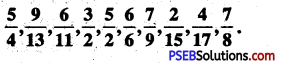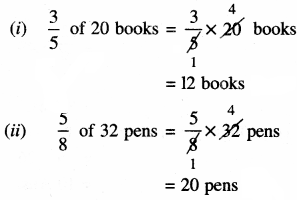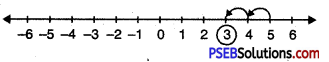Punjab State Board PSEB 6th Class Maths Book Solutions Chapter 5 Fractions Ex 5.1 Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
PSEB Solutions for Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Fractions Ex 5.1
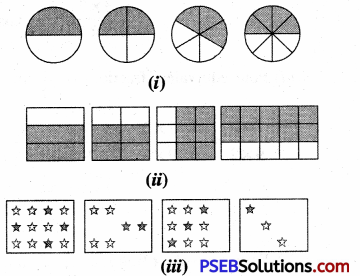
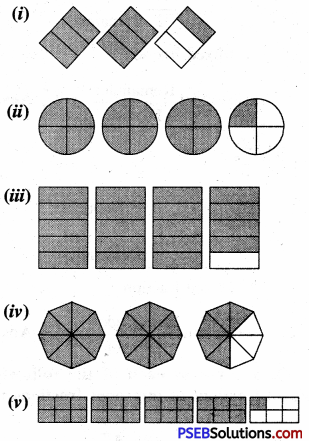
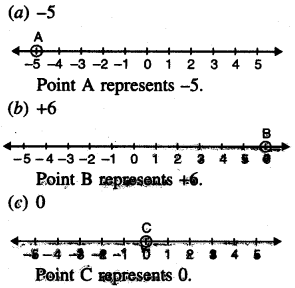
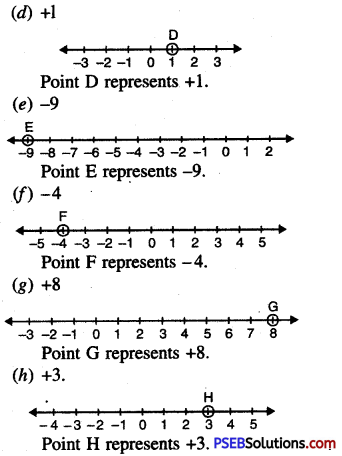
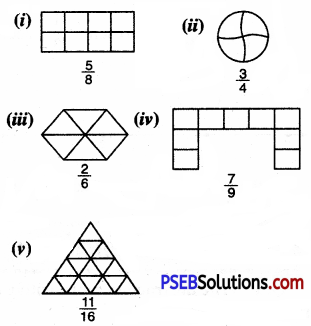
1. Write the fraction representing the shaded portion:
Solution:


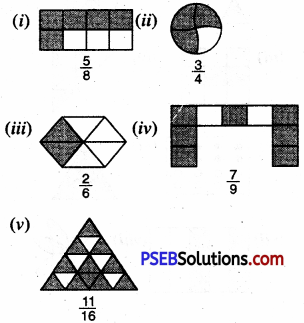
2. Colour the part according to the given fraction:
Solution:
3. Write the fraction for each of the following:
Question (i)
(i) Three-Fourth
(ii) Seven-Tenth
(iii) A Quarter
(iv) Five-Eighth
(v) Three-Twelvth.
Solution:
(i) \(\frac {3}{4}\)
(ii) \(\frac {7}{10}\)
(iii) \(\frac {1}{4}\)
(iv) \(\frac {5}{8}\)
(v) \(\frac {3}{12}\)

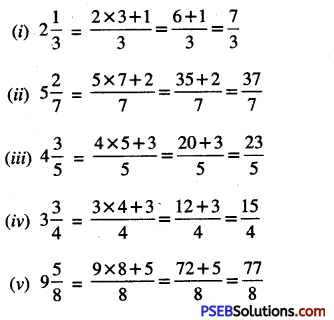
4. Write the fraction for the followings:
Question (i)
numerator = 5
denominator = 9
Answer:
\(\frac {5}{9}\)
Question (ii)
numerator = 2
denominator = 11
Answer:
\(\frac {2}{11}\)
Question (iii)
numerator = 6
denominator = 7
Answer:
\(\frac {6}{7}\)
5. Write the numerator and the denominator for the followings:
Question (i)
\(\frac {2}{3}\)
Solution:
Given fraction is \(\frac {2}{3}\) = \(\frac {Numerator}{Denominator}\)
∴ Numerator = 2
and Denominator = 3
Question (ii)
\(\frac {1}{4}\)
Solution:
Given fraction is \(\frac {1}{4}\) = \(\frac {Numerator}{Denominator}\)
∴ Numerator = 1
and Denominator = 4

Question (iii)
\(\frac {5}{11}\)
Solution:
Given fraction is \(\frac {5}{11}\) = \(\frac {Numerator}{Denominator}\)
∴ Numerator = 5
and Denominator = 11
Question (iv)
\(\frac {9}{13}\)
Solution:
Given fraction is \(\frac {9}{13}\) = \(\frac {Numerator}{Denominator}\)
∴ Numerator = 9
and Denominator = 13
Question (iv)
\(\frac {17}{16}\) = \(\frac {Numerator}{Denominator}\)
∴ Numerator = 17 and
Denominator = 16
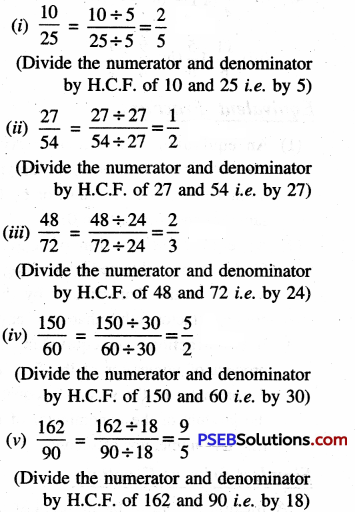
6. Express:
Question (i)
1 day as a fraction of 1 week.
Solution:
We know 1 week = 7 days
∴ Required fraction= \(\frac {1}{7}\)
Question (ii)
40 seconds as a fraction of 1 minute.
Solution:
We know 1 minute = 60 seconds
∴ Required fraction = \(\frac {40}{60}\) or \(\frac {2}{3}\)
(Dividing both terms by 20)

Question (iii)
15 hours as fraction of 1 day.
Solution:
We know 1 day = 24 hours
∴ Required fraction = \(\frac {15}{24}\) or \(\frac {5}{8}\)
(Dividing both terms by 3)
Question (iv)
2 months as a fraction of 1 year.
Solution:
We know 1 year = 12 months
∴ Required fraction = \(\frac {2}{12}\) or \(\frac {1}{6}\)
(Dividing both terms by 2)
Question (v)
45 cm as a fraction of 1 metre.
Solution:
We know 1 metre = 100 cm
∴ Required fraction = \(\frac {45}{100}\) or \(\frac {9}{20}\)
(Dividing both terms by 5)
7. Write the numbers from 1 to 25.
Question (i)
What fraction of them are even numbers?
Solution:
Numbers from 1 to 25 are:
1,2, 3, 4,5,6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25 i.e. 25 in number.
Even numbers out of these numbers are:
2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18; 20, 22, 24 i.e. 12 in number
∴ Required fraction = \(\frac {12}{25}\)

Question (ii)
What fraction of them are prime numbers?
Solution:
Prime number out of these numbers are:
2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23 i.e. 9 in number
∴ Required fraction = \(\frac {9}{25}\)
Question (iii)
What fraction of them are multiples of 3?
Solution:
Multiples of 3 out of these numbers are:
3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21, 24 i.e. 8 in number
∴ Required fraction = \(\frac {8}{25}\)
8. In class 6th, there are 24 boys and 18 girls. What fraction of total students represent boys and girls?
Solution:
Boys = 24
Girls = 18
Total students = 24 + 18 = 42
Fraction which represents boys
= \(\frac {24}{42}\) or \(\frac {4}{7}\)
(Dividing both terms by 6)
Fraction which represents girls
= \(\frac {18}{42}\) or \(\frac {3}{7}\)
(Dividing both terms by 6)
9. A bag contains 6 red balls and 7 blue balls. What fraction of balls represent red and blue colour?
Solution:
Red balls = 6
Blue balls = 7
Total number of red and blue balls = 6 + 7 = 13
Fraction which represents red balls = \(\frac {6}{13}\)
Fraction which represents blue balls = \(\frac {7}{13}\)

10. Sidharth has a cake. He cuts it into 10 equal parts. He gave 2 parts to Naman, 3 parts to Nidhi, 1 parts to Seema and the remaining four parts he kept for himself. Find:
Question (i)
What fraction of cake, he gave to Naman?
Solution:
Total parts = 10
Fraction of cake, he gave to Naman = \(\frac {2}{10}\) or \(\frac {1}{5}\)
Question (ii)
What fraction of cake, he gave to Nidhi?
Solution:
Fraction of cake, he gave to Nidhi = \(\frac {3}{10}\)
Question (iii)
What fraction of cake, he kept for himself?
Solution:
Fraction of cake, he kept for himself = \(\frac {4}{10}\) or \(\frac {2}{5}\)
Question (iv)
Who has more cake than others?
Solution:
Sidharth has more cake than others
11. In a box, there are 12 apples, 7 oranges and 5 guavas. What fraction of fruits in box represents each?
Solution:
Apples = 12, Oranges = 7
and Gauvas = 5
Total fruits = 12 + 7 + 5 = 24.
Fraction which represents apples
= \(\frac {12}{24}\) or \(\frac {1}{2}\)
Fraction which represents oranges
= \(\frac {7}{24}\)
Fraction which represents Gauvas
= \(\frac {5}{24}\)

12. Dishmeet has 20 pens. He gives one-fourth to Balkirat. How many pens Dishmeet and Balkirat have?
Solution:
Total pens = 20
Pens Balkirat has = One-fourth of 20
= \(\frac {22}{7}\) × 20 = 5
Pens Dishmeet has = 20 – 5 = 15
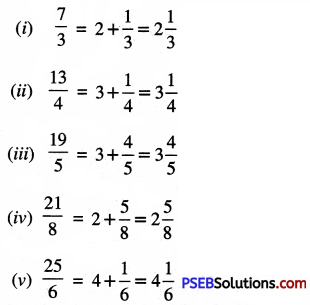
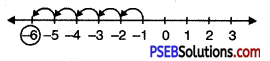
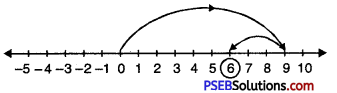
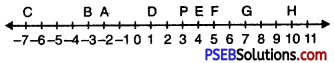
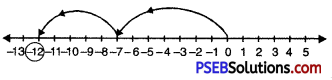
13. Represent the following fraction on the number line?
Question (i)
\(\frac {2}{5}\)
Solution:
In order to represent \(\frac {2}{5}\) on number line, we divide the gap between 0 and 1 into 5 equal parts, which are, (as shown)

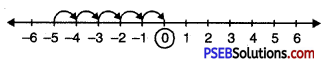
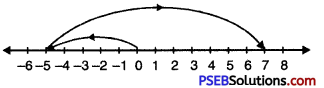
Question 2.
\(\frac {5}{7}\)
Solution:
In order to represent \(\frac {5}{7}\) on number line, we divide the gap between 0 and 1 into 7 equal parts, which are, (as shown)


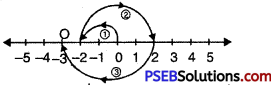
Question 3.
\(\frac {3}{10}\), \(\frac {5}{10}\), \(\frac {1}{10}\)
Solution:
In order to represent \(\frac {3}{10}\), \(\frac {5}{10}\), \(\frac {1}{10}\) on number line, we divide the gap between 0 and 1 into 10 equal parts, which are (as shown)

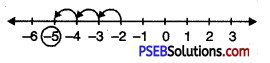
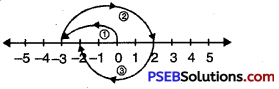
Question 4.
\(\frac {3}{8}\), \(\frac {5}{8}\), \(\frac {7}{8}\)
Solution:
In order to represents \(\frac {3}{8}\), \(\frac {5}{8}\), \(\frac {7}{8}\) on number line, we divide the gap between 0 and 1 into 8 equal parts, which are (as shown)

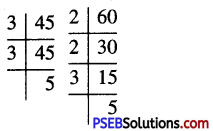
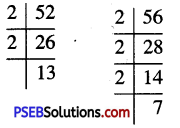
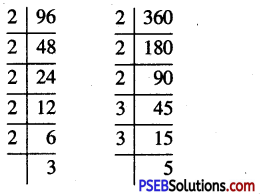
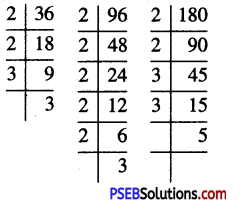
14. Find:
(i) \(\frac {3}{5}\) of 20 books
(ii) \(\frac {5}{8}\) of 32 pens
(iii) \(\frac {1}{6}\) of 36 copies 6
(iv) \(\frac {4}{7}\) of 21 apples
(v) \(\frac {3}{4}\) of 28 pencils.
Solution:
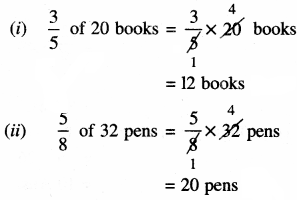


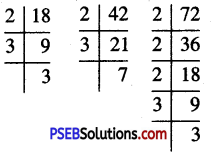
15. Balkirat had a box of 36 erasers. He gave \(\frac {1}{2}\) of them to Rani, \(\frac {2}{9}\) of them to Yuvraj and keeps the rest.
Question (i)
(i) How many erasers does Rani get?
(ii) How many erasers does Yuvraj get?
(iii) How many erasers does Harnik keep?
Solution:
Total erasers = 36
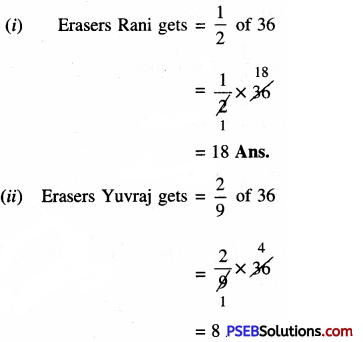
(iii) Erasers Harnik gets = 36 – (18 + 8)
= 36 – 26
= 10
16. State True/False
Question (i)
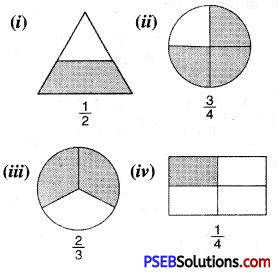
Solution:
(i) False
(ii) True
(iii) True
(iv) True
![]()

![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()