Punjab State Board PSEB 6th Class Science Book Solutions Chapter 14 Water Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
PSEB Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 14 Water
Science Guide for Class 6 PSEB Water Intext Questions and Answers
Think and Answer (Textbook Page No. 145)
Question 1.
Does every person use same quantity of water every day ?
Answer:
No, every person does not use same quantity of water every day.
Think and Answer (Textbook Page No. 146)
Question 1.
What happens to ice-cream when it is taken out of the refrigerator ?
Answer:
It melts.
Question 2.
What is the state of ice-cream ?
Answer:
Solid.
![]()
Think and Answer (Textbook Page No. 147)
Question 1.
What happens when you spill water on the floor in hot summer days ?
Answer:
It evaporates
Question 2.
Why cow’ dung cakes are kept in sunlight ?
Answer:
To become dry as a result of evaporation of water.
Think and Answer (Textbook Page No. 148)
Question 1.
Why do we observe water droplets outside water bottle when taken out from a refrigerator ?
Answer:
The temperature outside refrigerator is warmer and when the bottle comes out of refrigerator, the water vapour present in air condenses and forms droplets of water on surface of bottle. This process is known as condensation.
PSEB 6th Class Science Guide Water Textbook Questions and Answers
Fill in the Blanks:
(a) The process of changing of water into its vapour is called ………………….
Answer:
evaporaion
(b) The process of changing water vapour into water is called …………………
Answer:
condensation
(c) No rainfall for a year or more may lead to ……………… in that region.
Answer:
drought
(d) Excessive rains may cause …………………..
Answer:
clood
(e) Three states of water are …………………….. , ……………….. and ………………. .
Answer:
solid, liquid and gas
![]()
(f) In plants, transpiration takes place through …………….
Answer:
stomata
2. Write True or False:
(a) Ice on cooling changes to steam.
Answer:
Flase
(b) Evaporation of water takes place in sunlight.
Answer:
Flase
(c) We should not repair the pipe having leakage.
Answer:
Flase
(d) Water in ocean is fit for drinking.
Answer:
Flase
(e) Drip irrigation method is useful for farming.
Answer:
True
3. Match the Column A with Column B:
| Column A | Column B |
| 1. Water conservation | (a) Solid form of water |
| 2. Snow | (b) Sunny day |
| 3. Precipitation | (c) Rainwater harvesting |
| 4. Evaporation | (d) Ground water |
| 5. Fresh water | (e) Rain from clouds |
Answer:
| Column A | Column B |
| 1. Water conservation | (c) Rainwater harvesting |
| 2. Snow | (a) Solid form of water |
| 3. Precipitation | (e) Rain from clouds |
| 4. Evaporation | (b) Sunny day |
| 5. Fresh water | (d) Ground water. |
![]()
4. Choose the Correct Answer:
Question (i)
How much part of earth is covered with water ?
(ci) two third
(b) half
(c) one third
(d) three fourth.
Answer:
(d) three fourth
Question (ii)
Fog appearing on a cold winter morning is the result of:
(a) Condensation
(b) evaporation
(c) Precipitation
(d) none.
Answer:
(a) Condensation
Question (iii)
Which of the source of water is not used for drinking?
(a) river
(b) ocean
(c) dam
(d) lake.
Answer:
(b) ocean
Question (iv)
Process of conversion of gas into liquid is called:
(a) Evaporation
(b) Melting
(c) Condensation
(d) Boiling.
Answer:
(c) Condensation
Question (v)
About how much percentage of water is present in human body:
(a) 60%
(b) 70%
(c) 80%
(d) 90%.
Answer:
(b) 70%
5. Very Short Answer Type Questions:
Question (i)
What are two main sources of water ?
Answer:
Main sources of water are surface water and ground water.
Question (ii)
What is the advantage of drip irrigation ?
Answer:
Advantage of drip irrigation is that water and other nutrients are directly delivered to plants.
Question (iii)
What is the effect of temperature on evaporation ?
Answer:
The rate of evaporation increases with increase of temperature.
![]()
Question (iv)
Differentiate between ground water and surface water.
Answer:
Ground water is found below the surface of earth and is safe for drinking.
Surface water is found in lakes, rivers, wells and reservoirs.
Question (v)
What is transpiration ?
Answer:
The process by which water is lost in the air by plants is called transpiration.
6. Short Answer Type Questions:
Question (i)
Explain floods and its effects.
Answer:
The overflow of large amount of water beyond its normal limits is known as flood. Effects of Flood.
- Many people and animals die.
- Some people become homeless.
- Wide-spread of communicable diseases.
Question (ii)
Define condensation. Give two examples.
Answer:
The process of conversion of gaseous form back to liquid form is called condensation.
Examples are :
- Fogging of windshield or rear view of car.
- Dew on leaves of grass on a winter morning.
Question (iii)
Explain formation of clouds.
Answer:
When we go higher from the surface of earth, the temperture falls. The air becomes so cool that the water vapours condense to form water droplets. These water droplets together in air are clouds.
Question (iv)
Write three ways to conserve water.
Answer:
Three ways to conserve water are :
- Rain water harvesting
- Recycling of water
- Turning off tap when not in use.
Question (v)
What is drought and what are its effects ?
Answer:
A period when there is very little or no rainfall is called drought. Effects of Drought :
- Soil becomes dry and infertile due to loss of water.
- Ponds become dry and level of water in wells goes down.
![]()
7. Long Answer Type Questions:
Question (i)
Explain the uses of water.
Answer:
Water is a very vital resource and is used for many purposes. Some of the uses of water are mentioneded below :
Uses of Water.
- It maintains temperature on earth.
- It is used for drinking, bathing, washing, etc.
- Running or flowing water is used for generating electricity.
- It is used for irrigation of crops.
- It is also used for cleanng, cooking, watering plants, etc.
Question (ii)
Explain water cycle with diagram.
Answer:
Water cycle in nature. Water falls on earth in the form of rain, dew, snow etc. This
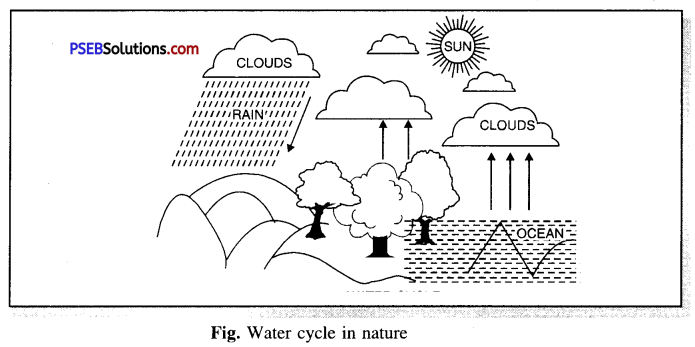
water falls in ponds, streams, oceans and some water seeps down the earth. With the heat of sun, the water evaporates from the streams, ponds, oceans etc. and fills the atmosphere with water vapours. These water vapours on cooling get condensed and form clouds. These clouds come back on earth in form of rains. So, this cycle goes on.
Question (iii)
Why there is need to conserve water ? Write technique of rain water harvesting.
Answer:
Fresh water is only 2.59% on earth and is in very low amount that can be used for drinking or human consumption. So, we must conserve the water.
Rain Harvesting. It is a technique which involves collection and storage of rain water and its reuse, it is the simplest and oldest method.
Techniques of rain harvesting. The most commonly used technique used for rain water harvesting is roof top rain water harvesting.
Roof Top Rain Water harvesting. In this rain water is collected on the roof of house and then stored in storage tank through pipes. This stored water can be used for any purpose.

PSEB Solutions for Class 6 Science Water Important Questions and Answers
Multiple Choice Questions:
Question 1.
The process of conversion of water into vapours is:
(a) Evaporation
(b) Transpiration
(c) Condensation
(d) None.
Answer:
(a) Evaporation
Question 2.
The process of converting water vapours into water is:
(a) Evaporation
(b) Transpiration
(c) Condensation
(d) None.
Answer:
(c) Condensation
Question 3.
We use water in:
(a) Industry
(b) Agriculture
(c) Domestic needs
(d) Industry agriculture and domestic needs.
Answer:
(d) Industry agriculture and domestic needs.
![]()
Question 4.
Saline water is found in:
(a) Seas
(b) Taps
(c) Lakes
(d) nowhere.
Answer:
(a) Seas
Question 5.
Hot air causes:
(a) Transpiration
(b) Evaporation
(c) Condensation
(d) None.
Answer:
(b) Evaporation
Question 6.
Water cycle is a phenomenon:
(a) Fast
(b) Slow
(c) Medium
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(b) Slow
Question 7.
To get 1 kg of wheat grains evaporated. from wheat plant litre water gets
(a) 100
(b) 200
(c) 400
(d) 500.
Answer:
(d) 500
Question 8.
Excessive rainfall causes:
(a) Drought
(b) Flood
(c) Storm
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(b) Flood
Question 9.
of earth is covered with water.
(a) 33%
(b) 67%
(c) 25%
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(b) 67%
Question 10.
Water is available in plenty from:
(a) River
(b) Well
(c) Sea
(d) Rain.
Answer:
(c) Sea
![]()
Question 11.
Change of water vapours into water is called:
(a) Vaporisation
(b) Transpiration
(c) Condensation
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(a) Vaporisation
Question 12.
Change of water vapours into water is called:
(a) Evaporation
(b) Transpiration
(c) Condensation
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(c) Condensation
Fill in the Blanks:
(a) We use water for many …………….. .
Answer:
activities
(b) We get water from …………… .
Answer:
taps
(c) ……………. , ……………… and …………… are sources of water.
Answer:
Ponds, lakes, wells
(d) About …………… of earth is covered with water.
Answer:
2/3rd
(e) ………………. water is saline.
Answer:
Sea
(f) ………………… is needed to convert water into water vapour.
Answer:
Heat
![]()
(g) The warm air provides heat for evaporation of water in ……………… areas.
Answer:
shady
(h) About …………….. litres of water is transpirated by wheat plants to provide 1 kilogram of wheat.
Answer:
500
(i) Clouds are ………………. that remain floating in air.
Answer:
tiny droplets
(j) Snow is another form of ……………… .
Answer:
water
(k) Open wells are fed by ………….. .
Answer:
ground water
(l) Water cycle is a ……………. process.
Answer:
slow
(m) Excess rainfall leads to many ………………..
Answer:
problems
![]()
(n) In ……………… conditions, food and fodder are scarce.
Answer:
drought
(o) The ………………. of water is increasing day-by-day.
Answer:
demand
(p) Collecting rain water is ……………… .
Answer:
rain water harvesting
(q) Excess rains are cause of …………….. .
Answer:
floods
Write (T) against true and (F) against false statements.
(a) Every region in the world get same amount of water.
Answer:
False
(b) Plants need water to grow.
Answer:
True
(c) Industries have no use of water.
Answer:
False
(d) Water can evaporate from any place either in shade or sunlight.
Answer:
True
(e) Plants transpirate water in the absence of sunlight.
Answer:
True
![]()
(f) Heating increases the evaporation.
Answer:
True
(g) Clouds are nothing but condensed water.
Answer:
True
(h) Never waste water.
Answer:
True
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
In which structures, the vast quantity of water is available ?
Answer:
Seas or Oceans.
Question 2.
What is nature of water in seas ?
Answer:
Salty (Saline).
Question 3.
When water evaporates from the seas, lakes, rivers etc, what happens to the salts dissolved in it ?
Answer:
Salts remain behind.
Question 4.
Is evaporation a fast process ?
Answer:
No, it is a slow process.
Question 5.
What is dew ?
Answer:
Dew is condensed water vapour.
![]()
Question 6.
What is rain ?
Answer:
Falling of droplets on earth after becoming heavy is rain.
Question 7.
Besides rain, how water returns to the earth ?
Answer:
In the form of hail or snow.
Question 8.
Evaporation, Transpiration, Condensation are processes of which cycle ?
Answer:
Water cycle.
Question 9.
What is ground water ?
Answer:
Rain water seeps into the soil and gets collected on a rock. This collected water is ground water. It is pure.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Write few uses of water.
Answer:
Uses of water.
- For drinking, bathing, washing etc.
- For cooking, cleaning, watering the plants etc.
- For crop growth.
- For generating electricity.
- In many industries like textile industries and food processing industries.
Question 2.
What is evaporation ? Which factors increase the evaporation ?
Answer:
Evaporation. The process of conversion of liquid into its vapours is called evaporation. Factors responsible for increasing evaporation are :
- Wind. More wind results in speedy evaporation
- Sunlight. More sunlight increases the speed of evaporation. This is why evaporation is fast during summer and slow during winter.
- Exposed Surface Area. When the surface area is large, the speed or rate of evaporation is high.
- Humidity. If the humidity in the surrounding is high then the speed of evaporation is low and if the humidity is low then the rate of evaporation is low.
Question 3.
Water disappears from the wet clothes. Why ?
Answer:
Heat from sun converts water into water vapours which get disappeared in the air.
Question 4.
What are clouds ?
Answer:
Clouds are nothing but condensed water vapours in the sky.
![]()
Question 5.
Why is sea water not fit for drinking purposes ?
Answer:
Sea water contains many salts in it thus giving water a salty or saline taste. This salty water is not fit for drinking purposes.
Question 6.
What are effects of excessive rains ?
Answer:
Effects of excessive rains.
- Excessive rains will increase the level of water in ponds, rivers, seas etc. resulting in floods.
- Excessive rains can result in floods. These floods can cause damage to property, life and crops.
Question 7.
What is rain water harvesting ? Why is it done ?
Answer:
Rain water harvesting. The collection of rain water in tanks etc. is called rain water harvesting.
Need of rain water harvesting. We must do rain harvesting because of the following reasons :
- To increase the availability of water.
- To store water for later use when its scarcity is felt.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
List sources of water. Explain briefly.
Answer:
Sources of water. At homes we get water from taps, but the main sources of water are :
(i) Ponds
(ii) Lakes
(iii) Rivers
(iv) Wells
(v) Sea water
(vi) Rain.
(i) Ponds. Ponds are low lying areas in which rain water or river water gets collected.
(ii) Lakes. Lakes are natural sources of water. They may contain salts in them.
(iii) Rivers. Rivers contain water formed by melting of snow on the mountains. These rivers many be flowing all year round or temporarily during a particular season. These rivers also have rain water in it. There may be or may not be impurities in them.
(iv) Wells. A part of rain-water seeps into the ground through soil. It reaches the bottom areas of earth’s crust and collects there as a water body. This water is put to use by bor wells and hand pumps.
(v) Sea water. Oceans are big reservoirs of water. Most of the rivers fall into the sea and thus carry dissolved salts and impurities into the sea. That is why, sea water is salty in taste.
(vi) Rain. The rain drops in the form of a cloud are almost pure. But rain water gets contaminated due to gases from atmosphere, particulate matter, acid fumes and micro-organisms floating in the air. We get rain only during specific period i.e. monsoon season in our country.
Question 2.
What is Rain ? What will happen if it does not rain at all ?
Answer:
Rain. When the water vapours in the cloud become too heavy, it falls back to the ground as rain. The earth receives heavy rain at some part of the year. Some parts do not get enough of rainfall. It affects the human, plants and animal life. If at certain places there will not be rain for a year then the soil becomes dry and drought. As most of the soil water evaporates and transpirates from the plants, rivers, ponds and wells, it will dry and water table would lower down. All this affects the humans, animals and wild plants. If it continues for one or two years in continuation, it results into drought.
Question 3.
What will happen if it keeps raining continuously ?
Answer:
Consequences of continuous rains. Rains bring a lot of enjoyment and pleasant weather especially after hot days. However, if it rains heavily, you might have noticed water getting collected here and there and at times causing disruption of normal life.
In case of continuous rains the water level of rivers, lakes and ponds will rise. The soil surface will get laden with water resulting into flood. When the soil gets too much of water, air in the soil comes out of it. Due to lack of air the animals living inside the soil also come out of it. Heavy rains also result in the loss of crops due to overflooding.
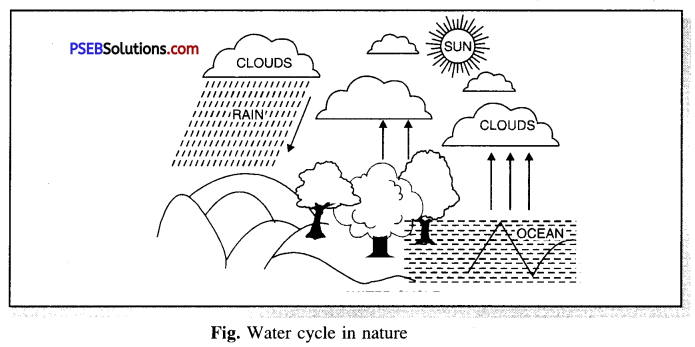
Question 4.
Explain and draw a neat diagram of water cycle in nature.
Answer:
Answer:
Water cycle in nature. Water falls on earth in the form of rain, dew, snow etc. This
waterfalls in ponds, streams, oceans, and some water seep down the earth. With the heat of the sun, the water evaporates from the streams, ponds, oceans, etc., and fills the atmosphere with water vapours. These water vapours on cooling get condensed and form clouds. These clouds come back on earth in form of rains. So, this cycle goes on.