Punjab State Board PSEB 6th Class Computer Book Solutions Chapter 3 Basics of Working with Computers Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
PSEB Solutions for Class 6 Computer Science Chapter 3 Basics Of Working With Computers
Computer Guide for Class 6 PSEB Basics Of Working With Computers Textbook Questions and Answers
1. Fill in the Blanks
Question 1.
Screen appeared after login of Computer is called:
(a) Start Menu
(b) Desktop
(c) Taskbar
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(b) Desktop
Question 2.
All the Deleted files go to?
(a) My Computer
(b) Network
(c) Recycle bin
(d) All of above.
Answer:
(c) Recycle bin
![]()
Question 3.
Which part of window remains visible all the time when we use other applications?
(a) Recycle bin
(b) Desktop
(c) Taskbar
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(c) Taskbar
Question 4.
Which one is an example of Operating System?
(a) Windows
(b) Android.
(c) DOS
(d) Ail of above.
Answer:
(d) All of adove
Question 5.
To open a file we can double click on:
(a) File itself
(b) Shortcut of file
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(c) Both (a) and (b).
2. Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Write the name of any three window applications.
Answer:
The three window based applications are:
- Notepad
- Wordpad
- Calculator.
Question 2.
Write the name of any three Icons.
Answer:
The names of three icons are:
- My computer
- Network
- Recycle Bin
Question 3.
Write the names of components of a Desktop.
Answer:
The Components of Desktop are icon, taskbar and wallpaper.
![]()
Question 4.
What is Desktop?
Answer:
Desktop is a screen which is displayed on the monitor after the user logs in to the computer. It is just like the dashboard of the computer. It may contain an icon on Taskbar and wallpaper.
3. Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is Operating System? Explain different types of Operating Systems.
Answer:
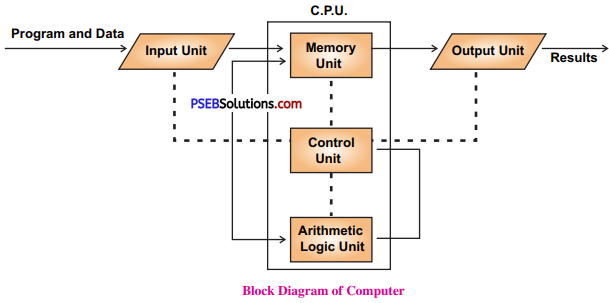
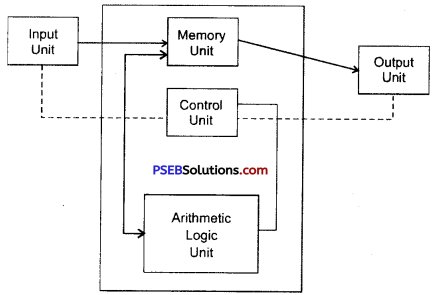
Operating system is a system software without which a computer cannot work. IT acts as an interface between the hardware and the user. Each computer has an operating system installed on it. Operating system is displayed in the form of screens, menus, dialogue box, icons and widgets etc.
Definition of Operating System:
An Operating System is an interface between a computer user and computer hardware. It makes computer hardware work by controlling all the internal processes of the computer. There are many types of operating system. Each operating system is developed for different types of machines. Each operating system has a different set of commands and it understands the machine architecture very well.
1. Windows:
Windows is an operating system developed by Microsoft. It. is a graphical user interface. It means it is easy to work with pointing devices such as mice in windows. Most of the computers in this world are using windows operating systems. Everything is displayed in a rectangular frame on the screen in this operating system. That is by which operating system is named as windows. It is the most popular operating system in the world.
![]()
2. DOS:
DOS stands for Disc Operating System. This operating system is also developed by Microsoft. It is a character user interface operating system. This operating system is not very powerful. The user types commands to instruct the computer. This operating system was used on computers with small memory and low speed hardware. The user has to remember a lot of commands to work in it. That is why it was difficult to work in this operating system. Also the user cannot do a variety of work simultaneously in this operating system.
3. Android:
The Android operating system is one of the latest operating systems in digital word. It is the operating system which is used in mobile phones. This operating system was developed by Google. This operating system is developed for devices which have touchscreen in them. It provides a very beautiful and convenient interface which can be used by finger touch. The user can do the tasks like pinching, swiping and typing. Now the Android operating system is also used in televisions, cars, wrist watches and many other digital devices. Each of these devices have different user interfaces.
Question 2.
What is a Taskbar ? Explain the functions of its parts.
Answer:
Taskbar is located at the bottom of the screen. This bar is a part of the Operating System. It allows us to start a program using the Start menu. This bar always remains visible during working in any application. We can navigate through Active programs using the taskbar. The area on the right side of the taskbar is called “Notification Area”. This area allows us to check date and time, items running in the background etc.
The taskbar was first introduced with Microsoft Windows 95 and is found in all subsequent versions of Windows. We can have a look of taskbar and its all parts as under :
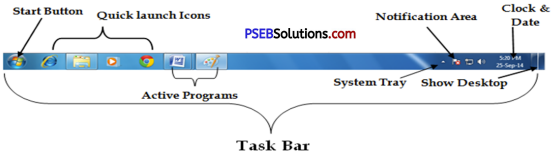
All these parts of the taskbar are having their own functions. Let’s discuss the use of each one of them. It. has a logo of windows on it. It is the first item on Taskbar. Its icon is :
- Start Button : We can start any application and program with the help of the Start button.
- Quick Launch Bar : This section of the taskbar enables us to launch programs without locating them from the Start menu. It is located next to the Start button.
- System Tray : It is located at the right side of Taskbar. It contains miniature icons for easy access to system functions such as fax, printer, modem, volume etc.
- Notification Area : This area is a part of the taskbar that provides notifications and status of devices. It can also be used to display icons for system and program features that are not on the desktop.
- Clock : At the end of taskbar, Clock is displayed where Current Time and Date can be seen. We can change Time and Date by clicking on it. It requires Administration access to change the Time or Date.
- Active Programs : This area of taskbar is between quick access bar and System Tray area. In this area of taskbar, all the active programs appeared as an icon and we can easily navigate among them.
Question 3.
What do you mean by Icon ? Explain any three Desktop Icons.
Answer:
Icons are the small pictures on the desktop. These icons represent a file or a program or folder on the computer. The user has to click on this icon to open.dat file or program. The following types of icons are available on Windows desktop.
1. My Computer:
This icon is used to assess the hard disc of the computer. This icon opens a window on the computer screen which displays all the hard disks attached to the computer and other removable media such as pen drives or CDs. The user can work in this window, no
2. Network:
This icon is used to connect to the network location attached to this computer system. This icon is used when the computer is connected to a local area. This icon displays icons of all the computer systems which are connected to users’ computers through Local area networks. The user can go to the other computer and work on files.
![]()
3. Recycle Bin:
Recycle Bin is a folder which works like a dustbin. In this folder contains all the deleted files folder icons on the computer. When anything is not required on the computer system the user can delete that item. That item is shifted to the recycle bin folder. If the user deletes an item accidentally he can restore that item from the recycle bin.
Question 4.
Explain the different options of shutting down a Computer System. ’
Answer:
Windows provide following shutting down options:
1. Sleep:
Sleep means letting the computer system to sleep without shutting it down. This option menu can be used when we want to leave a computer for some time. During this mode, the power of Monitor/LCD gets OFF and all your data is kept safe. When we put a computer into sleep mode then its power remains ON and its power light starts blinking. This blinking Red-Colour LED on the CPU shows that the computer is in sleep Mode. We can press the power button to resume the computer from this mode.
2. Shut Down:
Shut down means stopping all the processes which the computer is running.This option of Power menu can be used when we have finished all our work. When we shut-down a computer, all parts of computer systems are turned off and no power remains active in the Computer System. We can switch off the main power-supply of the computer when it is shut down. This process can take some time and we must wait till it is over. This process may take time according to the size of data being used and number of programs currently running.
3. Log Off:
Logging off means the process of disconnecting the current user from working and taking the user to the login screen. Windows 7 allows us to access a computer differently among users. We can keep our data secure from other users with the help of user accounts in it. If we have finished our work and want to leave a computer but another user is there to access the same computer for own work in a different user account then we can use the Log-off option of Power Menu.
4. Restart:
Restart means shutting down the computer and then starting it again by the computer itself. This option of power menu can be used when any new program is installed or any updation in the system is done. Sometimes when a new device or hardware is attached to the computer, it is required to restart our computer. In such a case, we can use the restart option of the Power menu to shut down our computer and start it again. When the restart button is pressed then the computer automatically gets started after being shut-down.
Activity
Name the Following Icons:

Answer:
- Notepad
- MS Paint
- Calculator
- My Computer
- Network
- Recycle bin
- Start button.
PSEB 6th Class Computer Guide Basics of Working with Computers Important Questions and Answers
1. Fill in the Blanks
Question 1.
The Primary screen (first to open) of computer is called
(a) My Network
(b) Icon
(c) Desktop
(d) Recycle Bin.
Answer:
(c) Desktop
Question 2.
The bar lying at the bottom of the desktop is called
(a) Title Bar
(b) Status Bar
(c) Task Bar
(d) Scroll Bar.
Answer:
(c) Task Bar
Question 3.
The bar present at the top of the window is called
(a) Title Bar
(b) Status Bar
(c) Task Bar
(d) Scroll Bar.
Answer:
(a) Title Bar
![]()
Question 4.
Deleted files go to
(a) My Network
(b) My Documents
(c) My Computer
(d) Recycle Bin.
Answer:
(d) Recycle Bin
Question 5.
button is used to close the window.
(a) Minimize
(b) Maximize
(c) Close
(d) Start.
Answer:
(c) Close.
2. Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is operating system ?
Answer:
Operating system is an interface between user and computer.
Question 2.
What is windows ?
Answer:
Windows is an operating system of Microsoft company.
Question 3.
What is Windows Desktop ?
Answer:
The basic screen of computer is called desktop. It is seen after booting of windows. All the programs in windows are run with the help of desktop. The on-screen work area on which windows, icons, menus, and dialog boxes appear.
Question 4.
What are Icons ? Name any three types of Icons.
Answer:
A small image displayed on the screen to represent an object that can be manipulated by the user. Icons serve as visual mnemonics and allow the user to control certain computer actions without having to remember commands or type them at the keyboard.
Three Types if Icons are:
- My Computer
- My Document
- Recycle Bin
Question 5.
Name different components of windows.
Answer:
- Title Bar
- Menu Bar
- Scroll Bar
- Minimize Button
- Maximize Button
- Close Button.
Question 6.
Write down about Show Desktop button on Taskbar.
Answer:
Desktop is the first screen displayed when you start your computer. Icons, menus, dialog boxes, start button and taskbar are the part of desktop screen.
![]()
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Explain Taskbar.
Answer:
Taskbar is located at the bottom of the screen. This bar is a part of the Operating System. It allows us to start a program using the Start menu. This bar always remains visible during working in any application. We can navigate through Active programs using the taskbar. The area on the right side of the taskbar is called “Notification Area”. This area allows us to check date and time, items running in the background etc.
The taskbar was first introduced with Microsoft Windows 95 and is found in all subsequent versions of Windows. We can have a look of taskbar and it’s all parts as under:

All these parts of the taskbar are having their own functions. Let’s discuss the use of each one of them. It has a logo of windows on it. It is the first item on Taskbar. Its icon is :
(i) Start Button : We can start any application and program with the help of the Start button.
(ii) Quick Launch Bar : This section of the taskbar enables us to launch
programs without locating them from the Start menu. It is located next to the Start button. –
(iii) System Tray : It is located at the right side of Taskbar. It contains miniature icons for easy access to system functions such as fax, printer,
modem, volume etc.
(iv) Notification Area : This area is a part of the taskbar that provides notifications and status of devices. It can also be used to display icons for system and program features that are not on the desktop.
(v) Clock : At the end of taskbar, Clock is displayed where Current Time and Date can be seen. We can change Time and Date by clicking on it. It requires Administration access to change the Time or Date.
(vi) Active Programs : This area of taskbar is between quick access bar and System Tray area. In this area of taskbar, all the active programs appeared as an icon and we can easily navigate among them.
![]()
Question 2.
What do you mean by Recycle Bin ?
Answer:
Icons are the small pictures on the desktop. These icons represent a file or a program or folder on the computer. The user has to click on this icon to open.dat file or program. The following types of icons are available on Windows desktop.
1. My Computer : This icon is used to assess the hard disc of the computer. This icon opens a window on the computer screen which displays all the hard disks attached to the computer and other removable media such as pen drives or CDs. The user can work in this window.

2. Network : This icon is used to connect to the network location attached to this computer system. This icon is used when the computer is connected to a local area. This icon displays icons of all the computer systems which are connected to users’ computers through Local area networks. The user can go to the other computer and work on files.

3. Recycle Bin : Recycle Bin is a folder which works like a dustbin. In this folder contains all the deleted files, folder, icons on the computer. When anything is not required on the computer system the user can delete that item. That item is shifted to the recycle bin folder. If the user deletes an item accidentally he can restore that item from the recycle bin.

4. Users File : This icon is used to assess the current user data. Thus it can hold all the default locations for the different types of files. It may include my documents, my pictures, my videos desktop etc. The name of this icon changes as per the user logged in.