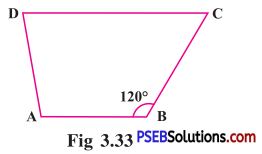
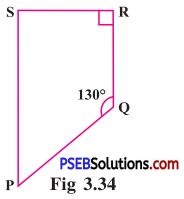
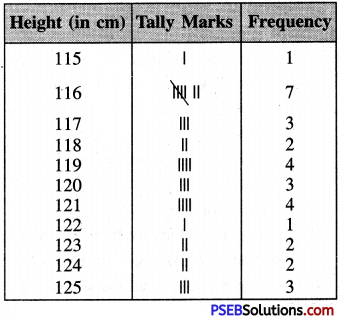
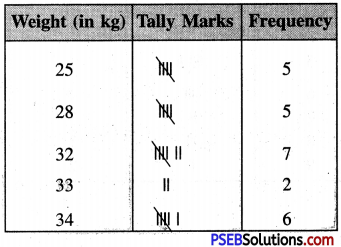
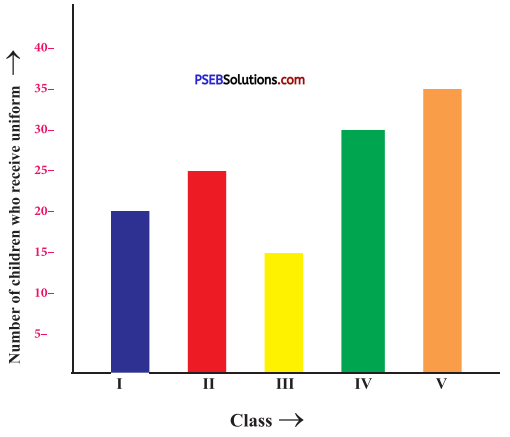
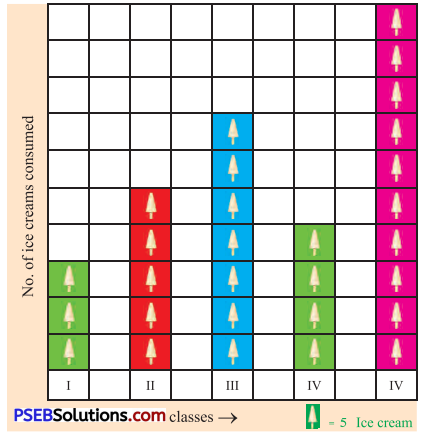
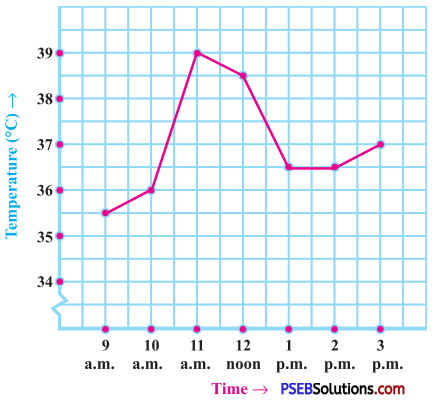
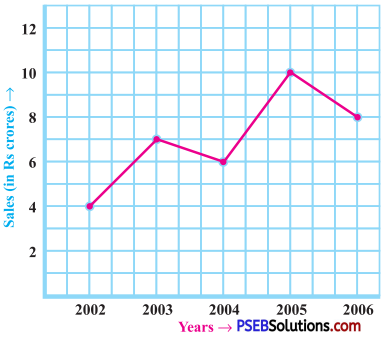
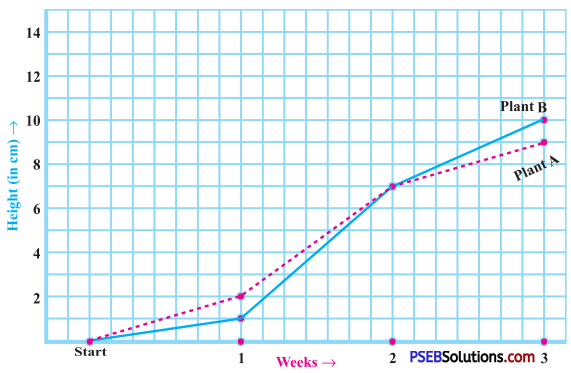
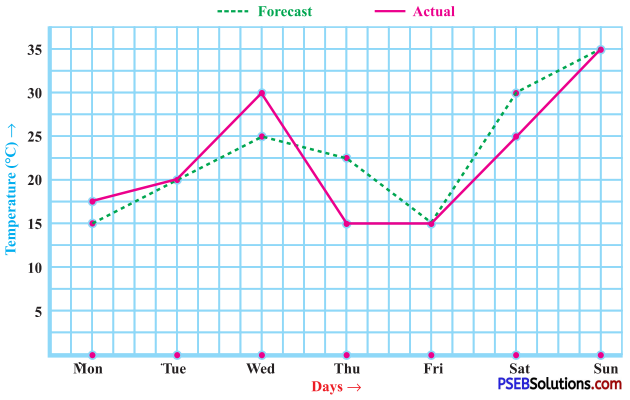
Punjab State Board PSEB 8th Class English Book Solutions English Creative Writing Exercise Questions and Answers, Notes.
PSEB 8th Class English Creative Writing
(A) Picture Composition
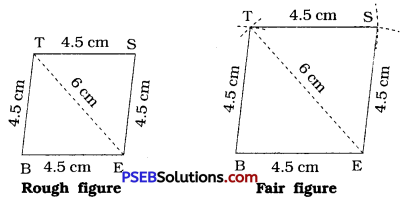
Now write some sentences on a bicycle. You can take help from the picture.
1.

Answers:
I have a bicycle. Its colour is black. It has a shining strong rims with tyres on them. There are spokes in the rims. Its tongs are tightly fitted to the wheels. Its chain is very light and runs smoothly. I sit on the saddle on my bicycle. Catches its handle and moves its paddles. My bicycle runs very fast.

2.

1. This picture shows the protection of forest trees.
2. A little girl has put her loving arms around a tree.
3. He does not want it to be cut down.
4. Her love for trees has inspired many other women too.
5. They all try to stop people from cutting trees.
6. Whenever people come to their village to cut trees they reach there crying ‘Chipko ! Chipko !” Hug the trees.
7. It has now become a big movement called ‘Chipko Movement’.
8. They cling to the trees till the tree fallers go back.
9. They tell them the great benefits of trees.
Trees, for example, give us fruits, firewood, medicines and many other things.
10. They check air pollution and supply us with fresh oxygen.
11. Above all our forest trees along with various birds and animals living in the forests are the beauty of our earth.
3. Family Picnic
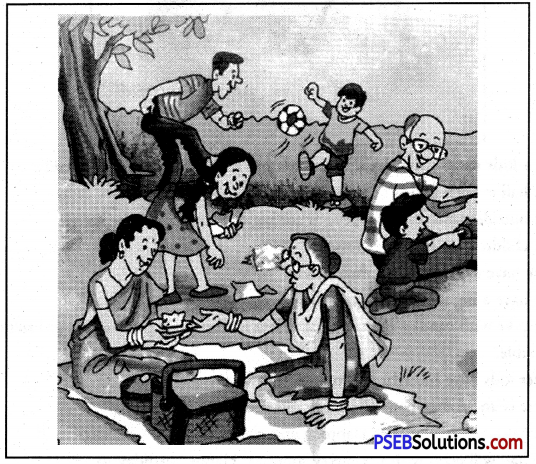

1. The picture depicts (Gericht) a family picnic.
2. Three children with their parents and grand parents have come to enjoy the day.
3. It is bright morning.
4. They have spread a mat near a tree.
5. They have brought some food in g big box. There is another dish in a steel container.
6. The house wife is giving some slikes to the old lady to eat.
7. Her grand-daughter is also giving her something.
8. Father and the son are enjoying the game of chakri/chakti.
9. The grandfather is busy in playing some other game with his grandson.
10. The scene is a feast to the eyes.
11. All look happy and carefree.
4.

1. It is a kids party-five, kids are celebrating it in a beautiful hall outside.
2. The hall is open and is decoated with colourful balloons.
3. The outside panorama (figga) is adding new colours to the scene.
4. The children are in fancy dresses.
5. They have clown caps on their heads.
6. The have a big table in front of them.
7. The cake with candles on it suggest that it is a birthday party of the girl standing near the table.
8. Other kids have brought different gifts for her.
9. There is an arrangement of cold drinks too.
10. The cake will be cut with clappie and cheers
11. The hall will echo with the merry songs of ‘Happy Birthday to ……….

(B) Guided Composition
Write a paragraph with the help of the given, hints:
1. My Best Friends
Hints : True friends rare……….. name……….. classmate……….. tall, smart, hard-working,: intelligent………..family……..one of the best students………. kind, gentle, helpful.
True friends are rare in the world. But I am very lucky to have a true friend. His name is Mohan. He is my classmate. He is tall and smart. He is hard-working and intelligent. He is one of the best students of our school. He comes of a noble family. His father is a doctor. His mother is a teacher. He has many good habits. He gets up early and goes for a walk. He wears neat and clean dress. He is never late for school. He obeys the school rules. He respects his teachers. He is a good player of hockey. He is very kind and gentle. He helps the poor and the needy. He is like a rose among flowers.
Word-Meanings : Rare-दुर्लभ, Classmate-सहपाठी, Habits-आदतें, Needy-ज़रूरतमंद।
2. The Postman:
Hints : Nathu Ram our postman……..to post office……… sorts…….. arranges…….. New bag……. keeps……..letters and parcels……..from house to house………..busy…….. hardworking……….. punctual………..enjoys work………..few holidays……….. brings news………..
Sh. Nathu Ram is our postman. He gets early in the morning. He puts on his dress. He goes to the post office in the morning. He sorts the daak there. He arranges letters and parcels. He has a bag round his shoulder. He keeps letters and parcels in it. He goes from house to house. He gives letters and parcels to the right persons. He is busy from morning to evening. He is very hard-working. He is very regular and punctual. He is never late. He enjoys his work very much. He knows no rest. He has a few holidays. He brings all types of news to us. We wait for him every day.
Word-Meanings : Sorts-छांटता है, Arranges-क्रम में रखता है, Punctual-समय का पाबन्द।
3. My Favourite Teacher
Hints : My teacher……. able and hard-working…….like Sh. K.S. Bedi the most……….tall and handsome………..M.A.; B.Ed……….. noble family………..good habits………..gets up early………. prays to God………..school in time……… well dressed……….polite………. way of teaching………good speaker……….Singer……….. helps the needy.
There are many teachers in our school. They are verable and hard-working. But I like Sh. K.S. Bedi the most. He is my favourite teacher. He is ofr class-in-charge. He is about 42 years old. He is tall and handsome. He is an M.A.; B.Ed. He belongs to a noble family. My teacher has many good habits. He gets up early in the morning He goes out for a walk. He prays to God daily. He always comes to school in time. He is an ays well dressed. He never gets angry.
He is polite to all. He teaches us English. His way of teaching is very simple. He takes part in games. He is a good speaker and fine singer. He is a lover of books. He helps the poor and the needy. All like him very much. May be live long!
Word-Meanings : Handsome – संदर, Belongs-संबंध रखते है, Noble – नेक.
4. Our School Library
Hints : School is a temple of learning………..library an altar……. a big library in my school………..50,000 books………. kept subject-wise………. newspapers and magazines ……….. librarian very helpful and kind……….. really useful.
A school is a temple of learning. A library is an altar ( èÁæ-SÍÜ) in it. My school too has a big library. It is housed in a corner. It has about 50,000 books in it. The books are kept subject-wise. They are kept in almirahs with glass-panes. The library has a number of newspapers and magazines too. They are in Punjabi, Hindi and English. We can borrow books from the library. But no student can keep a book for more than fifteen days. The librarian is very helpful, kind and gentle. But he is very strict. He maintains perfect silence and discipline in the library. We go to the library thrice a week. We read newspapers and magazines. The library is really very useful to all of us.
Word-Meanings : Housed in a corner- एक कोने में स्थित हैं, Magazines- पत्रिकाएं, Perfect silence-पूर्ण खामोशी, Strict-सख्त।

5. A Cricket Match
Hints: We played against the KVM School………..won the toss………. decided to bat……….skipper Abdul made 20 runs………..Surinder and Hira Singh………201 runs………KVM team scored 180 runs………..we won………..dancing.
Last Sunday we played a cricket match against the KVM Sen. Sec. School. It was a 50 over match. Both the teams were equally strong. We won the toss. We decided to bat. Our skipper Abdul opened the innings with his partner Hamid. He made twenty runs. Then came Surinder. He delighted the spectators with five sixes. Hira Singh was the next batsman. He stayed there for two hours and scored seventy runs. The whole team was out for 201 runs. It was now our turn to field. Our bowlers bowled very well. Our opponents were in great difficulty. They were not in a good form. They were all out for 180 runs. As a result we won the match. All of us started dancing in the field. Other students also joined us.
Word-Meanings : Equally-एक समान, Delighted-प्रसन्न किया, Spectators-दर्शक, Opponents-विरोधी
6. A Street Quarrel
Hints : A common sight……….. last night………..studying in my room………..loud noise in the street………..two persons………. hot words exchanged………. blows……….both injured……….had started over a trifle………..pacified by people……….. boys playing……….a ball struck another……….. parents joined………..should be avoided.
A street quarrel is a common sight. Mostly, an ordinary quarrel of children takes an ugly shape. Last night I happened to see a street quarrel. I was studying in my room. Suddenly, I heard a loud noise in the street. I saw a big crowd there. Two persons were exchanging hot words. Soon they came to blows. Both got injured and started bleeding. With great difficulty some people pacified them. The quarrel had started over a trifle. Some boys were playing in the open. By chance a ball struck another boy. They started fighting. Someone informed the parents of both the boys. They came out and started fighting. Thus a big scene was created out of a small thing. Such quarrels should be avoided.
Word-Meanings : Quarrel-झगड़ा, Common sight- आम दृश्य, Ugly shape – गंदा रूप, Exchanging hot words-गुस्से में बोल रहे थे, Blows-मुक्के, Bleeding-खून बहना, Pacified – रांत क्रिया, Trifle – तुच्छ बात
7. A Picnic
Hints : Sunday morning….party of fifteen boys…..carried fruit and cold drinks…. reached bank of a river……splashed water at one another….chatted and laughed…….titbits…….. tea and snacks………. took a bus and reached home ………. remember the day.
“It was Sunday morning. My friends and I decided to go for a picnic. We were a party of fifteen boys. We carried fruit, cold drinks and some snacks with us. We went to a river by bus. We reached the bank of the river at 9 a.m. We took some rest. Then we took off our clothes and jumped into the water. We splashed water at one another. After half an hour we came out of the water. We took fruit and cold drinks. We took rest for some time. Once again we jumped into the water. After half an hour we came out. We were in a cheerful mood. We chatted and laughed. Gurvinder related a few titbits. We had tea and snacks. At 6 p.m. we took a bus and reached our homes at 7 p.m. We remember the day even today.
Word-Meanings : Took off-उतरे, Splashed-छुटि उड़ाए, Related- सुनाये, Titbits – चुटकले, Chatted-बतें की.
8. A Journey by Train
Hints : Travelled from Chandigarh to Delhi by train ……… reached before time ……… bought a ticket ………. the train late, arrived, comfortable seat …….. trees, houses running backwards …….. stopped at Ambala ……. took tea ……… reached Delhi ……. sigh of relief.
Last Sunday, I travelled from Chandigarh to Delhi by train. I reached the railway station before the arrival of the train. I bought a ticket and came to the platform. The train was late. At last the train arrived. The platform was crowded with people. It was very difficult to get a seat. But I was lucky. I got a very comfortable seat near the window. The train started moving. I looked out of the window. The trees, the houses and the electric poles seemed running backwards. The train stopped even at small stations. At Ambala it stopped for half an hour. I came down and took tea. After some time the train started again. I reached Delhi at sunset. I heaved a sigh of relief.
Word-Meanings – Arrival-आगमन, Crowded-मश हुआ था, Seemed- लगता था, Comfortable-आरामदायक, Heaved a sigh of relief-चैन की सांस ली।
9. Going to the Market
Hints : There is a………… in our ……….. Men and women………… Some buy fruit, vegetables, some ……… grains open ………… Sunday ……….. I visited ………… last Sunday ………… many shops………. sari ………. my mother, shirt ……….. book shop …………. a story book ………… my younger sister ………… toys ………… no money left ………… back home.
There is a big market near our town. Men, women and children go there. They buy different things. Some buy fruit and vegetables. Some buy grains. Cloth is also sold there. The market is open on Sunday too. I visited it last Sunday. I went to many shops. First of all I went to a cloth shop. I bought a sari for my mother and a shirt for my brother. Then I visited a book shop. It had all types of books. I bought a story book for my younger sister. I saw a beautiful toy at toy shop. I wanted to buy it. But I had spent all the money. So I came back home.
Word-Meanings : Market- बाजर, Different- भिन्न-भिन्न, Grains-अनज, Bought-खरीदी, Types-प्रकार, Spent-खर्च कर दिए.

10. A Morning Walk
Hints : A morning walk …………. useful ………… fit and healthy ………… I get up ….. friend’s house ………… to the canal ……….. meet people ………… scene very beautiful …………. birds ……… dew-drops ……….. everything fresh ……….. cool breeze ……….. refreshes mind………… reach canal ………… Some people bathing ………… praying………. return home.
A morning walk is very useful. It is a light exercise. It keeps us fit and healthy. Therefore, I go for a morning walk daily. I get up at 5 a.m. and go to my friend’s house. We go out for a walk together. We go to the canal. We meet many people on the way. They are also going for a walk. The morning scene is very beautiful. The birds are chirping. There are dew-drops on the grass. They shine like pearls. Everything looks fresh. A cool breeze is blowing. It refreshes our mind and body. We feel very happy. We reach the canal at about 6 a.m. We walk along the bank. Many men are there. Some are praying. Others are bathing. We also take our bath in the canal. The sun rises and we come back home.
Word-Meanings : Light Exercise-हल्का व्यायम, Canal-नहर, Dew-drops-ओस की बूंदें, Pearls-मोती, Refreshes-ताज़गी देती है।
11. Our Neighbour
Hints : Mohan Babu our neighbour ………… a shopkeeper ………… goes out for a walk ……. returns ………… vegetable market ………… buys vegetables ………… temple ………… devotee of goddess Lakshmi ……….. back from temple ……….. breakfast ……….. leaves for shop ………… a cloth merchant ……….. clever ………. comes home with money ……….. hearty meal with family sleeps early ………. a happy life.
A neighbour is a person who lives near us. Mohan Babu is our neighbour. He is a happy person. He is a shopkeeper. He gets up early in the morning. He goes out for a walk. He comes back after an hour. Then he goes to the vegetable market. He buys vegetables for the family. He goes to the temple daily. He is a devotee of Lakshmi, the goddess of wealth. He takes his breakfast and leaves for his shop. He is a cloth merchant. He is very clever. He deals with his customers well. He returns home late in the evening. His purse is full. He enjoys his meal with his family. He goes to bed early. Thus he leads a real happy life.
Word-Meanings : Neighbour-पड़ोसी, Vegetable market-सब्जी मंडी, Devotee-उपासक, Wealth-धन दौलत, Customers-ग्रहक
12. My Father-A Farmer Hints : Father a farmer ………… not well-educated ………… hard-working ………. truthful and honest ………… respected in village ………… proud of him ………… an open minded man ………… ready to accept things ………… a pleasant person………… settles village quarrels ……….. the wisest man of the village ………… simple and clean life ………… does not lose temper ………… respected by all.
My father is an able person. He is a farmer. Though he is not well-educated, he knows his work well. He is very hard-working. He is truthful and honest. All the villagers respect him. They greet him respectfully. They often consult him about their private affairs. My father has an open mind. He accepts things easily. Moreover, he settles the quarrels among the people of the village. He is the wisest man of the village. He leads a simple and clean life. He does not lose temper with anybody. He is respected by one and all. I am proud of my father.
Word-Meanings-Well-educated-सुरिक्षित, Hard-working-परिश्मी, Greet-अभिवादन करना, Respectfully-आदरपूर्वक, Consult-सलाह लेना, Accept things-बात मान लेना/समझ जाना, Private affairs-निजी मामले, Quarrels-झगड़े, Lose temper-क्रोध करना।
Completion of Incomplete Paragraphs
1. My Mother-A Nurse My mother is a nurse. She spends her day according to a set time-table. She gets up early in the morning. She prepares bed tea for all of us…………..
My mother is a nurse. She spends her day according to a set time-table. She gets up early in the morning. She prepares bed tea for all of us. Then she goes out for a walk. On coming back, she prepares breakfast. She then changes her clothes. She goes to the hospital for her duty. She takes care of every patient. She looks after them very nicely. She comes back in the evening. She prepares tea. We all sit together and talk for some time. Then she starts preparing dinner for us. Really, my mother is a noble lady.
Word-Meanings : According to-के अनुसार, Prepares-तैयार करती है, Breakfast- नारता, Take care of-देखभाल करना, Patients-मरीज, Together-इकट्ठे, Noble- नेक
2. A Football Match Yesterday, a football match was played between our school and Khalsa High School. It was final match. It was played on our school playground…. ……….
Yesterday a football match was played between our school and Khalsa High School. It was final match. It was played on our school playground. The students of both the schools had come to see the match. The match started at 4 p.m. Both the teams were equally strong. The match was very brisk from the very start. The players were in high spirits. Both the teams tried hard to score a goal. But there was no score till interval. After the interval, our team attacked hard. Our centre forward got the ball and scored the first goal. The other team tried hard to equalize but in vain. After a few minutes, the referee blew a long whistle and the match was over. Our team won the match by one goal to nil.
Word- Meanings: Equally-सामन रूप से, Brisk-तेज/ शेचक
उत्सहित In high spirits-Jnifen, Score a goal-गोल करना, Equalize-बराबर करना।

3. An Indian Festival
Or
Diwali
The Diwali is a great Indian festival. It comes off in the month of October or November. It has a story behind it. ……….. .
The Diwali is a great Indian festival. It comes off in the month of October or November. It has a story behind it. Rama came back to Ayodhya after 14 years of exile. This festival is held to mark this day. This festival is held with great pomp and show. People whitewash their houses. They hang pictures on the walls. The Diwali day is a happy day. The bazaars look beautiful. A few years ago the sweets were in great demand on Diwali. But today the taste of the people has changed. They prefer dry fruits to sweets. The Diwali night is a beautiful night. Everywhere there is light. There are rows of candles on the roofs. There is a great noise of crackers. Lakshmi Pooja is held. Some people drink and gamble. It is bad. We should celebrate this festival with purity.
Word-Meanings : Festival-त्योहार, Exile-वनवास, Pomp and show-धूमधाम से, Prefer-अधिक पसन्द करना, Crackers-पटाखे, Gamble-जुआ खेलना, Celebrate-उत्सव मनाना, Purity-fastati
4. A Visit To Shimla
I went to Shimla last year. My uncle was with me. We left by the Kalka Mail. …
I went to Shimla last year. My uncle was with me. We left by the Kalka Mail. It left Jalandhar City at 11 p.m. and reached Kalka at 6 a.m. There we changed the train. The train passed through many tunnels. It snaked its way to Shimla. We stayed there in a good hotel. As we were tired, we slept for three or four hours. In the evening we visited the Mall. There was a great rush at the Mall. The next day we visited Kufri. We also visited Jakhoo hill and other places of interest. We stayed at Shimla for a fortnight. We had a nice time there.
Word-Meanings : Changed the train-रेलगाड़ी बदली, Passed through-गुजरी, Tunnels-सुरंगें, Stayed-ठहरे, Snaked-बल खाते हुए चली, Fortnight-पखवाड़ा (पंद्रह दिन)।
5. The Morning Assembly of Our School
Our school begins at half past eight in the morning. All the students and the teachers reach the school in time. The morning assembly begins……….
Our school begins at half past eight in the morning. All the students and the teachers reach the school in time. The morning assembly begins. All the students stand in rows. They stand facing the school building. Four boys stand facing the assembly. They say prayer. The other students say after them. A student from the seniormost class reads out the main news of the day. A teacher gives the thought for the day and explains it. Sometimes our Headmaster makes some important announcement. Then there is roll-call. The assembly ends with the National Anthem and we go to our class-rooms.
Word-Meanings : Morning Assembly–प्राता: कालीन प्रार्थन साभा, Rows-पंक्तियां, Seniormost सबसे ऊंची, Thought-विचार, Explain-व्याख्या करना, Announcement-घोषणा, Rollcall – हाजिरी
6. A Fire Scene
Or
A House On Fire
It was a summer night. I was sleeping on the roof of my house. I was awakened by the cries of Fire ! Fire ! I got up and reached the spot………….
It was a summer night. I was sleeping on the roof of my house. I was awakened by the cries of Fire ! Fire ! I got up and reached the spot. The house of the Mahajans was on fire. I saw flames rising higher. Many people had gathered there. Some were throwing water on the fire. Others were throwing sand. A few people were taking out goods. The youngest son was sleeping in the upper storey. He was crying loudly. I at once took a ladder and climbed up. The boy was safe. I took him down before the fire reached the upper storey. The boy’s mother was very happy. She thanked and blessed me. Soon the fire-brigade arrived. The firemen struggled hard to put out the fire. After an hour, they brought the fire under control. There was a great loss of property. But thank God there was no loss of life.
Word-Meanings: Awaken- नींद से उठना, Spot-जगह, Flames-लपटें, Sand-रेत, Upper storey-ऊपरी मंज़िल, Ladder-सीढ़ी, Blessed-आशीर्वाद दिया, Under control नियन्त्रण में, Property-सम्मत्ति
C-Picture Description
1.

A boy was coming back from the school. He was on a bicycle. He was cycling very fast. A stone was lying on the road. He did not notice it. His bicycle hit it and lost its balance. He fell down and injured his leg.
One of his schoolmates was coming after him. She was on foot. She saw her wounded classmate and a clinic on the road side. Unluckily, the clinic was closed. Soon the girl remembered a piece of bandage in her bag. She bandanged the wound of the boy. The blood stopped and the boy started walking with her. Soon the boy’s parents reached there. They thanked the girl for her timely help.
2.
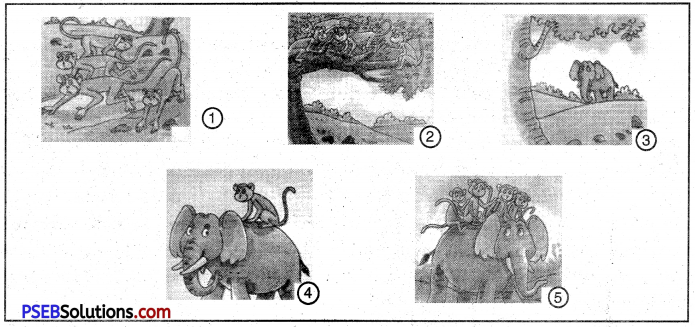
Some monkeys were playing in a jungle. Suddenly, they heard the loud sound of an elephant’s trumpet. They got afraid. They ran up and down a tree.
Soon the elephant reached very close to the tree. A little monkey looked towards the elephant and smiled.
The elephant picked him up and put him on his back. The little monkey had a joyful ride. The other monkeys saw him and one by one also jumped on to elephant’s back. The elephant started moving. The monkeys had a jolly good elephant ride.
3.

Once there was a donkey. One day he was wandering in the forest. Suddently he found a lion’s skin lying on the ground. He wore it. Animals saw him and ran away with fear. The donkey was very happy. After some time he heard some donkeys braying. He also stared braying. The animals heard his braying and came to know that he was donkey not a lion. They chased him and drove him away from the forest.
4.
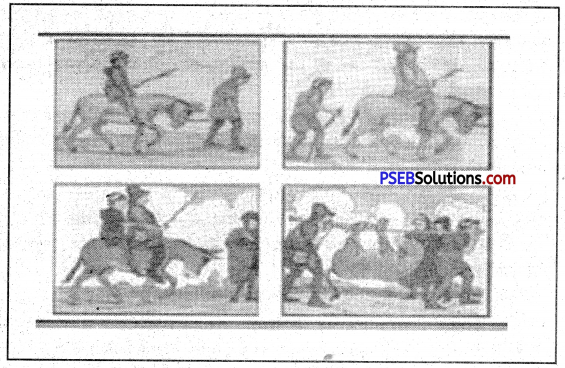
A man was going to the market with his son and ass (गंधा). They met a couple (दम्मत्ति पति- पत्नी) on the way. ‘Why walk when you have an ass to ride ?” called out the husband ‘Seat (बिठा दो) at the boy on the ass.” “I would like that,” said the boy. “Help me up. Father.”
Soon they met another couple. How shameful; (शर्म की बात हे) of you !” cried the woman. “Let your father ride. Won’t he be tired ?” So, the boy got down and the father ride the ass.
Again they marched on. “Poor boy”, “said the next person they met. “Why should the lazy father ride while his son is walking ?” So, the boy got onto the ass too. As they went on, they met some travellers (यात्री). “How cruel of them! They are up to kill the poor ass” cried one of the travellers. Hearing this the father and the son got down. Now they decided (फैसला किया) to carry the ass on their shoulders. As they did so, the travellers brake into laughter (जोर से हंसने लगे) The laughter frightened (डरा दिया) the ass. It broke free and ran away.
![]()


![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()