Punjab State Board PSEB 6th Class Science Book Solutions Chapter 12 Electricity and Circuits Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
PSEB Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 12 Electricity and Circuits
Science Guide for Class 6 PSEB Electricity and Circuits Intext Questions and Answers
Think and Answer (Textbook Page No. 124)
Question 1.
The part of the bulb which produces light is called ……………….
Answer:
The part of the bulb which produces light is called a filament.
Question 2.
The electric bulb has ……………. terminals.
Answer:
The electric bulb has two terminals.
Think and Answer (Textbook Page No. 128)
Question 1.
What is the function of electric switch ?
Answer:
The function of electric switch is to make (complete) or break the flow of current in the circuit.
Question 2.
In an electric circuit the circuit breaks when switch is in position.
Answer:
In an electric circuit the circuit breaks when switch is OFF in position.
![]()
PSEB 6th Class Science Guide Electricity and Circuits Textbook Questions and Answers
Exercise – 1
1. Fill in the Blanks:
(a) A device that is used to break or make an electric circuit is called …………….
Answer:
switch
(b) An electric bulb glows when …………… flows through it.
Answer:
current
(c) ……………… are the materials through which electric current can pass.
Answer:
Conductors
(d) Current cannot pass through ……………..
Answer:
Insulators
2. Write True or False:
(a) Electric current can flow through metals.
Answer:
True
(b) Instead of metal wires, a jute string can be used to make a circuit.
Answer:
False
(c) Electric current can pass through a pencil lead.
Answer:
True
(d) When chemicals in dry cell are used up, it stops working.
Answer:
True
![]()
(e) Led based lamps are eco-friendly.
Answer:
True
3. Match the Column A with Column B:
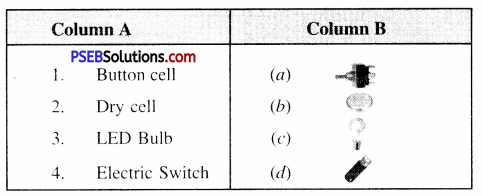
Answer:

4. Choose the Correct Answer:
Question (i)
Battery is a combination of:
(a) Conductors
(b) Insulators
(c) Electric cells
(d) Filaments.
Answer:
(c) Electric cells
Question (ii)
The basic electric circuit needs to have:
(a) Only a source of electric current
(b) Only a few conducting wires
(c) Only a device or appliance
(d) All the above.
Answer:
(d) All the above
Question (iii)
On passing current through an electric bulb, bulb starts emitting light because its:
(a) Filament starts emitting light and then gets heated up
(b) Thick connecting wires start emitting light and then get heated up
(c) Filament gets heated up and then starts emitting light
(d) Thick wires get heated up and then starts emitting light.
Answer:
(c) Filament gets heated up and then starts emitting light
5. Very Short Answer Type Questions:
Question (i)
What is electric cell ?
Answer:

Electric Cell.
It is a device used to produce electric current. In electric cell chemical energy is converted into electrical energy. An electric cell has two terminals positive ( + ) terminal and negative (-) terminal. The metal cap is the positive terminal of the cell while the metal disc is the negative terminal.
Question (ii)
What is Electric Current ?
Answer:
Electric Current. The flow of charge per unit time is called electric current. Electric current flows from positive terminal to negative terminal outside the cell.
Question (iii)
What is Electric Circuit ?
Answer:
Electric Circuit.
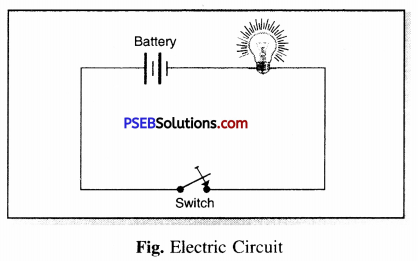
The arrangement between the two terminals of electric cell that provides complete path for flow of current is called electric circuit.
The diagram of an electric circuit is given in the above figure in which one electric cell is connected to bulb with the help of a switch. The bulb glows when the switch is in its “ON” position.
![]()
6. Short Answer Type Questions:
Question (i)
Tools like screw drivers and pliers, used by electricians have handles made up of plastic, rubber, wood. Why ?
Answer:
Handles of electirical tools are made up of plastic, rubber or wood to provide insulation, so that the person/electrician can be safe from electrical shock.
Question (ii)
Why should we dry our hands before touching an electric appliance or a switch ?
Answer:
We should not touch electric gadgets live open wires or electric switches with wet hands because in such situation we can get electric shock due to easy flow of current. This may prove fatal in some cases. So we should dry our hands before touching electric appliance or a switch.
Question (iii)
A student while performing an experiment in the science lab, connected an electric bulb to an electric cell through an electric switch. He noticed that the bulb does not glow when the electric switch was set in its ON position. Mention any two reasons for this observation.
Answer:
An electric bulb connected in an electric circuit with switch in its “ON’ position if does not glow there. There can be two possible reasons which are given here below :
- The filament of the bulb may be broken or the bulb may be fused. If it is so then the electric circuit will not become complete resulting in not glowing of the bulb.
- The connecting wires may have been left loose at same point.
Question (iv)
Distinguish between the terms conductors and insulators of electricity. Give two examples of each type.
Answer:
Conductors. Those substances which allow electric current to pass through them are called conductors of electricity e.g. copper wire, key made of iron. Human body.
Insulators. Those substances (materials) which do not allow current to pass through them are called insulators e.g. Rubber, Plastic and Wood.
Question (v)
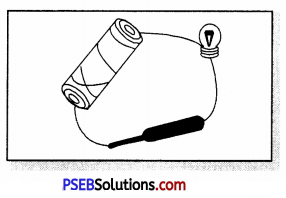
Explain why the bulb would not glow in the arrangement shown at below.
Answer:
We know that the bulb would light up when the electric cell starting from one terminal of the cell and ending at the other terminal of the cell is complete so that there is a continuous flow of current. In the present set up we find the elpctric circuit is incomplete (broken) and this is why the electric bulb does not glow.
Question (vi)
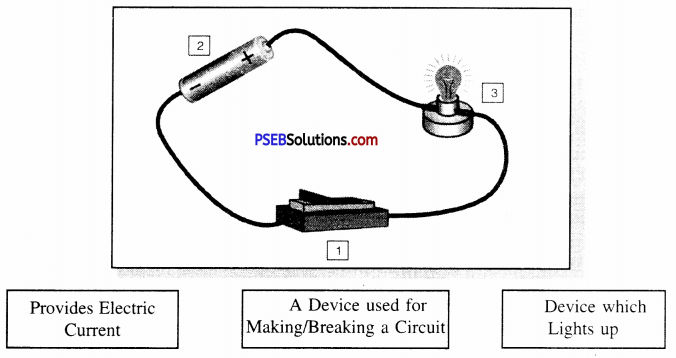
Match the labels with the correct parts of the circuit given below :
Answer:
- Switch (A device used for Making/Breaking a circuit).
- Cell (Provides Electric Current).
- Electric Bulb (Device which Lights up).
![]()
7. Long Answer Type Questions:
Question (i)
Using the “conduction tester” on an object it was found that the bulb begins to glow. Is that object conductors or insulator. Explain.
Answer:
Because with this object the bulb begins to glow showing that the electric current is flowing in the circuit i.e. The electric circuit is complete. This can be possible only when the material of the object allows the current to flow through it and we know that only conductors allow current to flow through them. Therefore, the object is a conductor.
Question (ii)
The handles of the tools like screw drivers and pliers used by electrician for repair work usually have plastic or rubber covers on them. Can you explain why ?
Answer:
The handles of tools used by electrician for repair work usually have handles made of plastic, rubber or wood. These covers are of non-conducting material and therefore, do not allow current to pass through them. So such handles protect electricians from getting electric shock.
PSEB Solutions for Class 6 Science Electricity and Circuits Important Questions and Answers
Multiple Choice Questions:
Question 1.
A device which is used to break the circuit is:
(a) Electric cells
(b) Switch
(c) Electric bulb
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(b) Switch
Question 2.
An electric cell has terminals:
(tt) Three
(b) One
(c) Two
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(c) Two
Question 3.
To make electric wires is used :
(a) Rubber
(b) Aluminium
(c) Plastic
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(b) Aluminium
Question 4.
In electric cell the source of current is:
(a) Positive terminal
(b) Negative terminal
(c) Chemical stored in it
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(c) Chemical stored in it
Question 5.
In an electric circuit the direction of current in a cell is
(a) from positive to negative terminal
(b) from negative to positive terminal
(c) for half time from positive to negative terminal and for other half time from negative to positive terminal.
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(a) from positive to negative terminal
Question 6.
A subsance through which electric current can flow is :
(a) Conductor
(b) Insulator
(c) Electric circuit
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(a) Conductor
![]()
Question 7.
Cell is a device used to convert:
(a) electrical energy into light energy
(b) magnetic energy into electric energy
(c) chemical energy into electrical energy
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(c) chemical energy into electrical energy
Question 8.
The filament of electric bulb is made of ……………
(a) Tungsten
(b) Copper
(c) Platinum
(d) Aluminium.
Answer:
(a) Tungsten
Question 9.
What is the name of a device used for making or breaking an electric circuit ?
(a) cell
(b) wire
(c) bulb
(d) switch.
Answer:
(d) switch
Fill in the Blanks:
(a) A device that is used to break an electric circuit is called …………… .
Answer:
switch
(b) An electric cell has ……………… terminals.
Answer:
two
(c) The bulb glows in the circuit when the circuit is …………… .
Answer:
complete
(d) Our body is a ……………….. of electricity.
Answer:
conductor
(e) Electric cell is a source of ……………….. .
Answer:
current
![]()
Write (T) against true and (F) against false statements:
(a) Electric current can flow through matals.
Answer:
True
(b) Instead of metal wires, a jute string can be used to make a circuit.
Answer:
False
(c) Electric current can pass through a sheet of thermocol.
Answer:
False
(d) Switch can only break a circuit.
Answer:
False
(e) Electric current can pass through human body.
Answer:
True
Match the Column:
Match the items in Column A with items in Column B.
| Column A | Column B |
| (1) Electric cell | Electric Insulators |
| (2) Bakelite | To protect themselves from electric shock |
| (3) Electric wires | Source of electric current |
| (4) Electricians use rubber gloves | Copper |
Answer:
(1) – Source of electric current,
(2) – Electric Insulators,
(3) – Copper,
(4) – To protect themselves from electric shock.
![]()
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is the source of electric current on a torch ?
Answer:
In a torch electric energy is obtained from chemicals stored in the cell.
Question 2.
Where is electric cell used ?
Answer:
Electric cell is used in alarm clocks, hand watch, Radio, Camera and other devices.
Question 3.
What is the positive terminal of electric cell ?
Answer:
Carbon rod is the positive terminal of electric cell.
Question 4.
What is the negative terminal of cell ?
Answer:
Zinc disc is the negative terminal of electric cell.
Question 5.
When does electric cell stop working ?
Answer:
When the chemicals stored in the cell are consumed up. the cell stops doing work.
Question 6.
What is filament of bulb made of ?
Answer:
The thin metallic wire which gives out light is called filament.
Question 7.
What do the two terminals of Electric cell or electric bulb represent ?
Answer:
Two terminals of Electric bulb or electric cell represent positive terminal and negative terminal.
![]()
Question 8.
If you connect wires connected to two terminals of the cell to a switch and device like bulb then what will happen ?
Answer:
By doing so the chemicals stored in the cell would be used up.
Question 9.
What is Electric circuit ?
Answer:
Electric Circuit. It is the complete path between the two terminals of the cell for continuous flow of current.
Question 10.
What is the direction of flow of current in an electric circuit ?
Answer:
In an electric circuit, the direction of flow of current is from positive terminal to negative terminal of electric cell.
Question 11.
When does electric bulb fuse ?
Answer:
When the filament of the bulb is broken, then electric circuit does not become complete and as a result the bulb does not glow than the bulb is said to have become fused.
Question 12.
What is Switch ?
Answer:
Switch. It is a simple device which is used to make or break electric circuit.
Question 13.
What type of material can be used to complete electric circuit ?
Answer:
For making electric circuit electric conducting materials can be used.
Question 14.
List three such materials which are conductors of electricity.
Answer:
- Keys
- Alpins
- Aluminium strip metal.
![]()
Question 15.
Name four electric insulating materials.
Answer:
- Cork
- Rubber
- Glass
- Block of wood.
Question 16.
Which metal is used for making electric wires ?
Answer:
Ordinarily copper and Aluminium metals are used for making electric wires.
Question 17.
Is our body a conductor or Insulator ?
Answer:
Human body is conductor of electricity. Therefore, we should not touch uncovered open wires.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What are the various tasks for which we can use electricity ?
Answer:
Uses of electricity :
- We light our homes with electricity.
- Electricity helps us to run fan, refrigerator, television and other devices.
- Electricity can also work telephones and computers.
Question 2.
Why should an electrician use gloves while repairing an electric switch at your home ? Explain.
Answer:
Electricians use rubber gloves while repairing an electric switch as rubber is an insulator and current cannot pass through it. So electrician uses rubber gloves while carrying out electrical repairs without getting electric shock.
Question 3.
What is the purpose of using an electric switch ? Name some electrical gadgets that have switches built into them.
Answer:
Switches are used to light up an electric bulb and to work other electric devices. Switches used at homes work on same principle but they have complex designs. T.V., computer, automatic electric iron have switches built into them.
Question 4.
Would the bulb glow after completing the circuit shown in the figure; if instead of safety pin we use eraser ?
Answer:
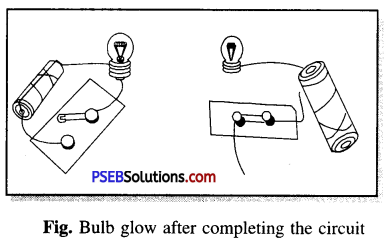
No the bulb will not glow because eraser is a non-conducting (insulating) material which does not allow the current to pass through it and complete electric circuit.
![]()
Question 5.
Would the bulb light up in the circuit shown in the figure ?
Answer:
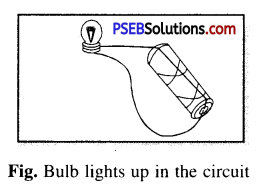
Yes, as the current flows easily because wire is connected directly and properly and moreover the circuit is complete.
Question 6.
Pick out conductors and insulators from the following:
Coin, cork, Glass, Rubber, Keys, Pin, Plastic scale, Wooden block, Aluminium foil, Candle, Sewing needle, Thermocol, Paper and Lead of pencil.
Answer:
Conductors. Coin, Keys, Pin, Aluminium foil, Sewing needle, pencil lead.
Insulators. Cork, Rubber, Glass, Plastic scale, Wooden block, Thermocol, Candle, Paper.
Question 7.
Why are metals used for making wire ?
Answer:
Metals are good conductors of electricity therefore, metals are used for making wires. Usually copper and aluminium, metals are used to make wires.
Question 8.
Why should we not keep connected the wires attached to the terminal of an electric cell to the bulb ?
Answer:
The wires attached to the two terminals of cell should not be kept connected to the bulb and devices like switch. If we will do so then the chemicals stored in the cell will be consumed quickly and the cell will stop working as a result of this.
Question 9.
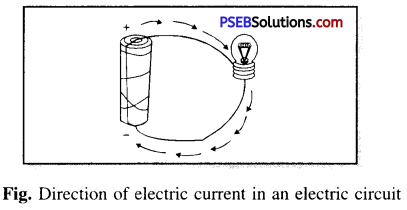
What is the direction of electric current in an electric circuit ?
Answer:
In an electric circuit the direction of electric current will be from positive terminal (+) of the cell to its negative terminal (-) as shown in the figure. When the terminals of electric bulb are joined to the terminals of the cell with the help of connecting wires, then electric current flows through the filament of the bulb and the bulb lights up.
Long Answer Type Question
Question 1.
Explain the construction and working of an electric bulb.
Answer:
Electric bulb.
It is an electric device that provides light when an electric current is passed through it.
Construction.
A bulb has an outer case of glass that is fixed on a metallic base as shown in the figure. A thin wire is fixed in the middle of the glass case which gives off light. This thin wire is called the filament. This filament is fixed to two other thick wires to provide support to the filament. One of two thick wires is connected to the metal case at the base of the bulb. The other thick wire is connected to the metal base. The base and the metal tip at the base are the two terminals of the bulb. These two terminals are so placed that they do not touch each other.
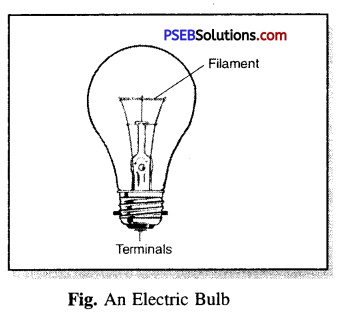
Working.
On connecting the bulb in an electric circuit electric current begins to flow through the filament of the bulb as a result of which the filament first becomes hot and then on more heating the temperature increases and it becomes red hot and ultimately white-hot and starts emitting light.