Punjab State Board PSEB 6th Class Science Book Solutions Chapter 7 Getting to Know Plants Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
PSEB Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 7 Getting to Know Plants
Science Guide for Class 6 PSEB Getting to Know Plants Intext Questions and Answers
Think and Answer (Textbook Page No.63)
Question 1.
Rose plant is a ………………
Answer:
Shrub.
Question 2.
Mango plant is a ………………
Answer:
Tree.

Question 3.
Wheat plant is a ……………….
Answer:
Herb.
Think and Answer (Textbook Page No.65)
Question 1
………….. help in absorption of water and minerals from the soil.
Answer:
Roots.
Question 2.
Why does plant in pot B, wilt ?
Answer:
Because, its roots have been cut.
Think and Answer (Textbook Page No.66)
Question 1.
It is not easy to pull out a plant from the soil because it has strong ……………….
(i) Roots
(ii) Flower
(iii) Stem
(iv) Leaves.
Answer:
(i) Roots.
Think and Answer (Textbook Page No.67)
Question 1.
…………… always grows upwards.
Answer:
Stem.
Question 2.
Why white flower of balsam plant show specks of red colour ?
Answer:
Because, the coloured water moves through the stem. This proves that stems help in movement of water.
Think and Answer (Textbook Page No.69)
Question 1.
What are stomata ?
Answer:
Small pores on the surface of a leaf are called stomata.
Question 2.
Define transpiration.
Answer:
Loss of water vapour from plants through stomata is called transpiration.

Exercise – 1
PSEB 6th Class Science Guide Getting to Know Plants Textbook Questions and Answers
Fill in the Blanks:
(a) ……………… roots do not have any main root.
Answer:
Fibrous
(b) The arrangement of veins in a leaf is called ……………….
Answer:
Venation
(c) …………… is the female part of the flower.
Answer:
Pistil
(d) The stem of a tree is called ……………….
Answer:
Trunk
2. Write True or False:
(a) Loss of water from leaves is called transpiration.
Answer:
True
(b) Chlorophyll is responsible for the green colour in leaves.
Answer:
True
(c) The portion of stem between two intemodes is called node.
Answer:
False

(d) Stamen is the female reproductive part of a flower.
Answer:
False
3. Match the Column A with Column B:
| Column A |
Column B |
| 1. Root |
(a) protects the flower in bud |
| 2. Climber |
(b) absorbs water |
| 3. Sepal |
(c) keeps the plant upright |
| 4. Stem |
(d) money plant |
Answer:
| Column A |
Column B |
| 1. Root |
(b) absorbs water |
| 2. Climber |
(d) money plant |
| 3. Sepal |
(a) protects the flower in bud |
| 4. Stem |
(c) keeps the plant upright |
4. Choose the Correct Answer:
Question (i)
Mango plant is a …………….
(a) Herb
(b) Shrub
(c) Tree
(d) Root.
Answer:
(c) Tree
Question (ii)
Photosynthesis takes place in:
(a) Stem
(b) Root
(c) Pistill
(d) Leaves.
Answer:
(d) Leaves.
Question (iii)
The points on the stem where leaves grow are called:
(a) Buds
(b) Nodes
(c) Axiles
(d) Internodes.
Answer:
(b) Nodes
Question (iv)
The process of losing water by leaves is known as:
(a) Absorption
(b) Transpiration
(c) Photosynthesis
(d) Anchorage.
Answer:
(b) Transpiration
Exercise – 2
5. Very Short Answer Type Questions:
Question (i)
What is the flat green portion of a leaf called ?
Answer:
Leaf blade or Lamina is a flat green portion of a leaf.
Question (ii)
What is venation ? Write its different types.
Answer:
The arrangement of veins in a leaf is called venation. It is of two types.
- Parallel venation
- Reticulate venation.

Question (iii)
What is calyx ?
Answer:
Collection of sepals (the outermost green leafy structure) is called calyx.
6. Short Answer Type Questions:
Question (i)
What is the difference between tap root and fibrous root ?
Answer:
| Tap root |
Fibrous root |
| (1) Penetrate deep into soil |
(1) Shallow and do not penetrate deep. |
| (2) Have long main root. |
(2) Do not contain any main root. |
| (3) Roots are of different thickness. |
(3) Roots are of same thickness |
| (4) For example: Radish, neem, mango etc. |
(4) For example: Grass, wheat, banana etc. |
Question (ii)
Write the main functions of leaves.
Answer:
Main functions of leaves are :
- To prepare food from carbon dioxide and water, in the presence of chlorophyll and sunlight called Photosynthesis.
- Stomata present in leaves help in exchange of gases.
- Transpiration is performed by stomata in leaves.
- In some plants leaves are used for protection. For example opuntia.
Question (iii)
What are creepers ? Give one example.
Answer:
The Herbs which have weak stem that cannot stand upright and spread on ground called creepers.
For example : Pumpkin.
7. Long Answer Type Questions :
Question (i)
What are the different parts of a leaf ? Explain with labelled diagram.
Answer:
Parts of the leaf are : Petiole, Lamina, Leaf base, midrib and veins.
(1) Petiole. The leaf is attached to stem by a short stalk called Petiole.
(2) Lamina. The flat, green, expanded portion of leaf called Lamina or leaf blade.
(3) Leaf base. The end of Lamina joining the petiole is called leaf base.
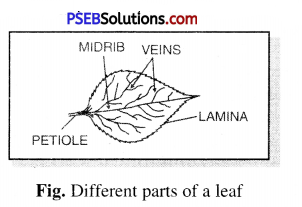
(4) Midrib. The thick vein in the middle of the leaf called midrib.
(5) Veins. The lines on leaf called veins.
Question (ii)
Draw the diagram of a flower and describe its parts.
Answer:
Flower is an attractive, colourful and beautiful part of flowering plant. It is attached to stem by pedicel.
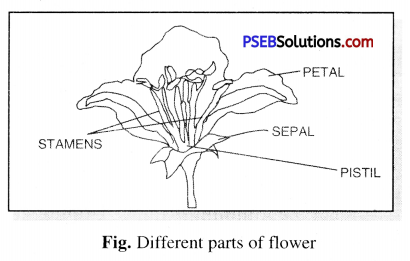
Parts of a Flower :
Parts of flower consist of : Sepals, petals. Stamens, Pistil.
- Sepals. Outermost green leaves are sepals and collectively claled calyx. It protect flower in bud stage.
- Petals. The coloured leaf like structure are petals, and collectively called Corolla. Petals attract insects for pollination.
- Stamens. It is the male part of flower. It consist of :
(a) Filament : The thin stalk
(b) Anther. The two lobed head that produes pollen grans.
- Pistil. It is the female part of flower and is a flask shaped structure in the middle of flower. It consists of :
(a) Ovary. Lower broader portion and contains ovary. It takes part in reproduction.
(b) Style. Narrow middle portion.
(c) Stigma. Sticky end at top of style

PSEB Solutions for Class 6 Science Getting to Know Plants Important Questions and Answers
Multiple Choice Questions:
Question 1.
Example of climber is :
(a) grape vine
(b) gourd plant
(c) maize
(d) rose.
Answer:
(a) grape vine
Question 2.
Reticulate venation is found in the leaves of:
(a) rose plant
(b) mango plant
(c) money plant
(d) all the above
Answer:
(d) all the above
Question 3.
The most prominent part of a bud is:
(a) sepal
(b) petal
(c) stamen
(d) pistil
Answer:
(b) petal
Question 4.
The number and colour of petals of rose plants are:
(a) one
(b) two
(c) five
(d) many.
Answer:
(d) many.
Question 5.
The process of producing food by leaves is:
(a) Photosynthesis
(b) Venation
(c) Herb
(d) Stimulus.
Answer:
(a) Photosynthesis
Question 6.
A change that produces a reaction in an organism is:
(a) Respiration
(b) Stimulus
(c) Photosynthesis
(d) Venation.
Answer:
(b) Stimulus
Question 7.
The process by which living organisms make energy is:
(a) Respiration
(b) Stimulus
(c) Venation
(d) Photosynthesis.
Answer:
(a) Respiration
Question 8.
Tulsi is a:
(a) Herb
(b) Shrub
(c) Tree
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(a) Herb

Question 9.
Palm is a:
(a) Herb
(b) Shrub
(c) Tree
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(c) Tree
Question 10.
Rose is a:
(a) Herb
(b) Shrub
(c) Tree
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(b) Shrub
Question 11.
Guava, papaya and banana are:
(a) flowering plants
(b) non-flowering plants
(c) stem
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(a) flowering plants
Question 12.
The autotrophs are:
(a) All animals
(b) All animals and plants
(c) All green plants
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(c) All green plants
Question 13.
Carrot, radish and turnip are:
(a) Modified stem
(b) Modified root
(c) Modified leaf
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(b) Modified root
Question 14.
Which of the following is not a part of flower?
(a) Petals
(b) Sepals
(c) Pistil
(d) Lamina.
Answer:
(d) Lamina.
Question 15.
Potato is an underground:
(a) Root
(b) Leaf
(c) Stem
(d) Fruits.
Answer:
(c) Stem

Question 16.
Horse is an animal:
(a) Carnivorous
(b) Herbivorous
(c) Omnivorous
(d) None.
Answer:
(b) Herbivorous
Question 17.
The growth in animals is:
(a) Reversible
(b) Irreversible
(c) Uncertain
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(b) Irreversible
Question 18.
Which one of the following is a unicellular animal ?
(a) Jelly fish
(b) Mimosa pudica
(c) Amoeba
(d) All of the above.
Answer:
(c) Amoeba
Question 19.
Green plants prepare their own food with the help of:
(a) carbon dioxide
(b) water
(c) sunlight
(d) all of the above.
Answer:
(d) all of the above.
Fill in the Blanks:
(a) Plants having hard, taller and thicks stem are called ……………….
Answer:
trees
(b) Some unwanted plants grown along with crop are …………………
Answer:
weeds
(c) ……………. are plants with weak stem.
Answer:
creepers

(d) Climbers take ……………… on neighbouring structures and climb up.
Answer:
support
(e) Stem …………….. water.
Answer:
conducts
(f) There are ……………… tubes inside stem which transport water and mineral to leaves.
Answer:
narrow
(g) The part of a leaf by which it is attached to the stem is called …………….. .
Answer:
Petiole
(h) The thick vein in the middle of leaf is ……………… .
Answer:
midrib
(i) Plants release a lot of water into ………………. through transpiration.
Answer:
air
(j) Roots ………….. the plant to the soil.
Answer:
anchor
(k) There exists a relation between type of a root and leaf ……………….
Answer:
venation
(l) Some roots like …………… ,…………… and …………….. eaten as food.
Answer:
carrot, radish, turnip

(m) …………… are the coloured parts of a flower.
Answer:
Petals
(n) Small bead like structure inside the ovary are ……………. .
Answer:
ovules
(o) Never ……………… flowers.
Answer:
pluck
Write (T) against true and (F) against false statements.
(a) Plants having small, green and tender stem are called Shrubs.
Answer:
False
(b) Grape vine is an example of a creeper.
Answer:
False
(c) The middle thick vein of leaf is called petiole.
Answer:
False
(d) Plants with parallel venation have fibrous roots.
Answer:
True
(e) Photosynthesis process is done in stems of plants.
Answer:
False
(f) Grass, wheat, maize have flowers.
Answer:
False
(g) Sepals are coloured part of a flower.
Answer:
False

(h) Marigold is group of flowers.
Answer:
True
(i) Different flowers have different number of stamens.
Answer:
True
(j) Pistil of all flowers is same.
False
Match the following:
| Column A |
Column B |
| (1) Root |
Making food. |
| (2) Stem |
Absorbing salts and water. |
| (3) Leaf |
Supplying food to the plant. |
| (4) Seed |
Creating a new plant. |
Answer:
(1) Root – Absorbing salts and water
(2) Stem – Supplying food to the plant
(3) Leaf – Making food
(4) Seed – Creating a new plant.
Match the items given in column A with those given in column B in the following:
| Column A |
Column B |
| (1) Neem |
Storage of food |
| (2) Radish |
Modified stem |
| (3) Potato |
Tap root |
| (4) Tendrils |
Photosynthesis |
| (5) Chlorophyll |
Grapevine |
Answer:
(1) Neem – Tap root
(2) Radish – Stroage of food
(3) Potato – Modified stem
(4) Tendrils – grapevine
(5) Chlorophyll – Photosynthesis.
Very Short ANswer Type Questions
Question 1.
Define Trees.
Answer:
Trees. The tall plants having a single strong stem branched at top are called trees.
Question 2.
Give two examples of herbs.
Answer:
Herbs. Wheat, balsam.

Question 3.
Which type of plants are Moss, Algae and Fern ?
Answer:
Non-flowering type.
Question 4.
Which part of a flower attracts insects ?
Answer:
Petals (colourful part) attracts insects.
Question 5.
Bud is protected by some leaves. What are they known as ?
Answer:
Sepals protect the bud.
Question 6.
Name two root systems found in plants.
Answer:
Two roots systems in plants are :
- Tap root
- Fibrous root.
Question 7.
What are parts of a leaf ?
Answer:
Parts of a leaf are :
- Lamina
- Midrib
- Petiole.
Question 8.
Which underground stems are used as food ?
Answer:
Potato, Ginger.
Question 9.
Name different parts of a flower.
Answer:
Parts of a flower,
- Sepals
- Petals
- Stamens
- Pistils.

Question 10.
Name reproductive parts of a flower.
Answer:
- Stamen
- Pistil.
Question 11.
Name the male reproductive part of a flower.
Answer:
Stamen.
Question 12.
In which part of a flower ovary is found ?
Answer:
Pistil.
Question 13.
How plants are classified on the basis of size and structure ?
Answer:
Herbs, shrubs and trees.
Question 14.
What are shrubs ? Give examples.
Answer:
Medium sized plants within branches starting just above the ground are shrubs, e.g. heena, lemon etc.
Question 15.
What are herbs ? Give examples.
Answer:
Herbs. Small and non-woody plants are herbs e.g. wheat, balsam.
Question 16.
What is photosynthesis ?
Answer:
Photosynthesis. The process by which green leaves produce food for plants in the presence of sun light, water and carbon dioxide is called photosynthesis.
Question 17.
Why are leaves generally green ?
Answer:
The green colour of leaves is because of presence of chlorophyll.

Question 18.
What are non-flowering plants ? Give example ?
Answer:
The plants which do not bear flowers are non-flowering plants e.g. Moss, algae, fern.
Question 19.
What are Creepers ?
Answer:
Creepers. Plants which run on the ground are creepers.
Question 20.
What are Climbers ?
Answer:
Climbers : Plants which need support to stand up are climbers.
Question 21.
Define node ?
Answer:
Node. The part of stem where branches and leaf attached are called nodes.
Question 22.
Define Internode.
Answer:
Internode. The part of stem between two consecutive nodes is intemode.
Question 23.
What is difference between the stems of shrub and tree ?
Answer:
Stem of shrub is hard and thin but that of tree is hard and bulky.
Question 24.
Name two flowers with joined sepals ?
Answer:
Dhatura and Loki.
Question 25.
Name two flowers with separate sepals ?
Answer:
Gurkal and mustard.

Question 26.
What is a cell ?
Answer:
Cell. A cell is a structural and functional unit of life.
Question 27.
What is nutrition ?
Answer:
Nutrition. It is the process of taking food.
Question 28.
What is respiration ?
Answer:
Respiration is the process of taking oxygen and giving out carbon dioxide.
Question 29.
What is food of fish ?
Answer:
Aquatic insects and micro-organisms.
Question 30.
What is food of frog ?
Answer:
Food of Frog. Small insects.
Question 31.
Name an organism whose body consists of only one cell.
Answer:
Amoeba is a unicellular organism.
Question 32.
What are autotrophs ?
Answer:
Autotrophs. Living organisms that prepare their own food.
Question 33.
What are heterotrophs ?
Answer:
Heterotrophs. Living organisms that depend upon other living or dead organisms for their food.

Question 34.
Why do animals need food ?
Answer:
Animals need food for growth and maintenance of the body.
Question 35.
What is the process of removal of wastes by plants called ?
Answer:
The process of removal of wastes in plants is called secretions.
Short Answer Type Questions
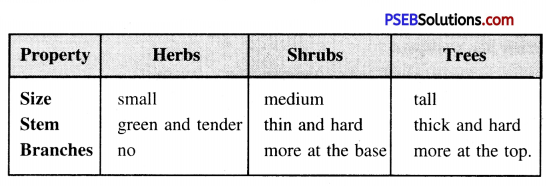
Question 1.
Differentiate between Herbs, Shrubs and Trees.
Answer:
Question 2.
What is meant by conduction of water ?
Answer:
Conduction of water. The movement or transportation of water from roots to different parts of a plant against the gravity pull is called conduction of water i.e. an upward movement of water.
Question 3.
Write the functions of a leaf.
Answer:
Functions of leaf.
- It helps in transpiration of water.
- It carries out photosynthesis process to manufacture food.
- It stores food also.
Question 4.
What are veins ? What is their arrangement known as ?
Answer:
Veins are small lines present on the lamina of a leaf. They may be parallel to one another or net like on both sides of the midrib. This arrangement is known as Leaf Venation.
Question 5.
Define Photosynthesis.
Answer:
Photosynthesis. The process of preparation of food by leaves of green plants using sunlight, water and carbondioxide is called photosynthesis.
Question 6.
Name the underground part of a plant and state its function.
Answer:
Underground part of a plant is called a Root.
Functions of a root :
- It fixes the plant to the soil.
- It absorbs water and dissolved salts from soil.
- Some roots store food.

Question 7.
What is a flower ? Name its different parts.
Answer:
Flower. It is a modified shoot which develops from the flower buds.
Parts of a flower :
- Sepals
- Petals
- Stamens
- Pistils.
Question 8.
What is a thalamus ? What is its function ?
Answer:
Thalamus. The uppermost end of the pedicel is somewhat swollen. This swollen part of the pedicel is known as thalamus.
It is used to bear all the four whorls of a flower.
Question 9.
What are stamens ?
Answer:
Stamens. It is the male reproductive organ. Each consists of a thin stalk or filament and two lobed head called anthers. Inside the anthers there are pollen sacs. The pollen sac contains minute pollen grains.
Question 10.
Differentiate between root and stem.
Answer:
Differences between Root and Stem :
| Root |
Stem |
| (1) It is an underground part of a plant. |
(1) It is the part of the plant mostly above the ground. |
| (2) It grows away from light but in direction of water. |
(2) It grows in the direction of light. |
| (3) It does not bear nodes and internodes. |
(3) It bears nodes and internodes. |
Question 11.
State the meaning of the following terms :
(i) Tap roots
(ii) Fibrous roots
(iii) Root Cap
(iv) Root hair.
Answer:
(i) Tap roots. The main root is called tap root. Tap roots have branches which grow sideways and spread all around the main root.
(ii) Fibrous roots. Roots which seem similar are fibrous roots. They are short and fibrelike. They do not have branches. These roots are called fibrous roots.
(iii) Root cap. The yellowish cover over the tip of the root is called the root cap. The root cap protects the delicate tip of the root from injury.
(iv) Root hair. The hair-like structure of the tender ends of the roots is called root hair. Root hairs absorb salt and water from the soil.
Question 12.
State the meaning of the following terms :
(i) Leat blade
(ii) Leaf apex
(iii) Leaf base.
Answer:
(i) Leaf blade. The broad flat portion of the leaf is called the leaf blade.
(ii) Leaf apex. The tip of the leaf is called the leaf apex.
(iii) Leaf base. The part of the leaf which is joined to the stalk is called the leaf base.
Question 13.
State the meaning of following terms :
(i) Calyx
(ii) Corolla.
Answer:
(i) Calyx. The outermost portion of the flower consisting of a whorl of green leaflike structure is called the calyx.
(ii) Corolla. The whorl inside the calyx is called the corolla. Corolla is made up of partially or fully joined multi-coloured petals.

Question 14.
Why is the leaf an important organ of the plant ?
Answer:
The leaf is an important organ because :
- It prepares food by photosynthesis.
- It performs the function of respiration.
- It performs the function of transpiration.
Question 15.
What is a root ?
Answer:
Root. A root is an underground part of the plant. Roots grow downwards in the soil. Usually roots are light yellow or white in colour. There are small branches on the main root. These branches are known as secondary roots. Small fibre-like structures are seen on the surface of the root. These structures are called root hairs. Root hairs absorb water and minerals from the soil.
Question 16.
Discuss the types of roots.
Answer:
Types of Roots. There are two types of roots
(i) Tap root
(ii) Fibrous root.
(i) Tap root. The root that develops from the radicle is called tap root. It grows vertically down into the soil. The tap root gives out branches.
Examples : Pea, neem, mango.
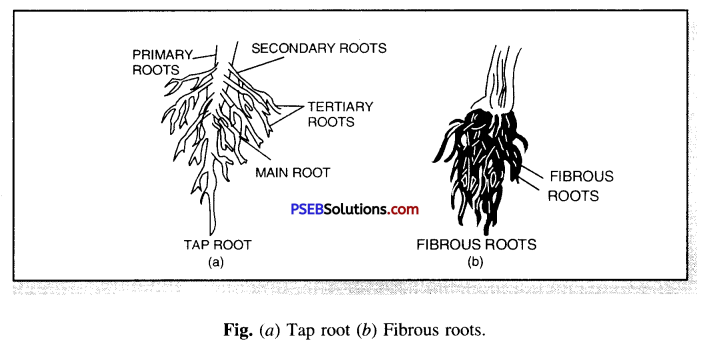
(ii) Fibrous root. Some plants do not have any main root. They have many fibre-like roots. These roots spread out in the soil and give support to the plant.
Examples : Wheat, maize, millet, grass.
Question 17.
What are fleshy roots ?
Answer:
Fleshy roots. In some plants, for example, radish, carrot and turnip, the roots store the food. Such roots become thick and fleshy due to the storing of food are also called fleshy roots.
Question 18.
Why are stamens and pistils important parts of the flower ?
Answer:
Importance of stamens and pistils. The formation of seeds by the process of fertilisation takes place in the flowers. In this process, pollen grains from the androecium combine with the ovules of the ovary to form a seed.
Question 19.
Give one or two-word terms for the following statements :
(i) The underground part of the plant.
(ii) The type of roots found in wheat, maize and sugarcane.
(iii) The portion of plant above the ground.
(iv) Green expanded part of the plant which arises on the nodes of the stem.
(v) The plants which have stems modified for photosy-nthesis and leaves modified into spines for protection.
(vi) The process of manufacture of food by plants in the presence of sunlight and chlorophyll.
(vii) The reproductive part of the plant.
(viii) The stem between two nodes.
Answer:
(i) Root system
(ii) Fibrous roots
(iii) Shoot system
(iv) Leaf
(v) Cacti
(vi) Photosynthesis
(vii) Flower
(viii) Intemode.

Question 20.
Which parts of a flower are useful for reproduction ?
Answer:
Useful parts for reproduction are : (i) Stamens or Androecium and (ii) Carpels or Gynaecium.
Question 21.
Which organ of the flower does the function of producing fruit and seed ?
Answer:
Carpel of the flower does the function of producing fruit and seed.
Question 22.
Give two examples of each :
(i) Plants with fibrous roots
(ii) Roots storing food
(iii) Supporting roots
(iv) Stems storing food
(v) Stems with tendrils
(vi) Leaves with tendrils.
Answer:
(i) Coconut tree, Maize plant
(ii) Radish, Carrot
(iii) Maize, Aerial roots of a banyan tree
(iv) Potato, Ginger
(v) Grapevine, Pumpkin
(vi) Pea plant, Gloriosa.
Question 23.
State whether the following are roots, stems or leaves :
(i) Potato
(ii) Carrot
(iii) Cabbage
(iv) Radish
(v) Amorphophallus
(vi) Turmeric
(vii) Ginger
(viii) Beet
(ix) Turnip
(x) Sweet potato.
Answer:
Roots : Carrot, Radish, Beet, Turnip, Sweet potato.
Stems : Potato, Amorphophallus, Turmeric, Ginger.
Leaves : Cabbage.
Question 24.
Name the systems of flowering plants. Draw them.
Answer:
All flowering plants have two main systems : (i) Root System (ii) Shoot System.
The Root System which grows mainly underground. The Shoot system grows above the ground as shown in diagram.
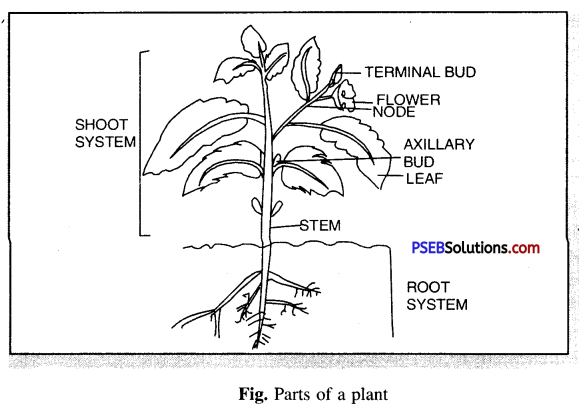
Question 25.
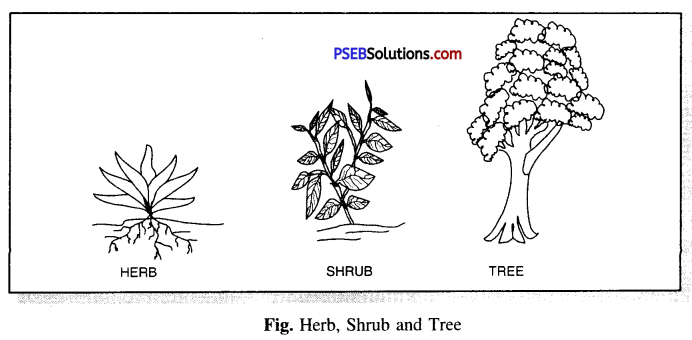
What are herbs, shrubs and trees ? Give examples.
Answer:
Plants are classified as herbs, shrubs and trees.
Herbs. Plants with green and tender stems are called Herbs. They are usually short and sometimes do not have branches e.g. grasses, Dhania etc.
Shrubs. Medium sized plants with branches starting just above the ground are shrubs. Trees. The plants which are very tall and have hard and thick stem. They have branches arising from upper part of the stem. They are called trees. For example, Mango tree, Lemon tree etc.
Question 26.
What is a leaf and what is its role in the life of a plant ?
Answer:
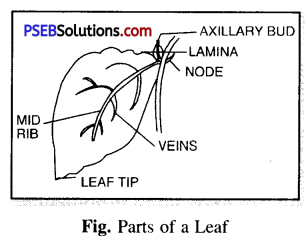
The leaf is a flattened, thin green lateral structure borne on the stem.
A leaf is borne on the stem at a node. It usually has a stalk called petiole and very small leaves at the base of the petiole called the stipules. It has broad expanded green part called leaf blade or Lamina. It has thick midrib in the centre.

Question 27.
What is Venation ? Also classify it.
Answer:
Venation. The pattern of thread-like structures in the leaves forming a network is venation.
Reticulate venation. When the design is net-like on both the sides of mid rib, the venation is said to be reticulate. Examples : rose, tulsi, mint, cabbage.
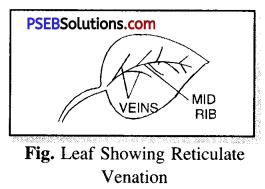
Parallel Venation. When the leaf has veins parallel to one another. Such venation is called Parallel venation. Examples : grass, maize, sugarcane.
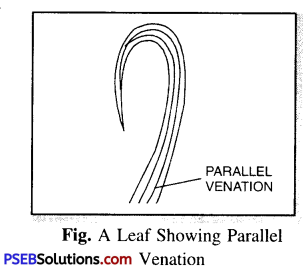
Question 28.
What are the functions of roots ?
Answer:
Roots of plants have following functions :
- Fixation. It fixes the plant firmly in the soil.
- Absorption. Root hairs help in the absorption of water and minerals from the soil.
- Transportation. Water and minerals absorbed by the roots are transported up to the stem and into the branches.
- Prevention of soil erosion. Roots prevent soil erosion.
Question 29.
What are the characteristics of roots ?
Answer:
The root and its branches make up the root system of a plant.
Characteristics of roots.
The root is the underground, non-green part of the plant. It generally grows from the radicle of the embryo of a seed. It grows into the soil, away from sunlight. It does not possess nodes or internodes.
Question 30.
Name some modified roots and stems which we eat.
Answer:
Radish, carrot, potato, sweet potato, beet etc.are modified roots and stems which we eat.
Question 31.
Write three modifications each of stems and roots.
Answer:
Modification of roots : (!) Storage roots (ii) supporting roots (iii) Breathing roots. Modification of stems : (i) Storage of food (ii) Support (iii) Protection.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Explain experimentally that stem helps in conducting water upwards.
Answer:
Experiment. Gently pull out a balsam plant or any other plant with white flowers from the soil. Wash its roots well. Then cut the roots under water. Dip the lower end of the cut stem in a bottle containing water to which few drops of red ink has been added as shown in
fig.
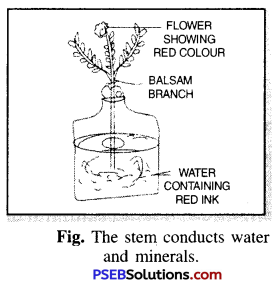
Leave the plant undisturbed for a few hours. Observe the plant carefully. You will notice that the colour of the white flowers changes to red, this is because of conduction of water from stem to flower. This experiment proves that stem helps in conducting water upwards.

Question 2.
Explain through activity the process of Transpiration.
Answer:
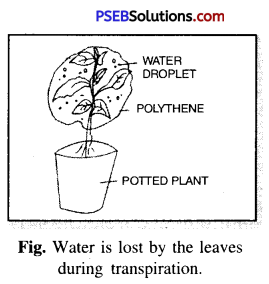
Experiment.
Take a potted plant and cover it with a polythene bag as shown in figure. Observe it after few hours. What do you see in the bag ? You will notice a few droplets of water in the bag. This shows that the water is lost by the leaves during Transpiration.
Question 3.
Discuss the various parts of a flower.
Answer:
A flower may be defined as a modified shoot highly condensed. It develops from the floral buds.
Parts of a flower. Flowers vary in size, shape and colour but all flowers have the same basic parts. The main parts are :
(i) Pedicel and thalamus
(ii) Calyx or sepals
(iii) Corolla or petals
(iv) Androecium or stamens
(v) Gynoecium or carpels.
(i) Pedicel. A flower is borne on a stalk called pedicel. The upper swollen part of pedicel is called thalamus. It bears all the four whorls of a flower.
(ii) Sepals. It is the 1 st outermost whorl of a flower. It consists of leaf like structures called sepals. Sepals are generally green, manufacture food and supply it to other floral parts.
(iii) Petals. It is 2nd whorl of a flower. Each segment of the petal is known as a petal. These are usually brightly coloured due to presence of pigments. The bright colour, sweet smell and nectar attract the insects which in turn help in pollination.
(iv) Androecium or stamens. It is the third floral whorl which is composed of one or more male reproductive organs called stamens. Each stamen consists of a thin stalk or filament and two lobe head called the anther. Each anther lobe has two pollen-sacs which are filled with pollen grains.
(v) Gynoecium or Carpels. It is the innermost floral whorl which is composed of one or more female reproductive organs called carpels. Each carpel consists of three parts : Stigma, Style and Ovary.
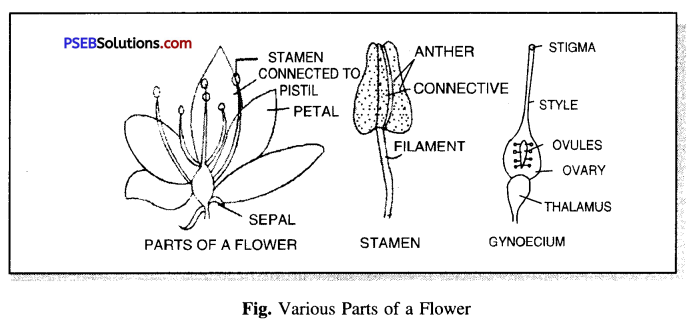
Question 4.
What is a stem? What are the different parts of a stem?
Answer:
Stem. The ascending aerial part of the plant that directly develops from the plumule is called a stem. It is the link between the roots and the leaves and flowers. The stem is the strongest part of a tree and is known as the trunk.
Parts of a stem. A stem consists of the following three parts :
(i) Node. It is a place on the stem or a branch from which a leaf is produced.
(ii) Internode. This is the part of the stem which lies in between the two successive nodes.
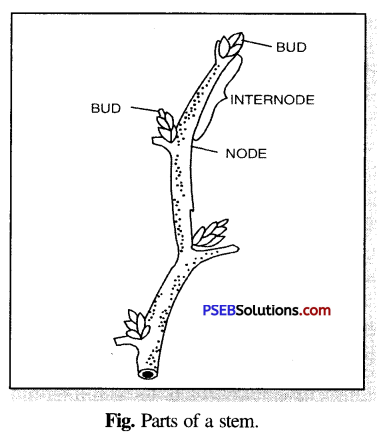
(iii) Bud. It is the condensed part of the stem lying either at the apex of a stem or in the axil of a leaf.
Question 5.
Explain the normal and special functions of stems.
Answer:
Normal functions of stems: The normal functions of stems are :
(i) Stems support the branches of the plant bearing leaves, flowers and fruits.
(ii) They spread the leaves so that every leaf gets sufficient light and air.
(iii) They transport water and salts absorbed by the roots upto the leaves and other parts of the plant.
(iv) The food prepared in the leaves is distributed to the different parts of the plant by the stem.
Special functions of stems.
The special functions of the stems are as follows :
(i) The manufacture of food material. Some plants such as Opuntia, Asparagus, etc., have either no leaves or very small leaves. The stems of such plants are green due to the presence of chlorophyll. Such green stems manufacture food material in the presence of sunlight.
(ii) Support. Some plants such as passionflower, bitter gourd, and grapevines have weak stems. Fiber-like tendrils develop.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()



![]()