Punjab State Board PSEB 10th Class Physical Education Book Solutions Kabaddi Game Rules.
Kabaddi Game Rules – PSEB 10th Class Physical Education
Question 1.
Mention the length and breadth of the Kabaddi ground. Describe the main rules of the game?
Answer:
Playground:
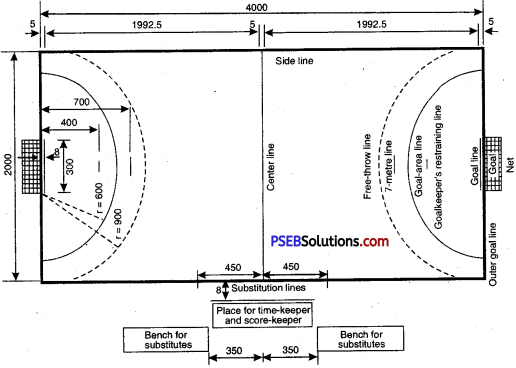
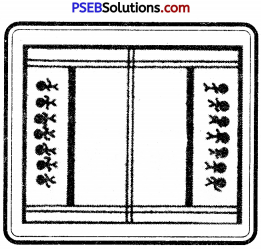
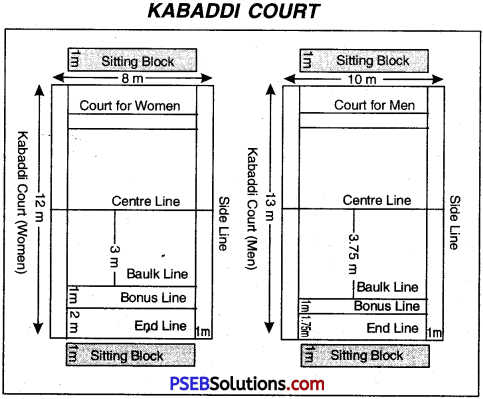
The playground shall be rectangular, level and soft. It should be made of earth, manure or saw dust. For men, it is 12.50 metre long and 10 metre wide. For women and juniors, it is 11 metre long and 8 metre wide. It is divided by a centre line into two equal parts. There shall be a strip of one metre on each side of the playfield. It is called Lobby. In each half at a distance of 3 metres on the centre line and parallel to it, lines of the full width of ground shall be drawn.
These lines are called Baulk lines. The mid-line should be distinctly marked. The width of the mid-line and other lines should not exceed 5 cms, or 2 inches. Outside the side line and towards the end line a space of 4 metres should be left empty. The sitting block shall be 2 metres away from the end line. The sitting block for men shall be 2 m × 8 m., and for women and juniors it shall be 2 m × 6 m.
Bonus Line:
- This line is at a distance of 10 cms. from the baulk line, and for seniors, it is at a distance of 1 metre from the baulk line.
- When a raider comes after having crossed it fully, he does not get any point for it.
- If a raider after having crossed the bonus line is caught, the opposing team is awarded a point.
- If a raider succeeds in crossing the bonus line and also touching an opponent, he is given one point.
Officials:
- One referee
- Two umpires
- Two linesmen
- One scorer
The decisions of the umpire are final, but they can be changed under special circumstances. When the referee considers the decision wrong, he announces his own decision.
Players Dress:
The player’s dress includes a banyan and nicker (half pant). Then there is ‘jangian’ or join-cloth below. The use of safety pin and ring is prohibited. Nails should be pared.
![]()
Rules of The Game
1. The toss winning team shall have the right to choose the end of raid.
2. A player who goes out of the boundary during the play shall be considered ‘out’.
3. If anjapponent goes out of the boundary and catches the raider, the raider shall not be considered ‘out’ but all the players catching him shall be ‘out’. The raider shall come back to his side and take part in their game.
4. Lobby is also considered to be the limit of the game when the struggle starts. When the struggle is over, players in the struggle can enter the respective lobby.
5. A raider should go on sounding the words ‘Kabaddi-Kabaddi’ while entering the court of the opponents. If he starts the cant of Kabaddi only after he has entered the opponent’s court, he is ordered back by the umpire and the opponent shall be given the chance of raiding.
6. If even after the warning the raider deliberately violates the rule, the umpire shall declare his turn over, and his opponent shall be awarded one point, but he shall not be declared out.
7. After a raider has returned to his court, the opposing team shall immediately send its raider. So each side shall send its raiders alternately until the end of the play.
8. If a raider caught by opponents escapes and reaches his side safely, he shall not be pursued thereafter.
9. Only one raider shall go to the anti-court at a time. If more than one raiders reach the anti-court, the umpire shall order them to return to their court, and their turn of raiding shalLbe over. The opponents who touch them shall not be declared out. They shall not pursue the raiders to send them out.
10. If after the warning a player violates the rule, the umpire shall end his turn, and award one point to the opponents, but he shall not be declared ‘out’.
11. If a raider loses his cant in the anti-court, he shall be reckoned to be ‘out’. But if it happens as a result of the use of unfair means by the opponents, then he shall be deemed to have returned safely to his court.
12. No player shall push his opponent violently out of his boundary. The one who does so shall be considered ‘out’, and the raider shall return safely to his court.
13. Until the raider is in the anti-court, no opposing player shall touch with any part of his body the ground of the raider’s court beyond the mid-line.
14. If a player who violates the Rule no. 12 catches the raider or helps others in catching him, the raider shall safely return to his court, and all the opponents involved in the struggle shall be ‘out’.
15. If a player enters the anti-court out of turn, the umpire shall order him to come back. If after the warning by the umpire he does so again, the opponents shall be given one point.
16. According to new rules, it is not a foul to get water from outside and drink it.
17. When a team makes the entire opposing team out, it is successful. Two points are added to the points it has scored in making the opponents out. The players of both the sides shall enter their respective courts, and the game shall continue upto the end of time.
18. If a player warns a raider against any danger by the opponents, the umpire shall award one point against him.
19. No raider or opponent can be held by any part of his body other than his waist, hand or foot. He who violates this rule shall be declared ‘out’.
20. During any play if only one or two players of a team are left and the captain of the opposing team declares them out in order to bring in the play the whole of his team, the opponents shall score as many points as there are players and additional two scores of Lona.
21. With the opponents being out, the out-players of the team shall be put in the game in the same order in which they were out.
22. New Rules – If the match remains suspended for 20 minutes because of injury to some players, the match can be replayed.
23. The match can be started with five players. But when the five players are out, we shall consider full Lona, that is, 5 + 2 score, of players and 2 scores of Lona.
24. Lona has two scores.
![]()
Question 2.
Write five main rules of the Kabaddi match and its violations?
Answer:
Rules Of The Match
1. Each team has twelve members in all, out of which only 7 shall enter the ground together. The remaining shall remain in reserve.
2. For men the game shall have two durations of 20 minutes, and for women, two durations of 15 minutes. There shall be an interval of 5 minutes between these durations of play. The ends shall be changed after the interval.
3. For each player going ‘out’, the opposing team shall be given one score. The team getting Lona shall be given two scores.
4. At the end of the game the team having more scores shall be declared the winner.
5. If the match ends in a draw, two extra durations of 5-5 minutes for play shall be granted. During the extra time the game shall be continued by the end players of the other team. If the tie occurs at the end of 50 minute game for men or 40 minute game for women, the team that scores the first point shall be the winning one.
6. If no score is made during the whole 50 minute game for men or 40 minute game for women, the toss winning team shall be declared the winner.
7. If a match cannot be completed due to some reason, it shall be re-played.
8. In case of an injury to a player, the captain shall ask for a time out. But the duration of the time-out shall not be more than two minutes. The injured player can be substituted. Before starting the second turn of the game, two players can be substituted.
The game can be started by one or two or minimum number of players. At the start of the game those players who are absent can join the game later at any time, but the referee must be informed. If the injury to a player is serious, the injured player can be substituted. By the end of the first game, only two players can be substituted.
9. A match may be started if there are five players in a team but
(i) when the seven players of the team are out, the absent players shall also be ‘out’ and the opposing team shall be awarded Lona, (ii) the absent players can join the game with the referee’s permission.
(iii) the substitutes can be taken in place of absent players any time, but when they are so taken, no player can be substituted till the end of the match, and (iv) any player can be substituted in case the match is re-played.
10. Playing by using oil on the body is not permissible. The nails of the players should be pared well. The players shall wear banyan, underwear the nicker (half pant). Rubber-soled shoes and socks may be put on, if necessary.
11. During the play except the captain or leader, no player shall instruct. The captain can instruct only in his own half.
12. For junior boys and girls the duration of play is 15-5-15 minutes, out of which the interval is of 5 minutes.
Various Fouls and Violations in Kabaddi Fouls.
- To try to stifle a raider by shutting his mouth or throttling him.
- Using violent tackling by one player against the other.
- Instruction or coaching cannot be done from the outside.
- To hold the raider with the half of leg-scissors.
- It is a foul when player on rest takes more than five minutes.
- To take more than five seconds to send a raider by a team.
- The referee can remove such players from the game by deducting their scores or marks. The whistle shall not be blown during the time of struggle.
- To catch by hair or clothes intentionally is foul.
Violations
- Violating the rules or decisions time and again.
- Using derogatory remarks against the officials.
- To show insulting behaviour to the officials or to try to influence their decisions.
- To make insulting remarks to the opponent.
FOULS PLAY:
Referee or umpire will control the match of tournament by using the cards:
GREEN CARD:
Warning to player or coach.
YELLOW CARD:
Temporary suspension for 2 minutes.
RED CARD:
Suspension for the match or for the tournament
![]()
Important Information About the Kabbadi Game
- The length of the ground for men = 13 Metre
- The Breadth of the ground for men = 10 Metre
- The length of‘the ground for women = 12 Metre
- The breadth of ground for women = 8 Metre
- The length and breadth for Junior boys & girls = 11 × 8 metre
- Total number of players in a team = 12
- Duration of the match for men = 20-5-20 Minutes
- Duration of play for women = 15-5-15 M.
- Breadth of the lines = 5 cms.
- Points of Iona = 2 points
- Size of sitting block for men = 1 × 8 M.
- Size of sitting block for women = 1 × 6 M.
- Officials of the match = One referee, Two umpires, one scorer, one time-keeper, two linemen
- Each team has 7 players. Seven players shall play in ground at one time. There are 5 substitutes.
- The team that wins the toss chooses the end and also gets an opportunity of the raid first.
- The game has two durations of 20 minutes each with an interval of 5 minutes. For women and juniors the duration of the game is 15-5-15 minutes, out of which there is an interval of 5 minutes.
- If any player leaves the ground, he shall be declared ‘out’.
- If any part of the body of a player touches the outside of the boundary of the ground, he shall be ‘out’.
- If the match is not completed for some reason, it shall be replayed.
- A player cannot use oil or any greasy matter on his body.
- During the game no player can hold the other player by leg scissors.
- A substitute may take the place of a player if he is injured.
- The captain can take a time-out with the permission of the referee, but the duration of the time-out should not be more than 2 minutes.
- The player can be given water from outside the boundary. If water is given inside the boundary, it is a foul.
- A team can substitute three players.
- If a team gets a Lona, it is given additional two points.
- Substitutes cannot be substituted again.