Punjab State Board PSEB 7th Class Computer Science Book Solutions Chapter 8 Storage Devices Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
PSEB Solutions for Class 7 Computer Science Chapter 8 Storage Devices
Computer Guide for Class 7 PSEB Storage Devices Textbook Questions and Answers
1. Fill in the Blanks
Question 1.
Primary memory is also called ……………..
(a) Internal memory
(b) External memory
(c) Physical memory
(d) Auxiliary memory.
Answer:
(a) Internal memory
Question 2.
…………….memory is not a Read-Only Memory.
(a) ROM
(b) PROM
(c) EPROM
(d) RAM.
Answer:
(a) ROM

Question 3.
…………….is not a portable storage device.
(a) External Hard Disk
(b) Pen Drive
(c) Hard Disk Drive
(d) Memory Card.
Answer:
(c) Hard Disk Drive
Question 4.
The memory is divided into number of small parts called ……………. .
(a) Cells
(b) Area
(c) Inter-section
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(a) Cells
Question 5.
USB means ……………. .
(a) Uniform Service Book
(b) Universal Serial Bus
(c) Universal Straight Bus
(d) Uniform Serial Bus.
Answer:
(b) Universal Serial Bus

2. Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is the capacity of floppy disk?
Answer:
1.4 MB.
Question 2.
What is the capacity of Compact Disc (CD)?
Answer:
650-700 MB.
Question 3.
Which memory unit is usually used to measure the Storage capacity of a hard disks?
Answer:
1 GB Memory unit is used to measure the storage capacity of a hard disk.
Question 4.
Which is having greater storage capacity out of CD or DVD?
Answer:
DVD has higher storage capacity.
Question 5.
Which computer port is used to attach Pen Drive?
Answer:
USB Port.

3. Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is memory? Write down two main categories of memories.
Answer:
Computer memory is a physical device capable of storing data and information. It is a storage space where data and instructions are stored either for processing or for further uses. It can store data and instructions either temporarily (RAM) or permanently (ROM).
Memory can be of two types, Primary Memory and Secondary Memory.
Question 2.
Write the name of any four Secondary Memory devices.
Answer:
Hard Disk, Floppy Disk, Pen Drive and Memory Card.
Question 3.
What is Memory Card?
Answer:
A memory card is a flash memory. It is used in electronic devices such as digital cameras, mobile phones or video game consoles. The memory card can , store data, images, music, games or other computer files. Memory cards have no J moving parts so they are not easily damaged. They are more compact and portable than CDs or DVDs, and they can store more data than CDs. The data stored in the memory card can be read with the help of card reader.

Question 4.
Write a short note on Pen Drive.
Answer:
A pen drive is a portable Universal Serial Bus (USB) flash memory device. It is used to store and transfer audio, video and data files from a computer. The major advantage of USB pen drives over other portable storage devices such as floppy disks or DVDs / CDs is their compact shape and size; they work faster and can store more data.
Question 5.
Write about CD.
Answer:
A compact disc (CD) is a type of optical secondary storage media. It is circular in shape and small in size. A CD is a portable device that we use for ,, storing text, video, audio, graphics, images, or taking backup of data, programs and software. A CD can store around 700 MB data.
4. Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Write a note on Primary Memory.
Answer:
The primary memory is also known as the main memory of a computer. It is in-built memory of a computer in which data and instructions are stored for processing. It is essential for the working of a computer.
There are two types of primary memory: RAM and ROM.
RAM:
RAM stands for Random Access Memory. This is a volatile memory. This means it stores data or instructions temporarily. It is located on the motherboard. When you start the computer, Data and instructions from the hard disk are stored in RAM.
RAM is further divided into two types:
- SRAM (Static Random Access Memory): This stores a bit of data using the state of a six transistor memory cell.
- DRAM (Dynamic Random Access Memory): This stores a bit data using a pair of transistor and. capacitor which constitute a DRAM memory cell.
ROM:
The term ROM stands for Read Only Memory. It is a non-volatile memory. As the name indicated, information can only be read from this type of – memory. It stores the data permanently.
Types of Read Only Memory (ROM):
- PROM (Programmable Read Only Memory)
- EPROM (Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory)
- EEPROM (Electrically Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory).

Question 2.
What is HDD? Explain.
Answer:
Hard disks are the secondary storage devices used to store data permanently. It is directly connected to the disk controller on the motherboard. Hard disks are flat, circular plates made of aluminum or glass and coated with a magnetic material. Hard disk platters typically spin very fast at 5400 to 7200 cycles/minute.
There are two types of Hard disks:
1. Internal Hard Disk:
Internal hard drives are located inside your computer. Most computers come with a single internal hard drive, which includes the operating system and pre-installed applications.
2. External Hard Drive:
An external hard drive, also called a portable hard drive. It is a device connected to the outside of a computer via a USB connection. It is often used to back up a computer or portable storage.
Question 3.
What is Secondary Memory? Explain any one secondary memory device.
Answer:
Secondary memory is permanent memory. It is not directly accessible by CPU. It communicates with the CPU through the main memory. Secondary memory stores data and holds it even when power is off. It is used to store large amount of data or programs. It is less expensive than the primary memory.
Pen Drive:
A pen drive is a portable universal serial bus (USB) flash memory device. It is used to store and transfer audio, video and data files from a computer. The major advantage of USB pen drives over other portable storage devices such as floppy disks or DVDs/CDs is their compact shape and size; they work faster and can store more data.
Question 4.
Write precautions that we must follow while using CD/DVD.
Answer:
While using CDs and DVDs, we should keep the following in mind :
- CD / DVD should always be covered.
- The back shiny part of the CD / DVD should not be touched.
- Don’t write on the back of the CD / DVD.
- CD / DVD should not be folded.
- To clean CDs / DVDs, a soft cloth should be used. You can also use water to remove dust from it.

Question 5.
What is External Hard Disk drive? Write its advantages.
Answer:
External disk drive is a portable secondary memory. It has large storage capacity. It is a removable device. The external disk drive is connected to computer through USB port. These disks allow user to put sensitive, confidential or important information on them, then disconnect them and store them in secure locations.
Activity
Question 1.
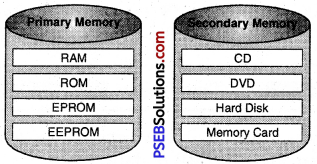
Put the following Terms in respective Groups
1. RAM
2. CD
3. Hard Disk
4. ROM
5. EPROM
6. Memory Card
7. DVD
8. EEPROM
Answer:

PSEB 7th Class Computer Guide Storage Devices Important Questions and Answers
1. Fill in the Blanks
Question 1.
The size of a commonly used floppy is ……………. inches.
(a) 2.5
(b) 3.5
(c) 4.5
(d) 5.25
Answer:
(b) 3.5
Question 2.
A CD can store ……………..MB data.
(a) 600
(b) 700
(c) 800
(d) 200.
Answer:
(b) 700
Question 3.
1 GB ……………. is equal to MB.
(a) 512
(b) 8
(c) 1024
(d) 256.
Answer:
(c) 1024
Question 4.
Primary memory is divided into ……………. parts.
(a) Two
(b) Three
(c) Four
(d) Five.
Answer:
(a) Two
Question 5.
Used to store a lot of multimedia information ……………. .
(a) CD
(b) DVD (Digital Versatile Disk)
(c) B.D.
(d) Floppy.
Answer:
(b) DVD (Digital Versatile Disk)

Question 6.
1024 bytes = ……………. .
(a) 1 MB
(b) 1 GB
(c) 1 KB
(d) 10 MB.
Answer:
(c) 1 KB
Question 7.
Which of the following is an optical storage media?
(a) Hard disk
(b) CD
(c) RAM
(d) Floppy.
Answer:
(b) CD
Question 8.
Which of the following stores high definition videos?
(a) CD
(b) DVD
(c) Blu-ray
(d) Floppy Disk.
Answer:
(c) Blu-ray
Question 9.
The CPU directly retrieves information or data from the ……………. .
(a) Hard disk
(b) CD
(c) RAM
(d) DVD.
Answer:
(c) RAM
Question 10.
Which of the following is a secondary storage device?
(a) ROM
(b) Cache
(c) Hard disk
(d) RAM.
Answer:
(c) Hard disk

2. True/False
1. The main memory is available in the form of an electronic chip.
Answer:
True
2. The floppy disk can store 700 MB of data.
Answer:
False.
3. A DVD can store 4.7 GB data.
Answer:
True
4. Always write with a sharpened pen on the back of the CD/DVD.
Answer:
False.
5. Do not keep the floppy in a dry, clean and cool place.
Answer:
False.
6. A hard disk can store 2 TB to 5 TB data.
Answer:
True
7. The primary memory comprises of RAM and ROM.
Answer:
True

8. The secondary memory is also known as main storage.
Answer:
False.
9. 1 GB is equal to 1024 MB.
Answer:
True
10. Individually, a binary number is known as bit.
Answer:
True
11. RAM is not faster than secondary storage devices.
Answer:
True
12. Bits and bytes are units of computer memory.
Answer:
True
13. A portable hard disk is generally used for taking back up.
Answer:
True
14. The instructions that are written onto ROM can be altered.
Answer:
False.

3. write the Full Forms
Question 1.
1. KB.
2. MB,
3. GB,
4. TB,
5. ROM,
6. RAM,
7. CD,
8. DVD.
Answer:
1. KB: Kilobytes
2. MB: Megabytes
3. GB: Gigabytes
4. TB: Terabytes
5. ROM: Read Only Memory
6. RAM: Random Access Memory
7. CD: Compact Disc
8. DVD: Digital Versatile Disc.

4. Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Name two types of primary memory.
Answer:
- RAM (Random Access Memory)
- ROM (Read Only Memory).
Question 2.
Name four storage devices.
Answer:
- CD (Compact Disc)
- DVD (Digital Versatile Disk)
- Floppy disk
- Hard disk.
Question 3.
Explain the differences between RAM and ROM.
Answer:
Following are the important differences between RAM and ROM:
| RAM |
ROM |
| 1. RAM stands for Random Access Memory |
1. ROM stands for Read Only Memory. |
| 2. RAM data is volatile. Data is present till power supply is present. |
2. ROM data is permanent. Data remains even after power supply is not present. |
| 3. RAM data can be read, erased or modified. |
3. ROM data is read only. |
| 4. RAM is used to store data that CPU needs for current instruction processing. |
4. ROM is used to store data that is needed to bootstrap the computer. |
| 5. RAM speed is quite high. |
5. ROM speed is slower than RAM. |
| 6. CPU can access data stored on RAM. |
6. Data to be copied from ROM to RAM so that CPU can access its data. |
| 7. RAM memory is large and of high capacity. |
7. ROM is generally small and of low capacity. |
| 8. RAM is used as CPU Cache, Primary Memory. |
8. ROM is used as firmware by micro controllers. |
| 9. RAM is costly. |
9. ROM is cheap. |

Question 4.
What is a floppy disk?
Answer:
It is a secondary device in which data is stored. It is a circular plastic plate. It is 3.5 inches in size. The floppy disk can store 1.44 MB of data.
Question 5.
Provide information about CD ROM.
Answer:
The full name of CD ROM is Compact Disk Read Only Memory. It can store up to 700 MB of data. The information is written only once in Read Only CD. It cannot be changed after that.
Question 6.
Why we use DVD?
Answer:
The full name of DVD is Digital Versatile Disk. It can store a lot of data. DVD is a type of optical media used to store digital data. A DVD can store 2 TB to 5 TB data.
5. Long Answer Type Questions

Question 1.
Describe the types of memory. Answer in detail.
Answer:
Types of Computer Memory –
There are many types of memory in a computer; the most basic is primary memory, also called system memory, and the secondary memory, commonly called storage. Details about these memories are given ahead:
Primary Memory:
Primary memory is the main memory of a computer system. It stores the data temporarily. It holds only those data on which computer is currently working. Primary memory is directly accessed by the CPU. It has limited storage capacity and data is lost when power is switched off. Primary memory is a semiconductor memory because it is manufactured using semiconductor devices. The capacity of primary memory is very limited and is always less than that of secondary memory. It is more expensive than secondary memory.
Characteristics of Main Memory:
- These are semiconductor memories.
- It is known as the main memory.
- Usually volatile memory.
- Data is lost in case power is switched off.
- It is the working memory of the computer.
- Faster than secondary memories.
- A computer cannot run without the primary memory.
Types of Primary Memory:
There are two types of primary memory:
1. RAM (Random Access Memory)
2. ROM (Read Only Memory)
1. RAM:
RAM stands for Random Access Memory. This is a volatile memory. This means it stores data or instructions temporarily. It is located on the motherboard. When you start the computer, Data and instructions from the hard disk are stored in RAM. The CPU uses this data to perform the required functions. RAM loses all data as soon as you shut down the computer.
The most important thing to understand about RAM is that RAM memory is very fast, it is a read/write memory. It is much more expensive than secondary memory. Due to the high cost of RAM, most computer systems use both primary and secondary memory, RAM is further divided into two types :
(a) SRAM (Static Random Access Memory): This stores a bit of data using the state of a six transistor memory cell.
(b) DRAM (Dynamic Random Access Memory): This stores a bit data using a pair of transistor and capacitor which constitute a DRAM memory cell.
SRAM:
- Transistors are used to store information in SRAM.
- Capacitors are used to store data in DRAM.
- SRAM is faster as compared to DRAM.
- DRAM provides slow access speeds.
- These are expensive.
- These are cheaper.
- SRAMs are low density devices.
- DRAMs are high density devices.
- These are used in cache memories.
- These are used in main memories.
2. ROM:
This means read only memory. It is a non-volatile memory. It stores the data permanently. These are the IC (integrated circuits) inside the PC that makes up the ROM. ROM stores a startup program called ‘Bootstrap Loader’. When the computer’s power is turned on “Bootstrap Loader” checks and starts the device connected to the PC. ROM can only be read by CPU but cannot be changed.
Types of Read Only Memory (ROM) :
(a) PROM (Programmable Read Only Memory):
PROM is read¬only memory that can be modified only one time by a user.. Once programmed, the data and instructions contained in it cannot be changed.
(b) EPROM (Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory):
It can be reprogrammed. To delete data from it, place it in front of an ultra violet light. To re-program it, delete all previous data
(c) EEPROM (Electrically Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory):
Data stored in EEPROM can be deleted and modified as many times as user wants. Implementing electric field can erase data, no need for ultra-violet light. We can only delete parts of the chip.
Secondary Memory:
Secondary memory is permanent memory. It is not directly accessible by CPU. It communicates with the CPU through the main memory. Secondary memory stores data and holds it even when power is off. It is used to store large amount of data or programs. It is less expensive than the primary memory.
Secondary memory refers to the various storage media on which a computer can store data and programs. Floppy disks, Hard Disks, magnetic disks, magnetic tapes are the examples of secondary memory.
The Secondary storage media are of two types :
- Fixed: Fixed Storage media is an internal storage medium like hard disk that is fixed inside the computer.
- Removable: Storage medium that are portable and can be taken outside the computer are termed as removable storage media like CD, DVD, Pen drive etc.
Characteristics of Secondary Memory:
- These are magnetic and optical memories.
- It is known as the backup memory.
- It is a non-volatile memory.
- Data is permanently stored even if power is switched off.
- It is used for storage of data in a computer.
- Computer may run without the secondary memory.
- Slower than primary memories.
(i) Magnetic Tapes:
Magnetic discs are made of hard metal or synthetic plastic material. Magnetic material is coated on both sides of the disc platter and both sides can be used for storage. The magnetic disk provides direct access to both small and large computer systems. Magnetic audio tapes are used to record sound and music. Magnetic video tapes are used to record analog voice and video signals. These are low cost tapes. Hard disks and floppy disks are examples of magnetic tapes.
(ii) Floppy Disk:
Also known as floppy diskette, it is a removable, portable secondary storage device. This was created in 1964 by IBM. It is a small plastic disc about 3.5 inches in size. These disks have very low storage capacity and can store approximately 1.4 MB of data. It can be read or written by a floppy disk drive.
(iii) Hard Disk:
Hard disks are the secondary storage devices used to store data permanently. It is directly connected to the disk controller on the motherboard. Hard disks are flat, circular plates made of aluminum or glass and coated with a magnetic material. Hard disk platters
typically spin very fast at 5400 to 7200 cycles/minute.
It has unlimited storage space and its storage capacity ranges from 20 GB to 500 GB. It used to install a new program or application on the device. Software programs, images, videos, etc. all can be saved to the hard drive. There are two types of hard disks.
1. Internal Hard Disk: Internal hard drives are located inside your computer. Most computers come with a single internal hard drive, which includes the operating system and pre-installed applications.
2. External Hard Drive:
An external hard drive, also called a portable hard drive. It is a device connected to the outside of a computer via a USB connection. It is often used to back up a computer or portable storage.
(iv) Optical Drives:
Optical drives are a storage medium from which data is read and written by a laser. Optical disks can store up to 6GB of data. Optical storage devices are the most widely used and reliable storage devices. The most commonly used types of optical storage devices are:
-
- CD-ROM
- DVD-ROM
- CD-RECORDABLE
- CD-REWRITABLE
- PHOTO-CD
CD:
A compact disc is a flat, round, optical storage medium invented by James Russell. It is a portable storage medium that was used to digitally store and play the audio, video and other data. Compact discs have greater storage capacity than floppy disks. These disks can store 650-700 MB of data. This is a very reliable storage media. There are two types of CDs :
(а) CD-R:
CD-R stands for Compact Disc-Recordabie, also known as ROM is a digital optical disk storage format. A CD-R disc is a compact disc that can be written once and arbitrarily read multiple times.
(b) CD-RW:
CD-RW (compact disc-rewritable) is a digital optical disk storage format introduced in 1997. A CD-RW compact disc (CD-RW) can be read, written, erased, and rewritten.
2.DVD:
Stands for Digital Video Disc or Digital Versatile Disc. It is a digital optical disc data storage format that was invented and developed in 1995 and released in late 1996. DVD is a type of optical media used to store digital data. It is the same size of a CD, but it has a large storage capacity. Some DVDs are specifically formatted for video playback, while others contain different types of data, such as software programs and computer files.
While using CDs and DVDs, we should keep the following in mind:
- CD / DVD should always be covered.
- The back shiny part of the CD / DVD should not be touched.
- Don’t write on the back of the CD / DVD.
- CD / DVD should not be folded.
- To clean CDs / DVDs, a soft cloth should be used. You can also use water to remove dust from it.
Pen Drive:
A pen drive is a portable universal serial bus (USB) flash memory device. It is used to store and transfer audio, video and data files from a computer. The major advantage of USB pen drives over other portable storage devices such as floppy disks or DVDs / CDs is their compact shape and size; they work faster and can store more data. Memory Card: A memory card is a flash memory. It is used in electronic devices such as digital cameras, Mobile phones or video game consoles. The memory card can stores data, images, music, games or other computer files. Memory cards have no moving parts so they are not easily damaged. They are more compact and portable than CDs or DVDs, and they can store more data than CDs. The data stored in the memory card can be read with the help of card reader.

Question 2.
What is secondary memory? Explain its types in detail.
Answer:
Secondary Memory:
Secondary memory is permanent memory. It is not directly accessible by CPU. It communicates with the CPU through the main memory. Secondary memory stores data and holds it even when power is off. It is used to store large amount of data or programs. It is less expensive than the primary memory.
Secondary memory refers to the various storage media on which a computer can store data and programs. Floppy disks, Hard Disks, magnetic disks, magnetic tapes are the examples of secondary memory.
The Secondary storage media are of two types:
- Fixed: Fixed Storage media is an internal storage medium like hard disk that is fixed inside the computer.
- Removable: Storage medium that are portable and can be taken outside the computer are termed as removable storage media like CD, DVD, Pen drive etc.
Characteristics of Secondary Memory:
- These are magnetic and optical memories.
- It is known as the backup memory.
- It is a non-volatile memory.
- Data is permanently stored even if power is switched off.
- It is used for storage of data in a computer.
- Computer may run without the secondary memory.
- Slower than primary memories.
(i) Magnetic Tapes:
Magnetic discs are made of hard metal or synthetic plastic material. Magnetic material is coated on both sides of the disc platter and both sides can be used for storage. The magnetic disk provides direct access to both small and large computer systems. Magnetic audio tapes are used to record sound and music. Magnetic video tapes are used to record analog voice and video signals. These are low cost tapes. Hard disks and floppy disks are examples of magnetic tapes.
(ii) Floppy Disk:
Also known as floppy diskette, it is a removable, portable secondary storage device. This was created in 1964 by IBM. It is a small plastic disc about 3.5 inches in size. These disks have very low storage capacity and can store approximately 1.4 MB of data. It can be read or written by a floppy disk drive.
(iii) Hard Disk:
Hard disks are the secondary storage devices used to store data permanently. It is directly connected to the disk controller on the motherboard. Hard disks are flat, circular plates made of aluminum or glass and coated with a magnetic material. Hard disk platters typically spin very fast at 5400 to 7200 cycles/minute.
It has unlimited storage space and its storage capacity ranges from 20 GB to 500 GB. It used to install a new program or application on the device. Software programs, images, videos, etc. all can be saved to the hard drive. There are two types of hard disks.
1. Internal Hard Disk: Internal hard drives are located inside your computer. Most computers come with a single internal hard drive, which includes the operating system and pre-installed applications.
2. External Hard Drive:
An external hard drive, also called a portable hard drive. It is a device connected to the outside of a computer via a USB connection. It is often used to back up a computer or portable storage.
(iv) Optical Drives:
Optical drives are a storage medium from which data is read and written by a laser. Optical disks can store up to 6 GB of data. Optical storage devices are the most widely used and reliable storage devices. The most commonly used types of optical storage devices are:
-
- CD-ROM
- DVD-ROM
- CD-RECORDABLE
- CD-REWRITABLE
- PHOTO-CD
1. CD:
A compact disc is a flat, round, optical storage medium invented by James Russell. It is a portable storage medium that was used to digitally store and play the audio, video and other data. Compact discs have greater storage capacity than floppy disks. These disks can store 650-700 MB of data. This is a very reliable storage media. There are two types of CDs :
(а) CD-R:
CD-R stands for Compact Disc-Recordabie, also known as ROM is a digital optical disk storage format. A CD-R disc is a compact disc that can be written once and arbitrarily read multiple times.
(b) CD-RW:
CD-RW (compact disc-rewritable) is a digital optical disk storage format introduced in 1997. A CD-RW compact disc (CD-RW) can be read, written, erased, and rewritten.
2. DVD:
Stands for Digital Video Disc or Digital Versatile Disc. It is a digital optical disc data storage format that was invented and developed in 1995 and released in late 1996. DVD is a type of optical media used to store digital data. It is the same size of a CD, but it has a large storage capacity. Some DVDs are specifically formatted for video playback, while others contain different types of data, such as software programs and computer files.
While using CDs and DVDs, we should keep the following in mind:
- CD / DVD should always be covered.
- The back shiny part of the CD / DVD should not be touched.
- Don’t write on the back of the CD / DVD.
- CD / DVD should not be folded.
- To clean CDs / DVDs / DVDs, a soft cloth should be used. You can also use water to remove dust from it.
3. Pen Drive:
A pen drive is a portable universal serial bus (USB) flash memory device. It is used to store and transfer audio, video and data files from a computer. The major advantage of USB pen drives over other portable storage devices such as floppy disks or DVDs / CDs is their compact shape and size; they work faster and can store more data.
4. Memory Card:
A memory card is a flash memory. It is used in electronic devices such as digital cameras, Mobile phones or video game consoles. The memory card can stores data, images, music, games or other computer files. Memory cards have no moving parts so they are not easily damaged. They are more compact and portable than CDs or DVDs, and they can store more data than CDs. The data stored in the memory card can be read with the help of card reader.

Question 3.
Explain the difference between primary and secondary memory.
Answer:
Differences between Primary Memory and Secondary Memory:
In this lesson, we have talked about both primary and secondary memory. Both are quite useful in their own way, now we will look at the difference between the both.
- Primary memory is also called internal memory. Secondary memory is also called backup memory or auxiliary memory.
- Primary memory can be accessed by data bus while secondary memory is accessed through I/O channels.
- Primary memory data is accessed directly by the processing unit. Secondary memory data cannot be accessed directly by the processor.
- Primary memory is more expensive than secondary memory. Secondary memory is cheaper than primary memory.
- Primary memory is both unstable and static. Secondary memory is always unchanging memory.
Question 4.
What is DVD? Explain in detail.
Answer:
DVD:
Stands for Digital Video Disc or Digital Versatile Disc. It is a digital optical disc data storage format that was invented and developed in 1995 and released in late 1996. DVD is a type of optical media used to store digital data. It is the same size of a CD, but it has a large storage capacity. Some DVDs are specifically formatted for video playback, while others contain different types of data, such as software programs and computer files.
While using CDs and DVDs, we should keep the following in mind :
- CD / DVD should always be covered.
- The back shiny part of the CD / DVD should not be touched.
- Don’t write on the back of the CD / DVD.
- CD / DVD should not be folded.
- To clean CDs / DVDs / DVDs, a soft cloth should be used. You can also use water to remove dust from it.

Question 5.
What is a magnetic tape? Explain in detail.
Answer:
Magnetic Tapes:
Magnetic discs are made of hard metal or synthetic plastic material. Magnetic material is coated on both sides of the disc platter and both sides can be used for storage. The magnetic disk provides direct access to both small and large computer systems. Magnetic audio tapes are used to record sound and music. Magnetic video tapes are used to record analog voice and video signals. These are low cost tapes. Hard disks and floppy disks are examples of magnetic tapes.
Question 6.
What is a hard disk and how many types are there?
Answer:
Hard Disk:
Hard disks are the secondary storage devices used to store data permanently. It is directly connected to the disk controller on the motherboard. Hard disks are flat, circular plates made of aluminum or glass and coated with a magnetic material. Hard disk platters typically spin very fast at 5400 to 7200 cycles/minute.
It has unlimited storage space and its storage capacity ranges from 20 GB to 500 GB. It used to install a new program or application on the device. Software programs, images, videos, etc. all can be saved to the hard drive. There are two types of hard disks.
1. Internal Hard Disk:
Internal hard drives are located inside your computer. Most computers come with a single internal hard drive, which includes the operating system and pre-installed applications.
2. External Hard Drive:
An external hard drive, also called a portable hard drive. It is a device connected to the outside of a computer via a USB connection. It is often used to back up a computer or portable storage.

Question 7.
What do you mean by Optical drive?
Answer:
Optical Drives:
Optical drives are a storage medium from which data is read and written by a laser. Optical disks can store up to 6 GB of data. Optical storage devices are the most widely used and reliable storage devices. The most commonly used types of optical storage devices are:
-
- CD-ROM
- DVD-ROM
- CD-RECORDABLE
- CD-REWRITABLE
- PHOTO-CD
1. CD:
A compact disc is a flat, round, optical storage medium invented by James Russell. It is a portable storage medium that was used to digitally store and play the audio, video and other data. Compact discs have greater storage capacity than floppy disks. These disks can store 650-700 MB of data. This is a very reliable storage media. There are two types of CDs :
(а) CD-R:
CD-R stands for Compact Disc-Recordabie, also known as ROM is a digital optical disk storage format. A CD-R disc is a compact disc that can be written once and arbitrarily read multiple times.
(b) CD-RW:
CD-RW (compact disc-rewritable) is a digital optical disk storage format introduced in 1997. A CD-RW compact disc (CD-RW) can be read, written, erased, and rewritten.
2. DVD:
Stands for Digital Video Disc or Digital Versatile Disc. It is a digital optical disc data storage format that was invented and developed in 1995 and released in late 1996. DVD is a type of optical media used to store digital data. It is the same size of a CD, but it has a large storage capacity. Some DVDs are specifically formatted for video playback, while others contain different types of data, such as software programs and computer files.
While using CDs and DVDs, we should keep the following in mind:
- CD / DVD should always be covered.
- The back shiny part of the CD / DVD should not be touched.
- Don’t write on the back of the CD / DVD.
- CD / DVD should not be folded.
- To clean CDs / DVDs / DVDs, a soft cloth should be used. You can also use water to remove dust from it.
3. Pen Drive:
A pen drive is a portable universal serial bus (USB) flash memory device. It is used to store and transfer audio, video and data files from a computer. The major advantage of USB pen drives over other portable storage devices such as floppy disks or DVDs / CDs is their compact shape and size; they work faster and can store more data.
4. Memory Card:
A memory card is a flash memory. It is used in electronic devices such as digital cameras, Mobile phones or video game consoles. The memory card can stores data, images, music, games or other computer files. Memory cards have no moving parts so they are not easily damaged. They are more compact and portable than CDs or DVDs, and they can store more data than CDs. The data stored in the memory card can be read with the help of card reader.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()