Punjab State Board PSEB 5th Class EVS Book Solutions Chapter 6 ਧਰਤੀ ਸਾਡਾ ਵੀ ਘਰ Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
PSEB Solutions for Class 5 EVS Chapter 6 ਧਰਤੀ ਸਾਡਾ ਵੀ ਘਰ
EVS Guide for Class 5 PSEB ਧਰਤੀ ਸਾਡਾ ਵੀ ਘਰ Textbook Questions and Answers
ਪੇਜ-35
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 1.
ਸਾਡੇ ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰੀ ਜਾਨਵਰ ਅਤੇ ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰੀ ਪੰਛੀ ਦਾ ਨਾਂ ਲਿਖੋ।
ਉੱਤਰ :
ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰੀ ਜਾਨਵਰ – ਬਾਘ
ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰੀ ਪੰਛੀ – ਮੋਰ।
![]()
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 2.
ਖ਼ਾਲੀ ਥਾਂਵਾਂ ਭਰੋ :
(ਉ) ਬਾਘ …………………………. ਪਰਿਵਾਰ ਨਾਲ ਸੰਬੰਧਿਤ ਜੀਵ ਹੈ।
(ਆ) ਬਾਘ ਦੇ ਸਰੀਰ ‘ਤੇ …………………………. ਅਤੇ ਚੀਤੇ ਦੇ ਸਰੀਰ ‘ਤੇ …………………………. ਹੁੰਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ।
(ਈ) ਭਾਰਤ ਵਿੱਚ ਸੰਨ 2008 ਤੱਕ ਲਗਭਗ …………………………. ਬਾਘ ਸਨ
ਉੱਤਰ :
(i) ਬਿੱਲੀ,
(ii) ਕਾਂਲੀਆਂ ਧਾਰੀਆਂ, ਕਾਲੀਆਂ ਦਿੱਤੀਆਂ,
(iii) 1411
ਪੇਜ – 35 – 36
ਕਿਰਿਆ 1. ਤੁਸੀਂ ਵੀ ਆਪਣੇ ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰੀ ਪਸ਼ੂ ਨੂੰ ਬਚਾਉਣ ਵਿਚ ਆਪਣਾ ਯੋਗਦਾਨ ਪਾ ਸਕਦੇ ਹੋ। ਆਓ ਜਾਣੀਏ, ਕਿਵੇਂ?
- ਤੁਸੀਂ ਆਪਣੇ ਸਕੂਲ ਵਿਚ ਟਾਈਗਰ ਕਲੱਬ ਬਣਾ ਸਕਦੇ ਹੋ। ਇਹ ਟਾਈਗਰ ਕਲੱਬ ਬਹੁਤ ਸਾਰੇ ਕੰਮ ਕਰ ਸਕਦਾ ਹੈ।
- ਤੁਸੀਂ ਆਪਣੇ ਸਾਥੀਆਂ ਅਤੇ ਆਪਣੇ ਮਾਤਾ ਪਿਤਾ ਜਾਂ ਹੋਰ ਲੋਕਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਗੱਲਬਾਤ ਰਾਹੀਂ ਇਸ ਗੱਲ ਲਈ ਸਚੇਤ ਕਰ ਸਕਦੇ ਹੋ ਕਿ ਬਾਘ ਦੀ ਹੋਂਦ ਖ਼ਤਰੇ ਵਿੱਚ ਹੈ।
- ਤੁਸੀਂ ਇਸ ਸੰਬੰਧੀ ਪੱਤਰ-ਅਭਿਆਨ ਵੀ ਸ਼ੁਰੂ ਕਰ ਸਕਦੇ ਹੋ। ਜਿਸ ਵਿਚ ਲੋਕਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਪੱਤਰ ਲਿਖ ਕੇ ਵੀ ਬਾਘਾਂ ਦੀ ਸੁਰੱਖਿਆ ਅਤੇ ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਦੇ ਚਮੜੇ ਦੀਆਂ ਬਣੀਆਂ ਚੀਜ਼ਾਂ ਨਾ ਖ਼ਰੀਦਣ ਲਈ ਪ੍ਰੇਰਿਤ ਕਰ ਸਕਦੇ ਹੋ।
- ਤੁਸੀਂ ਸਹਾਇਤਾ ਫੰਡ ਇਕੱਠਾ ਕਰ ਕੇ ਵੀ ਟਾਈਗਰ ਪਰਿਯੋਜਨਾ ਵਿਚ ਆਪਣਾ ਯੋਗਦਾਨ ਪਾ ਸਕਦੇ ਹੋ।
- ਟਾਈਗਰ ਵਾਂਗ ਕਿਸੇ ਹੋਰ ਜੰਤੂ ਦੀ ਹੋਂਦ ਪ੍ਰਤੀ ਜਾਗਰੂਕਤਾ ਪੈਦਾ ਕਰਨ ਲਈ ਵੀ ਉਸ ਦੇ ਨਾਂ ‘ਤੇ ਕਲੱਬ ਦਾ ਗਠਨ ਕੀਤਾ ਜਾ ਸਕਦਾ ਹੈ। ਤੁਸੀਂ ਕਿਸ ਜੰਤੁ ਬਾਰੇ ਕਲੱਬ ਦਾ ਗਠਨ ਕਰਨਾ ਚਾਹੋਗੇ?
ਉੱਤਰ :
ਖ਼ੁਦ ਕਰੋ।
ਪੇਜ – 36 – 37
ਆਓ ਇੱਕ ਚਿੱਤਰਖੰਡ (ਜਿਗਸਾਅ) ਪਹੇਲੀ ਹੱਲ ਕਰੀਏ –
ਚਿੱਤਰਖੰਡ (ਜਿਗਆ ਪਹੇਲੀ-ਇਸ ਪਹੇਲੀ ਵਿੱਚ ਕਿਸੇ ਤਸਵੀਰ ਨੂੰ ਕਈ ਟੁਕੜਿਆਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਇਸ ਤਰੀਕੇ ਨਾਲ ਕੱਟਿਆ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ਕਿ ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਟੁਕੜਿਆਂ ਨੂੰ ਜੋੜ ਕੇ ਮੁੜ ਚਿੱਤਰ ਬਣਾਉਣ ਲਈ ਕਾਫ਼ੀ ਸੋਚਣਾ ਪੈਂਦਾ ਹੈ। ਕਿਸੇ ਜੰਤੁ ਦੀ ਜਿਗਸਾਅ ਪਹੇਲੀ ਬਣਾਉਣ ਲਈ ਉਸ ਦੀ ਤਸਵੀਰ ਨੂੰ ਇੱਕ ਤੇ ਉੱਪਰ ਚਿਪਕਾਓ। ਫਿਰ ਉਸਨੂੰ ਬੇਤਰਤੀਬ ਟੁਕੜਿਆਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਕੱਟ ਲਓ। ਇਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਟੁਕੜਿਆਂ ਨੂੰ ਸਹੀ ਤਰਤੀਬ ਵਿੱਚ ਜੋੜਨਾ ਹੀ ਇਸ ਪਹੇਲੀ ਦਾ ਹੱਲ ਹੈ।
ਉੱਤਰ :
ਖ਼ੁਦ ਕਰੋ।
![]()
ਕਿਰਿਆ-ਡਾਕ ਵਿਭਾਗ ਸਮੇਂ-ਸਮੇਂ ਕਈ ਜੰਤੂਆਂ ਦੀਆਂ ਤਸਵੀਰਾਂ ਵਾਲੇ ਡਾਕ-ਟਿਕਟ ਜਾਰੀ ਕਰਦਾ ਹੈ। ਤੁਸੀਂ ਵੀ ਅਜਿਹੀਆਂ ਡਾਕ-ਟਿਕਟਾਂ ਇਕੱਠੀਆਂ ਕਰ ਸਕਦੇ ਹੋ।

ਚਿੱਤਰ-ਜੰਤੂਆਂ ਵਾਲੇ ਡਾਕ ਟਿਕਟ
ਪੇਜ – 38
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 3.
ਖ਼ਾਲੀ ਥਾਂਵਾਂ ਭਰੋ :
(ਉ) ਬਾਘ ………………………….. ਪਰਿਵਾਰ ਨਾਲ ਸੰਬੰਧਿਤ ਜੀਵ ਹੈ।
(ਅ) ਬਾਘ ਦੇ ਸਰੀਰ ਤੇ ………………………….. ਅਤੇ ਚੀਤੇ ਦੇ ਸਰੀਰ ਤੇ ………………………….. ਹੁੰਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ।
(ਇ) ਭਾਰਤ ਵਿਚ ਸੰਨ 2008 ਵਿੱਚ ਲਗਭਗ ………………………….. ਬਾਘ ਸਨ।
(ਸ) ਬਾਘ ਦਾ ਭਾਰ ………………………….. ਕਿਲੋਗ੍ਰਾਮ ਤੱਕ ਹੋ ਸਕਦਾ ਹੈ।
(ਹ) ਬਿੱਲੀਆਂ ਨੂੰ ………………………….. ਸਵਾਦ ਮਹਿਸੂਸ
ਉੱਤਰ :
(ੳ) ਬਿੱਲੀ,
(ਅ) ਕਾਲੀਆਂ ਧਾਰੀਆਂ, ਤੋਂ ਕਾਲੀਆਂ ਦਿੱਤੀਆਂ
(ਇ) 1411,
(ਸ) 300,
(ਹ) ਮਿੱਠਾ
![]()
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 4.
ਹੇਠਾਂ ਦਿੱਤੇ ਬਾਘ ਰਿਜ਼ਰਵ ਦਾ ਸੰਬੰਧਿਤ ਰਾਜ ਨਾਲ ਮਿਲਾਣ ਕਰੋ :
1. ਜਿਮ ਕਾਰਬੈਟ – (ੳ) ਪੱਛਮੀ ਬੰਗਾਲ
2. ਸੁੰਦਰਵਨ – (ਅ) ਉੱਤਰਾਖੰਡ
3. ਬਾਂਦੀਪੁਰ – (ਇ) ਮੱਧ ਪ੍ਰਦੇਸ਼
4. ਕਾ – (ਸ) ਕਰਨਾਟਕ
ਉੱਤਰ :
1. (ਅ),
2. (ਉ),
3. (ਸ),
4. (ਇ)
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 5.
ਸਹੀ ਕਥਨ ਅੱਗੇ (✓) ਦਾ ਨਿਸ਼ਾਨ ਲਗਾਓ ਅਤੇ ਗਲਤ ਅੱਗੇ (✗) ਦਾ ਨਿਸ਼ਾਨ ਲਗਾਓ :
(ਉ) ਬਾਘ ਮਨੁੱਖ ਨਾਲੋਂ ਛੇ ਗੁਣਾ ਵੱਧ ਦੇਖ ਸਕਦਾ ਹੈ।
(ਅ) ਬਿੱਲੀਆਂ ਨੀਂਦ ਸਮੇਂ ਆਲੇ-ਦੁਆਲੇ ਦੇ ਖ਼ਤਰੇ ਨੂੰ ਮਹਿਸੂਸ ਨਹੀਂ ਕਰ ਸਕਦੀਆਂ।
(ਇ) ਭੁਚਾਲ ਦੇ ਖ਼ਤਰੇ ਨੂੰ ਮਨੁੱਖ ਪੰਛੀਆਂ ਨਾਲੋਂ ਪਹਿਲਾਂ ਮਹਿਸੂਸ ਕਰ ਸਕਦੇ ਹਨ।
(ਸ) ਸਾਨੂੰ ਬਾਘ ਦੀ ਚਮੜੀ ਤੋਂ ਬਣੀਆਂ ਵਸਤੂਆਂ ਦੀ ਵਰਤੋਂ ਨਹੀਂ ਕਰਨੀ ਚਾਹੀਦੀ।
(ਹ) ਬਾਘ ਆਪਣੀ ਆਵਾਜ਼ ਨੂੰ ਮੌਕੇ ਅਨੁਸਾਰ ਨਹੀਂ ਬਦਲ ਸਕਦਾ।
ਉੱਤਰ :
(ਉ) ✓
(ਅ) ✗
(ਇ) ✗
(ਸ) ✓
(ਹ) ✗
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 6.
ਜੰਗਲੀ ਜੀਵ ਸੁਰੱਖਿਆ ਹਫ਼ਤਾ ਮਨਾਉਣ ਦਾ ਕੀ ਮਹੱਤਵ ਹੈ?
ਉੱਤਰ :
ਇਸ ਦਾ ਮੰਤਵ ਲੋਕਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਜੰਗਲੀ ਜੀਵਨ ਸੁਰੱਖਿਆ ਬਾਰੇ ਜਾਗਰੂਕ ਕਰਨਾ ਹੈ। ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਜੰਗਲੀ ਜੀਵ ਜੰਤੂਆਂ ਦੇ ਅਲੋਪ ਹੋਣ ਬਾਰੇ ਦੱਸਣਾ ਹੈ। ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਸਮਝਾਉਣਾ ਹੈ ਕਿ ਸਾਨੂੰ ਕਿਹੜੇ ਕੰਮ ਨਹੀਂ ਕਰਨੇ ਚਾਹੀਦੇ ਜੋ ਕਿ ਜੰਗਲੀ ਜੀਵਨ ਲਈ ਖ਼ਤਰਾ ਹੋ ਸਕਦੇ ਹਨ।
![]()
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 7.
ਘਰੇਲੂ ਚਿੜੀ ਦੀ ਗਿਣਤੀ ਘਟਣ ਦਾ ਮੁੱਖ ਕਾਰਨ ਕੀ ਹੈ?
ਉੱਤਰ :
ਘਰੇਲੂ ਚਿੜੀ ਦੀ ਗਿਣਤੀ ਘਟਣ ਦਾ ਮੁੱਖ ਕਾਰਨ ਇਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਦੇ ਨਿਵਾਸ ਸਥਾਨ ਦਾ ਨਸ਼ਟ ਹੋਣਾ ਹੈ ਪਹਿਲਾਂ ਕੱਚੇ ਘਰਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਚਿੜੀਆਂ ਆਲਣੇ ਬਣਾ ਲੈਂਦੀਆਂ ਸਨ। ਹੁਣ ਤਾਂ ਵਧੇਰੇ ਘਰ ਪੱਕੇ ਹਨ। ਰੁੱਖਾਂ ਦੀ ਵੀ ਘਾਟ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਜਾ ਰਹੀ ਹੈ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 8.
ਬਾਘ ਪਰਿਯੋਜਨਾ ਕੀ ਹੈ?
ਉੱਤਰ :
ਬਾਘ ਪਰਿਯੋਜਨਾ 1 ਅਪ੍ਰੈਲ, 1973 ਨੂੰ ਸ਼ੁਰੂ ਕੀਤੀ ਗਈ। ਇਸਦਾ ਉਦੇਸ਼ ਟਾਈਗਰਾਂ ਦੇ ਸ਼ਿਕਾਰ ਕਰਨ ਤੇ ਰੋਕ ਲਾਉਣਾ ਅਤੇ ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਦੇ ਰਹਿਣ ਲਈ ਸੁਰੱਖਿਅਤ ਇਲਾਕੇ ਦੀ ਨਿਸ਼ਾਨਦੇਹੀ ਕਰਨਾ ਹੈ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 9.
ਬਾਘ ਅਤੇ ਚੀਤੇ ਵਿੱਚ ਕੀ ਅੰਤਰ ਹੈ?
ਉੱਤਰ :
ਬਾਘ ਦੇ ਸਰੀਰ ‘ਤੇ ਕਾਲੀਆਂ ਧਾਰੀਆਂ ਅਤੇ ਚੀਤੇ ਦੇ ਸਰੀਰ ‘ਤੇ ਕਾਲੀਆਂ ਦਿੱਤੀਆਂ ਧਾਰੀਆਂ ਹੁੰਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ।
ਕਿਰਿਆ-ਤੁਸੀਂ ਆਪਣੇ ਮਨਪਸੰਦ ਜੰਤੂ ਬਾਰੇ ਐਲਬਮ ਵੀ ਤਿਆਰ ਕਰ ਸਕਦੇ ਹੋ। ਇਸ ਵਿੱਚ ਉਸ ਨਾਲ ਸੰਬੰਧਿਤ ਤਸਵੀਰਾਂ, ਡਾਕ-ਟਿਕਟਾਂ ਚਿਪਕਾਉਣ ਦੇ ਨਾਲ-ਨਾਲ ਹੋਰ ਜਾਣਕਾਰੀ ਜਿਵੇਂ-ਉਸ ਦਾ ਰਹਿਣ ਸਥਾਨ, ਭੋਜਨ, ਆਦਤਾਂ, ਕੱਦ, ਭਾਰ, ਰੰਗ ਅਤੇ ਪ੍ਰੋਚਕ ਗੱਲਾਂ ਲਿਖ ਸਕਦੇ ਹੋ। ਚਾਹੋ ਤਾਂ ਖੁਦ ਵੀ ਤਸਵੀਰਾਂ ਬਣਾ ਕੇ ਰੰਗ ਭਰ ਸਕਦੇ ਹੋ।
ਉੱਤਰ :
ਡਾਕ-ਟਿਕਟਾਂ ਇਕੱਠੀਆਂ ਕਰਕੇ ਖ਼ੁਦ ਚਿਪਕਾਓ ਤੇ ਹੋਰ ਜਾਣਕਾਰੀ ਇਕੱਠੀ ਕਰੋ ਤੇ ਲਿਖੋ।
ਨੋਟ-ਡਾਕ-ਟਿਕਟਾਂ ਇਕੱਠੀਆਂ ਕਰਨ ਦੇ ਸ਼ੌਕ ਨੂੰ ਫਿਲੈਟਲੀ ਕਹਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ।
![]()
PSEB 5th Class EVS Guide ਧਰਤੀ ਸਾਡਾ ਵੀ ਘਰ Important Questions and Answers
1. ਬਹੁ-ਵਿਕਲਪੀ ਚੋਣ ਸਹੀ ਉੱਤਰ ਅੱਗੇ ਸਹੀ ਦਾ ਨਿਸ਼ਾਨ (✓) ਲਗਾਓ)
(i) ………………………… ਭਾਰਤ ਦਾ ਰਾਸ਼ਟਰੀ ਜਾਨਵਰ ਹੈ।
(ਉ) ਕੁੱਤਾ।
(ਅ) ਬਿੱਲੀ
(ਇ) ਟਾਈਗਰ
(ਸ) ਘੋੜਾ।
ਉੱਤਰ :
(ਇ) ਟਾਈਗਰ
(ii) 1900 ਵਿਚ ਦੁਨੀਆ ਵਿਚ ………………………… ਟਾਈਗਰ ਸਨ।
(ਉ) 500
(ਅ) 100000
(ੲ) 3200
(ਸ) 1411
ਉੱਤਰ :
(ਅ) 100000
2. ਇੱਕ ਵਾਕ ਤੋਂ ਛੋਟੇ ਉੱਤਰਾਂ ਵਾਲੇ ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ (ਛੋਟੇ ਉੱਤਰਾਂ ਵਾਲੇ ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ)
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 1.
ਟਾਈਗਰ ਦੀ ਸੁਣਨ ਸ਼ਕਤੀ ਬਾਰੇ ਦੱਸੋ
ਉੱਤਰ :
ਟਾਈਗਰ ਦੀ ਸੁਣਨ ਸ਼ਕਤੀ ਬਹੁਤ ਤੇਜ਼ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ ਉਹ ਆਪਣੇ ਦੋਵੇਂ ਕੰਨ ਵੱਖ-ਵੱਖ ਦਿਸ਼ਾ ਵਿਚ ਮੋੜ ਸਕਦਾ ਹੈ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 2.
ਪ੍ਰੋਜੈਕਟ ਟਾਈਗਰ ਦਾ ਉਦੇਸ਼ ਕੀ ਹੈ?
ਉੱਤਰ :
ਇਸਦਾ ਉਦੇਸ਼ ਟਾਈਗਰਾਂ ਦੇ ਸ਼ਿਕਾਰ ਕਰਨ ਤੇ ਰੋਕ ਲਾਉਣਾ ਅਤੇ ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਦੇ ਰਹਿਣ ਲਈ ਸੁਰੱਖਿਅਤ ਇਲਾਕੇ ਦੀ ਨਿਸ਼ਾਨਦੇਹੀ ਕਰਨਾ ਹੈ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 3.
ਪ੍ਰੋਜੈਕਟ ਟਾਈਗਰ ਦੇ ਅਧੀਨ ਕਿੰਨੇ ਇਲਾਕੇ ਹਨ?
ਉੱਤਰ :
ਪਹਿਲਾਂ ਇਹ 9 ਸਨ ਤੇ ਹੁਣ 48 ਹਨ।
![]()
3. ਖ਼ਾਲੀ ਥਾਂਵਾਂ ਭਰੋ :
(i) ਟਾਈਗਰ ਇੱਕ ………………………… ਸ਼ਿਕਾਰੀ ਹੈ।
(ii) ਟਾਈਗਰ, ਮਨੁੱਖ ਨਾਲੋਂ ………………………… ਗੁਣਾਂ ਵੱਧ ਦੇਖ ਸਕਦਾ ਹੈ !
(iii), ਜਿਮ ਕਾਰਬੇਟ ………………………… ਵਿੱਚ ਹੈ।
(iv) ਦੁਨੀਆ ਦੇ ………………………… ਟਾਈਗਰ, ਸਫ਼ੇਦ ਟਾਈਗਰ ………………………… ਦੇ ਵੰਸ਼ਜ ਹਨ।
(y) ਬਿੱਲੀਆਂ ………………………… ਘੰਟੇ ਸੌਂਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ।
ਉੱਤਰ :
(i) ਕੁਸ਼ਲ,
(ii) ਛੇ,
(iii) ਉਤਰਾਖੰਡ,
(iv) ਸਫ਼ੇਦ, ਮੋਹਨ,
(v) 16.
4. ਸਹੀ/ਗਲਤ :
(i) ਟਾਈਗਰ ਦਾ ਭਾਰ 1000 ਕਿਲੋਗ੍ਰਾਮ ਤੱਕ ਹੋ ਸਕਦਾ ਹੈ।
(ii) ਟਾਈਗਰ ਦੇ ਸਰੀਰ ਤੇ ਕਾਲੀਆਂ ਧਾਰੀਆਂ ਹੁੰਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ।
(iii) ਦੁਨੀਆਂ ਵਿਚ ਟਾਈਗਰਾਂ ਦੀ ਗਿਣਤੀ ਘੱਟ ਕੇ 3200 ਰਹਿ ਗਈ ਹੈ।
(iv) ਸਫ਼ੇਦ ਟਾਈਗਰ ਦਾ ਨਾਂ ਮੋਹਣ ਹੈ।
ਉੱਤਰ :
(i) ਗਲਤ,
(ii) ਸਹੀ,
(iii) ਗ਼ਲਤ,
(iv) ਸਹੀ।
5. ਮਿਲਾਨ ਕਰੋ :
(i) ਕਾਨ੍ਹ – (ਉ) ਆਸਾਮ
(ii) ਮਾਨਸ – (ਅ) ਔਡੀਸ਼ਾ
(iii) ਸਿਮਲੀਪਾਲ (ਬ) ਕਰਨਾਟਕਾ
(iv) ਬਾਂਦੀਪੁਰ – (ਸ) ਮੱਧ ਪ੍ਰਦੇਸ਼
ਉੱਤਰ :
(i) (ਸ),
(ii) (ੳ),
(iii) (ਅ),
(iv) (ਈ)।
![]()
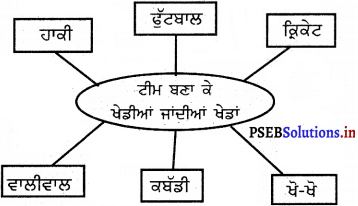
6. ਦਿਮਾਗੀ ਕਸਰਤ (ਮਾਈਂਡ ਮੈਂਪਿਗ) –

ਉੱਤਰ :
7. ਵੱਡੇ ਉੱਤਰ ਵਾਲਾ ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ
![]()
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ-
ਬਿੱਲੀ ਦੇ ਸੰਬੰਧ ਵਿਚ ਕੁੱਝ ਵਾਕ ਲਿਖੋ।
ਉੱਤਰ :
ਬਿੱਲੀ ਇੱਕ ਦਿਨ ਵਿਚ 16 ਘੰਟੇ ਸੌਂਦੀ ਹੈ। ਬਿੱਲੀ ਨੂੰ ਮਿੱਠੇ ਸੁਆਦ ਦਾ ਪਤਾ ਨਹੀਂ ਲੱਗ ਸਕਦਾ। ਉਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਦੀ ਨਜ਼ਰ ਦੀ ਸਮਰੱਥਾ ਦਿਨ ਸਮੇਂ ਮਨੁੱਖਾਂ ਵਾਂਗ ਹੈ ਤੇ ਮੱਧਮ ਰੌਸ਼ਨੀ ਵਿਚ ਇਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਦੀ ਦੇਖਣ ਦੀ ਸਮਰੱਥਾ 6 ਗੁਣਾਂ ਵੱਧ ਜਾਂਦੀ ਹੈ।