Punjab State Board PSEB 7th Class Science Book Solutions Chapter 11 Transportation in Animals and Plants Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
PSEB Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 11 Transportation in Animals and Plants
Science Guide for Class 7 PSEB Transportation in Animals and Plants Intext Questions and Answers
Think and Answer (Textbook Page No. 131)
Question 1.
What is pulse rate ?
Answer:
Pulse rate. The number of times a person’s heart beats per minute, called pulse rate.
Question 2.
Where can we feel the pulse ?
Answer:
We can feel the pulse on the neck, behind the knee and near the ankle and wrist joints.

Think and Answer (Textbook Page No. 134)
Question 1.
What is a stethoscope ?
Answer:
Stethoscope. Doctors use a stethoscope to hear the sounds of the heart and lungs inside the patient’s body while examining his condition. The stethoscope has a chest piece at one end and an ear piece at the other end. The two pieces are connected by a rubber tube.
Question 2.
Is there any relationship between heart beat and pulse rate ?
Answer:
Both the pulse rate and the heart rate are the same because the contraction of the heart increases the blood pressure in the arteries which is detected by the pulse rate. Therefore, a pulse test is a direct measure of the heart rate.
Think and Answer (Textbook Page No. 137)
Question 1.
Define osmosis.
Answer:
Osmosis. This is the process by which a solvent passes through a semi-permeable membrane from a low-concentration solution to a solution of high concentration so that the concentration of solutions on both sides of the membrane become equal.
Question 2.
Define semi-permeable membrane.
Answer:
Semi-permeable membrane. It is a type of organic or organic polymer membrane through which some molecules or ions (charged particles) can pass through diffusion.
PSEB 7th Class Science Guide Transportation in Animals and Plants Textbook Questions and Answers
1. Fill in the Blanks:
(i) In plants, water and minerals are transported by ………………. .
Answer:
Roots
(ii) Doctors use …………………. to listen the internal sounds of the body.
Answer:
stethoscope
(iii) Sweat contains water and …………………
Answer:
salts

(iv) The blood vessels having thick elastic walls are called ………………….
Answer:
artery
(v) The rhythmic contraction and expansion of heart is called …………………..
Answer:
heartbeat
2. State True or False:
(i) Phloem vessels transport food materials in plants.
Answer:
False
(ii) Deoxygenated blood is carried back to heart by veins.
Answer:
True
(iii) The veins have thick walls.
Answer:
True
(iv) Blood plasma is the solid component of blood.
Answer:
False
(v) The red colour of blood is due to the presence of plasma.
Answer:
False
3. Match the Column ‘A’ with Column ‘B’:
| Column ‘A’ |
Column ‘B’ |
| (i) Transport of water |
(a) Stomata |
| (ii) Red in colour |
(b) Xylem |
| (iii) Exchange of gases |
(c) Haemoglobin |
| (iv) Blood clotting |
(d) Phloem |
| (v) Transport of food |
(e) Platelets |
Answer:
| Column ‘A’ |
Column ‘B’ |
| (i) Transport of water |
(b) Xylem |
| (ii) Red in colour |
(c) Haemoglobin |
| (iii) Exchange of gases |
(a) Stomata |
| (iv) Blood clotting |
(e) Platelets |
| (v) Transport of food |
(d) Phloem |

4. Choose the Correct Answer:
Question (i)
Blood cells responsible for clotting are:
(a) Plasma
(b) WBC’s
(c) RBC’s
(d) Platelets
Answer:
(d) Platelets.
Question (ii)
The lower chambers of heart are called:
(a) Atria
(b) Valves
(c) Veins
(d) Ventricles
Answer:
(b) Valves.
Question (iii)
The excretory system consists of:
(a) Kidney
(b) Bladder
(c) Urethra
(d) All of these.
Answer:
(d) All of these.
Question (iv)
The muscular organ which beats continuously to act as a pump
(a) Auricles
(b) Kidney
(c) Heart
(d) Veins.
Answer:
(c) Heart.
Question (v)
Blood contains:
(a) Plasma
(b) WBC’s
(c) RBC’s
(d) All of these.
Answer:
(d) All of these.
5. Very Short Answer Type Questions:
Question (i)
Why is blood red in colour ?
Answer:
Red colour of blood is due to a pigment called haemoglobin which is a protein. It combines with iron molecules to form a complex compound and carries oxygen to different parts of the body. Due to the high amount of iron in it, it reflects the red color, which makes the colour of blood red.
Question (ii)
Define translocation.
Answer:
Translocation. The process of transmitting food materials from the leaves to other parts of the plant is called translocation.

Question (iii)
What is dialysis ?
Answer:
Dialysis. If a person’s both kidneys are damaged, the blood does not get filtered properly, causing harmful solids and fluid to pile up in the body. Such person cannot live long unless his blood is filtered regularly through an artificial kidney. The process of removing toxins from the blood with the help of a machine (artificial kidney), is called dialysis.
6. Short Answer Type Questions:
Question (i)
State three functions of blood.
Answer:
Functions of blood:
- Oxygenated blood transfers nutrients to the lungs and tissues.
- The blood carries the waste products to the kidneys.
- The blood carries antibodies to fight infection.
- Blood controls body temperature.
Question (ii)
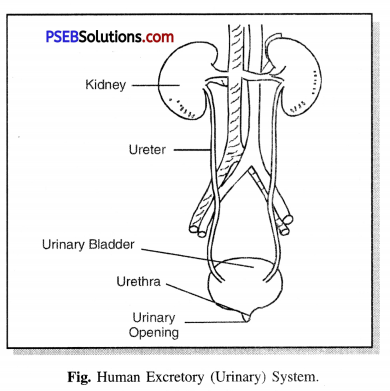
Name the parts of excretory system in humans.
Answer:
Parts of Excretory System in humans. The following are the main components of the humipi excretion system :
- Kidneys
- Ureters
- Urinary bladder
- Urethra.
Question (iii)
Why do veins have valves ?
Answer:
The main function of the valves in the veins is to stop the blood from coming back because they have low blood pressure. That is, it is ensured that the blood is flowing in one direction. The valves in the veins help the blood to flow to the heart in the opposite direction of gravity.
7. Long Answer Type Questions:
Question (i)
Write and explain the components of blood.
Answer:
Components of Blood. Blood is a fluid connective tissue, made up of four main components :
(1) Red blood cells,
(2) White blood cells,
(3) Platelets and
(4) Plasma.
(1) Red blood cells (R.B.C.). These contain proteins called haemoglobin which carry oxygen and carbon dioxide in the respiration process.
(2) White Blood Cells (W.B.C.). They destroy harmful bacteria and dead cells from the body and protects from infection.
(3) Platelets. They help build blood clotting. Thus stop the loss of precious blood.
(4) Plasma. It is also part of the blood, which contains proteins, hormones, glucose, fatty acids, amino acids, mineral salts, digestible and excretory substances. It is a major component of blood.
Question (ii)
Describe the function of Heart.
Answer:
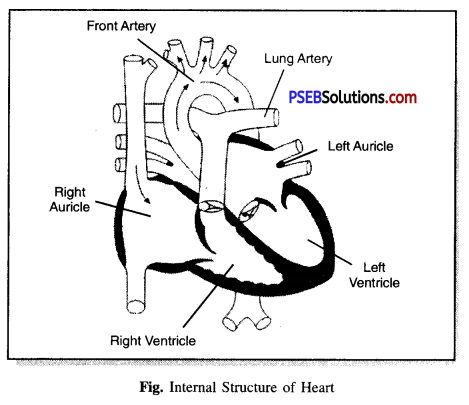
Function of the Heart. The heart is an organ which beats continuously to act as a pump for the transportation of blood. The arteries receive oxygenated blood from the heart and supply it throughout the body. Whereas, the veins carry the deoxygenated blood from the body parts to the heart for oxygenation.
The right atrium receives blood from veins and pumps it to the right ventricle.
The right ventricle pumps the blood received from the right atrium to the lungs.
The left atrium receives oxygenated blood from the lungs and pumps it to the left ventricle. The left ventricle pumps the oxygenated blood throughout the body.
The valves in the heart allow blood to flow in only one direction and prevent the blood from flowing backwards.
Question (iii)
Draw a labelled diagram of excretory system.
Answer:
Diagram of Human Excretary System.
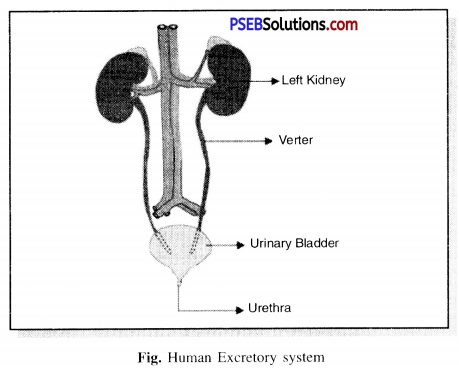

Question (iv)
Differentiate between Arteries and Veins.
Answer:
Differences between the Arteries and Veins:
| Arteries |
Veins |
| (1) The arteries carry blood from the heart to different parts of the body. |
(1) Veins collect blood from different parts of the body and carry it to the heart. |
| (2) They do not have valves. |
(2) They have valves. |
| (3) Their walls are thick. |
(3) Their walls are thin. |
| (4) All the arteries except the pulmonary artery carry pure blood. |
(4) Veins other than lung veins carry impure blood containing Carbon dioxide. |
| (5) These are present deep under the skin. |
(5) These are present at shallow depths under the skin |
| (6) Blood flow is fast and jerky. |
(6) Blood flow is slow. |
Question (v)
Explain the transportation of substances in plants.
Answer:
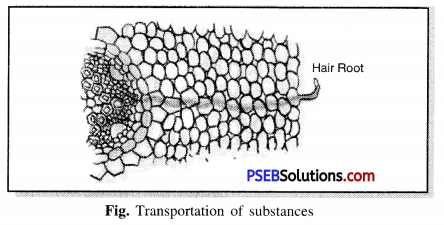
Transport of substances in plants. Plants take water and carbon dioxide present in the atmosphere to prepare their food with the help of chlorophyll in the presence of sunlight. Water and mineral salts are absorbed by the roots and transported to the leaves where photosynthesis takes place.
Transport of water and minerals in plants. Plants get water and minerals from the soil. This is usually done by the roots. The roots have root hairs which increase the surface area of the roots which helps the roots to absorb water and the minerals dissolved in it. The emission of water in the leaves creates a force of attraction which helps water and nutrients to reach the top of plant. Plants have pipe-like vessels to transport water and nutrients from the soil. Veins are made up of a special type of dead cell called a Xylem.
Transportation of Food. Food produced by photosynthesis in plant leaves needs to be transported to every part of the plant. The tissue responsible for transporting food to plants is called the Phloem. The phloem carries the glucose produced in the leaves to all parts of the plant. The process of transfer of food prepared in the leaves to other parts of the plant is called transport.
PSEB Solutions for Class 7 Science Transportation in Animals and Plants Important Questions and Answers
1. Fill in the Blanks:
(i) The blood from heart is transported to all parts of the body by …………….. .
Answer:
Arteries
(ii) Haemoglobin is present in ………………. cells.
Answer:
Red blood
(iii) Arteries and veins are joined by a network of ……………………….
Answer:
Capillaries
(iv) The rhythmic expansion and contraction of heart is called ………………….
Answer:
Heart beat
(v) The main excretory product in human beings is ……………….. .
Answer:
Urine

(vi) Sweat contains water and ………………….
Answer:
Salts
(vii) Kidneys eliminate the waste materials in the liquid form called ………………. .
Answer:
Urine
(viii) Water reaches great height in the trees because of sunction pull caused by …………………….. .
Answer:
transpiration
2. Match the Column T with Column ‘II’:
| Column ‘I’ |
Column ‘II’ |
| (i) Stomata |
(a) Absorption of water |
| (ii) Xylem |
(b) Transpiration |
| (iii) Root hairs |
(c) Transport of food |
| (iv) Phloem |
(d) Transport of water |
Answer:
| Column ‘I’ |
Column ‘II’ |
| (i) Stomata |
(b) Transpiration |
| (ii) Xylem |
(d) Transport of water |
| (iii) Root hairs |
(a) Absorption of water |
| (iv) Phloem |
(c) Transport of food. |
3. Choose the Correct Answer:
Question (i)
How many chambers are there in human heart ?
(a) One
(b) Two
(c) Three
(d) Four.
Answer:
(d) Four.
Question (ii)
Name the instrument used to measure heart beat.
(a) Stethoscope
(b) Horoscope
(c) Microscope
(d) Telescope.
Answer:
(a) Stethoscope.
Question (iii)
Which is excretory organ of man ?
(a) Lung
(b) Kidney
(c) Stomach
(d) Heart.
Answer:
(b) Kidney.

Question (iv)
What are the components of blood ?
(a) R.B.C.
(b) W.B.C.
(c) Blood platelets
(d) All of the above.
Answer:
(d) All of the above.
Question (v)
What is heart beat rate per minute of a healthy human being ?
(a) 72-80
(b) 52-60
(c) 92-100
(d) 62-70.
Answer:
(a) 72-80.
Question (vi)
Which of the following is not a part of excretory system ?
(a) Kidney
(b) Lungs
(c) Urinary bladder
(d) Urethra.
Answer:
(b) Lungs.
4. State True or False:
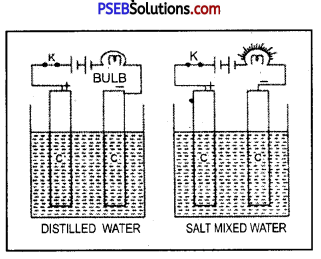
(i) The transport of substances in Spirogyra occurs by diffusion method.
Answer:
True
(ii) Platelets are not required for blood clotting.
Answer:
False
(iii) Emissions in Hydra are not by diffusion method.
Answer:
False
(iv) Xylem and phloem are vascular tissues.
Answer:
True

Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What are the main conducting tissues in plants ?
Answer:
Xylem and phloem are the main conducting tissues of plants.
Question 2.
What is the function of valves in heart ?
Answer:
Valves present in heart allow one way flow of blood.
Question 3.
Name the procedure used in the working of an artificial kidney.
Answer:
Haemodialysis.
Question 4.
To which part of body is urine carried through ureter ?
Answer:
Urinary bladder.
Question 5.
What is Urethra ?
Answer:
Urethra. It is a muscular tube which carries urine from urinary bladder to outside through the opening at its end.
Question 6.
Name the substance which is excreted by lungs.
Answer:
Carbon dioxide.
Question 7.
What is dialysis ?
Answer:
Dialysis. The process of removing waste products form blood using artificial kidney in place of natural kidney, is called dialysis.

Question 8.
What is transpiration ?
Answer:
Transpiration. The loss of water in the form of water vapours from the surface of leaves is called transpiration.
Question 9.
What red pigment is present in red blood cells ?
Answer:
Haemoglobin.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What are capillaries ? Give their functions.
Answer:
Capillaries. They are blood vessels present in the terminals of artery and vein. They are thin walled and extremely narrow tubes. Exchange of food materials, gases, w ater, hormones etc. take place across the thin walls of capillaries.
Question 2.
Name the parts of the human circulatory system.
Answer:
The circulatory system of the human body consists of:
- Heart, centrally located pump.
- Blood, liquid tissue.
- Arteries. Blood carrying tubes from the heart to different body parts.
- Veins. Blood bringing tubes from different body parts to the heart.
- Capillaries. Union of arteries and veins.
Question 3.
What are heart beat and pulse rate ?
Answer:
Heart beat. A heart beat consists of one auricular systole, one ventricular systole and then a short pause. At rest, human heart beats 72 times per minute. It can be listened with the help of stethoscope.
Pulse rate. When the ventricles contract, the blood is forced into the aorta and exerts the pressure on the wall of the aorta. The pressure difference between systole (about 120 mm Hg) and diastole (about 80 mm Hg) is known as pulse pressure (about 40 mm Hg). This blood pressure is expressed as 120/ 80. The heart beats 72 times per minute is referred to as the pulse rate.
Question 4.
Give reasons:
(i) Veins have valves at intervals in their inner lining whereas the arteries do not have valves.
(ii) The wall of the ventricles is thicker than that of the auricles.
(iii) The blood from the right ventricle enters the pulmonary artery, but cannot go back from the pulmonary artery to the right ventricle.
(iv) The left auricle contains oxygenated blood.
(v) The red blood corpuscles cannot divide.
(vi) Pulmonary artery contains deoxygenated blood.
(vii) Auricles are thin walled chambers.
(viii) Left ventricle is much thicker and muscular than the right ventricle of the heart.
Answer:
(i) Veins are thin walled and collapsible. Their lumen is comparatively wide. They take deoxygenated blood from various parts of the body back to heart. To prevent the backflow of blood, valves are present at intervals.
Arteries are thick walled and non-collapsible. Their lumen is narrow. As the blood in arteries flows with jerks the latter do not have valves.
(ii) Since blood is supplied to different organs of the body by ventricles, their wall is thicker than those of auricles because a thick wall exerts more pressure on the blood.
(iii) The opening of right ventricle into the pulmonary artery is guarded by semilunar valves which allow the flow of blood from the right ventricle into the pulmonary artery, but not in the reverse direction. Hence blood from the right ventricle enters the pulmonary artery, but cannot go back from pulmonary artery to right ventricle.
(iv) The left auricle contains oxygenated blood, because it receives blood from the lungs where blood is oxygenated.
(v) The red blood corpuscles cannot divide because they lack nuclei.
(vi) Pulmonary artery carries deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle to the lungs for oxygenation.
(vii) Auricles are collecting chambers for the blood, so they are thin walled to accommodate large volume of blood.
(viii) Left ventricle has to pump blood all over the body, under pressure, through the dorsal aorta. Hence, more muscular.
Question 5.
Name the different organs of excretory system.
Answer:
Different organs of excretory system:
- Kidney
- Ureter
- Urinary bladder
- Urethra
- Urinary opening.

Question 6.
Why is transportation of food materials necessary in plants ?
Answer:
Necessity of transportation of food materials. Each and every part of plant needs food for obtaining energy, growth and maintaining body. As the food is prepared in the leaves and water is absorbed by roots from the soil, so, it is necessary to transport the food materials in plants.
Question 7.
Why is transport of materials necessary in plant or an animal ? Explain.
Answer:
Transportation of materials in plants and animals is necessary as each and every part of organism need food for obtaining energy and building and maintaining body. As the food is prepared in leaves and water is absorbed by roots in plants and absorbed by digestive system in living organisms. So it is necessary to transport the materials in the plants and animals.
Question 8.
What will happen if there are no platelets in the blood ?
Answer:
Platelets help in clotting of blood. So, in absence of platelets, blood will not clot. So, if a person gets injured once, the whole blood will flow out and hence a person may die.
Question 9.
What are components of blood ?
Answer:
Components of blood are:
- Fluid matrix called plasma.
- Red blood corpuscles (RBC)
- White blood corpuscles (WBC)
- Blood Platelets.
Question 10.
Why is blood needed by all parts of a body ?
Answer:
Need of blood:
- It transports oxygen and carbon dioxide.
- It helps in clotting.
- It carries nutritive and waste materials, enzymes and hormones etc.
- It helps in excretion of wastes.
Question 11.
What makes the blood look red ?
Answer:
Blood is red in colour due to presence of a pigment, haemoglobin in red blood corpuscles.
Question 12.
Describe the function of the heart.
Answer:
Functions of the heart :
The main function of heart is to pump blood to various parts of the body through blood
vessels.
The heart receives blood from the veins and pumps it to arteries. During relaxation both the atria get filled with blood. The left atrium is filled with oxygenated blood and right atrium gets filled with deoxygenated blood collected from different parts of the body.
When atria contracts, the valves open. As a result of this the oxygenated blood enters from the left atrium into the left ventricle while deoxygenated blood from right atrium enters into right ventricle.
When the ventricles contract, the valves get closed. Owing to it, the oxygenated blood is supplied to different parts of the body and deoxygenated blood is carried to lungs for purification.

Question 13.
Why is it necessary to excrete waste products ?
Answer:
Necessity to excrete waste products. As a result of various functions of cells, number of waste materials are formed in the body. Accumulation of these waste products may become toxic. So, these must be removed from the body as soon as these are formed.
Question 14.
Differentiate between Heart beat and Pulse rate.
Answer:
Differences between Heart beat and Pulse rate
| Heart beat |
Pulse Rate |
| (i) It is the rhythmic contraction and relaxation of heart. |
(i) It is the rhythmic contraction and relaxation in aorta and its main arteries. |
| (ii) One complete heart beat consists of one systole and one diastole and lasts for about 0.8 second. |
(ii) Pulse is a regular jerk of an artery. It depends on the rate of heart beat. |
Question 15.
Differentiate between Transpiration and Respiration.
Answer:
Difference between Transpiration and Respiration
| Transpiration |
Respiration |
| (i) It takes place in plants. |
(i) It takes place in animals. |
| (ii) Only water vapour is removed. |
(ii) Sweat containing urea, uric acid and salts are removed. |
| (iii) It takes place through the leaves and stem and through the stomata and lenticles. |
(iii) It takes place through the skin. It takes place through the sweat pores of the sweat glands. |
Long Answer Type Question
Question 1.
Describe the structure of the human excretory (urinary) system.
Answer:
The human excretory (urinary) system consists of the following organs:
- Kidneys
- Ureters
- Urinary bladder
- Urethra.
(i) Kidneys. The kidneys are a pair of bean-shaped delicate organs. They are situated one on each side of the mid-dorsal line of the abdominal cavity, just below the level of the stomach.
(ii) Ureters. They are two tubes about 30 cm long, emerging from each kidney with the pelvis of which they are continuous. The ureters run downwards and inwards and open into the urinary bladder.
(iii) Urinary bladder. It serves as a reservoir for the urine. It is a hollow muscular organ lined with stratified epithelium. Its average capacity for storage of urine is about 500 ml.
(iv) Urethra. The urethra in the two sexes differs. The male urethra is about 20 cm in length. While that of females is only 1.5 cm in length.
![]()
![]()
![]()