Punjab State Board PSEB 12th Class Geography Book Solutions Chapter 7 परिवहन/यातायात, संचार तथा व्यापार Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
PSEB Solutions for Class 12 Geography Chapter 7 परिवहन/यातायात, संचार तथा व्यापार
PSEB 12th Class Geography Guide परिवहन/यातायात, संचार तथा व्यापार Textbook Questions and Answers
प्रश्न 1. निम्नलिखित प्रश्नों के उत्तर एक वाक्य में दें:
प्रश्न 1.
यातायात प्रबंध को मुख्य रूप में कौन-सी किस्मों में विभाजित किया जाता है ?
उत्तर-
यातायात प्रबंध को मुख्य रूप में इन किस्मों में विभाजित किया जाता है-
- स्थल मार्ग यातायात।
- जल मार्ग यातायात।
- वायु मार्ग यातायात।
प्रश्न 2.
स्थल मार्ग यातायात की कौन-सी तीन किस्में होती हैं ?
उत्तर-
स्थल मार्ग यातायात की सड़कें, रेलवे तथा पाइप लाइन तीन मुख्य किस्में होती हैं।
प्रश्न 3.
कौन-से राज्य भारत के दोनों गलियारा (सड़कों) योजनाओं में संभेद हैं ?
उत्तर-
उत्तर प्रदेश तथा मध्य प्रदेश दोनों गलियारा योजनाओं में संभेद राज्य हैं।

प्रश्न 4.
रेल गेज कौन-सी किस्मों की होती हैं ?
उत्तर-
भारतीय रेल गेजों की निम्नलिखित तीन किस्में होती हैं-
- चौड़ी गेज (Broad Gauge)
- मीटर गेज (Metre Gauge)
- perluf 1757 (Narrow Gauge).
प्रश्न 5.
विश्व की प्रथम रेलवे लाइन कब बिछाई गई ?
उत्तर-
विश्व की प्रथम रेलवे लाइन सन 1863 से 1869 में अमेरिका में बिछाई गई।
प्रश्न 6.
ट्रांस साइबेरियाई रेलवे लाइन कहा तक हैं ?
उत्तर-
ट्रांस साइबेरियाई रेलवे लाइन मास्को से रूस के पर्व में ब्लादिवोस्तोक तक हैं।
प्रश्न 7.
भारत में कितने रेलवे गलियारे हैं ?
उत्तर-
भारत में 2014 के बजट के अनुसार 9 रेलवे गलियारे हैं।

प्रश्न 8.
IRCTC का पूरा नाम क्या है ?
उनर-
IRCTC का पूरा नाम इण्डियन कैटरिंग एंड टूरिज्म कार्पोरेशन लिमिटेड है।
प्रश्न 9.
भारत में कितने जल मार्गों को राष्ट्रीय स्तर के माना जाता है ?
उत्तर-
भारत में 10 जल मार्गों को राष्ट्रीय स्तर के माना जाता है।
प्रश्न 10.
उत्तरी अमेरिका की कोई दो बड़ी झीलों के नाम लिखो।
उत्तर-
उत्तरी अमेरिका की बड़ी झीलें हैं-सुपीरियर, मिशिगन, हायरन, एरी, ओटारियो तथा सेंट लॉरेस।
प्रश्न 11.
भारत की पहली वायु सेवा कब शुरू हुई तथा कहां तक थी ?
उत्तर-
भारत की पहली वायु सेवा 1911 में शुरू हुई तथा इसका इलाहाबाद से नैनी तक, 10 कि०मी० की दूरी के लिए वायु डाक का प्रयोग किया गया।

प्रश्न 12.
पंजाब के कौन-से दो अंतर्राष्ट्रीय हवाई अड्डे हैं ?
उत्तर-
पंजाब में अंतर्राष्ट्रीय हवाई अड्डे अमृतसर तथा मोहाली में हैं।
प्रश्न 13.
TAPI पाइप लाइन का पूरा नाम लिखो।
उत्तर-
तुर्कमेनिस्तान-अफ़गानिस्तान-पाकिस्तान-भारत पाइप लाइन।
प्रश्न 14.
संचार की कौन सी प्रमुख किस्में हैं ?
उत्तर-
संचार की मुख्य किस्में हैं-
- व्यक्तिगत संचार
- जन संचार।
प्रश्न 15.
GATT का पूरा नाम क्या है ?
उत्तर-
जनरल ऐग्रीमैंट ओन टैरिफज एंड ट्रेड। (शुल्क तथा व्यापार पर समझौते)।

प्रश्न 2. निम्नलिखित प्रश्नों के उत्तर चार पंक्तियों में दें: .
प्रश्न 1.
भारत की ग्रामीण सड़क योजना से पहचान करवाओ।
उत्तर-
इस योजना का उद्देश्य ग्रामीण क्षेत्रों में सड़कों का विकास करना है तथा ऐसा करके कम से कम 1500 व्यक्तियों की तथा इससे अधिक जनसंख्या वाले गांवों को आपस में सड़क मार्ग के साथ जोड़ा जाता है। यह सड़कें इस प्रकार बनाई जाती हैं कि हर प्रकार की मौसमी मुसीबतों को सहन कर सकें।
प्रश्न 2.
सूबाई सड़क मार्ग क्या होते हैं ?
उत्तर-
जब किसी राज्य में व्यापारिक तथा भारी यात्री यातायात के लिए सड़कें बनाई जाए, वह राज्य सड़क मार्ग होते हैं। यह सड़कें जो कि आर्थिक कारवाई की नब्ज़ मानी जाती हैं, जिला मुख्य केंद्रों को राज्यों की राजधानियों के राष्ट्रीय शाहमार्ग के साथ मिलाती हैं।
प्रश्न 3.
‘सुनहरी चतुर्भुज’ कौन से शहरों को आपस में जोड़ती हैं ?
उत्तर-
‘सुनहरी चतुर्भुज’ भारत के अहमदाबाद, भुवनेश्वर, जयपुर, कानपुर, पुणे, सूरत, नैलूर विजयवाड़ा, गंटूर तथा बंगलुरु इत्यादि शहरों को आपस में जोड़ती हैं।

प्रश्न 4.
19वीं सदी के अंत तक भारत में कौन-से तीन रेलवे-मार्ग बने हैं ?
उत्तर-
19वीं सदी के अंत तक भारत में कोलकाता, मुंबई तथा चेन्नई तीन प्रमुख नये रेलवे-मार्ग बने हैं।
प्रश्न 5.
कोलकाता कौन-कौन से रेलवे जोनों का मुख्यालय है ?
उत्तर-
कोलकाता पूर्वी रेलवे तथा मैट्रो रेलवे जोनों का मुख्यालय है।
प्रश्न 6.
कैनेडियन पैसेफ़िक रेलवे क्या है ?
उत्तर-
कैनेडियन पैसेफिक रेलवे, पार महाद्वीप रेल मार्ग की एक उदाहरण है जो कि उत्तरी अमेरिका महाद्वीप में कैनेडा के नागरिकों की सेवा कर रहा है इसका कुछ हिस्सा संयुक्त राज्य अमेरिका में भी निकलता है। इस मार्ग का निर्माण 1881 में शुरू हुआ था तथा अभी तक विस्तार चल रहा है।

प्रश्न 7.
डाइमंड चतुर्भुज कौन-से राज्यों को छू पाएगी?
उत्तर-
डाइमंड चतुर्भुज उत्तर प्रदेश, राजस्थान, महाराष्ट्र, गुजरात, दिल्ली, हरियाणा, आन्ध्र प्रदेश, तेलंगाना, कर्नाटक, बिहार, उड़ीसा, झारखण्ड तथा पश्चिमी बंगाल राज्यों को छू पाएगी।
प्रश्न 8.
दिल्ली आगरा रेल गलियारा से पहचान करवाओ।
उत्तर-
दिल्ली आगरा रेल गलियारा का उद्घाटन 5 अप्रैल, 2016 में हुआ है। दिल्ली से आगरा तक 160 किलोमीटर प्रति घंटा की रफ़्तार के साथ आगरा गतिमान ऐक्सप्रैस चलाई गई।
प्रश्न 9.
भारत में आंतरिक जल यातायात कौन-से दरियाओं में होती है ?
उत्तर-
भारत में आंतरिक जल यातायात के अनुकूल दरिया हैं-गंगा, भगीरथी, हुगली, ब्रह्मपुत्र, महानदी, कृष्णा, जुयारी, काली, शरावति, नेर्तावति इत्यादि।

प्रश्न 10.
व्यक्तिगत संचार के साधन कौन-कौन से हैं ?
उत्तर-
व्यक्तिगत संचार के प्रमुख साधन हैं-
- डाक सेवाएं
- ई-मेल सेवा
- फैक्स संदेश
- टैलीफोन
- कोरियर सेवा
- कम्प्यूटर या सैलफोन सेवाएं।
प्रश्न 3. निम्नलिखित प्रश्नों के उत्तर 10-12 पंक्तियों में दें:
प्रश्न 1.
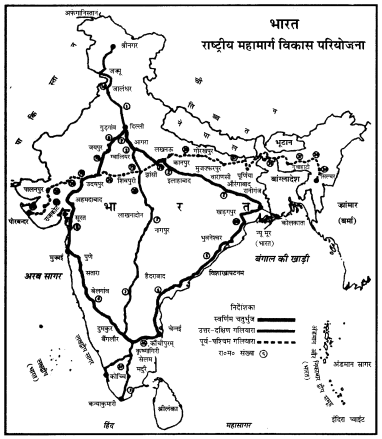
भारत के उत्तर दक्षिण तथा पूर्व-पश्चिम गलियारा प्रोजैक्टों से पहचान करवाओ।
उत्तर-
भारत के उत्तर-दक्षिण तथा पूर्व-पश्चिम गलियारा प्रोजैक्टों का मुख्य उद्देश्य देश के हर कोने तक बढ़िया सड़क-मार्गों का जाल बिछाने का है। इस योजना की देख-रेख की पूरी ज़िम्मेदारी नैशनल हाईवे अथॉरिटी ऑफ इंडिया के अंतर्गत की गई जो कि केंद्रीय सड़क यातायात तथा शाहमार्ग मंत्रालय के अंतर्गत काम कर रही है। इस प्रकल्प का मुख्य उद्देश्य चार से छः मार्गी, कुल 7300 कि०मी० लंबी सड़क का निर्माण करने से है जो उत्तर से दक्षिण की तरफ श्रीनगर से कन्या कुमारी, पूर्व से पश्चिम की तरफ पोरबंदर से सिलचर तक बनाना था। उत्तर-दक्षिण गलियारा जो कि श्रीनगर से कन्या-कुमारी तक है, इसकी लंबाई 4000 कि०मी० है तथा यह कोची के साथ जुड़ता है। पूर्व-पश्चिम गलियारा जो कि पोरबंदर से सिलचर तक है इसकी लंबाई 3300 किलोमीटर है। यह दोनों सड़क मार्ग गलियारे 17 राज्यों को छूते हैं। जो हैं-जम्मू तथा कश्मीर, पंजाब, हरियाणा, दिल्ली, उत्तर प्रदेश, मध्य प्रदेश, महाराष्ट्र, तेलंगाना, आन्ध्र प्रदेश, कर्नाटक, तमिलनाडु, केरल, गुजरात, राजस्थान, बिहार, पश्चिमी बंगाल तथा असम। यहां यह भी है कि उत्तर-दक्षिण तथा पूर्व-पश्चिम गलियारे बनाने के लिए सिर्फ राष्ट्रीय शाहमार्ग ही प्रयोग किये जाते हैं। उत्तर प्रदेश का झाँसी प्रदेश वह रेलवे जंक्शन है जहाँ सड़क गलियारे आपस में काटते हैं।

प्रश्न 2.
सुनहरी चतुर्भुज सड़क मार्ग योजना पर नोट लिखो।
उत्तर-
सुनहरी चतुर्भुज, राष्ट्रीय शाहमार्ग विकास प्रकल्प के अधीन भारत में सम्पूर्ण होने वाली सबसे बड़ी सड़क निर्माण योजना है। इसका प्रबंध भी राष्ट्रीय शाहमार्ग अथॉरिटी के अंतर्गत ही था। यह दुनिया की पांचवीं बड़ी सड़क निर्माण योजना है। यह योजना साल 2001 में प्रधानमंत्री श्री अटल बिहारी वाजपेयी द्वारा प्रारंभ की गई जो 2012 में सम्पूर्ण होनी थी। इस प्रकल्प में भारत के चार महानगरों दिल्ली, मुंबई, चेन्नई तथा कोलकाता को आपस में मिसाली सड़क-मार्ग के साथ जोड़े जाने की एक योजना है जो कि रेखा-गणितिक आकृति होने के कारण तथा चतुर्भुज का आकार होने के कारण सुनहरी चतुर्भुज कहलाती है। इस योजना से जुड़े सड़क-मार्ग के साथ कुछ बड़े शहर लगते हैं जैसे बंगलूरु, अहमदाबाद, जयपुर, भुवनेश्वर, कानपुर, पुणे, सूरत, नैलूर, विजयवाड़ा तथा गंटूर। इस सुनहरी चतुर्भुज की लंबाई 5846 कि०मी० है तथा इसके अंतर्गत चार तथा छः मार्गी ऐक्सप्रेस हाईवे बनाए गए हैं। इस चतुर्भुज का शाहमार्ग देश के 13 राज्यों में से निकलता है तथा सबसे अधिक हिस्सा आंध्र प्रदेश में है तथा सबसे कम हिस्सा दिल्ली में पड़ता है।
प्रश्न 3.
भारतीय रेलवे नीति के मुख्य उद्देश्य क्या हैं ? लिखो ?
उत्तर-
भारतीय रेलवे नीति के मुख्य उद्देश्य निम्नलिखित हैं-
- रेलवे मार्गों की लंबाई बढ़ाना।
- गेज का परिवर्तन भाव सौड़ी मीटर गेज को चौड़ी लाइन में बदलता।
- रेल मार्ग का बिजलीकरण करना।
- रेल प्रबंध की कार्य कुशलता में सुधार करना।
- पुराने भाप के इंजनों तथा डीज़ल इंजनों को बदल कर बिजली इंजन प्रयोग में लाने।
- सिगनल संचार तकनीक को सुधारना।
- मुसाफ़िरों के लिए अच्छी सुविधाएं उपलब्ध करवाना।
- यात्री किराया में स्थिरता लाना।
- ऊंची रफ़्तार की गाड़ियों को चलाना।
- रेलवे कार्य के लिए कंप्यूटर प्रयोग में लाना।

प्रश्न 4.
भारतीय रेलवे जोनों पर नोट लिखो।
उत्तर-
स्वतन्त्रता के पश्चात् भारतीय रेल प्रबंध को भारतीय रेलवे बोर्ड ने 6 जोनों में विभाजित किया था जो थेउत्तरी खंड, पश्चिमी खंड, पूर्वी खंड, मध्यम खंड, दक्षिणी खंड तथा उत्तर-पूर्वी खंड परंतु बाद में सन् 1958 से 1960 तक तीन अन्य खंड बना दिए गए जिस के साथ रेलवे के कुल 9 जोन बन गए तथा लगभग तीन दहाकों के पश्चात् रेलवे में अब 18 जोन हैं, जो ये हैंक्रम संख्या
रेलवे जोन — मुख्यालय
- उत्तरी रेलवे — नई दिल्ली
- उत्तर-पूर्वी रेलवे — गोरखपुर
- उत्तर-पूर्वी फ्रंटीयर — मालीगाऊ (गुवाहाटी)
- पूर्वी रेलवे — कोलकाता
- दक्षिणी-पूर्वी रेलवे — बिलासपुर
- दक्षिणी-मध्यम रेलवे — सिकंद्राबाद
- दक्षिणी रेलवे — चेन्नई
- मध्य रेलवे — मुंबई
- पश्चिमी रेलवे — मुंबई
- दक्षिणी-पश्चिमी रेलवे — हुँबली
- उत्तर-पश्चिमी रेलवे — जयपुर
- पश्चिमी-मध्यम रेलवे — जबलपुर
- उत्तरी-मध्यम रेलवे – इलाहाबाद
- दक्षिणी-पूर्वी मध्यम रेलवे — बिलासपुर
- पूर्वी तटवर्ती — भुवनेश्वर
- पूर्वी रेलवे मध्यम रेलवे — हाजीपुर मध्यम रेलवे
- कोंकण रेलवे — नई दिल्ली
- मैट्रो रेलवे — कोलकाताइलाहाबाद
प्रश्न 5.
अन्तर्राष्ट्रीय व्यापार के आधार क्या हो सकते हैं ? भारत की दरामद तथा बरामद पर नोट लिखो।
उत्तर-
अन्तर्राष्ट्रीय व्यापार के आधार-
- प्राकृतिक साधनों के अस्तित्व में फर्क।
- मांग तथा पूर्ति में अंतर।
- तकनीकी विकास में अंतर।
- जलवायु तथा आर्थिक विकास में अंतर।
- व्यापारिक देशों की जंग तथा अमन के हालात।
- व्यापारिक नीतियां तथा देशों के बीच आपसी राजनीतिक संबंध
भारत की दरामद तथा बरामद-भारत में उत्पादन किया गया फालतू सामान बेच दिया जाता है तथा जिसकी आवश्यकता होती है वह सामान खरीद लिया जाता है जो सामान बेचा जाता है उसको बरामद तथा जो सामान खरीदा जाता है उसे दरामद कहते हैं। भारत खनिज ईंधन, खनिज तेल, मोम, जैविक रसायन, फार्मेसी उत्पादन, गेहूं से बनी वस्तुएं, अनाज, बिजली की मशीनरी, कपास से सूती कपड़ा, प्लास्टिक/कहवा, मसाले इत्यादि का बरामद करता है तथा पैट्रोल, खनिज, मशीनरी, खाद्य, लोहा तथा इस्पात, मोती तथा कीमती पत्थर, सोना तथा चांदी, रसायन, दवाइयां फाईबर इत्यादि दरामद की जाती हैं।

प्रश्न 6.
भारत के अन्तर्राष्ट्रीय हवाई अड्डों तथा प्रमुख बंदरगाहों के नाम लिखो।
उत्तर-
भारत के अन्तर्राष्ट्रीय हवाई अड्डे-भारत के प्रमुख हवाई अड्डे निम्नलिखित हैं-
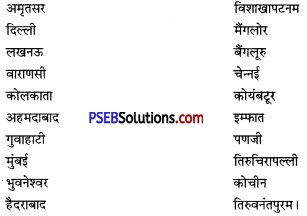
भारतीय बंदरगाहें-कांडला, पोरबंदर, सूरत, पणजी, मर्मागाओ, मंगलौर, कोची, तूतीकोरन, नागापट्नम, चेन्नई, ईनौर, मछलीपटनम, काकीनाड़ा, विशाखापटनम, पाराद्वीप, हलदिया प्रमुख बंदरगाहें हैं।
प्रश्न 7.
व्यक्तिगत संचार तथा जन संचार की आपसी तुलना करो।
उत्तर-
व्यक्तिगत संचार –
- जब दो व्यक्ति या दो से अधिक व्यक्ति आमने सामने होकर किसी साधन की सहायता के साथ अपनी भावनाओं, विचारों तथा संदेशों को बांटना व्यक्तिगत संचार कहलाता है।
- ऐसे संचार में दोनों पक्ष एक दूसरे से परिचित होते हैं।
- इसमें कुछ साधनों का प्रयोग किया जाता है जैसे- डाक सेवाएं, ई-मेल, फैक्स, टैलीफोन, कोरियर, कंप्यूटर इत्यादि।
जन संचार-
- जब कोई संदेश एक बड़ी गिनती में लोगों के साथ बाँटा जाता है उसको जन संचार कहते हैं।
- संचार पक्ष में शामिल लोग एक-दूसरे से परिचित नहीं होते।
- जन संचार में कुछ साधन प्रयोग किए जाते हैं जैसे-जनतक ऐलान, रेडियो, टी०वी०, सिनेमा,अख़बार, सैटेलाईट, इंटरनैट संचार इत्यादि।

प्रश्न 8.
कांडला-बठिंडा पाइप लाइन पर नोट लिखो।
उत्तर-
कांडला-बठिंडा पाइप लाइन ऑयल कार्पोरेशन (IOC) की ओर बठिंडा के तेल शोधक कारखाने को कच्चा तेल पहुँचाने के लिए 1443 किलोमीटर लंबी पाइप लाइन 2392 करोड़ रुपए खर्च कर बिछाने की योजना बनाई गई थी। इस योजना का पहला चरण जो कांडला से सागानौर तक था। 1996 में पूरा हो गया तथा मई 1996 में सागानोर से पानीपत तथा जून 1996 में पानीपत से बठिंडा तक का चरण पूरा कर दिया गया था। इस प्रकल्प का अगला चरण शुरू कर दिया गया जो कि चल रहा है। यह बठिंडा-जम्मू-श्रीनगर गैस पाइप लाइन बिछाने का है। इस प्रकल्प के पूरा होने से जम्मू तथा कश्मीर को हर समय रसोई गैस की सप्लाई मिल सकेगी। इसलिए यह प्रकल्प जम्मू कश्मीर सूबे के लिए विशेष महत्त्व रखता है।
प्रश्न 9.
भारतीय राष्ट्रीय जल मार्गों पर नोट लिखो।
उत्तर-
भारतीय राष्ट्रीय जल मार्ग-भारत में 10 मार्गों को राष्ट्रीय जल-मार्ग का दर्जा हासिल है। यह हैं-
- गंगा, हल्दिया तथा इलाहाबाद के बीच।
- ब्रह्मपुत्र, सेतिया तथा युबड़ी के बीच।
- पश्चिमी उटी नहर, कोल्लम से कोटापुर्म के बीच।
- केरल में चंपाकारा नहर के साथ का क्षेत्र।
- केरल में उद्योगमंडल नहर के साथ का क्षेत्र।
- ब्रह्मनी नदी तलचर से धर्मरा तक।
- काकीनाड़ा से पांडिचेरी तक।
- गोदावरी नदी में भदराचलम से राजामुंदरी तक।
- कृष्णा नदी में वज़ीरावाद से विजयवाड़ा तक।
- लखीमपुर से भंग तक।

प्रश्न 10.
भारतीय वायु यातायात से पहचान करवाओ।
उत्तर-
भारत जैसे बड़े तथा घनी जनसंख्या वाले देश के लिए वायु यातायात का बहुत महत्त्व है। भारत में वायु यातायात का आरंभ 1911 के साल में हुआ जब इलाहाबाद से लेकर नैनी तक, 10 कि०मी० की दूरी के साथ वायु डाक सेवा का प्रयोग किया गया था। इसके बाद कई वायु अड्डे भी बनाये गए तथा फलाईंग क्लब भी बनाए गए जिसके साथ वायु यातायात को प्रोत्साहन मिला। देश की आज़ादी के बाद तथा विभाजन समय (1947) भारत में चार वायु सेवाएं हैं-टाटा सन्ज लिमिटेड, इण्डियन नैशनल एयरवेज़, एयर सर्विसज़ आफ इंडिया तथा डैकन एयरवेज तथा 1951 में चार कंपनियां भारत में वायु सेवाएं लाने के काम में जुट गई। बाद में इन कंपनियों की मलकियत सरकार ने अपने हाथों में ले ली तथा दो कार्पोरेशनें बना दीं। एयर इंडिया जो अन्तर्राष्ट्रीय उड़ानों के लिए थी तथा दूसरी इण्डियन एयर लाइन्ज़ घरेलु उड़ानों के लिए थी।
प्रश्न 4. निम्नलिखित प्रश्नों के उत्तर 20 पंक्तियों में दो :
प्रश्न 1.
भारत की अलग-अलग सड़क योजनाओं से पहचान करवाओ।
उत्तर-
किसी भी देश में सड़कों के लिए विशेष स्थान होता है। लोगों तथा समान को एक स्थान से दूसरे स्थान तक पहुँचाने के लिए सड़कों का ही प्रयोग किया जाता है। इसके अलावा सड़क यातायात अन्य यातायात के साधनों से सबसे सस्ता है। सड़क मार्गों का जाल फैलाने के लिए कई सड़क योजनाओं को बनाया गया है। जैसे-
1. नागपुर योजना (Nagpur Plan)-यह योजना भारत में सड़कों के प्रसार के लिए 1943 में बनाई गई थी।
इस योजना के अधीन देश की मुख्य सड़कों तथा आम सड़कों तथा अन्य सड़कों की लंबाई भी बढ़ती गई।
2. बीस वर्षीय योजना (Twenty Year Plan)-इस योजना की शुरुआत 1961 में हुई। इस योजना का मुख्य उद्देश्य देश में सड़कों की कुल लंबाई 6 लाख 56 हजार किलोमीटर से बढ़ाकर 10 लाख 60 हज़ार किलोमीटर तक करना था तथा सड़क घनत्व भी प्रति 100 कि०मी० रकबे में 32 कि०मी० करना था। इस योजना को पूरा करने के लिए 20 सालों का समय तय किया गया।
3. ग्रामीण सड़क योजना (The Rural Road Development Plan)-इस योजना का मुख्य उद्देश्य ग्रामीण क्षेत्रों के बीच सड़कों का विकास करके कम-से-कम 1500 व्यक्तियों की तथा इससे अधिक आबादी वाले गाँवों को आपस में सड़क मार्गों के साथ जोड़ना था। यह सड़कें इस तरह बनाई जाती हैं कि मौसमी कठिनाइयों को सहन कर सके।
4. बी०ओ०टी० (निर्माण, उपयोग तथा हवाले करो) (Built, Operate and Transfer Scheme)-इस योजना में प्राइवेट बिल्डरों तथा ठेकेदारों को सड़कों तथा पुलों का निर्माण करने के लिए ठेके दिए गए थे तथा यह सहमति भी दी गई कि यह अपना निर्माण सड़क से जाने वाले वाहनों के चालकों से सीमित किए समय के लिए टोल टैक्स इकट्ठा करना तथा फिर सड़कों को सरकार के हवाले कर देना। यह योजना एक सफल योजना रही तथा देश के कई हिस्सों में इस योजना को सफलता हासिल हुई।
5. केंद्रीय सड़क फंड (Central Road Fund)-इस फंड के साथ संबंधित एक्ट दिसंबर 2000 में लागू किया गया था। इस एक्ट के अनुसार सड़कों का विकास पैट्रोल तथा डीज़ल पर लगे टैक्स तथा कस्टम कर को इकट्ठा करके किया जाएगा।

प्रश्न 2.
नए राष्ट्रीय शाहमार्ग अंकण योजना पर विस्तार सहित नोट लिखो।
उत्तर-
राष्ट्रीय शाह मार्ग अंकण योजना एक नई अंकण योजना थी। भारत में यह मार्ग प्रबंध भारत सरकार की एजेन्सियों की तरफ से चलाया तथा संभाला गया है। राष्ट्रीय शाह मार्ग की लंबाई जून 2016 तक एक लाख 87 किलोमीटर थी। इनमें लगभग 26,200 किलोमीटर शाहमार्ग 4 मार्ग तथा बाकी 2 मार्ग हैं। केंद्रीय सरकार के तय किए उद्देश्य के मुताबिक सन् 2017 से हर रोज 30 कि०मी० शाह मार्ग विकसित किए जाए तथा नए विकास के लिए लुक तथा कोयले की बजाए सीमेंट का प्रयोग किया जाए। हाल ही में कई सड़क मार्गों को राष्ट्रीय मार्ग घोषित किया गया है। अब बड़े क्षेत्रों तथा शहरों के इधर-उधर बाईपास बनाये जा रहे हैं, ताकि शाह मार्गों पर यातायात का बहाव बिना रोक-टोक के निरंतर चलता रहे। इन शाहमार्ग का विकास तेजी से हो रहा है। 2004 से 2014 के समय में शाह मार्ग में सिर्फ 18,000 कि०मी० की वृद्धि हुई है।
भारतीय सड़क यातायात तथा हाईवेज़ मंत्रालय ने 28 अप्रैल, 2010 को एक नोटीफिकेशन निकाला तथा इसमें राष्ट्रीय शाहमार्ग को नए अंकों का प्रबंध दिया। यह नया नम्बर राष्ट्रीय शाहमार्ग के भौगोलिक क्षेत्र का ज्ञान हमें करवाता है। अब पूर्व से पश्चिम दिशा की तरफ जा रहे सारे शाहमार्ग का क्रम पहचान अंक टांक अंक हैं जिन की शुरुआत उत्तर में हो रही है तथा जैसे-जैसे हम दक्षिण दिशा की ओर जाते हैं क्रम अंक में वृद्धि होनी शुरू हो जाती है तथा जैसे ही विस्तार अंक में वृद्धि होगी, शाहमार्ग पहचान अंक कम होता चला जाएगा, विस्तार अंक के कम होने के साथ पहचान अंक में वृद्धि होगी।
उदाहरण के तौर पर राष्ट्रीय शाहमार्ग नंबर 1 जम्मू कश्मीर में है तथा नंबर 87 तमिलनाडु में है। अब इससे पता चलता है कि उत्तर-दक्षिण दिशा की ओर जाते शाहमार्ग का क्रम पहचान अंक जिस्त है तथा इसकी शुरुआत पूर्व में होकर पश्चिम की ओर जाते समय बढ़ती है। जैसे ही लंबकार अंक कम होगा तब शाहमार्ग पहचान अंक के वृद्धि होगी तथा लंबकार अंक बढ़ेगा तो शाहमार्ग पहचान अंक कम हो जाएगा। जैसे कि राष्ट्रीय शाहमार्ग नंबर-2 उत्तर-पूर्वी राज्यों में पड़ता है तथा नंबर 68 राजस्थान से गुजरात की ओर जा रहा है।
राष्ट्रीय शाहमार्ग की एक और विशेषता यह है कि प्रमुख राष्ट्रीय शाहमार्गों का पहचान अंक एकहरा, दोहरा होता है परंतु उनमें निकल रहे अगले शाहमार्ग के पहचान अंक तीहरे होते हैं, भाव सैंकड़ों में होते हैं। जहाँ यह भी वर्णन योग्य है कि नई अंकण योजना में सिर्फ पुराने शाहमार्गों के अंक ही नहीं बदले गए, बल्कि मार्गों का सारा प्रबंध दुबारा से किया गया है, जैसे कि राष्ट्रीय शाहमार्ग नंबर 27 जो पोरबंदर से सिलचर तक है तथा पूर्व से पश्चिमी गलियारा है। कितने ही पुराने राष्ट्रीय शाहमार्ग को हर मार्ग आपस में जोड़ रहा है। आज के नये प्रबंध के अनुसार अब देश में 218 राष्ट्रीय शाहमार्ग हैं तथा 78 प्रमुख शाहमार्ग तथा 140 राष्ट्रीय मार्ग है जो शाह राज्यों में ही निकल रहे हैं। इन को ऑफ सूट हाईवेज कहा जाता है। इन ऑफ सूट हाईवेज की पहचान अंक सैंकड़ों में हुआ है तथा अधिक पहचान अंक का ईकाई अंक दिशा निर्धारण करता है, जैसे कि यह इकाई अंक टांक हैं, तो शाहमार्ग में निकला मार्ग भी पूर्व-पश्चिम दिशा में है तथा यह अंक इकाई है, जिस्त हैं तब शाहमार्ग में निकला मार्ग भी उत्तर-दक्षिण दिशा में है।
प्रश्न 3.
पार-महाद्वीपीय रेलवे जालों से पहचान करवाओ।
उत्तर-
पार-महाद्वीपीय रेलवे मार्ग लंबी दूरी तय करने वाले रेल मार्ग हैं। इन रेल-मार्गों का जाल ऐसा है जो कि महाद्वीप की सारी भूमि को पार करके दूसरे महासागर के साथ लगते महाद्वीप के सिरे तक पहुंच जाता है। पार-महाद्वीप रेल-मार्गों का इतिहास आज से तकरीबन 150 साल पुराना है। संसार की सबसे पहली रेल लाईन 1863 से 1869 के बीच अमेरिका में पसारी गई जो कि यू०एस०ए० में से गुजरती हुई अंध-महासागर के तट पर होती हुई प्रशांत महासागर तक 1776 मील का रास्ता तय करती थी। संसार में और भी कई पार-महाद्वीप रेल मार्गों का निर्माण हुआ है जो कि बहुत बड़ी संख्या में मुसाफिरों तथा माल को एक स्थान से दूसरे स्थान तक पहुंचाने के लिए जाने गए। ट्रांस साइबेरियाई रेल मार्ग मास्को से रूस के पूर्व के तरफ वलादिवोस्तोक तक 9,289 किलोमीटर लंबा है तथा इसका निर्माण 1891 से 1916 तक के समय हुआ था। इस की कई शाखाएं हैं जो मास्को से इस मार्ग की सहायता के साथ चीन, मंगोलिया तथा उत्तरी कोरिया से जोड़ती हैं। इस मार्ग का विस्तार अभी भी चल रहा है।
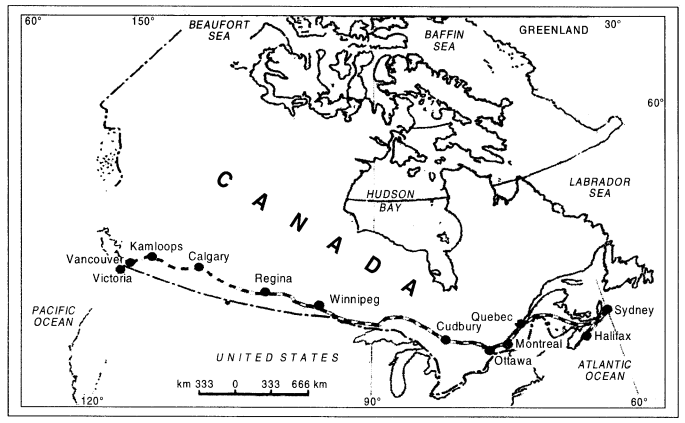
कैनेडियन पैसेफिक रेल-मार्ग-रेलवे मार्ग की यह एक बहुत अच्छी उदाहरण हैं। यह रेल मार्ग कनाडा में पूर्वी भाग में हैलीफैक्स से चलकर पश्चिमी में बैन्कूवर तक पहुंचता है। यह रेल मार्ग दुर्ग पर्वत क्षेत्रों में से गुजरता है। इस रेल मार्ग से लकड़ी, खनिज पदार्थ, गेहूँ व लोहे का परिवहन होता है। इस मार्ग का निर्माण 1881 में शुरू किया गया तथा अभी तक इसका विस्तार हो रहा है।
पार ऑस्ट्रेलिया रेलवे मार्ग-यह रेलवे मार्ग पोर्ट ओगस्ता से लेकर कालगुरली तक फैला है। इसका काम 1917 में पूरा हो गया था यह रेल-मार्ग ऑस्ट्रेलिया के पूर्व से पश्चिमी सिरो को आपस में मिलाता है। ब्रिसबेन से बारस्ता सिडनी-मैलबोरन-ऐडिलेड इस मार्ग पथ तक पहुँचता है। इसके निर्माण के समय से ही इसमें तीन गेजों का उपयोग किया गया था जिस कारण इसकी शुरुआत तक का सफर सच हो गया। बाद में 1970 के साल में इसको एक रेलवे गेज में बदला गया। आज के समय सिडनी पथ के बीच वाले रेलवे मार्ग को इण्डिन पैसेफिक रूट कहते हैं।
पनामा कैनाल रेलवे-यह रेलवे मार्ग पनामा नहर के समांतर चलता है तथा मध्य अमेरिका में अंध महासागर के तट से प्रशांत महासागर के तट तक चली जाती है जो कि 77 कि०मी० तक लंबी है। अंध महासागर के शहर कोलेन से प्रशांत महासागर के शहर बल्लबरा तक का रेलवे मार्ग ज्यादा लंबा तो नहीं परंतु यह मार्ग विश्व के बड़े महासागरों को मिलाता है जिस कारण इसका महत्त्व काफी बढ़ गया है। यह रेल मार्ग मुसाफिरों तथा माल को एक स्थान से दूसरे स्थान तक पहुंचाता है।
दक्षिणी अमेरिका में पार इण्डियन तथा पार ऐमेजीयन रेलवे प्रकल्प हैं। अफ्रीकन यूनियन ऑफ रेलवेज़ भी अफ्रीका में पार-महाद्वीपी रेल प्रकल्प बनाने की योजना बना रहे हैं।
भारत का रेलवे नैटवर्क दुनिया का सबसे बड़ा नैटवर्क है, जो कि हर रोज 1 करोड़ 80 लाख यात्रियों को तथा 20 लाख टन माल को एक स्थान से दूसरे स्थान पर पहुँचाया जाता है। ऐसा विस्तृत रेल प्रबंध ही भारतीय रेलवे कहलाता हैं।

प्रश्न 4.
देश की तेज रफ़्तार शाही गाड़ियों से पहचान करवाओ।
उत्तर-
रेल के द्वारा सफर बाकी यातायात के साधनों से सस्ता तथा अधिक आरामदायक होता है। भारत में रेल मार्गों का महत्त्व बढ़ रहा है क्योंकि देश में सफर को आसान बनाने के लिए तेज़ रफ़्तार गाड़ियों को चलाया जा रहा है। ताकि समय की बचत की जा सके। सरकार इस तरफ काफी मेहनत कर रही है देश में पहले ही कुछ तेज़ रफ़्तार गाड़ियां हैं। जिनमें से मुख्य हैं
- नयी दिल्ली-आगरा गतिमान ऐक्सप्रैस, रफ़्तार 160 कि०मी०/घंटा।
- नयी दिल्ली-भोपाल शताब्दी एक्सप्रैस, इसकी रफ़्तार 91 कि०मी०/घंटा है।
- मुंबई-नई दिल्ली राजधानी एक्सप्रैस, इसकी रफ़्तार 90.46 कि०मी०/घंटा है।
- सियालदा-नई दिल्ली दुरंतो एक्सप्रैस, इसकी रफ्तार 91.0 कि०मी० प्रति घंटा है।
- नयी दिल्ली-कानपुर शताब्दी एक्सप्रैस, इसकी रफ़्तार 89.63 कि०मी०/घंटा है ।
- नयी दिल्ली-हावड़ा, दुरांतो एक्सप्रैस, इसकी रफ़्तार 88.21 कि०मी०/घंटा है।
- नयी दिल्ली-हावड़ा, दुरांतो ऐक्सप्रैस, इसकी रफ्तार 87.06 कि०मी०/घंटा है।
- नयी दिल्ली-इलाहाबाद, दुरांतो ऐक्सप्रैस, इसकी रफ़्तार 86.85 कि०मी०/घंटा है।
- सियालदा-नयी दिल्ली राजधानी ऐकस्प्रेस, इसकी रफ़्तार 87.06 कि०मी०/घंटा है।
- निजामुद्दीन-बांद्रा गरीब रथ, इसकी रफ्तार 82.80 कि०मी० प्रति घंटा।
तेज़ रेल गाड़ियों के अलग देश में रेल गाड़ी की एक और सहूलियत भी है जिसमें सफर शाही सुविधाओं से लैस होता है। इनको लग्ज़री गाड़ियां कहते हैं। इनका प्रबंध इण्डियन रेलवे कैटरिंग एंड टूरिज्म कार्पोरेशन लिमिटड (IRCTC) द्वारा किया गया। कुछ शाही गाड़ियों की सूची निम्नलिखित है-
I. महाराजा ऐक्सप्रैस-यह ऐक्सप्रैस देश के सैलानी महत्त्व रखने वाले स्थानों की शाही सैर करवाती है।
II. पैलेस ऑन वहील्ज़-यह ऐक्सप्रैस राजस्थान के सबसे बढ़िया सैलानी स्थानों की शाही सैर करवाती है।
III. द डैकन उड़ीसी-यह ऐक्सप्रैस शाही ढंग से दक्षिणी भारत की सैर करवाती है।
IV. रॉयल राजस्थान ऑन व्हील्स-यह हमें भारत की संस्कृति की शाही यात्रा करवाती है।
V. रॉयल ओरिएंट ट्रेन-यह रेलवे हमें मध्य भारत की शाही सैर करवाती है।
VI. गोल्डन चैरीयट- यह रेल हमें महाराष्ट्र तथा गुजरात की शाही सैर करवाती है।
VII. फैरी कुईन ऐक्सप्रैस-यह हमें राजस्थान तथा अलवर तथा सरिसका की यात्रा करवाती है।
प्रश्न 5.
संसार के प्रमुख समुद्री मार्गों पर नोट लिखो।
उत्तर-
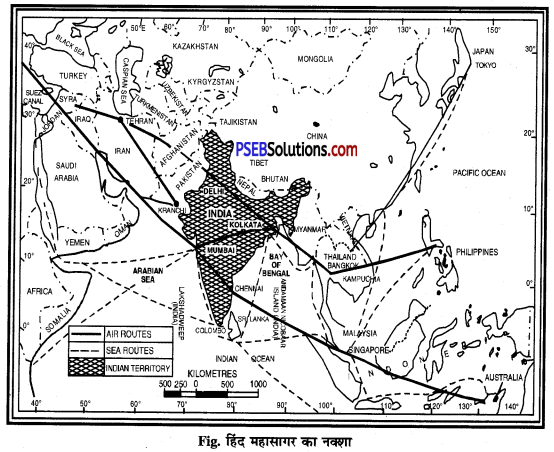
संसार में व्यापार का एक बड़ा हिस्सा समुद्री मार्गों के द्वारा किया जाता है। समुद्री जहाजों की सहायता से भारी तथा आवश्यक चीज़ों को एक स्थान से दूसरे स्थान तक पहुँचाया जाता है। यह स्थान बदली का एक सस्ता ढंग है। संसार में व्यापार अलग-अलग समुद्री मार्गों द्वारा किया जाता है तथा व्यापार के लिए छोटे मार्ग को चुना जाता है। संसार के प्रसिद्ध समुद्री मार्ग निम्नलिखित हैं-
1. उत्तरी अंध-महासागरीय मार्ग (North Atlantic Route)- यह समुद्री मार्ग विश्व में सबसे अधिक उपयोग किया जाता है तथा इसके द्वारा ही संसार का आधे से ज्यादा समुद्री व्यापार हो रहा है। इस क्षेत्र की मुख्य व्यापारिक बंदरगाहें हैं-रॉटरडैम, एंटवर्प, लंडन, बोस्टन, न्यूयॉर्क, फिलाडेल्फिया हैं।
2. केप ऑफ़ गुड होप (Cape of Good Hope)-यह समुद्री मार्ग अमेरिका महाद्वीप के दक्षिणी हिस्से से लेकर आशा अंतरीप हिस्से के आस-पास घूमता है।
3. भू-मध्य सागरीय स्वेज़ ऐशियाई मार्ग (The Mediterranean-SuejAsiatic Route)—यह मार्ग ऐशियाई तथा यूरोपीय देश को स्वेज़ नहर की सहायता से आपस में जोड़ता है।
4. पनामा नहर मार्ग (Panama Canal Route)-यह मार्ग अंध-महासागर तथा प्रशांत महासागर को आपस में मिलाता है तथा प्रशांत महासागर द्वार कहलाता है।
5. दक्षिणी अंध महासागरीय मार्ग (South Atlantic Route)-यूरोप के पश्चिमी देशों को अंध महासागर के रास्ते की सहायता के साथ दक्षिणी अमेरिका के पूर्वी उटी क्षेत्रों से मिलाकर व्यापार का मौका दिया जाता है।
6. पार प्रशांत-मार्ग (The Transpacific Route)-इस मार्ग का मुख्य केंद्र हवाई टापू में स्थित है।

Geography Guide for Class 12 PSEB परिवहन/यातायात, संचार तथा व्यापार Important Questions and Answers
I. वस्तुनिष्ठ प्रश्नोत्तर (Objective Type Question Answers)
A. बहु-विकल्पी प्रश्न :
प्रश्न 1.
भारत में सबसे लंबा राष्ट्रीय महामार्ग कौन-सा है ?
(A) NH
(B) NHS
(C) NH
(D) NHA
उत्तर-
(C) NH
प्रश्न 2.
संसार में सबसे लंबा रेलमार्ग कौन-सा है ?
(A) यूनियन पैसिफ़िक
(B) कैनेडियन नैशनल
(C) ट्रांस साइबेरियन
(D) ट्रांस इण्डियन।
उत्तर-
(C) ट्रांस साइबेरियन
प्रश्न 3.
ट्रांस साइबेरियन रेलमार्ग के पूर्वी छोर पर स्थित स्टेशन है ?
(A) हनोई
(B) शंघाई
(C) टोकियो
(D) ब्लाडी वास्टेक।
उत्तर-
(D) ब्लाडी वास्टेक।

प्रश्न 4.
भारतीय रेलवे सिस्टम को कितने रेलवे जोन में विभाजित किया है ?
(A) 9
(B) 16
(C) 14
(D) 12.
उत्तर-
(B) 16
प्रश्न 5.
निम्नलिखित में से कौन-सी स्थल मार्ग यातायात की किस्म नहीं है :
(A) सड़कें
(B) रेलें
(C) पाइप लाइनें
(D) हवाई अड्डा।
उत्तर-
(C) पाइप लाइनें
प्रश्न 6.
राष्ट्रीय मार्गों का निर्माण तथा देखभाल कौन करता है ?
(A) केंद्र सरकार
(B) ज़िला सरकार
(C) बी०ओ०टी०
(D) NHAY.
उत्तर-
(A) केंद्र सरकार

प्रश्न 7.
यमुना एक्सप्रेस हाईवे किस के हवाले है ?
(A) नोएडा तथा आगरा
(B) आगरा तथा दिल्ली
(C) दिल्ली तथा हिमाचल
(D) दिल्ली तथा पंजाब।
उत्तर-
(A) नोएडा तथा आगरा
प्रश्न 8.
सुनहरी चतुर्भुज सड़क मार्ग प्रकल्प में निम्नलिखित महानगरी में किसको शामिल नहीं किया जाता ?
(A) दिल्ली
(B) मुंबई
(C) अहमदाबाद
(D) चेन्नई।
उत्तर-
(C) अहमदाबाद
प्रश्न 9.
भारत सरकार के सड़क यातायात मंत्रालय के 28 अप्रैल, 2010 के नोटिफिकेशन में राष्ट्रीय शाहमार्ग को क्या प्रदान किया गया ?
(A) नई सड़कें
(B) नए अंक
(C) नए मार्ग
(D) सड़कों की मुरम्मत।
उत्तर-
(B) नए अंक

प्रश्न 10.
देश में पहली रेल यात्रा मुंबई से थाने तक की गई :
(A) 1853
(B) 1854
(C) 1865
(D) 1868.
उत्तर-
(A) 1853
प्रश्न 11.
दूसरी रेलवे लाइन जो कोलकाता से रानीगंज तक थी यह कब बिछाई गई ?
(A) 1853
(B) 1854
(C) 1870
(D) 1865.
उत्तर-
(B) 1854
प्रश्न 12.
1950-51 के अंत तक रेलवे लाइनों की लंबाई कितनी थी ?
(A) 53,596 कि०मी०
(B) 53,000 कि०मी०
(C) 58,000 कि०मी०
(D) 60,000 कि०मी० ।
उत्तर-
(A) 53,596 कि०मी०

प्रश्न 13.
उत्तर पूर्वी रेलवे जोन का मुख्यालय कहां पर है ?
(A) गोरखपुर
(B) दिल्ली
(C) आगरा
(D) कोलकाता।
उत्तर-
(A) गोरखपुर
प्रश्न 14.
संसार की पहली रेलवे अमेरिका में कब बिछाई गई ?
(A) 1863 से 1869
(B) 1865-66
(C) 1870-75
(D) 1870-71.
उत्तर-
(A) 1863 से 1869
प्रश्न 15.
मध्य अमेरिका में कौन-सी नहर अंध-महासागर के तट तक जाती है ?
(A) पिली का
(B) पनामा
(C) राईन
(D) वूलर।
उत्तर-
(B) पनामा

प्रश्न 16.
साल 2014 के बजट अनुसार देश में कितने अर्ध तेज रेल गलियारे स्थापित किये जाते थे ?
(A) 9
(B) 10
(C) 6
(D) 5.
उत्तर-
(A) 9
प्रश्न 17.
निम्नलिखित में से कौन-सी लग्ज़री गाड़ी की उदाहरण नहीं है ?
(A) महाराजा ऐक्सप्रैस
(B) हावड़ा दुरांतो ऐक्सप्रेस
(C) पैलेस ऑन वहीक्लज़
(D) गोल्डन चैरीअट।
उत्तर-
(B) हावड़ा दुरांतो ऐक्सप्रेस
प्रश्न 18.
भारत में हवाई यातायात का प्रारंभ किस साल में हुआ ?
(A) 1910
(B) 1911
(C) 1921
(D) 1922.
उत्तर-
(B) 1911

प्रश्न 19.
संचार की प्रमुख कितनी किस्में हैं ?
(A) 2
(B) 1
(C) 3
(D) 4.
उत्तर-
(A) 2
प्रश्न 20.
भारत निम्नलिखित में कौन-सी चीज़ों की दरामद नहीं करता ?
(A) पैट्रोल
(B) खनिज
(C) लोहा तथा इस्पात
(D) गेहूँ।
उत्तर-
(D) गेहूँ।
B. खाली स्थान भरें :
1. यातायात सुविधाओं को मुख्य रूप में …………. भागों में बांटा जाता है।
2. नागपुर योजना ………………… के साल में बनाई गई।
3. देश में यातायात का बहाव संभव बनाने के लिए . ……………. नाम से शाह मार्ग का निर्माण किया गया।
4. सन् 1871 तक तीन प्रमुख शहरों कोलकाता, ………………….. तथा …………………. रेल तंत्र द्वारा आपस में जोड़े गए।
5. भारतीय रेल तीन गेज चौड़ी, सौड़ी तथा ……………… गेज में बांटी जाती हैं।
6. एशिया तथा यूरोप के देशों को .. ……………. नहर की सहायता के साथ आपस में मिलाया गया।
उत्तर-
- तीन,
- 1943,
- एक्सप्रेस हाईवेज,
- मुंबई, चेन्नई,
- मीटर,
- स्वेज।

C. निम्नलिखित कथन सही (√) हैं या गलत (x):
1. बीस वर्षीय योजना 1961 में आरंभ की गई।
2. पूर्व पश्चिमी गलियारा राजस्थान से पोरबंदर तक है।
3. सुनहरी चतुर्भुज दुनिया की पाँचवीं सबसे बड़ी सड़क योजना है।
4. देश में रेल-तंत्र विकसित करने का एक उद्देश्य था सिगनल संचार तकनीक में सुधार करना।
5. गोल्डन चैरीअट महाराष्ट्र और गुजरात की शाही सैर करवाती है।
उत्तर-
- सही
- गलत,
- सही,
- सही,
- सही।
II. एक शब्द /एक पंक्ति वाले प्रश्नोत्तर (One Word/Line Question Answers) :
प्रश्न 1.
ट्रशरी व्यवसाय क्या है ?
उत्तर-
जो सेवाएं प्रदान करते हैं।
प्रश्न 2.
परिवहन साधनों के तीन प्रकार बताएं।
उत्तर-
जल-मार्ग, थल मार्ग, हवाई-मार्ग।

प्रश्न 3.
भारतीय सड़क मार्ग की लंबाई बताओ।
उत्तर-
18 लाख कि०मी०।
प्रश्न 4.
स्वर्ण चतुर्भुज से क्या अभिप्राय है ?
उत्तर-
राष्ट्रीय मार्गों का जाल जो दिल्ली, मुंबई, चेन्नई, कोलकाता को जोड़ता है।
प्रश्न 5.
ट्रांस साईबेरियन रेलमार्ग कौन-से स्थानों को जोड़ता है ?
उत्तर-
वलादिवोस्तक और सेंट पीटरसबर्ग।

प्रश्न 6.
संसार में सबसे लंबा रेलमार्ग कौन-सा है ?
उत्तर-
ट्रांस साईबेरियन रेलमार्ग 8800 कि०मी० लंबा है।
प्रश्न 7.
भारत में रेलमार्गों की कुल लंबाई बताओ।
उत्तर-
63000 कि०मी०।
प्रश्न 8.
संसार के दो अंदरूनी जलमार्गों के नाम बताओ।
उत्तर-
राइन नदी और महान झीलें।

प्रश्न 9.
अंध-महासागर पर दो बंदरगाहें बताओ।
उत्तर-
लंदन और न्यूयार्क।
प्रश्न 10.
स्वेज नहर किन सागरों को जोड़ती है ?
उत्तर-
लाल सागर और रूम सागर।
प्रश्न 11.
पनामा नहर किन सागरों को जोड़ती है ?
उत्तर-
अंध महासागर और प्रशांत महासागर।

प्रश्न 12.
भारत के पश्चिमी तट पर दो बंदरगाहों के नाम बताओ।
उत्तर-
कांडला और मुंबई।
प्रश्न 13.
थल-मार्ग के यातायात प्रबंध की तीन किस्में बताओ।
उत्तर-
सड़कें, पाइप लाइन और रेल।
प्रश्न 14.
पहली रेल यात्रा कब और कहाँ तक की गई ?
उत्तर-
1853 में मुंबई से थाने तक।

प्रश्न 15.
लग्ज़री गाड़ियों का प्रबंध किसके अधीन है ?
उत्तर-
भारतीय रेलवे कैटरिंग और टूरिज्म कार्पोरेशन लिमिटेड।
प्रश्न 16.
राष्ट्रीय यातायात नीति कमेटी के अनुसार कितने जल मार्गों को राष्ट्रीय जलमार्ग ऐलान किया गया ?
उत्तर-
10 जल मार्गों को।
प्रश्न 17.
ऐयरपोर्ट्स अथारिटी ऑफ इण्डिया की ओर से दी जाने वाली जानकारी/सूचना के अनुसार कितने अंतर्राष्ट्रीय और घरेलू हवाई अड्डे हैं ?
उत्तर-
30 अंतर्राष्ट्रीय और 400 घरेलू हवाई अड्डे हैं।

प्रश्न 18.
संसार में सबसे लंबी कच्चे तेल की पाइप लाइन कहाँ बिछाई गई ?
उत्तर-
उत्तरी अमेरिका में।
प्रश्न 19.
TAPI पाइप लाइन किस ओर से विकसित की गई ?
उत्तर-
एशियाई विकास बैंक।
प्रश्न 20.
संचार की मुख्य किस्में बताओ।
उत्तर-
व्यक्तिगत और जन-संचार।

प्रश्न 21.
व्यापार से आपका क्या भाव है ?
उत्तर-
वस्तुओं और सेवाओं की खरीदो-फरोख्त की क्रिया को व्यापार कहा जाता है।
प्रश्न 22.
भारत की ओर से बरामद की जाने वाली वस्तुओं के नाम बताओ।
उत्तर-
खनिज तेल, मोम, ईंधन, जैविक रसायन, फार्मेसी, उत्पादन, कनक/गेहूँ से बनी वस्तुएँ।
प्रश्न 23.
भारत की मुख्य चार बंदरगाहों के नाम बताओ।
उत्तर-
मैंगलोर, कोची, सूरत, पणजी।

प्रश्न 24.
आलमी व्यापार संगठन क्या है ?
उत्तर-
यह एक अंतर-सरकारी संस्था है, जो अंतर्राष्ट्रीय व्यापार को क्रमबद्ध करती है और अलग-अलग देशों के मध्य व्यापारिक नियमावली निश्चित करती है।
अति लघु उत्तरीय प्रश्न (Very Short Answer Type Questions)
प्रश्न 1.
यातायात सविधाओं को कौन-से वर्गों में वर्गीकृत किया जाता है ?
उत्तर-
यातायात सुविधाओं को निम्नलिखित वर्गों में वर्गीकृत किया जाता है-
- स्थल मार्ग यातायात
- जल मार्ग यातायात
- वायु मार्ग यातायात।
प्रश्न 2.
यातायात के साधन कौन-से ज़रूरी तत्त्वों पर निर्भर करता है ?
उत्तर-
यातायात के साधन के विकास में कई तत्त्वों का योगदान रहता है। यातायात मार्ग का निर्धारण आवश्यक है। वाहन तथा ऊर्जा के साधन परिवहन मार्गों पर प्रभाव डालते हैं। स्थल आकृति, मौसम परिवहन साधनों को प्रभावित करते हैं। आर्थिक विकास में कच्चे माल की प्राप्ति परिवहन के लिए आवश्यक तत्त्व है।

प्रश्न 3.
अंतर-महाद्वीपी रेल-मार्ग किसे कहते हैं ? उदाहरण दो।
उत्तर-
अंतर महाद्वीपीय रेल-मार्ग उन रेल मार्गों को कहते हैं जो महाद्वीप के एक किनारे को दूसरे किनारे से जोड़ते हैं। यह रेल-मार्ग महाद्वीप के उल्ट तटों पर स्थित स्थानों को जोड़ते हैं। ट्रांस साइबेरियाई रेल-मार्ग तथा ट्रांस कैनेडियन रेल मार्ग इसकी दो उदाहरण हैं।
प्रश्न 4.
रेलमार्ग किन हिस्सों में बनाये जाते हैं ?
उत्तर-
- रेलमार्ग हमेशा मैदानी समतल हिस्सों में बनाये जाते हैं।
- रेल मार्ग हमेशा घनी जनसंख्या वाले प्रदेशों तथा आर्थिक रूप में विकसित प्रदेशों में बनाये जाते हैं।
- बंदरगाहों को देश के आंतरिक हिस्सों से जोड़ने के लिए रेलमार्गों का निर्माण किया जाता है।
प्रश्न 5.
भारत के सीमावर्ती सड़क मार्ग बताओ।
उत्तर-
भारत के सीमावर्ती प्रदेशों में सड़कों का निर्माण करने के लिए सीमा सड़क बोर्ड की सन् 1960 में स्थापना की गई। भारत में सीमा निकट प्रदेशों में 27,000 कि०मी० लंबी पक्की सड़कें बनाई गई हैं। जिन में मनाली से लेह तक मुख्य सड़क है। इस सड़क की औसत ऊंचाई 4270 मीटर है।

प्रश्न 6.
संसार के मुख्य समुद्री मार्गों का महत्त्व बताओ।
उत्तर-
यातायात के साधनों में समुद्री यातायात सबसे सस्ता तथा महत्त्वपूर्ण साधन है। संसार का अधिकतर व्यापार समुद्री मार्ग के द्वारा होता है। जब बहुत सारे जहाज एक निश्चित मार्गों पर चलते हैं, तब उसे समुद्री मार्ग कहते हैं।
प्रश्न 7.
भारतीय रेल-मार्गों की अलग-अलग आकार की पटरियां बताओ।
उत्तर-
भारत में रेल मार्ग तीन तरह के हैं:
- चौड़ी पटरी (Broad Gauge)-1.68 मीटर चौड़ी।
- छोटी पटरी (Metre Gauge)-1 मीटर चौड़ाई।
- तंग पटरी (Narrow Gauge)-0.68 मीटर चौड़ाई।
प्रश्न 8.
पनामा नहर की महत्ता बताओ।
उत्तर-
इस नहर के निर्माण के साथ अंध-महासागर के मध्य दूरी कम हो गई है। इससे पहले जहाज़ दक्षिणी अमेरिका के केप हारन का चक्कर ला कर जाते हैं। इस नहर से सबसे अधिक लाभ संयुक्त राज्य अमेरिका को हुआ है। इसके पश्चिमी तथा पूर्वी तटों के मध्य दूरी कम हो गई है। संयुक्त राज्य अमेरिका के पूर्वीतट से आस्ट्रेलिया, न्यूजीलैंड, दक्षिणी अमेरिका, जापान की बंदरगाहों की दूरी कम हो गई है। इस नहर द्वारा यूरोप को कोई विशेष लाभ नहीं है।

प्रश्न 9.
HBJ गैस पाइप लाइन का वर्णन करो।
उत्तर-
भारत में गैस परिवहन के लिए हजीरा-विजयपुर-जगदीशपुर पाइप लाइन बनाई गई है। यह पाइप लाइन 1700 किलोमीटर लंबी है। यह पाइप लाइन गुजरात, मध्य प्रदेश, राजस्थान, उत्तर प्रदेश राज्यों से गुजरती है। इस गैस के साथ विजयपुर, सवाई माधोपुर, जगदीशपुर, शाहजहांपुर, अंबाला तथा बबराला में खाद बनाने की योजना है।
प्रश्न 10.
व्यक्तिगत संचार से आपका क्या अर्थ है ?
उत्तर-
जब दो या दो से ज्यादा व्यक्ति आमने-सामने होकर या किसी साधन का उपयोग करके कोई जानकारी, विचार संदेश आपस में आदान-प्रदान करें उसे व्यक्तिगत संचार कहते हैं। ऐसे संचार के साधनों में व्यक्ति आपस में एक-दूसरे से पहचान करवाते हैं। मुख्य साधन हैं-डाक सेवाएं, टैलीफोन, ई-मेल इत्यादि।
प्रश्न 11.
राष्ट्रीय व्यापार के कोई चार आधार लिखो।
उत्तर-
राष्ट्रीय व्यापार के आधार निम्नलिखित हैं-
- मांग तथा पूर्ति में अंतर।
- प्राकृतिक साधनों के अस्तित्व में अंतर।
- माल के मूल्यों में अंतर।
- व्यापारिक नीतियां।

प्रश्न 12.
आलमी व्यापार संगठन (World Trade Organization) क्या हैं ?
उत्तर-
आलमी व्यापार संगठन पहली बार जनवरी, 1995 को मराकेश समझौते द्वारा अस्तित्व में आया। जिस में संसार के 123 देशों ने हस्ताक्षर किए तथा शुल्क और व्यापार पर सामान्य समझौता (General Agreement on Tarrifism and Trade) का अंत कर दिया। इस संगठन का मुख्य दफ्तर जनेवा में है। खासकर व्यापारिक मसलों का समाधान तथा नियमों को लागू इस द्वारा ही किया जाता है। यह संगठन आलमी व्यापार स्तर को सुधार से राष्ट्रीय व्यापार को ज्यादा महत्त्वपूर्ण बना रहा है।
प्रश्न 13.
NNB पाइप लाइन का वर्णन करो।
उत्तर-
NNB नाहरकटिया नानूमती बरोनी पाइप लाइन देश की पहली पाइप लाइन है जो कि नाहरकटिया के तेल के कुओं से नानूमती तक कच्चा तेल पहुँचाने के लिए बिछाई गई थी तथा बाद में यह पाइप लाइन बरोनी तक बढ़ा दी गई। इसकी लंबाई 1167 कि०मी० है तथा अब इसको उत्तर प्रदेश के कानपुर शहर तक बढ़ा दिया गया है। इस NNB पाइप लाइन का काम 1962 तक शुरू हो गया था जब तक कि बरोनी तक का भाग 1964 में शुरू किया गया।
प्रश्न 14.
उत्तरी अंध महासागरी मार्ग पर नोट लिखो।
उत्तर-
यह संसार के प्रमुख समुद्री मार्गों में एक है। यह जल-मार्ग संसार का सबसे अधिक उपयोग में आने वाला जल मार्ग है। इस जल मार्ग के द्वारा आधे से अधिक समुद्री व्यापार किया जा रहा है। उत्तरी अंध महासागर मार्ग की प्रमुख बंदरगाहें हैं-रॉटरडैम, फिलाडेल्फिया, ऐंटवर्प, लंदन, न्यूयॉर्क, बोस्टन इत्यादि हैं।

प्रश्न 15.
जल-मार्गी यातायात को कौन-से दो भागों में विभाजित किया जाता है ?
उत्तर-
जल मार्गी यातायात को मुख्य रूप में दो भागों में विभाजित किया जाता है :
- आंतरिक जल मार्ग
- समुद्री जल मार्ग।
प्रश्न 16.
सड़क मार्गों का जाल बिछाने के लिए कौन-सी योजनाएं देश में चल रही हैं ?
उत्तर-
सड़क मार्गों का जाल बिछाने के लिए मुख्य योजनाएं हैं :
- नागपुर योजना
- बीस वर्षीय योजना
- ग्रामीण सड़क योजना
- बी०ओ०टी०
- केंद्रीय सड़क फंड।
प्रश्न 17.
सड़क यातायात आसान क्यों है ?
उत्तर-
स्थल यातायात का मुख्य साधन सड़कें हैं। यह एक सस्ता तथा तेज़ यातायात का साधन है। सड़कें खेतों को फैक्ट्रियों के साथ तथा वस्तुओं को विक्रेताओं तथा खरीददारों तक पहुँचाने का एक साधन है। सड़कें असमतल तथा ऊँचे-नीचे स्थानों पर भी बनाई जा सकती हैं। घनी यूरोपीय सड़कें उन देशों के विकास का एक मुख्य साधन हैं।

प्रश्न 18.
पनामा नहर की मुख्य विशेषताएं बताओ।
उत्तर-
पनामा नहर-
- यह पनामा के स्थान पर स्थित है तथा U.S.A. का इस पर अधिकार है।
- इस नहर से निकलने वाले जहाजों पर टैक्स कम लगाया जाता है।
- इसके कारण अंध महासागर तथा प्रशांत महासागर के बीच दूरी कम हो गई।
- यह नहर संयुक्त राज्य अमेरिका के लिए बहुत उपयोगी है क्योंकि इस कारण अब जहाजों को केप होरन तक नहीं जाना पड़ता।
प्रश्न 19.
सड़क मार्गों के क्या दोष हैं ?
उत्तर-
- सड़क मार्ग महंगे हैं।
- इनसे वायु प्रदूषण होता है।
- अधिक दूरी तक भारी वस्तुओं का परिवहन नहीं होता।
- दुर्घटनाएं प्रतिदिन बढ़ रही हैं।
लघु उत्तरीय प्रश्न (Short Answer Type Questions)
प्रश्न 1.
परिवहन के विभिन्न साधनों के प्रकार बताओ।
उत्तर-
परिवहन के विभिन्न साधनों के प्रकार हैं-
- स्थल परिवहन
- जल परिवहन
- वायु परिवहन।
स्थल परिवहन में सड़कें, रेलें तथा पाइप लाइनें शामिल हैं। जल परिवहन के मुख्य रूप हैं-
- आंतरिक मार्ग
- समुद्री मार्ग।
वायु परिवहन में वायुयान सेवाएं गिनी जाती हैं।

प्रश्न 2.
ग्रामीण सड़कें तथा ज़िला सड़कों में अंतर स्पष्ट करो।
उत्तर-
ग्रामीण सड़कें-
- यह सड़कें गाँव को जिले से जोड़ती हैं।
- ग्रामीण सड़कें अकसर समतल तथा स्थाई नहीं होती।
- इन सड़कों में काफी मोड़ आते हैं जिन पर भारी वाहन नहीं चल सकते।
जिला सड़कें-
- यह सड़कें कस्बे, बड़े गांवों तथा जिला केंद्रों को आपस में जोड़ती हैं।
- यह सड़कें अकसर स्थाई होती हैं।
- यहां पर मोड़ ज्यादा नहीं होते तथा अक्सर भारी वाहन चलते हैं।
प्रश्न 3.
भारतीय सड़कों की मुख्य विशेषताएं बताओ।
उत्तर-
भारतीय सड़कों की विशेषताएं निम्नलिखित हैं-
- भारत में पक्की सड़कों की लंबाई 8 लाख 88 हजार कि०मी० है।
- भारत में कच्ची सड़कों की लंबाई 9 लाख 55 हजार कि०मी० है।
- भारत में हर 100 वर्ग किलोमीटर के पीछे 48 किलोमीटर सड़कें हैं जहां पर हर एक लाख लोगों के पीछे 293 किलोमीटर सड़कें हैं।
- देश में राष्ट्रीय राज मार्गों की लंबाई 313558 किलोमीटर है।
- इन सड़कों पर लगभग 37 लाख मोटर गाड़ियां चलती हैं।
- भारतीय सड़कों को हर साल ₹ 1580 करोड़ की आमदन होती है।
- भारत का 30% सामान सड़कों के द्वारा परिवहन किया जाता है।
प्रश्न 4.
रेल मार्गों के विकास का क्या महत्त्व है ?
उत्तर-
स्थलीय परिवहन में रेल-मार्ग एक महत्त्वपूर्ण साधन है। आधुनिक युग में देश में आर्थिक, सामाजिक तथा राजनीतिक दृष्टि से रेलों का बड़ा महत्त्व है।
महत्त्व-
- रेल-मार्ग किसी क्षेत्र के खनिज पदार्थों के विकास में सहायता करते हैं।
- रेल मार्ग औद्योगिक क्षेत्र में कच्चे माल तथा तैयार माल के वितरण में सहायता करते हैं।
- रेल मार्ग व्यापार को उन्नत करते हैं।
- रेल मार्ग राजनीतिक एकता व स्थिरता लाने में योगदान देते हैं।
- रेल मार्ग संकट काल में सहायता कार्यों में महत्त्वपूर्ण हैं।
- कम जनसंख्या वाले प्रदेशों में रेलमार्ग-जनसंख्या वृद्धि का आधार बनते हैं।
- लंबी-लंबी दूरियों को जोड़ने में रेलों ने महत्त्वपूर्ण भूमिका निभाई है। वास्तव में रेल मार्गों के विकास में मानव ने दूरी और समय पर विजय प्राप्त कर ली है।

प्रश्न 5.
आंतरिक जल मार्गों का क्या महत्त्व है ?
उत्तर-
जल मार्ग दो प्रकार के हैं-आंतरिक तथा महासागरी मार्ग। अंतर्राष्ट्रीय व्यापार के लिए समुद्री मार्गों का प्रयोग किया जाता है। किसी देश के प्रादेशिक व्यापार के लिए नदियां, नहरें, झीलों का आंतरिक जलमार्गों के रूप में प्रयोग किया जाता है। __मनुष्य प्राचीन काल से ही नदियों तथा नहरों का यातायात के लिए प्रयोग करता आया है। आजकल विकसित देशों में आंतरिक जल मार्गों को बड़े पैमाने पर उपयोग किया जाता है। कृषि तथा उद्योगों के विकास में आंतरिक जल मार्ग महत्त्वपूर्ण हैं।
प्रश्न 6.
गोल्डन कुआर्डीलेटरल या सुनहरी चतुर्भुज से आपका क्या भाव है ?
उत्तर-
गोल्डन कुआर्डीलेटर भारत में बनाई गई पहली सड़क निर्माण योजना है जो कि राष्ट्रीय शाहमार्ग विकास प्रकल्प के तहत शुरू की गई। इसको संसार की पाँचवीं बड़ी सड़क निर्माण योजना का दर्जा हासिल है। इस प्रकल्प में भारत के चार प्रसिद्ध महानगरों दिल्ली, मुंबई, चेन्नई तथा कोलकाता को आपस में मिलाये जाने की योजना है जोकि एक चतुर्भुज की आकृति लेती है जिस के कारण इसको सुनहरी चतुर्भुज भी कहते हैं। इस सड़क योजना से जुड़े बड़े शहर हैं-अहमदाबाद, बैंगलोर, भुवनेश्वर, जयपुर, कानपुर, पुणे, सूरत, नैलूर, विजयवाड़ा तथा गंटूर। इस चतुर्भुज की कुल लंबाई 5846 किलोमीटर है तथा इसके अधीन चार तथा छः मार्गी ऐक्सप्रेस हाईवे निर्मित किए गए हैं। इस योजना का शाहमार्ग देश 13 राज्यों में से गुजरता है तथा इन 13 राज्यों में आन्ध्र प्रदेश में सबसे अधिक तथा दिल्ली में सबसे कम भाग पड़ता है। इस प्रकल्प के कारण औद्योगिक व्यापार को प्रोत्साहन मिला है।
प्रश्न 7.
डाइमंड कुआर्डिलेटरल का वर्णन करो।
उत्तर-
डाइमंड कुआर्डिलेटरल भारत के प्रसिद्ध महानगरों (दिल्ली, मुंबई, कोलकाता तथा चेन्नई) को आपस में तेज रफ़्तार से चलने वाली रेल गाड़ियों के साथ जोड़ने की योजना को कहते हैं। यह सड़क योजना सुनहरी चतुर्भुज जैसी ही है। देश के रेल तंत्र को आरामदायक बनाने तथा इसमें सुधार लाने के लिए तेज रफ्तार रेल गाड़ियों तथा बुलेट ट्रेन जैसी गाड़ियों को चलाया गया जिस प्रकल्प में यह रेल गाड़ियां चलाई गई, उसको डायमंड कुआर्डीलेटरल प्रकल्प कहते हैं। इस रेल मार्ग द्वारा कई बड़े शहर आपस में जुड़ गए जैसे-उत्तर प्रदेश, राजस्थान, महाराष्ट्र, गुजरात, दिल्ली, हरियाणा, आन्ध्र प्रदेश, तेलंगाना, तमिलनाडु, कर्नाटक, केरल, बिहार, उड़ीसा, झारखण्ड तथा पश्चिमी बंगाल इत्यादि राज्यों में से गुजरते हैं। यहाँ बिजली की सुविधा भी है क्योंकि यह मार्ग चौड़ी गेज वाले हैं। इन रेलों की रफ्तार 250 किलोमीटर प्रति घंटा की होगी जब कि रेल गाड़ियों 320 कि०मी० प्रति घंटा की रफ्तार से दौड़ेगी।

प्रश्न 8.
समुद्री मार्गों की महत्ता बताओ।
उत्तर-
यातायात के साधनों में समुद्री यातायात सबसे सस्ता तथा महत्त्वपूर्ण साधन है। विश्व का ज्यादातर व्यापार समुद्री मार्गों द्वारा होता है। जब बहुत सारे जहाज़ एक निश्चित मार्ग से चलते हैं तब उसे समुद्री मार्ग कहते हैं।
समुद्री मार्गों की महत्ता (Importance of Ocean Routes)-
- यह सबसे सस्ता यातायात का साधन है।
- यह प्राकृतिक मार्ग है। समुद्र में मार्ग बनाने में कुछ खर्च नहीं होता।
- जहाजों को चलाने के लिए कोयला या पैट्रोल कम खर्च होता है।
- समुद्री मार्ग असल में अंतर्राष्ट्रीय मार्ग हैं, क्योंकि सारे महासागर एक-दूसरे से मिले हैं।
- ‘इन मार्गों पर जहाजों की कम दुर्घटना होती है।
- इन मार्गों द्वारा दूर-दूर के देशों के आपसी सम्पर्क बढ़े हैं।
- इन मार्गों द्वारा अंतर्राष्ट्रीय व्यापार में वृद्धि होती हैं।
प्रश्न 9.
जन संचार के साधनों का वर्णन करो।
उत्तर-
जब हम बडी गिनती में लोगों तक कोई संदेश या विचार पहुँचाना चाहते हैं या जनता के साथ बांटना चाहते हैं तो उसे जन संचार कहते हैं। ऐसा संचार कई प्रकार के साधनों द्वारा किया जाता है। जिसमें व्यक्तिगत संचार की तरह पक्ष एक-दूसरे से परिचित नहीं होता। जनसंचार के प्रमुख साधन हैं-
- जनतक घोषणा, रैली इत्यादि।
- रेडियो, टेलीविज़न।
- अख़बारें, रसाले, मैगज़ीन ।
- सिनेमा।
- कंप्यूटर की सहायता से ही जनतक सूचना।
- इंटरनैट संचार।
- औजू सैट।
प्रश्न 10.
व्यापार से आपका क्या अर्थ है ? इसकी किस्में बताओ।
उत्तर-
वस्तुओं को बेचने तथा खरीदने को व्यापार कहते हैं या किसी वस्तु के लेन-देन को व्यापार कहते हैं। यह खरीददार तथा विक्रेता के बीच की अदायगी की क्रिया है। व्यापार मुख्य रूप में दो प्रकार का होता है-
- निजी व्यापार।
- राष्ट्रीय व्यापार।

प्रश्न 11.
राष्ट्रीय व्यापार तथा इसके क्या कारण हैं ?
उत्तर-
जब व्यापार/बेच-खरीद/लेन-देन राष्ट्रीय स्तर पर होता है, तब उसे राष्ट्रीय व्यापार कहते हैं। अगर कोई देश अपने देश की सीमाओं से बाहर कोई व्यापार लेन-देन करता है उसको अंतर्राष्ट्रीय व्यापार कहते हैं। राष्ट्रीय व्यापार के कारण निम्नलिखित हैं-
- किसी देश में प्राकृतिक साधनों की कमी।
- देश में वस्तुओं की मांग तथा पूर्ति में अंतर।
- तकनीकी साधनों की कमी के कारण कई बार वस्तुओं को दूसरे देश से मंगवाना पड़ता है।
- भौगोलिक भिन्नता।
- आर्थिक विकास में कमी।
- व्यापारिक देशों में जंग तथा अमन शांति के हालात।
- व्यापारिक नीतियां।
- देश के आपसी संबंध।
प्रश्न 12.
भारतीय आयात तथा निर्यात पर नोट लिखो।
उत्तर-
उत्पादित फालतू सामान को जब किसी और देश में बेचा जाता है तब उसे निर्यात कहते हैं तथा स्रोतों की कमी के कारण जब किसी देश से स्रोतों को खरीदा जाता है तो उसे आयात कहते हैं।
भारतीय निर्यात-भारत खनिज तेल, खनिज मोम, जैविक रसायन, फार्मेसी उत्पादन, गेहूँ से बनी वस्तुओं, अनाज, बिजली की मशीनरी, कपास के सूती कपड़े, काहवा, चाय, मसाले इत्यादि बाकी देशों को निर्यात करता है।
भारतीय आयात-भारत पैट्रोल, खनिज मशीनरी, खाद्य, लोहा तथा इस्पात, मोती, कीमती पत्थर, सोना, चांदी, खुराकी तेल, रसायन, दवाइयां, कागज़ फाईबर इत्यादि दूसरे देशों से आयात करता है।
प्रश्न 13.
आलमी व्यापार संगठन (WTO) पर नोट लिखो।
उत्तर-
सन् 1995 में गैट का रूप बदलकर विश्व व्यापार संगठन बनाया गया। यह जनेवा में एक स्थायी संगठन के रूप में कार्यरत है तथा यह व्यापारिक झगड़ों का निपटारा भी करता है। यह संगठन सेवाओं के व्यापार को भी नियंत्रित करता है। किंतु इसे अभी भी महत्त्वपूर्ण कर रहित नियंत्रणों जैसे निर्यात निषेध, निरीक्षण की आवश्यकता, स्वास्थ्य एवं सुरक्षा स्तरों तथा आयात लाइसेंस व्यवस्था जिनसे आयात प्रभावित होना है, को सम्मिलित करना शेष है। आलमी व्यापार संगठन में 123 देशों ने हस्ताक्षर करके जनरल एग्रीमैंट का खात्मा कर दिया है। इस प्रकार आलमी व्यापार संगठन राष्ट्रीय व्यापार को अच्छा तथा महत्त्वपूर्ण बना देता है

निबंधात्मक प्रश्न (Essay Type Questions)
प्रश्न 1.
यातायात से आपका क्या भाव है ? देश में प्रशासकीय प्रबंध के आधार पर सड़कों का वर्गीकरण करो तथा सड़क-मार्गों का जाल बिछाने के लिए बनाई योजनाओं के बारे में विस्तार से चर्चा करो।
या
भारतीय सड़कों के विकास का वर्णन करो।
उत्तर-
यातायात-मनुष्य, जानवरों तथा वस्तुओं को एक स्थान से दूसरे स्थान तक पहुँचाने को या वस्तुओं के परिवहन को यातायात कहते हैं। यातायात के मुख्य वर्ग हैं
- स्थल-मार्ग यातायात।
- जल-मार्ग यातायात।
- वायु-मार्ग यातायात।
सड़कों का प्रशासकीय प्रबंध के आधार पर वर्गीकरण-प्रशासकीय प्रबंध के आधार पर सड़कों का वर्गीकरण निम्नलिखित किया गया है –
1. ग्रामीण सड़कें (Rural Roads)—जो सड़कें गाँव को जिले की सड़कों से मिलाती हैं, ग्रामीण सड़कें कहलाती हैं। इन सड़कों में मोड़ काफी होते हैं यहाँ बहुत भारी वाहनों को काफी मुश्किलों का सामना करना पड़ता है।
2. जिला सड़कें (District Roads)—यह सड़कें जिले की सड़कों, कस्बे तथा बड़े गाँवों को आपस में जोड़ती हैं। इन सड़कों की देखभाल जिला परिषद् तथा आम जनता की ज़िम्मेदारी होती है।
3. राज्य मार्ग (State Highways) राज्य के व्यापार तथा भारी यात्री यातायात की किस्म राज्य मार्गों के अधीन आती है। यह सड़कें आर्थिकता की मुख्य इकाई होती हैं, सड़कों के मुख्य केंद्रों को राज्य की राजधानियों तथा राष्ट्रीय शाहमार्गों के साथ मिलाती हैं।
4. राष्ट्रीय शाह मार्ग (National Highways)-राष्ट्रीय शाहमार्गों की देख-भाल की ज़िम्मेदारी केंद्रीय सरकार की होती है। भारत में राष्ट्रीय शाहमार्ग एथॉरिटी इन मार्गों की देख-रेख करती है। यह सड़कें देश के सारे कोनों तक फैली हुई हैं।
5. सीमान्त इलाकों की सड़के (Border Roads)-इन सड़कों की देख-भाल की ज़िम्मेदारी सीमान्त सड़क संगठन के अंतर्गत आती है।
सड़क योजनाएं-सड़कें किसी देश के विकास की रीढ़ की हड्डी हैं। यह वस्तुओं, मनुष्य, जानवरों, स्रोतों इत्यादि के परिवहन में अहम् तथा महत्त्वपूर्ण भूमिका अदा करती हैं। इसके अलावा इन सड़कों द्वारा सफर करना आसान तथा आरामदायक भी होता है। सड़कों का अच्छा तथा सड़क-मार्गों का जाल बिछाने के लिए कई योजनाएं देश अंदर चल रही हैं।
1. नागपुर योजना (Nagpur Plan)-नागपुर योजना सन् 1943 में भारत में सड़कें बिछाने के लिए बनाई गई। इस योजना में देश की प्रमुख सड़कों के अलावा और आम सड़कों की लंबाई भी बढ़ाई गई।
2. बीस वर्षीय योजना (Twenty Year Plan)-इस योजना की शुरुआत 1961 में हुई। इस योजना का उद्देश्य देश में सड़कों की लंबाई 6 लाख 56 कि०मी० से बढ़ाकर 10 लाख 60 हज़ार कि०मी० तक करना था तथा इसके लिए समय 20 साल तय किया गया।
3. ग्रामीण सड़क विकास योजना (The Rural Road Development Scheme)-इस योजना का मुख्य उद्देश्य ग्रामीण इलाकों में सड़कों का विकास करना था।
4. बी०ओ०टी० योजना (Build, Operate and Transfer Scheme)-इस योजना में प्राईवेट बिल्डरों तथा
ठेकेदारों को सड़कें तथा पुलों का निर्माण करने के लिए ठेके दिए गए तथा इज़ाजत दी गई कि वह निर्माण की गई सड़क पर गुजरने वाले वाहनों के चालकों से टोल टैक्स ले सकेंगे तथा बाद में सड़क भारत सरकार के हवाले कर देंगे।
5. केन्द्रीय सड़क फंड (Cential Road Fund)-इस फंड को दिसम्बर 2000 में शुरू किया गया। इसके अनुसार पैट्रोल तथा डीज़ल पर टैक्स तथा कस्टम ड्यूटी लगाकर इकट्ठा किया पैसा सड़कों के विकास पर लगाया जाएगा। भारत में प्राचीन काल से ही सड़कों की महत्ता रही हैं। शेरशाह सूरी ने जी०टी०रोड के राष्ट्रीय राजमार्ग का निर्माण किया। आजादी के बाद 10 वर्षीय नागपुर योजना के अधीन सड़कों के विकास की योजना बनाई गई। भारत की मुख्य सड़कें निम्न हैं।
राष्ट्रीय मार्ग (National Highways)
- ग्रैंड ट्रंक रोड (Grand Trunk Road)-कोलकाता से अमृतसर तक है। इसको शेरशाह सूरी मार्ग भी कहा जाता है।
- दिल्ली-मुंबई रोड।
- कोलकाता-मुंबई रोड।
- मुंबई-चेन्नई रोड।
- ग्रेट दक्षिण रोड।
- कोलकाता-चेन्नई रोड।
- पठानकोट- श्रीनगर रोड।
- भारत की सीमावर्ती प्रदेशों में सड़कों का निर्माण करने के लिए सीमा सड़क बोर्ड को सन् 1960 में स्थापित किया गया। भारत में सीमान्त प्रदेशों में 7000 कि०मी० लम्बी पक्की सड़कें बनायी गई हैं। जिनमें मनाली से लेकर लेह तक मुख्य सड़कें हैं। इस सड़क की औसत ऊंचाई 4270 मीटर है।

प्रश्न 2.
संसार के प्रमुख रेल मार्गों की स्थिति तथा महत्त्व का वर्णन करो।
उत्तर-
स्थल यातायात में रेलवे सबसे अधिक महत्त्वपूर्ण साधन है। सन् 1819 में भाप के इंजन की खोज के साथ रेल के यातायात का प्रारंभ ग्रेट ब्रिटेन में हुआ। आधुनिक युग में किसी देश में आर्थिक, सामाजिक तथा राजनीतिक दृष्टि से रेलवे का बड़ा महत्त्व है।
महत्त्व-
- रेलमार्ग किसी क्षेत्र के खनिज पदार्थों के विकास में सहायता करते हैं।
- रेलमार्ग औद्योगिक क्षेत्र में कच्चे माल तथा तैयार माल के वितरण में सहायता करते हैं।
- रेलमार्ग व्यापार को उन्नत करते हैं।
- रेलमार्ग राजनीतिक एकता व स्थिरता लाने में योगदान देते हैं।
- रेलमार्ग संकट काल में सहायता कार्यों में महत्त्वपूर्ण हैं।
- कम जनसंख्या वाले प्रदेशों में रेल-मार्ग जनसंख्या वृद्धि का आधार बनते हैं।
- लम्बी-लम्बी दूरियों को जोड़ने में रेलों ने महत्त्वपूर्ण भूमिका निभाई हैं। वास्तव में रेल-मार्गों के विकास से मानव ने दूरी और समय पर विजय प्राप्त कर ली है।
रेलमार्गों की स्तिति के तत्त्व (Factors of Location),
- अधिक जनसंख्या हो।
- समतल मैदानी धरातल हो।
- औद्योगिक तथा व्यापारिक विकास अधिक हो।
- खनिज पदार्थ के अधिक भंडार हो।
- तकनीकी ज्ञान प्राप्त हो।
संसार के मुख्य रेलमार्ग (Major Railways) रेलमार्गों की सबसे अधिक लंबाई संयुक्त राज्य अमेरिका में हैं। कई देशों में मोटर, सड़कें तथा जल मार्गों के अधिक विकास के कारण रेलमार्ग कम हैं।
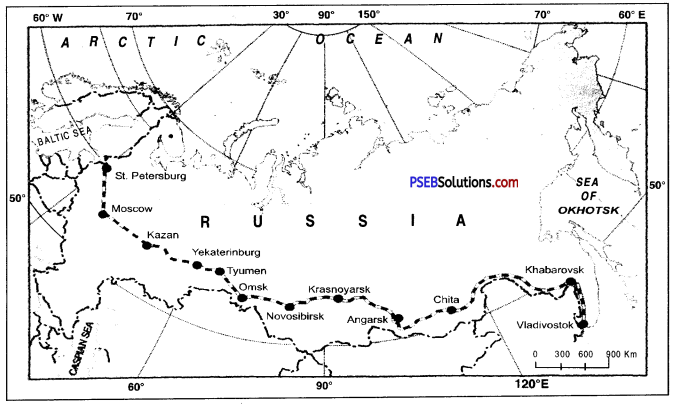
ट्रांस-साइबेरियन रेलमार्ग-यह रेलमार्ग 9289 कि०मी० लम्बा है तथा संसार में सबसे लम्बा रेलमार्ग है। यह रेल मार्ग साइबेरिया तथा यूराल प्रदेश के आर्थिक तथा औद्योगिक विकास का आधार है। यह एक अन्तः महाद्वीपीय मार्ग है। यह रेल-मार्ग पश्चिम में बाल्टिक सागर पर स्थित सेंट पीटर्जसवर्ग बन्दरगाह के पूर्व में प्रशान्त महासागर पर स्थित ब्लाडीवोस्टक बन्दरगाह को जोड़ता है। इस रेल-मार्ग के मुख्य स्टेशन मास्को, रंयाजन, कुइबाशेव चेलिया बिन्सक, ओमस्क, नीवी सिबीरस्क, चीता इकूटस्क तथा खाबारीवस्क हैं । इस रेलमार्ग द्वारा कोयला, तेल, लकड़ी, खनिज, कृषि उत्पाद, मशीनरी तथा औद्योगिक उत्पादों का आदान-प्रदान पूर्व से पश्चिम को होता है।
2. कैनेडियन पैसेफिक रेलमार्ग-कनाडा का पूर्व-पश्चिम में अधिक विस्तार है। यह रेलमार्ग कनाडा में पूर्वी भाग में हैली फैक्स से चलकर पश्चिम में बेन्कूवर तक पहुंचता है। यह रेलमार्ग दुर्गम पर्वत क्षेत्रों में से गुजरता है। इस रेलमार्ग से लकड़ी, खनिज पदार्थ, गेहूं व लोहे का परिवहन होता है। कैनेडियन पैसेफिक रेल-मार्ग की लम्बाई 7050 किलोमीटर हैं। इस मार्ग पर सेंटजॉन मांट्रिगल, ओटावा, विनीपेग इत्यादि नगर स्थित है। यह रेल-मार्ग क्यूबेक मांट्रियल के औद्योगिक क्षेत्र को कोणधारी वनों तथा प्रेयरीज के गेहूं से जोड़ता हैं। इस प्रकार यह रेल मार्ग राजनीतिक तथा आर्थिक रूप से एकता स्थापित करता है।
3. संयुक्त राज्य अमेरिका के रेलमार्ग संयुक्त राज्य अमेरिका के पूर्वी भाग में रेलवे का अधिक विकास हुआ है। पश्चिम में जनसंख्या कम है। यहां शुष्क जलवायु तथा पर्वतीय भागों के कारण रेलमार्ग कम हैं। यह रेलमार्ग देश के पश्चिमी तथा पूर्वी क्षेत्रों को आपस में मिलाता है। देश के मध्यवर्ती क्षेत्र की कृषि तथा खनिज क्षेत्रों के लिए यह बहुत योग्य सिद्ध हुए हैं। इस देश में मुख्य महाद्वीप रेलमार्ग निम्नलिखित हैं।
- उत्तरी पैसेफिक रेलमार्ग-यह मार्ग शिकागो से होकर सेंटपाल पोर्टलैंड तक जाता है।
- दक्षिणी पैसेफिक रेलमार्ग-यह रेलमार्ग पश्चिम में लॉस एंजिलस तक जाता है।
- महान् उत्तरी रेलमार्ग-यह रेलमार्ग सुपीरियर झील के तट से डिओलब में होकर सीटल तक जाता है।
- यूनियन पैसेफिक रेलमार्ग-यह रेलमार्ग एटलांटिक तट से लेकर न्यूयॉर्क और फिर यहां से शिकागो, उमाहा, सान फ्रांसिस्को तथा प्रशांत महासागर तट तक जाता है। शिकागो संसार का सबसे बड़ा रेलकेंद्र है।
4. केप काहिरा रेलमार्ग-यह रेलमार्ग अफ्रीका के दक्षिणी किनारे को उत्तरी किनारे से जोड़ता है। यह मार्ग केपटाऊन से प्रारम्भ होकर काहिरा तक है। इस मार्ग के मध्य में कई कठिनाइयां हैं जैसे सहारा मरुस्थल, ऊंचे पर्वत, जल प्रपात इत्यादि। इन प्रतिबन्धों के कारण रेलमार्ग पूरा नहीं हो सका। यह रेल मार्ग केपटाऊन से शुरू होकर किंबरले से जाइरे देश में बोकामा तक है। इसके पीछे विक्टोरिया झील तक सड़क या रेलमार्ग की सुविधा है। इसके आगे नील नदी के किनारे खरतूम तक सड़क मार्ग है। इसके आगे काहिरा तक रेलमार्ग है। इस रेलमार्ग के विकास के साथ अफ्रीका महाद्वीप के कई क्षेत्रों में खनिज पदार्थ तथा कृषि पदार्थों के निर्यात में भी वृद्धि हुई है।
5. ट्रांस एण्डियन रेलमार्ग (Trans Andean Railway)-यह रेलमार्ग दक्षिणी अमेरिका से चिली के वालप्रेसो नगर तथा अजेन्टाइना के ब्यूनस आयर्स नगर को मिलाता है। यह रेलमार्ग एण्डीज पर्वतों को 3485 मीटर की ऊंचाई से पार करके उस्पलाटा दर्रे तथा सुरंगों से गुजरता है। यह पम्पास के कृषि तथा पशुपालन क्षेत्रों को चिली के खनिज तथा फल उत्पादन क्षेत्र से जोड़ता है।
6. दिल्ली-लंदन-मार्ग (Delhi London Railway)—इस मार्ग के साथ यूरोप तथा एशिया के महाद्वीपों को मिलाने की योजना है। यह प्रकल्प आर्थिक तथा सामाजिक कमिशन के अधीन है। इस मार्ग पर कई देशों में इस योजना को पूरा करने के प्रयास किये जा रहे हैं ताकि लंदन को इण्डोनेशिया से मिलाया जा सके। यह भारत से पश्चिम की तरफ पाकिस्तान मध्य पूर्व (इरान, इराक, तुर्की) से यूरोप तक जाएगा। कई राजनीतिक बंदिशों के कारण कई स्थानों पर जैसे बर्मा-बंगला देश में यह काम सफल नहीं हो सका है। इस मार्ग पर तुर्की के पास बासकोर्स में इंग्लैंड चैनल के रास्ते समुद्र पार करना पड़ेगा तथा नावों का प्रयोग करना पड़ेगा। इण्डोनेशिया से लंदन तक यह यात्रा 15 दिनों में पूरी की जाएगी।
7. भारतीय रेलमार्ग (Indian Railway) परिवहन के साधनों में रेलों का महत्त्व सबसे अधिक है। 1853 ई० में भारत में प्रथम रेल लाइन 32 कि०मी० लम्बी मुम्बई से थाना स्टेशन तक बनाई गई। भारतीय रेलवे की मुख्य विशेषताएं निम्नलिखित हैं-
-
- भारतीय रेल-मार्ग एशिया का सबसे लम्बा रेलमार्ग है।
- भारतीय रेल-मार्ग 62211 कि०मी० लम्बा है।
- विश्व में भारत का चौथा स्थान है।
- भारतीय रेलों मे 18 लाख कर्मचारी काम करते हैं।
- प्रतिदिन 12670 रेलगाड़ियां लगभग 13 लाख कि०मी० दूरी पर चलती हैं तथा 7100 रेलवे स्टेशन हैं।
- प्रतिदिन लगभग 350 करोड़ यात्री यात्रा करते हैं तथा 22 करोड़ टन भार ढोया जाता है।
- भारतीय रेलों में 8000 करोड़ रुपए की पूंजी लगी हुई है तथा प्रतिवर्ष 21,000 करोड़ रुपए की आय होती है।
- भारतीय रेलों में 11,000 रेल इंजन, 38,000 सवारी डिब्बों तथा 4 लाख सामान ढोने वाले डिब्बे हैं।
- भारत में 80% सामान तथा 70% यात्री रेलों द्वारा ही ले जाए जाते हैं।
-
- भारतीय रेलों का अधिक विस्तार उत्तरी भारत के समतल मैदान में है।
- भारत में जम्मू कश्मीर, पूर्वी क्षेत्र, पश्चिमी घाट, छोटा नागपुर पठार तथा थार के मरुस्थल में रेलमार्ग कम
- दक्षिणी भारत में पथरीली, ऊंची-नीची भूमि के कारण, छोटी-छोटी नदियों पर जगह जगह पुल बनाने की असुविधा है।
- अब भारतीय रेलों पर 3454 डीजल इंजन तथा 1533 बिजली के इंजन 4950 भाप इंजन हैं।
-
- लगभग 9100 किलोमीटर लम्बे रेलमार्ग पर बिजली से चलने वाली गाड़ियां दौड़ती हैं। भारत में रेलमार्ग तीन प्रकार के हैं –
(i) चौड़ी पटरी (Broad Gauge)-1.68 मीटर चौड़ाई।
(ii) छोटी पटरी (Metre Gauge)-1 मीटर चौड़ाई।
(iii) तंग पटरी (Narrow Gauge)-0.68 मीटर चौड़ाई है।
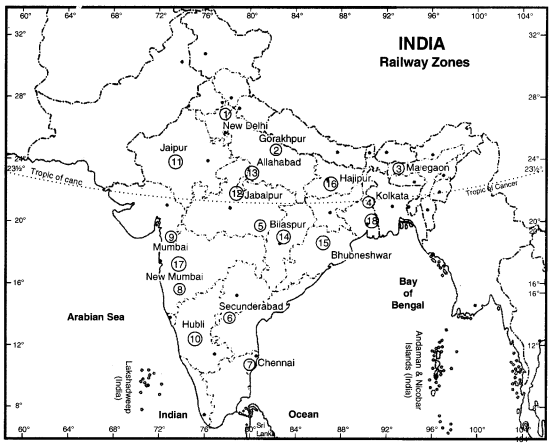
रेल क्षेत्र (Railway Zones)—अच्छे प्रबंध के लिए भारतीय रेलों में अलग-अलग तरह से विभाजित किया गया है। भारत में 1958 से 1966 तक भारतीय रेलवे के कुल 9 क्षेत्र थे। लगभग तीन दहाकों के बाद यही रेल प्रबंध जारी रहा पर अब भारतीय रेलवे के कुल 18 क्षेत्र हैं, जो इस प्रकार हैं –
रेल क्षेत्र — प्रमुख कार्यालय
1. उत्तरी रेलवे — नई दिल्ली
2. उत्तरी-पूर्वी रेलवे — गोरखपुर
3. उत्तर पूर्वी सीमान्त रेलवे — मालीगाऊ (गुवाहाटी)
4. पूर्वी रेलवे — कोलकाता
5. दक्षिणी-पूर्वी रेलवे — बिलासपुर (छत्तीसगढ़)
6. दक्षिण-मध्य रेलवे — सिकंदराबाद
7. दक्षिणी रेलवे — चेन्नई
8. मध्य रेलवे — मुंबई
9. पश्चिमी रेलवे — मुंबई
10. दक्षिण-पश्चिमी रेलवे — हुबली (बंगलौर)
11. उत्तर पश्चिमी रेलवे — जयपुर
12. पश्चिमी मध्य रेलवे — जबलपुर
13. उत्तर मध्य रेलवे — इलाहाबाद
14. दक्षिण-पूर्वी मध्य रेलवे — बिलासपुर
15. पूर्व तटवर्ती रेलवे — भुवनेश्वर
16. पूर्व मध्य रेलवे — हाजीपुर
17. कोंकण रेलवे — न्यू दिल्ली
18. मैट्रो रेलवे — कोलकाता।

प्रश्न 3.
जल यातायात तथा जल मार्ग यातायात की किस्में बताओ। विश्व के मुख्य समुद्री मार्गों का विस्तार सहित वर्णन करो।
उत्तर-
यातायात के साधनों में समुद्री यातायात सबसे सस्ता तथा महत्त्वपूर्ण साधन है। विश्व का अधिकतर व्यापार समुद्री मार्ग के द्वारा होता है। जब बहुत सारे जहाज़ एक निश्चित मार्ग पर चलते हैं तब उसे समुद्री मार्ग कहते हैं।
समुद्री मार्गों का महत्त्व (Importance of Ocean Routes)-
- यह सबसे सस्ता यातायात का साधन है।
- यह प्राकृतिक मार्ग है। समुद्र में मार्ग बनाने में कुछ खर्च नहीं होता।
- जहाजों को चलाने के लिए कोयला तथा पैट्रोल कम खर्च होता है।
- समुद्री मार्ग असलियत में अंतर्राष्ट्रीय मार्ग है क्योंकि सारे महामार्ग एक दूसरे से मिले हैं।
- इन मार्गों पर जहाजों की दुर्घटनाएं कम होती हैं।
- इन मार्गों द्वारा दूर दूर देशों के आपसी सम्पर्क बढ़ जाते हैं।
- इन मार्गों द्वारा अंतर्राष्ट्रीय व्यापार में भी वृद्धि होती है।
समुद्री मार्गों को प्रभावित करने वाले तत्व (Factors influencing the Ocean Routes) अधिकतर समुद्री मार्ग महान् चक्कर के अनुसार कम दूरी के कारण बनाये जाते हैं। जल मार्ग हिंद तोदियों से बचा कर बनाये जाते हैं। समुद्री मार्ग तूफानी क्षेत्रों तथा कोहरे से दूर होते हैं। समुद्री मार्गों में ईंधन के लिए कोयला, तेल तथा परिवहन के लिए माल ज्यादा प्राप्त हो।
जल मार्गों की किस्में-जल मार्ग मुख्य रूप में दो तरह के होते हैं-
1. आंतरिक जलमार्ग
2. समुद्री जलमार्ग
1. आंतरिक जलमार्ग-किसी देश या पृथ्वी पर स्थित जल साधनों, झीलों, नहरों इत्यादि के द्वारा यातायात को आंतरिक जलमार्गी यातायात कहते हैं। किसी देश के प्रादेशिक व्यापार के लिए नदियां, नहरें तथा झीलों का आन्तरिक जल मार्गों के रूप में प्रयोग किया जाता है। मनुष्य प्राचीन काल से ही नदियों तथा नहरों का यातायात के लिए प्रयोग करता आया है। आजकल विकसित देशों में आंतरिक जल-मार्गों का बड़े पैमाने पर प्रयोग किया जाता है। कृषि तथा उद्योगों के विकास में आंतरिक जल-मार्ग महत्त्वपूर्ण है। आन्तरिक जल मार्गों पर कई तत्वों का प्रभाव पड़ता है। नदियों तथा नहरों में जल अधिक मात्रा में हों, जल का प्रवाह सारा साल लगातार तथा सीधा होना चाहिए। अधिक ढाल जल प्राप्त अधिक घुमाव तथा रेत के जमाव से यातायात में बाधाएं उत्पन्न हो जाती हैं। शीतकाल में नदियां हिम से जमनी नहीं चाहिए।
प्रमुख आंतरिक जलमार्ग-
- फ्रांस में सीन तथा रीन नदियां यातायात के लिए प्रयोग की जाती हैं।
- पश्चिमी जर्मनी में राईन (Rhine) नदी सबसे महत्त्वपूर्ण जल मार्ग है। यह नदी पश्चिमी जर्मनी के व्यापार की जीवनरेखा है। इस नदी द्वारा रूहर घाटी से खनिज पदार्थों का परिवहन किया जाता है।
- यूरोप में कई अन्य नदियां, डैन्यूब, वेसर, ऐल्ब, ओडर, विसबूला भी महत्त्वपूर्ण जल मार्ग हैं।
- रूस में वोल्गा, नीपर नदियां यातायात के साधन के रूप में प्रयोग की जाती हैं।
- उत्तरी अमेरिका में महान झीलें तथा मिसीसिपी नदी तथा सेंट लारेंस जल-मार्ग महत्त्वपूर्ण है।
- भारत में गंगा तथा ब्रह्मपुत्र नदी, चीन में यंगसी नदी तथा बर्मा में इरावती नदी महत्त्वपूर्ण भीतरी जल-मार्ग हैं।
- दक्षिणी अमेरिका में अमेज़न नदी से तट से 1600 कि०मी० अन्दर तक जहाज़ चलाए जा सकते हैं। परन्तु कम जनसंख्या तथा पिछड़ेपन के कारण इस घाटी में इस जल-मार्ग का महत्त्व कम है।
- अफ्रीका में नील, नाईजर, कांगो तथा जैम्बजी नदियां जल प्रपातों के कारण अधिक उपयोगी नहीं हैं।
- संसार में कई देशों में नहरें भी यातायात के साधन के रूप में प्रयोग की जाती हैं। पश्चिमी जर्मनी में कील नहर और राईन नहर, रूस में वोल्गा-वाल्टिक नहर, उत्तरी अमेरिका में हडसन-मोहाक नहर, इंग्लैण्ड में मानचेस्टर, लिवरपूल नहर, भारत में बकिंघम नहर यातायात के लिए महत्त्वपूर्ण हैं।
II. समद्री जलमार्ग- अन्तर्राष्ट्रीय व्यापार मुख्यतः समुद्री मार्ग द्वारा ही होता है। स्थल मार्ग की अधिकता के कारण मुख्य समुद्री मार्ग मध्य अक्षांशों में स्थित हैं। संसार के मुख्य समुद्री मार्ग निम्नलिखित हैं-
1. उत्तरी अन्ध महासागरीय मार्ग (North Atlantic Route) यह संसार का सब से अधिक उपयोग किया जाने वाला समुद्री मार्ग है। यह मार्ग 40° – 50° उत्तर अक्षांशों में यूरोप तथा उत्तरी अमेरिका के बीच स्थित हैं। यह संसार का सबसे व्यस्ततम व्यापारिक मार्ग है। संसार के 75% जलयान इस मार्ग पर चलते हैं। संसार के आधे से अधिक बन्दरगाह इस मार्ग पर स्थित हैं। इस मार्ग के किनारों पर यूरोप तथा उत्तरी अमेरिका के उन्नत औद्योगिक प्रदेश हैं। इसलिए संसार का 25% व्यापार इसी मार्ग से होता है। यह मार्ग महान् वृत्त है। इस पर कोयला व तेल की सुविधाएं हैं। संसार के गहरे, सुरक्षित बन्दरगाह हैं। यहां बड़े-बड़े शिपयार्ड स्थित हैं। परन्तु न्यूयार्क के निकट रेतीले, तट, न्यूफाउण्डलैंड के निकट कोहरा व हिमखण्ड की कठिनाइयां हैं। यूरोप की ओर लन्दन/लिवरपूल, ग्लासगो, ओसलो, हैम्बर्ग, रोटरडम, लिस्बन प्रमुख बन्दरगाह हैं।
2. स्वेज नहर मार्ग (Suez Canal Route)—यह सागर रूम सागर तथा लाल सागर को जोड़ने वाली स्वेज नहर के कारण महत्त्वपूर्ण मार्ग है। यह संसार का दूसरा बड़ा मार्ग है। इसे सबसे अधिक लम्बा मार्ग होने के कारण ग्रांड ट्रंक मार्ग भी कहते हैं। इस मार्ग पर संसार की घनी जनसंख्या वाले प्रदेश स्थित हैं। इस मार्ग पर कोयला व तेल की सुविधाएं प्राप्त हैं। इस मार्ग के कारण यूरोप तथा एशिया के लगभग 81000 किलोमीटर की दूरी कम हो गई है। इस नहर द्वारा इंग्लैंड के साम्राज्य व व्यापार को बहुत सुरक्षा प्राप्त थी। इसे ब्रिटिश साम्राज्य की जीवन रेखा भी कहा जाता है। रूम सागर व लाल सागर को पार करने के पश्चात् इसकी तीन शाखाएं हो
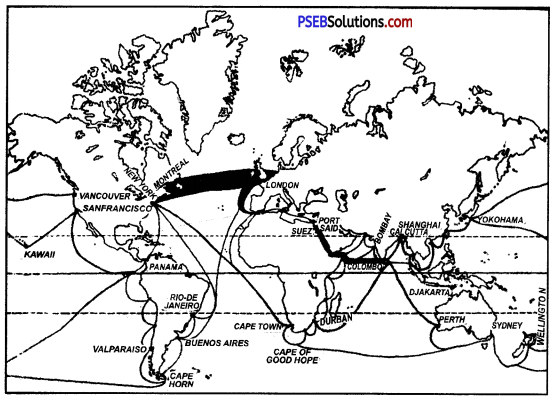
जाती हैं। अफ्रीका, ऑस्ट्रेलिया तथा एशिया की ओर लन्दन, लिवरपूल, मोर्सेल्ज, लिस्बन, नेपल्स, सिकन्दरिया प्रमुख बन्दरगाह हैं। लंदन, कराची, मुंबई, कोलकाता, चेन्नई, कोलम्बो, रंगून, सिंगापुर, हांगकांग, शंघाई योकोहामा, मेलबोर्न, विलिंगटन प्रमुख बंदरगाह हैं।
3. पनामा नहर मार्ग (Panama Canal Route)-अन्ध महासागर तथा प्रशांत महासागर को मिलाने वाली
पनामा नहर के 1914 में निर्माण होने से इस मार्ग का महत्त्व बढ़ गया है। इस मार्ग का विशेष महत्त्व संयुक्त ‘राज्य अमेरिका, ऑस्ट्रेलिया तथा न्यूज़ीलैंड को है। इस मार्ग के खुल जाने के कारण दक्षिणी अमेरिका के Cape Horn का चक्कर लगाने की आवश्यकता नहीं रही। इस प्रकार अमेरिका के पूर्वी तथा पश्चिमी तटों के बीच 10,000 किलोमीटर की दूरी कम हो गई। आकलैंड, वालपरेसी, लॉस ऐंजल्स, सानफ्रांसिस्को, बैनकूवर तथा प्रिंस रूपर्ट प्रमुख बन्दरगाह हैं। किंगस्टन हवाना, रियो-डी-जैनेरो, पनामा, न्यू ओरलियनज प्रमुख बन्दरगाह हैं।
4. आशा अन्तरीप मार्ग (Cope of Good Hope Route)—यह एक प्राचीन समुद्री मार्ग है। 1498 में वास्को डी-गामा ने इस मार्ग की खोज की। स्वेज नहर के बन्द हो जाने के कारण इस मार्ग का महत्त्व बढ़ गया है। यह मार्ग दक्षिणी अफ्रीका, ऑस्ट्रेलिया व न्यूज़ीलैंड के लिए महत्त्वपूर्ण है। इस मार्ग पर कोयला व तेल की सुविधाएं प्राप्त हैं। यह मार्ग स्वेज़ मार्ग की अपेक्षा सस्ता व ठण्डा है तथा बड़े-बड़े जहाज इस मार्ग पर गुज़र सकते हैं। लंदन, लिवरपूल, लिस्बन, लागोस, मानचेस्टर इत्यादि यूरोप की बन्दरगाहें हैं।
5. प्रशान्त महासागरीय मार्ग (Trans-Pacific Route)—यह मार्ग एशिया तथा अमेरिका महाद्वीपों को मिलाता है। यह मार्ग कम महत्त्वपूर्ण है। इस मार्ग की लम्बाई बहुत अधिक है तथा इसके किनारों पर कम उन्नत प्रदेश हैं। इस मार्ग पर हिमशिलाओं का अभाव है। इस मार्ग की कई शाखाएं होनोलूलू नामक स्थान पर मिलती हैं। योकोहामा, हांगकांग, शंघाई, मनीला, बेंकूवर, प्रिंस, रूपर्ट, सानफ्रांसिस्को, लास ऐंजल्स प्रमुख बन्दरगाह हैं।
6. दक्षिणी अन्ध महासागरीय मार्ग (South Atlantic Route)-यह मार्ग दक्षिणी अमेरिका तथा यूरोप के देशों को मिलाता है। ब्राज़ील के केप सन रोके से आगे इस मार्ग के दो भाग हो जाते हैं। यह यूरोप की तथा दूसरा अमेरिका की ओर यहां दक्षिणी अफ्रीका से आने वाले मार्ग भी मिलते हैं। उत्तर की ओर यूरोप तथा उत्तरी अमेरिका के प्रसिद्ध बन्दरगाह तथा दक्षिण की ओर व्यूनस आयर्स, मोण्टी वीडियो, रियो-डी-जेनेरो, बहियां, सैन्टाज़ हैं।

प्रश्न 4.
भारत की प्रमुख बन्दरगाहों का वर्णन करो। उनकी स्थिति, विशेषताएं तथा व्यापारिक महत्त्व बताएं।
उत्तर-
समुद्र पत्तन समुद्र के किनारे जहाजों के ठहरने के स्थान होते हैं। इनके द्वारा किसी देश का विदेशी व्यापार होता है। एक आदर्श बन्दरगाह के लिए कटी फटी तट रेखा, अधिक गहरा जल, सम्पन्न पृष्ठ-भूमि, उत्तम जलवायु तथा समुद्र मार्गों पर स्थित होना आवश्यक है। भारत की तट रेखा 61,00 किलोमीटर लम्बी है। इस तट रेखा पर अच्छी बन्दरगाहों की कमी है। केवल 10 प्रमुख बन्दरगाहें, 22 मध्यम बन्दरगाहें तथा 145 छोटी बन्दरगाहें हैं।
भारत की प्रमुख बन्दरगाहें-भारत के पश्चिमी तट पर कांडला, मुम्बई, मारमगाओ तथा कोचीन प्रमुख बन्दरगाहें हैं। पूर्वी तट पर कोलकाता पाराद्वीप, विशाखापट्टनम तथा चेन्नई प्रमुख बन्दरगाहें हैं। मंगलौर तथा तूतीकोरन का बड़े बन्दरगाहों के रूप में विस्तार किया जा रहा है। भारत की प्रमुख बन्दरगाहों का उल्लेख इस प्रकार है।
(क) पश्चिमी तट की बन्दरगाहें
1. कांडला (Kandla)-
(i) स्थिति (Location)—यह बन्दरगाह खाड़ी कच्छ (Gulf of Kutch) के शीर्ष (Head) पर स्थित है।
(ii) विशेषताएं (Characteristics)
(a) यह एक सुरक्षित व प्राकृतिक बन्दरगाह है।
(b) इसकी पृष्ठ-भूमि बहुत विशाल तथा सम्पन्न है, उसमें समस्त उत्तर-पश्चिमी भारत के उपजाऊ प्रदेश हैं।
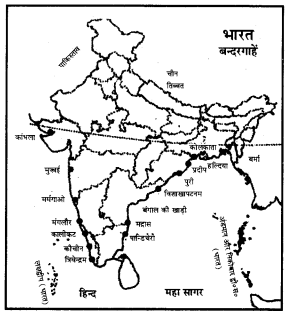
(c) समुद्र की गहराई 10 मीटर से अधिक है।
(d) यहां बड़े-बड़े जहाजों के ठहरने की सुविधाएं हैं।
(e) यह स्थान स्वेज़ (Suez) समुद्री मार्ग पर स्थित है।
(f) यह बन्दरगाह कराची की बन्दरगाह का स्थान लेगी।
(iii) व्यापार (Trade)
(a) आयात (Imports)—सूती कपड़ा, सीमेंट, मशीनें तथा दवाइयां।
(b) निर्यात (Exports)-सूती कपड़ा, सीमेंट, अभ्रक, तिलहन, नमक।
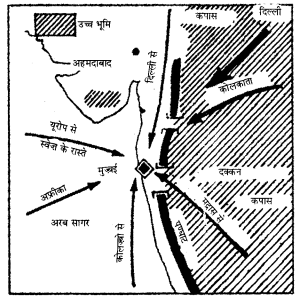
2. मुम्बई (Mumbai)
(i) स्थिति (Location)-यह बन्दरगाह पश्चिमी तट के मध्य भाग पर एक छोटे-से टापू पर स्थित है। यह टापू एक पुल द्वारा स्थल से मिला हुआ है।
(ii) विशेषताएं (Characteristics)
(a) यह भारत की सबसे बड़ी प्राकृतिक व सुरक्षित बन्दरगाह है।
(b) स्वेज़ मार्ग पर स्थित होने के कारण यूरोप (Europe) के निकट स्थित है।
(c) इसी पृष्ठ-भूमि में काली मिट्टी का कपास क्षेत्र तथा उन्नत औद्योगिक प्रदेश है।
(d) अधिक गहरा जल होने के कारण बड़े-बड़े जहाज़ ठहर सकते हैं, परन्तु यहां कोयले की कमी है।
(e) यहां पांच डॉको (Docks) में उत्तम गोदामों की व्यवस्था है।
(f) यह भारत की सबसे बड़ी बन्दरगाह है।
(g) इसे भारत का सिंहद्वार (Gateway of India) भी कहते हैं। यह महाराष्ट्र की राजधानी है। यहां ट्राम्बे में भाभा अणु शक्ति केन्द्र, मैरीन ड्राइव, इण्डिया गेट तथा ऐलीफेंटा गुफाएं दर्शनीय स्थान हैं। यह भारतीय जल-सेना का प्रमुख केन्द्र हैं।
(iii) व्यापार (Trade)-
(a) आयात (Import) मशीनरी, पैट्रोल, कोयला, कागज़ कच्ची फिल्में।
(b) निर्यात (Exports)-सूती कपड़ा, तिलहन, मैंगनीज, चमड़ा, तम्बाकू।
3. मारमगाओ (Marmago)
(i) स्थिति (Location)—यह बन्दरगाह पश्चिम तट गोआ (Goa) में स्थित है।
(ii) विशेषताएं (Characteristics)
(a) यह एक प्राकृतिक बन्दरगाह है।
(b) इसकी पृष्ठ-भूमि में महाराष्ट्र तथा कर्नाटक प्रदेश के पश्चिमी भाग हैं।
(c) इसमें 50 के लगभग जहाज़ खड़े हो सकते हैं।
(iii) 214P (Trade)—
(a) आयात (Imports)-खाद्यान्न, रासायनिक खाद, मशीनें, खनिज तेल।
(b) निर्यात (Exports)–नारियल, मूंगफली, मैंगनीज़, खनिज, लोहा।
4. कोचीन (Cochin)
(i) स्थिति (Location) यह बन्दरगाह मालबार तट पर केरल प्रदेश में पाल घाट दर्रे के सामने स्थित हैं।
(ii) विशेषताएँ (Characteristics)-
(a) यह बन्दरगाह एक लैगून झील (Lagoon) के किनारे स्थित होने के कारण सुरक्षित और प्राकृतिक बन्दरगाह है।
(b) इसकी पृष्ठ-भूमि में नीलगिरि का बागानी कृषि क्षेत्र तथा कोयम्बटूर का औद्योगिक प्रदेश स्थित है।
(c) यह जल-मार्ग द्वारा पृष्ठ-भूमि से मिला हुआ है।
(d) यह पूर्वी एशिया तथा ऑस्ट्रेलिया के जलमार्गों पर स्थित है।
(e) भारत का दूसरा पोत निर्माण केन्द्र (Shipyard) यहां पर है।
(iii) व्यापार (Trade)-
(a) आयात (Imports)-चावल, कोयला, पैट्रोल, रसायन, मशीनरी।
(b) निर्यात (Exports)-कहवा, चाय, काजू, गर्म मसाले, नारियल, इलायची, रबड़ सूती कपड़ा।
(ख) पूर्वी तट की बन्दरगाहें
1. कोलकाता (Kolkata)(i) स्थिति (Location)—यह एक नदी पत्तन (Riverport) है। यह खाड़ी बंगाल में गंगा के डेल्टा प्रदेश पर हुगली नदी के बाएं किनारे पर तट से 120 किलोमीटर भीतर स्थित है।
(ii) विशेषताएं (Characteristics)-
(a) इनकी पृष्ठ-भूमि बहुत विशाल तथा सम्पन्न है जिसमें गंगा घाटी का कृषि क्षेत्र, छोटा नागपुर का खनिज व उद्योग क्षेत्र तथा बंगाल, असम का चाय और पटसन क्षेत्र शामिल हैं।
(b) यह दूर पूर्व में जापान तथा अमेरिका के जल-मार्ग पर स्थित है।
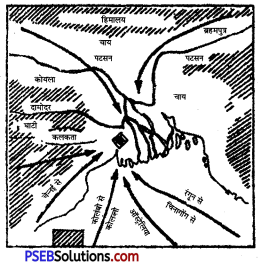
(c) परन्तु यह एक कृत्रिम बन्दरगाह है तथा गहरी नदी है।
(d) प्रति वर्ष नदियों की रेत और मिट्टी हटाने के लिए काफ़ी खर्च करना पड़ता है।
(e) जहाज़ केवल ज्वार-भाटा के समय ही आ जा सकते हैं। बड़े जहाजों को 70 किलोमीटर दूर
डायमण्ड हारबर (Diamond Harbour) में ही रुक जाना पड़ता है। () इस बन्दरगाह के विस्तार के लिए हल्दिया (Haldia) नामक स्थान पर एक विशाल पत्तन का निर्माण
किया जा रहा है। यह भारत की दूसरी बड़ी बन्दरगाह है।
(iii) व्यापार (Trade)-
(a) आयात (Imports)—मोटरें, पेट्रोल, रबड़, चावल, मशीनरी।
(b) निर्यात (Exports)—पटसन, चाय, खनिज लोहा, कोयला, चीनी, अभ्रक।
2. विशाखापट्टनम (Vishakhapatnam)-
(i) स्थिति (Location)—यह बन्दरगाह पूर्वी तट पर कोलकाता और चेन्नई के मध्य स्थित है।
(ii) fagtuang (Characteristics)
(a) डाल्फिन नोज (Dalphin-Nose) नाम की कठोर चट्टानों से घिरे होने के कारण यह एक सुरक्षित व प्राकृतिक बन्दरगाह है।
(b) इसकी पृष्ठ-भूमि में लोहा, कोयला तथा मैंगनीज़ का महत्त्वपूर्ण खनिज क्षेत्र है।
(c) यहां तेल, कोयला, ईंधन आदि सुलभ हैं।
(d) भारत का जहाज़ बनाने का सबसे बड़ा कारखाना यहां पर स्थित है।
(e) यह भारत की तीसरी प्रमुख बन्दरगाह है।
(ii) व्यापार (Trade)-
(a) आयात (Imports)-मशीनरी, चावल, पैट्रोल, खाद्यान्न।
(b) निर्यात (Exports)-मैंगनीज़, लोहा, तिलहन, चमड़ा, लाख, तम्बाकू।
3. पारादीप (Paradip)
(i) स्थिति (Location)—यह बन्दरगाह खाड़ी बंगाल में कटक से 160 किलोमीटर दूर स्थित है।
(ii) विशेषताएं (Characteristics)-
(a) यह एक नवीनतम बन्दरगाह है।
(b) यह एक सुरक्षित व प्राकृतिक बन्दरगाह है।
(c) पानी की अधिक गहराई के कारण यहां बड़े-बड़े जहाज़ ठहर सकते हैं।
(d) इसकी पृष्ठभूमि में उड़ीसा का विशाल खनिज क्षेत्र है।
(e) उड़ीसा के खनिज पदार्थों के निर्यात के लिए इस बन्दरगाह का विशेष महत्त्व है।
(iii) व्यापार (Trade)-
(a) निर्यात (Exports)-जापान का लोहा, मैंगनीज़, अभ्रक आदि खनिज पदार्थ ।
(b) आयात (Imports)-मशीनरी, तेल, चावल।
4. चेन्नई (Chennai)
(i) स्थिति (Location)—यह बन्दरगाह तमिलनाडु राज्य में कोरोमण्डल तट पर स्थित है।
(ii) विशेषताएं (Characteristics)-
(a) यह एक कृत्रिम बन्दरगाह है।
(b) कंकरीट की दो मोटी जल-तोड़ दीवारें (Break waters) बनाकर यह सुरक्षित बन्दरगाह बनाई गई है।
(c) इसकी पृष्ठभूमि में एक उपजाऊ कृषि क्षेत्र तथा औद्योगिक प्रदेश है।
(d) यहां कोयले की कमी है।
(iii) व्यापार (Trade)-
(a) आयात (Imports)-चावल, कोयला, मशीनरी, पैट्रोल, लोहा, इस्पात।
(b) निर्यात (Exports)-चाय, कहवा, गर्म मसाले, तिलहन, चमड़ा, रबड़।

प्रश्न 5.
स्वेज़ नहर के भौगोलिक, आर्थिक तथा सैनिक महत्त्व का वर्णन करो।
उत्तर-
स्वेज नहर (Suez Canal)
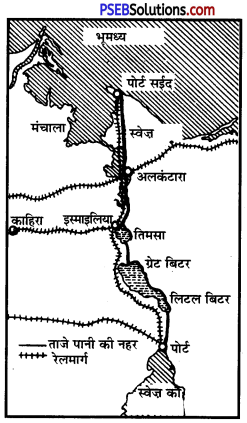
1. स्थिति (Location)-स्वेज़ नहर संसार की सबसे बड़ी जहाज़ी नहर (Navigation Canal) है। यह नहर अरब गणराज्य (U.A.R.) में स्थित है। यह नहर स्वेज़ के स्थलडमरू मध्य (Suez Isthmus) को काट कर बनाई गई है।
2. इतिहास (History)—इस नहर का निर्माण एक फ्रांसीसी इन्जीनियर फटनेण्ड डी लैसैप्स (Ferdinand De Lesseps) की देख-रेख में सन् 1859 ई० में शुरू हुआ। इस निर्माण में लगभग 10 वर्ष लगे। इस नहर को 17 नवम्बर, 1869 को चालू किया गया। इसके निर्माण काल में 1 लाख 20 हज़ार मजदूरों की जानें गईं। इस नहर के निर्माण पर 180 लाख पौंड खर्च हुए। इस नहर का निर्माण स्वेज नहर कम्पनी (Suez Canal Company) द्वारा किया गया। इस कम्पनी के अधिकतर हिस्से (Shares) फ्रांस तथा इंग्लैंड के थे। इस प्रकार इस नहर पर इंग्लैंड तथा फ्रांस का अधिकार था। यह नहर 99 वर्षों के पट्टे पर दी गई थी। परन्तु मिस्र के राष्ट्रपति कर्नल नासिर ने 26 जुलाई, 1956 को इस नहर के राष्ट्रीयकरण की घोषणा कर दी। 1967 में मिस्र व इज़राइल में युद्ध हुआ तथा नहर स्वेज़ जहाजों के लिए बन्द हो गई। 1975 में स्वेज़ नहर पुनः खुल गई है।
3. सागर तथा बन्दरगाह (Sea And Ports)—यह नहर रक्त सागर (Red Sea) तथा रूम सागर (Mediterranean Sea) को मिलाती है। रूम सागर की ओर पोर्ट सईद (Port Said) तथा रक्त सागर की ओर पोट स्वेज़ (Port Suez) की बन्दरगाह है। इस नहर की कुल लम्बाई 162 किलोमीटर, चौड़ाई 60 से 65 मीटर तक तथा कमसे-कम गहराई 10 मीटर है। यह नहर पूरी लम्बाई में समुद्र तल पर बनी है।
इस नहर के मार्ग में नमकीन पानी की तीन झीलें हैं-
- लिटिल बिटर झील (Little Bitter Lake)
- ग्रेट बिटर झील (Great Bitter Lake)
- टिमशाह झील (Timshah Lake) ।
इस नहर को पार करने में 12 घण्टे लग जाते हैं। जहाज़ औसत रूप से 14 किलोमीटर प्रति घण्टा की गति से चलते हैं। कम चौड़ाई के कारण एक साथ दो जहाज़ गुज़र सकते हैं। इसलिए एक जहाज़ को झील में ठहरा लिया जाता है।
4. महत्त्व (Importance)-
- यह मार्ग संसार की घनी जनसंख्या वाले मध्य क्षेत्र में से गुज़रता है।
- इस मार्ग पर बहुत अधिक देश स्थित हैं जिनके द्वारा विभिन्न वस्तुओं का व्यापार होता है।
- इस मार्ग पर ईंधन के लिए कोयला व तेल मिल जाते हैं।
- इस मार्ग पर छोटे-छोटे कई मार्ग मिल जाते हैं।
- इस मार्ग पर कई उत्तम बन्दरगाह स्थित हैं।
- यह नहर तीन महाद्वीपों के केन्द्र पर स्थित है। (It is located at the crossroads of three continents) यहां यूरोप, अफ्रीका तथा एशिया महाद्वीप के मार्ग निकलते हैं।
- इस नहर द्वारा इंग्लैंड के साम्राज्य तथा व्यापार की रक्षा होती है। इसलिए इसे ब्रिटिश साम्राज्य की जीवन रेखा (Life Line of British Empire) भी कहते हैं।
- इस नहर के खुल जाने से दक्षिणी अफ्रीका का चक्कर काटकर आने-जाने की आवश्यकता नहीं रही।
5. व्यापारिक महत्त्व (Commercial Importance)-इस नहर के बन जाने से यूरोप तथा एशिया सुदूर पूर्व के बीच दूरी काफ़ी कम हो गई। कई देशों की दूरी की बचत निम्नलिखित है –
| स्थान से |
स्थान तक |
दूरी की बचत |
| 1. लन्दन |
खाड़ी फारस |
8800 किलोमीटर |
| 2. लन्दन |
मुम्बई |
8000 किलोमीटर |
| 3. लन्दन |
सिंगापुर |
6000 किलोमीटर |
| 4. लन्दन |
मम्बासा |
4800 किलोमीटर |
| 5. लन्दन |
जकार्ता |
1500 किलोमीटर |
| 6. लन्दन |
सिडनी |
6000 किलोमीटर |
| 7. न्यूयार्क |
मुम्बई |
4000 किलोमीटर |
| 8. न्यूयार्क |
हांगकांग |
8800 किलोमीटर |
6. व्यापार (Trade)-इस नहर के कारण एशिया तथा यूरोप के बीच व्यापार अधिक हो गया है। नहर को चौड़ा व गहरा करने के कारण अब औसत रूप से 87 जहाज़ प्रतिदिन गुज़र सकते हैं। 1976 में इस नहर में लगभग 20,000 जहाजों ने प्रवेश किया। इस मार्ग पर संसार का 25% व्यापार होता है। इसमें से अधिकतर जहाज़ ब्रिटेन को जाते हैं। 70% जहाज़ तेल वाहक जहाज़ (Oil Tankers) होते हैं। इस मार्ग से यूरोप को कच्चे माल (Raw Materials) जाते हैं तथा यूरोप से तैयार माल व मशीनरी एशिया को भेजी जाती है। एशिया की ओर से कपास, पटसन, चाय, चीनी, काहवा, गेहूं, तेल, ऊन, मांस, डेयरी पदार्थ, रेशम, रबड़, चावल, तांबा, तम्बाकू, चमड़ा आदि पदार्थ यूरोप को भेजे जाते हैं। इस नहर द्वारा भारत का 60% निर्यात तथा 70% आयात व्यापार होता था। परन्तु अब यह व्यापार आशा अन्तरीप मार्ग से होता है।
7. त्रुटियां (Drawbacks)-इस नहर में निम्नलिखित त्रुटियां भी हैं-
- यह नहर कम चौड़ी व कम गहरी है। इसलिए बड़े-बड़े आधुनिक जहाज़ तथा बड़े-बड़े तेल वाहक जहाज़ (Oil Tankers) नहीं गुज़र सकते हैं।
- एक पक्षीय यातायात होने के कारण नहर पार करने में समय अधिक लगता है।
- यह मार्ग बहुत महंगा है। जहाज़ों से बहुत अधिक चुंगी कर (Taxes) वसूल किया जाता है।
- दोनों ओर से मरुस्थल की रेत उड़-उड़ कर नहर में गिरती है। इसे साफ करने पर बहुत व्यय करना पड़ता है।
8. भविष्य (Future)-स्वेज़ नहर पर आधुनिक सुविधाएं प्रदान करने की योजना है। कई बार म्रिस-इज़राइल
झगड़े के कारण यह नहर बन्द रही है। परन्तु अब संसार का अधिकतर व्यापार आशा अन्तरीप मार्ग पर तेज़ जहाज़ों से होने लग पड़ा है। भविष्य में स्वेज नहर इतनी महत्त्वपूर्ण नहीं होगी। (It will not be the same old romantic Suez Canal.)

प्रश्न 6.
पनामा नहर के भौगोलिक, आर्थिक व राजनीतिक महत्त्व का वर्णन करो।
उत्तर-
पनामा नहर (Panama Canal)-
1. स्थिति (Location)-यह नहर मध्य अमेरिका (Central America) के पनामा गणराज्य में स्थित है। यह नहर पनामा स्थल डमरू मध्य (Panama Isthmus) को काटकर बनाई गई है।
2. इतिहास (History)-स्वेज़ नहर की सफलता को देखकर पनामा नहर के निर्माण की योजना बनाई गई।
1882 ई० में फर्डिनेण्ड-डी-लैसैप्स ने इस नहर का निर्माण कार्य आरम्भ किया परन्तु पीले ज्वर तथा मलेरिया के कारण हजारों श्रमिक मर गए। अतः यह प्रयत्न असफल रहा। उसके पश्चात् सन् 1904 में संयुक्त राज्य (U.S.A.) सरकार ने इस नहर का निर्माण आरम्भ किया। यह नहर दस वर्ष में 15 अगस्त 1914 को बन कर तैयार हुई। इसके निर्माण पर 712 करोड़ पौंड खर्च हुए। यह नहर संयुक्त राज्य के अधीन है। इस नहर के निर्माण में कई कठिनाइयों का सामना करना पड़ा था। इसलिए नहर का सफलतापूर्वक निर्माण आधुनिक विज्ञान की बहुत बड़ी सफलता है। (“The construction of Panama Canal was a great feat of Engineering.”) इस नहर का निर्माण दो खाड़ियों (Bays), एक कृत्रिम झील (Artifical Lake), एक प्राकृतिक झील (Natural Lake) तथा तीन द्वार प्रणालियों (Lock Systems) द्वारा किया गया है। इस नहर का तल समुद्र तल के समान नहीं है। इसका निर्माण कुलबेरा (Culbera) नामक पहाड़ी को काट कर किया गया है। गातुन (Gatun) नामक कृत्रिम झील बनाई गई हैं। इस नहर में तीन स्थानों पर फाटक बनाए गए हैं।
1. गातुन (Gatun) द्वार।
2. पैड्रो मिग्वल (Padromiguel) द्वार।
3. मिरा फ्लोर्स (Miraflore) द्वार।
इन द्वारों को खोलकर जल-स्तर समान किया जाता है। फिर जलयान ऊपर चढ़ाए या नीचे गाटुन बाँध उतारे जाते हैं।
यह दोहरी द्वार प्रणाली (Double Lock System) है जिससे एक ही समय में दोनों ओर यातायात सम्भव है। इस प्रकार जहाज़ों को इस नहर में 45 मीटर तक ऊपर चढ़ना या नीचे उतरना पड़ता है। इस नहर को चार्जेस (Charges) नदी द्वारा जल-विद्युत प्रदान की जाती है जिसके प्रकाश व जलयानों को खींचने की शक्ति मिलती है।
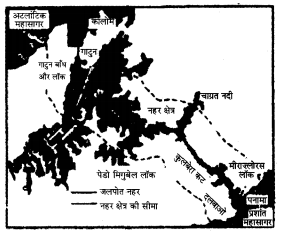
3. सागर तथा बन्दरगाह (Seas and Ports)—यह नहर प्रशान्त महासागर (Pacific Ocean) तथा अन्ध महासागर (Atlantic Ocean) को मिलाती है। इसे प्रशान्त महासागर का द्वार (Gateway of the Pacific) भी कहते हैं। प्रशान्त तट पर पनामा (Panama) तथा अन्धमहासागर तट पर कालोन (Colon) के बन्दरगाह हैं। यह नहर 8.16 किलोमीटर लम्बी, 12 मीटर गहरी तथा 90 से 300 मीटर चौड़ी है। इस नहर को पार करने में 8 घण्टे लगते हैं। इस नहर में से बड़े-बड़े जहाज़ नहीं गुज़र सकते।
4. महत्त्व (Importance)-(1) इस नहर के निर्माण से अन्ध महासागर तथा प्रशान्त महासागर के बीच दूरी कम हो गई है। (Panama Canal has changed the element of distance in geography of transport.”) इससे पहले दक्षिणी अमेरिका के (सिरे) केप हार्न (Cape Horn) का चक्कर लगा कर जाते थे। इस नहर से सबसे अधिक लाभ संयुक्त राज्य अमेरिका (U.S.A.) को हुआ है। इसके पश्चिमी व पूर्वी तट से ऑस्ट्रेलिया, न्यूजीलैंड, दक्षिणी अमेरिका, जापान की बन्दरगाहों की दूरी कम हो गई है। इस नहर के द्वारा यूरोप को कोई विशेष लाभ नहीं है। कई देशों की दूरी की बचत इस प्रकार है –
| स्थान से |
स्थान तक |
दूरी की बचत |
| 1. न्यूयार्क |
सान फ्रांसिस्को |
1300 किलोमीटर |
| 2. न्यूयार्क |
सिडनी |
6000 किलोमीटर |
| 3. न्यूयार्क |
हांगकांग |
7000 किलोमीटर |
| 4. न्यूयार्क |
वालपरेसो |
6800 किलोमीटर |
| 5. न्यूयार्क |
टोकियो |
6000 किलोमीटर |
| 6. न्यूयार्क |
सिडनी |
700 किलोमीटर |
| 7. न्यूयार्क |
सान फ्रांसिस्को |
9000 किलोमीटर |
(2) इस नहर के कारण पश्चिमी द्वीप समूह (West Indies) का महत्त्व बढ़ गया है।
(3) इस नहर के कारण संयुक्त राज्य संकट के समय एक ही नौ-सेना (Navy) से पश्चिमी व पूर्वी तट की रक्षा कर सकता है।
5. व्यापार (Trade)-इस नहर द्वारा व्यापार में बहुत वृद्धि हुई है। औसत रूप से प्रतिदिन 50 जहाज़ गुजरते हैं।
प्रति वर्ष लगभग 15,000 जहाज़ प्रवेश करते हैं। अन्ध महासागर से प्रशान्त महासागर की ओर अधिक व्यापार होता है। पूर्व की ओर से संयुक्त राज्य व यूरोप से शिल्पी वस्तुएं, खनिज पदार्थ, तेल, मशीनें, दवाइयां, सूती व ऊनी कपड़ा भेजा जाता है। पश्चिमी की ओर से डेयरी पदार्थ, मांस, रेशम, रबड़, चाय, तम्बाकू, नारियल, शोरा, तांबा भेजा जाता है।
6. त्रुटियां (Drawbacks)-इस मार्ग में निम्नलिखित दोष –
- इस नहर में बड़े-बड़े जहाज़ नहीं गुज़र सकते।
- द्वार प्रणाली के कारण काफ़ी असुविधा रहती है।
- इस मार्ग पर बन्दरगाह बहुत कम हैं।
- इस नहर के साथ के देश उन्नत नहीं हैं।
7. भविष्य (Future)-दक्षिणी अमेरिका के देश बड़ी तेज़ी से उन्नति कर रहे हैं। इनके विकास के कारण इस मार्ग पर व्यापार बढ़ेगा।

प्रश्न 7.
भारतीय में तेल तथा गैस पाइप लाइनों की विस्तार से व्याख्या करो।
उत्तर-
पाइप लाइन भी परिवहन का एक महत्त्वपूर्ण साधन है। इस साधन के द्वारा खास कर तरल पदार्थों का परिवहन किया जाता है। इन पाइप लाइनों की सहायता से तरल पदार्थ जैसे तेल तथा गैस को एक स्थान से दूसरे स्थान तक पहुंचाया जाता है। इन पाइप लाइनों की सहायता से कोयले को भी तरल पदार्थ के रूप में एक जगह से दूसरी जगह पहुँचाया जाता है। पाइप लाइन द्वारा लेकर जाए जाने वाले स्रोत हैं-पैट्रोलियम तथा पैट्रोलियम से बने पदार्थ, प्राकृतिक गैस, जैविक ईंधन इस तरीके से एक स्थान से दूसरे स्थान पर पहुंचाये जाते हैं। पंप स्टेशनों को तेल पाइपों के द्वारा ही चलाया जाता है। इसी प्रकार बहुत सारे प्राकृतिक पदार्थों को तरल रूप में तबदील करके इनको पाइप लाइनों के द्वारा एक स्थान से दूसरे स्थान तक पहुंचाया जाता है।
कुछ प्रमुख राष्ट्रीय पाइप लाइनें हैं-
1. तुर्कमेनिस्तान अफगानिस्तान-पाकिस्तान भारत (TAPI पाइप लाइन)-इस पाइप लाइन का विकास एशियाई विकास बैंक द्वारा किया गया तथा यह प्राकृतिक गैस पाइप लाइन है। यह पाइप लाइन, तुर्कमेनिस्तान, अफगानिस्तान तथा पाकिस्तान में से गुजरती है। इस प्रकल्प का प्रारम्भ 13 दिसंबर, 2015 में किया गया तथा 2019 तक पूरी करने की योजना बनाई गई है। इस पाइप लाइन की दिशा उत्तर से दक्षिण तक है। इसकी कुल लंबाई 1814 कि०मी० बनती है।
2. हजीरा-विजयपुर-जगदीशपुर ( HBJ) पाइप लाइन-यह पाइप लाइन मध्य प्रदेश के मध्य में स्थित विजयपुर या विजैपुर दोनों नामों से पहचानी जाती है। इसलिए इसको HBJ या HVJ कहते हैं। यह पाइप लाइन गैस अथॉरिटी ऑफ इण्डिया की तरफ से बिछाई गयी। इस प्रकल्प का प्रारम्भ 1986 में किया गया तथा 1997 में पूरा हो गया। भारत में गैस परिवर्तन के लिए हजीरा-विजयपुर, जगदीशपुर पाइप लाइन बनाई गई। यह पाइप लाइन 1700 किलोमीटर लम्बी है। यह पाइप लाइन गुजरात, मध्य प्रदेश, राजस्थान, उत्तर प्रदेश राज्यों में से गुजरती है। इस गैस से विजयपुर, सवाई माधोपुर, जगदीशपुर, शाहजहांपुर, अंबाला, बथराला खाद बनाने की योजना है।
3. नाहरकटिया-नानूमती-बरौनी पाइप लाइन-NNB देश की ऐसी पहली पाइप लाइन है जो कि नाहरकटिया के तेल के कुओं से नानूमती (असम) तक कच्चा तेल पहुंचाने के लिए बिछाई गई थी तथा इसके बाद बरौनी (बिहार) तक इसको बढ़ा दिया गया है। इस पाइप लाइन की लम्बाई 1167 किलोमीटर है तथा अब तक इसको उत्तर प्रदेश के शहर कानपुर तक बढ़ा दिया गया है। इस पाइप लाइन ने 1962 तक अपना काम आरम्भ कर लिया था तथा इसका बरौनी का भाग 1964 तक क्रियाशील हुआ।
4. जामनगर लोनी LPG पाइप लाइन-यह पाइप लाइन गैस अथॉरिटी ऑफ इंडिया लिमिटेड (GAIL) की तरफ 1250 करोड़ की लागत से तैयार की गई है। यह पाइप लाइन 1269 किलोमीटर लम्बी है। यह भारत के गुजरात, राजस्थान, हरियाणा तथा उत्तर प्रदेश इत्यादि राज्यों में से गुजरती है। यह पाइप लाइन दुनिया की सबसे लम्बी पाइप लाइन है तथा यह पाइप लाइन 3 लाख एल० पी०जी० सिलिंडरों जितनी गैस हर रोज़ 1269 कि०मी० की दूरी तक लेकर जाती है। पाइप लाइन द्वारा इस काम के लिए 500 करोड़ रुपये की बचत होती हैं।
5. कांडला-बठिंडा पाइप लाइन-कांडला-बठिंडा पाइप लाइन इण्डियन आयल कार्पोरेशन (IOC) की तरफ
से बठिंडा के तेल शोधक कारखाने को कच्चा तेल पहुंचाने के लिए 2392 करोड़ रुपये के खर्च से तैयार किये गए थे। इस पाइप लाइन की लम्बाई 1443 किलोमीटर है। इस योजना का पहला चरण कांडला से लेकर सांगानौर तक था। यह चरण 1996 में पूरा हो गया था। इस पाइप लाइन का अगला चरण जारी है। यह चरण बठिंडा-जम्मू-श्रीनगर तक गैस पाइप लाइन बिछाने का है।

प्रश्न 8.
भारतीय वायुमार्ग यातायात का वर्णन करो तथा राष्ट्रीय हवाई अड्डों की जानकारी दो।
उत्तर-
आधुनिक समय में वायुमार्ग यातायात सबसे अधिक तीव्रगामी यातायात है। यह यातायात लम्बे सफर के लिए बहुत लाभदायक है। आज के समय में संसार भर में वायु यातायात उपलब्ध है। भारतीय घनी आबादी वाले देशों में वायुमार्ग मौजूद है। भारत में वायु यातायात का प्रारम्भ 1911 में हुआ। इसके बाद भारत में कई हवाई अड्डों का निर्माण हो गया। संसार में वायु मार्गों का विकास प्रथम विश्व युद्ध के पश्चात् हुआ। इसमें मार्गों के निर्माण पर खर्च नहीं होता केवल हवाई अड्डों का निर्माण करना पड़ता है। 1947 में देश की आजादी के समय चार मुख्य कंपनियों के द्वारा ही हवाई यातायात शुरू किया। ये कंपनियां थीं टाटा-सन्ज लिमिटेड, इण्डियन नैशनल एयरवेज़, एयर सर्विस आफ इंडिया तथा डैकन ऐयरवेज़। 1951 तक 4 और कंपनियों ने भारत में हवाई यातायात के लिए काम शुरू कर दिया। इसके बाद कंपनियों का स्वामित्व भारत सरकार ने अपने अधिकार क्षेत्र में ले लिया तथा दो कॉर्पोरेशनें बना दीं। एयर इंडिया तथा इण्डियन एयरलाइन्ज/परंतु आज ये कॉर्पोरेशनें एक ही हो चुकी हैं।
Airports Authority of India की तरफ से दी गई जानकारी से पता चलता है कि 30 राष्ट्रीय हवाई अड्डे हैं तथा 400 के करीब घरेलू हवाई अड्डे हैं, जबकि विदेशी कंपनियों के जहाजों को सिर्फ राष्ट्रीय हवाई अड्डों से ही उड़ानें भरने की अनुमति है।
पंजाब में इस समय दो राष्ट्रीय हवाई अड्डे हैं जो अमृतसर तथा मोहाली में हैं तथा पंजाब में राष्ट्रीय हवाई अड्डों के अलावा बठिंडा, साहनेवाल, पटियाला तथा पठानकोट में घरेलू हवाई अड्डे हैं।
यू०एस०ए०, यूरोप तथा आसियान की विदेशी कंपनियों को भारत में उड़ानों को भरने की मन्जूरी दिए जाने के बाद कई प्राइवेट कंपनियों ने जिनमें एयरवेज, स्पाइस जैट, गो इंडिगो, किंग फिशर, विस्तारा इत्यादि के जहाज़ भी अब भारत के देशी तथा विदेशी उड़ानें चला रहे हैं।
संसार में हवाई मार्गों का विकास विश्वयुद्ध के बाद हुआ। आजकल इसका बहुत बड़ा महत्त्व है। यह एक तेज़ गति वाला साधन है। इस में मार्गों के निर्माण में कोई खर्च नहीं होता। इससे पर्वतों, विशाल महासागरों व मरुस्थलों के पार पहुँचा जा सकता है। जहां दूसरे साधन नहीं पहुँच सकते। विभिन्न संस्कृतियों के बड़े-बड़े नगरों के वायुमार्गों द्वारा जुड़े होने से अंतर्राष्ट्रीय भावना का विकास होता है।
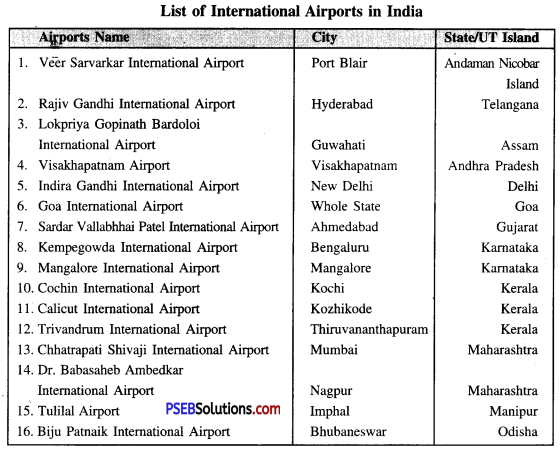
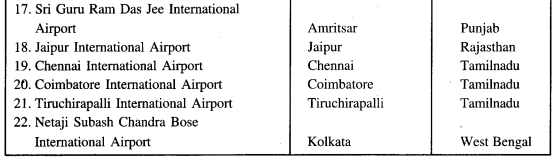
वायु मार्गों के गुण तथा दोष-
संसार के वायु मार्गों का विकास पहले विश्व युद्ध के पश्चात् हुआ। आजकल इसका बहुत बड़ा महत्त्व है। यह एक तीव्रगामी साधन है। इसमें मार्गों के निर्माण पर कोई खर्च नहीं होता। केवल हवाई अड्डों का निर्माण करना पड़ता है। इससे पर्वतों, विशाल महासागरों व मरुस्थलों के पार पहुंचा जा सकता है। जहाँ दूसरे साधन नहीं पहुँच सकते। विभिन्न संस्कृतियों के बड़े-बड़े नगरों के वायु मार्गों द्वारा जुड़े होने में अंतर्राष्ट्रीय भावना का विकास होता है।
परंतु इस साधन पर व्यय बहुत होता है। इसका व्यापारिक महत्त्व भी अधिक नहीं है। वायुयानों द्वारा यात्रियों, डाक व शीघ्र खराब होने वाले पदार्थों का परिवहन होता है।

प्रश्न 9.
व्यापार से आपका क्या भाव है ? इसकी किस्मों का विस्तार से वर्णन करो।
उत्तर-
वस्तुओं की क्रय-विक्रय/लेन-देन/खरीद-वेच को व्यापार कहते हैं। यह व्यापार की क्रिया खरीददार तथा विक्रेता के बीच का लेन-देन होता है। व्यापार मुख्य रूप में दो प्रकार का होता है।
1. निजी व्यापार-जो व्यापार निजी तौर पर या दो या अधिक लोगों के मध्य होता है वह छोटे स्तर का व्यापार होता है।
2. राष्ट्रीय स्तर का व्यापार-इस प्रकार के व्यापार में वस्तुओं को खरीदना बेचना राष्ट्रीय स्तर पर होता है। ज्यादातर राष्ट्रीय सीमाओं या इलाकों के पार किया व्यापार राष्ट्रीय व्यापार कहलाता है। राष्ट्रीय व्यापार करने के कई कारण हैं-
- किसी देश में प्राकृतिक साधनों की कमी।
- देश में वस्तुओं की मांग तथा पूर्ति में अंतर।
- तकनीकी साधनों की कमी कारण कई बार वस्तुएं किसी अन्य देश से मंगवानी पड़ती हैं।
- भौगोलिक भिन्नता के कारण स्रोतों में अंतर आ जाता है।
- व्यापारिक नीति तथा आर्थिक विकास में अंतर।
- देशों के आपसी संबंध।
विश्व व्यापार संगठन (WTO)- सन् 1995 में गैट का रूप बदलकर विश्व व्यापार संगठन बनाया गया। यह जेनेवा में एक स्थायी संगठन के रूप में कार्यरत है तथा यह व्यापारिक झगड़ों का निपटारा भी करता है। यह संगठन सेवाओं के व्यापार को भी नियंत्रित करता है, किंतु इसे अभी भी महत्त्वपूर्ण कर रहित नियंत्रणों जैसे निर्यात निषेध, निरीक्षण की आवश्यकता, स्वास्थ्य एवं सुरक्षा स्तरों तथा आयात लाइसैंस व्यवस्था, जिनसे आयात प्रभावित होता है, को सम्मिलित करना शेष है।
भारत सरकार की तरफ से Indian Institute of Foreign Trade की स्थापना की गयी है। इन संस्था की स्थापना 1963 में की गयी। यह भारत के पहले 10 चोटी के व्यापारिक तथा कारोबारी आदारों में एक संस्था है। इस संस्था के आदारे नई दिल्ली तथा कोलकाता में मौजूद है।
मौजूदा समय में 120 से अधिक क्षेत्र व्यापार संगठन संसार का 52% व्यापार कंट्रोल कर रहे हैं।

परिवहन/यातायात, संचार तथा व्यापार PSEB 12th Class Geography Notes
- वस्तुओं तथा यात्रियों को एक स्थान से दूसरे स्थान तक पहुँचाने को यातायात कहते हैं। किसी भी देश के ।
विकास के लिए यातायात से संबंधित गतिविधियां एक अहम भूमिका निभाती हैं। यातायात सुविधाओं को | मुख्य रूप में तीन वर्गों में विभाजित किया जाता है-
- स्थल मार्ग यातायात
- जल मार्ग यातायात
- वायु मार्ग यातायात
- स्थल मार्ग यातायात में सड़कें तथा रेलवे प्रारंभिक यातायात के साधन हैं।
- भारतीय यातायात का तंत्र एक विशाल प्रसार है। 1950-51 में कुल स्थल मार्ग 4 लाख किलोमीटर था जो कि 2007-08 में 33.1 लाख कि०मी० तक पहुँच गया।
- सड़कों का जाल पसारने के लिए कई योजनाएं, जैसे कि नागपुर पलान बीस वर्षीय, ग्रामीण सड़क विकास योजना, बी०ओ०टी० केंद्रीय सड़क फंड इत्यादि देश में चल रही हैं।
- सड़कों में ग्रामीण सड़कें, जिला, राज्य, राष्ट्रीय शाह मार्ग इत्यादि वर्गों में वर्गीकृत किया जाता है।
- उत्तर-दक्षिण तथा पूर्व-पश्चिम गलियारा प्रोजैक्ट देश के हर कोने तक बढ़िया सड़क-मार्गों का जाल | पसारने के लिए बनाया गया। इस योजना की देख-रेख की ज़िम्मेदारी राष्ट्रीय हाईवे एथारिटी ऑफ इंडिया के सुपुर्द की गई।
- भारत में राष्ट्रीय शाहमार्ग प्रबंध, भारत सरकार की एजैन्सी की ओर से चलाया तथा संभाला जाता है।
- भारतीय रेलवे तीन गेज पर गाड़ियां चलाती हैं-चौड़ी गेज पटरी, मीटर गेज पटरी तथा संकीर्ण गेज पटरी।
- भारतीय रेलवे के कुल 18 ज़ोन हैं।
- संसार की पहली रेलवे लाइन 1863 से 1869 के बीच अमेरिका में बिछाई गई।
- ट्रांस साइबेरियाई रेल मार्ग मास्को से रूस के पूर्व में व्लादिवोस्तोक तक 9,289 किलोमीटर लंबा है। यह विश्व का सबसे लंबा रेल मार्ग है।
- स्वेज नहर लाल सागर तथा रोम सागरों को आपस में जोड़ती है।
- पनामा नहर अंधमहानगरों दिल्ली, मुंबई, कोलकाता, चेन्नई को तेज़ी से चलने वाली रेल गाड़ी के तंत्र जोड़ने की योजना को डायमंड चतुर्भुज कहते हैं।
- भारत में अर्ध तेज़ रफ़्तार रेलवे गलियारे हैं।
- पाइप लाइन द्वारा तरल गैसीय पदार्थों की स्थान बदली की जाती है।
- जब हम अपने विचारों, संदेश, भावनाओं को लिखकर या बोलकर दूसरों तक पहुँचाते हैं, उसे संचार कहते हैं। इसके दो मुख्य प्रकार हैं-
- व्यक्तिगत संचार,
- जन-संचार।
- यातायात-वस्तुओं तथा मनुष्य को एक स्थान से दूसरे स्थान तक पहुँचाने को यातायात कहते हैं।
- यातायात के साधनों की किस्में-यातायात के साधनों को मुख्य रूप में तीन किस्मों में विभाजित किया जाता ‘ है-स्थल, जल तथा वायु मार्ग।
- राष्ट्रीय शाह मार्ग-राष्ट्रीय मार्गों का निर्माण तथा देखभाल भारत की केंद्र सरकार करती है। इस तरह की सड़कें राज्यों की राजधानियों, बंदरगाहों और नामवर तथा महत्त्वपूर्ण शहरों को आपस में मिलाती हैं।
- सुनहरी चतुर्भुज सड़क मार्ग-इस प्रोजैक्ट में भारत के चार महानगर दिल्ली, मुंबई, चेन्नई तथा कोलकाता को सड़क-मार्ग से जोड़ा गया है तथा इसका चतुर्भुज आकार होने के कारण इसको चतुर्भुज मार्ग कहते हैं।
- बंदरगाह-भारत में 12 मुख्य बंदरगाहें हैं।
- जलमार्गों की किस्में-
- आंतरिक जल मार्ग
- समुद्री जल मार्ग।
- संचार-जब हम अपने संदेश, भाव, विचारों को लिखकर या बोलकर पहुँचाते हैं इस क्रिया को संचार कहते हैं।
- संचार की किस्में-
- व्यक्तिगत संचार
- जन संचार।
- व्यापार-वस्तु को बेचने तथा खरीदने की क्रिया को व्यापार कहते हैं।
- भारत में ईंधन, खनिज तेल, खनिज मोम, जैविक रसायन फार्मेसी उत्पादन तथा चीजें निर्यात (बरामद) की जाती हैं। पैट्रोल, खनिज, मशीनरी, खादें, लोहा इस्पात, मोती के कीमती पत्थर, सोना-चांदी, खुराकी तेल, कागज़, दवाइयां, फर्नीचर इत्यादि का आयात (दरामद) किया जाता है।
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()