Punjab State Board PSEB 8th Class Physical Education Book Solutions Chapter 3 ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
PSEB Solutions for Class 8 Physical Education Chapter 3 ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ
Physical Education Guide for Class 8 PSEB ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ Textbook Questions and Answers
ਅਭਿਆਸ ਦੇ ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨਾਂ ਦੇ ਉੱਤਰ
ਹੇਠ ਦਿੱਤੇ ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨਾਂ ਦੇ ਉੱਤਰ ਦਿਓ :
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 1.
ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ਕਿਸ ਨੂੰ ਕਹਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ ?
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ਵੱਖ-ਵੱਖ ਭੋਜਨ ਪਦਾਰਥਾਂ ਵਿਚ ਪਾਏ ਜਾਣ ਵਾਲੇ ਰਸਾਇਣਿਕ ਤੱਤ ਹਨ । ਸਰੀਰ ਨੂੰ ਸਿਹਤਮੰਦ ਰੱਖਣ ਲਈ ਕੇਵਲ ਕਾਰਬੋਹਾਈਡੇਟਸ, ਚਿਕਨਾਈ (ਚਰਬੀ), ਪ੍ਰੋਟੀਨ, ਖਣਿਜ ਪਦਾਰਥ ਅਤੇ ਪਾਣੀ ਦੀ ਹੀ ਲੋੜ ਨਹੀਂ ਸਗੋਂ ਇਹਨਾਂ ਤੱਤਾਂ ਦਾ ਲਾਭ ਲੈਣ ਲਈ ਕੁਝ ਹੋਰ ਰਸਾਇਣਿਕ ਤੱਤਾਂ ਦੀ ਲੋੜ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ, ਜਿਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ਕਹਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 2.
ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨਾਂ ਦਾ ਕੀ ਮਹੱਤਵ ਹੈ ?
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨਾਂ ਦਾ ਮਹੱਤਵ-ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ਮਨੁੱਖੀ ਭੋਜਨ ਵਿੱਚ ਕਾਫ਼ੀ ਮਹੱਤਵ ਰੱਖਦੇ ਹਨ । ਇਹ ਪਾਚਨ ਅਤੇ ਉਪ ਪਾਚਨ ਦੀਆਂ ਕਿਰਿਆਵਾਂ ਲਈ ਬਹੁਤ ਸਹਾਈ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਇਹ ਸਰੀਰ ਦੇ ਵਾਧੇ ਅਤੇ ਵਿਕਾਸ ਲਈ ਬਹੁਤ ਜ਼ਰੂਰੀ ਹਨ । ਭਾਵੇਂ ਕਿ ਇਹ ਆਪ ਸਰੀਰ ਵਿੱਚ ਗਰਮੀ ਅਤੇ ਸ਼ਕਤੀ ਪੈਦਾ ਨਹੀਂ ਕਰਦੇ ਪਰ ਇਹ ਦੂਜੇ ਪੌਸ਼ਟਿਕ ਤੱਤਾਂ ਦੀ ਸਹਾਇਤਾ ਕਰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਇਹ ਸਰੀਰ ਦੀਆਂ ਅੰਦਰੂਨੀ ਕਿਰਿਆਵਾਂ ਦਾ ਸੰਚਾਲਨ ਕਰਨ ਵਿੱਚ ਸਹਾਈ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਇਹ ਲਹੂ ਨੂੰ ਸਾਫ਼ ਕਰਦੇ ਹਨ ਅਤੇ ਲਹੂ ਰਕਤਾਣੂਆਂ ਨੂੰ ਵਧਾਉਂਦੇ ਹਨ । ਇਹ ਸਰੀਰ ਨੂੰ ਬਿਮਾਰੀਆਂ ਨਾਲ ਟਾਕਰਾ ਕਰਨ ਦੀ ਸ਼ਕਤੀ ਦਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਇਹ ਪਾਚਨ ਸ਼ਕਤੀ ਨੂੰ ਵਧਾਉਂਦੇ ਹਨ । ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ਸਰੀਰ ਦੇ ਵਿਕਾਸ ਦਾ ਆਧਾਰ ਮੰਨੇ ਜਾਂਦੇ ਹਨ । ਇਸ ਕਰਕੇ ਇਹਨਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਜੀਵਨ ਦਾਤਾ ਵੀ ਕਿਹਾ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 3.
ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ਏ ਕੀ ਹੈ ? ਇਸ ਦੀ ਘਾਟ ਅਤੇ ਅਧਿਕਤਾ ਦੇ ਨੁਕਸਾਨ ਲਿਖੋ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ‘ਏ’ ਚਰਬੀ ਵਿਚ ਘੁਲਣਸ਼ੀਲ ਹੈ ।
ਕੰਮ-
- ਇਸ ਨਾਲ ਅੱਖਾਂ ਦੀ ਰੌਸ਼ਨੀ ਵਧਦੀ ਹੈ ।
- ਭੁੱਖ ਵੱਧਦੀ ਹੈ ।
- ਪਾਚਨ ਸ਼ਕਤੀ ਠੀਕ ਰਹਿੰਦੀ ਹੈ ।
- ਇਹ ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ਸਰੀਰ ਨੂੰ ਵਧਾਉਣ ਤੇ ਮਜ਼ਬੂਤ ਕਰਨ ਵਿਚ ਮੱਦਦ ਦਿੰਦਾ ਹੈ !
- ਸਰੀਰ ਵਿਚ ਰੋਗਾਂ ਦਾ ਮੁਕਾਬਲਾ ਕਰਨ ਦੀ ਸ਼ਕਤੀ ਪੈਦਾ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ ।
ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ‘ਏ’ ਦੀ ਘਾਟ ਦੇ ਨੁਕਸਾਨ-ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ‘ਏ’ ਦੀ ਘਾਟ ਨਾਲ ਛੂਤ ਦੇ ਰੋਗਾਂ ਨਾਲ ਲੜਨ ਦੀ ਸ਼ਕਤੀ ਘੱਟ ਜਾਂਦੀ ਹੈ ਅਤੇ ਵਿਅਕਤੀ ਬਿਮਾਰੀਆਂ ਦਾ ਸ਼ਿਕਾਰ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦਾ ! ਹੈ । ਅੱਖਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਖਾਰਸ਼ ਅਤੇ ਜਲਨ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ । ਇਸ ਦੀ ਘਾਟ ਨਾਲ ਰਾਤ ਨੂੰ ਸਾਫ਼ ਨਹੀਂ ਦਿਖਾਈ ਦਿੰਦਾ ਅਤੇ ਵਿਅਕਤੀ ਨੂੰ ਅੰਧਰਾਤਾ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ !

ਹੰਝੂ ਗੰਥੀਆਂ ਕੰਮ ਨਹੀਂ ਕਰਦੀਆਂ, ਚਮੜੀ ਖੁਸ਼ਕ ਅਤੇ ਸ਼ਖਤ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦੀ ਹੈ । ਗੁਰਦਿਆਂ ਵਿਚ ਪੱਥਰੀ ਬਣਨ ਦੀ ਸੰਭਾਵਨਾ ਵੱਧ ਜਾਂਦੀ ਹੈ : ਦੰਦ ਜਲਦੀ ਟੁੱਟਣ ਲੱਗ ਪੈਂਦੇ ਹਨ । ਦੰਦਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਪਾਇਉਰੀਆ ਨਾਂ ਦੀ ਬਿਮਾਰੀ ਲੱਗ ਜਾਂਦੀ ਹੈ |

ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 4,
ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ, ‘ਬੀ’ ਕੰਪਲੈਕਸ ਸਮੂਹ ਕਿਸ ਨੂੰ ਕਹਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ ? ਇਸ ਦੀ ਪ੍ਰਾਪਤੀ ਦੇ ਸ਼ਤ ਲਿਖੋ :
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ਬੀ ( Vitamin B)-ਇਹ ਕਈ ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨਾਂ ਦਾ ਮਿਸ਼ਰਨ ਹੈ । ਇਸ ਵਿਚ ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ਬੀ- 1, ਬੀ2 ਅਤੇ ਬੀ-2 ਮਿਲੇ ਰਹਿੰਦੇ ਹਨ । ਇਹ ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ਬੀ ਸੰਯੁਕਤ (3-Complex) ਦੇ ਨਾਂ ਨਾਲ ਜਾਣਿਆ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ।
ਕੰਮ-
- ਇਸ ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ਨਾਲ ਨਾੜੀ ਸਿਸਟਮ (Nervous System) ਠੀਕ ਰਹਿੰਦਾ ਹੈ ।
- ਇਹ ਨਾੜੀਆਂ, ਪੱਠਿਆ, ਦਿਲ ਤੇ ਦਿਮਾਗ਼ ਨੂੰ ਸ਼ਕਤੀ ਦਿੰਦਾ ਹੈ ।
- ਭੁੱਖ ਤੇਜ਼ ਕਰਦਾ ਹੈ ।
- ਚਮੜੀ ਦੇ ਰੋਗ ਤੋਂ ਰੱਖਿਆ ਕਰਦਾ ਹੈ ।
ਪ੍ਰਾਪਤੀ ਦੇ ਸੋਮੇ (Sources)-ਇਹ ਦੁੱਧ, ਦਹੀਂ, ਮੱਖਣ, ਪਨੀਰ, ਸਾਬਤ ਦਾਲਾਂ, ਅਨਾਜ, ਸੋਇਆਬੀਨ, ਮਟਰ ਅਤੇ ਆਂਡੇ, ਹਰੀਆਂ ਸਬਜ਼ੀਆਂ ਦੇ ਪੱਤਿਆਂ ਜਿਵੇਂ ਬੰਦ ਗੋਭੀ, ਪਿਆਜ਼, ਪਾਲਕ, ਟਮਾਟਰ, ਸ਼ਲਗਮ ਤੇ ਸਲਾਦ ਆਦਿ ਵਿਚ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ । ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ‘ਬੀ’ ਦੀ ਘਾਟ ਦੇ ਨੁਕਸਾਨ- ਇਸ ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ਦੀ ਘਾਟ ਨਾਲ ਬੇਰੀ-ਬੇਰੀ ਰੋਗ ਲੱਗ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ । ਵਿਅਕਤੀ ਨੂੰ ਚਮੜੀ ਦੇ ਰੋਗ, ਜੀਭ ਤੇ ਛਾਲੇ, ਵਾਲ ਡਿੱਗਣ ਲੱਗ ਪੈਂਦੇ ਹਨ । ਵਿਅਕਤੀ ਦਾ ਹਾਜ਼ਮਾ ਕਮਜ਼ੋਰ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ਅਤੇ ਭੁੱਖ ਵੀ ਘੱਟ ਲਗਦੀ ਹੈ । ਵਿਅਕਤੀ ਦੇ ਸਰੀਰ ਦਾ ਵਿਕਾਸ ਰੁਕ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ਅਤੇ ਅਨੀਮੀਆ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ।

ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 5.
ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ‘ਸੀਂ ਕੀ ਹੈ ? ਇਸ ਦੇ ਕੰਮ ਅਤੇ ਸੋਤ ਲਿਖੋ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ਸੀ (Vitamin C)-ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ‘ਸੀ’ ਪਾਣੀ ਵਿਚ ਘੁਲਣਸ਼ੀਲ ਹੈ ।
ਕੰਮ-
- ਇਹ ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ਲਹੂ ਨੂੰ ਸਾਫ਼ ਰੱਖਦਾ ਹੈ ।
- ਦੰਦਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਮਜ਼ਬੂਤ ਰੱਖਦਾ ਹੈ ।
- ਜ਼ਖ਼ਮਾਂ ਤੇ ਟੁੱਟੀਆਂ ਹੱਡੀਆਂ ਨੂੰ ਵੀ ਜਲਦੀ ਠੀਕ ਕਰਦਾ ਹੈ ।
- ਸਰੀਰ ਨੂੰ ਛੂਤ ਦੀਆਂ ਬਿਮਾਰੀਆਂ ਤੋਂ ਬਚਾਉਂਦਾ ਹੈ ।
- ਗਲੇ ਨੂੰ ਠੀਕ ਰੱਖਦਾ ਹੈ ।
- ਜ਼ੁਕਾਮ ਤੋਂ ਬਚਾਉਂਦਾ ਹੈ ।
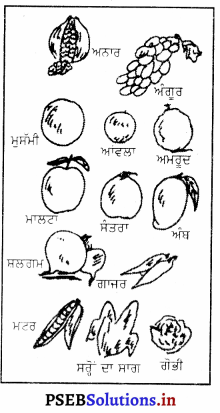
ਪਾਪੜੀ ਦੇ ਸੋਮੇ (Sources)-ਇਹ ਆਮ ਤੌਰ ਤੇ ਰਸਦਾਰ ਖੱਟੇ ਫਲਾਂ ਵਿਚ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ, ਜਿਵੇਂ-ਸੰਤਰਾ, ਸ਼ਲਗਮ ਮਾਲਟਾ, ਮੁਸੱਮੀ, ਅੰਗੂਰ, ਅਨਾਰ, ਨਿੰਬੂ, ਅਮਰੂਦ ਅਤੇ ਔਲਾ ਆਦਿ । ਇਸ ਤੋਂ ਬਿਨਾਂ ਹਰੀਆਂ ਸਬਜ਼ੀਆਂ, ਟਮਾਟਰ, ਬੰਦ ਗੋਭੀ, ਗਾਜਰ, ਪਾਲਕ, ਸ਼ਲਗਮ ਆਦਿ ਵਿਚ ਵੀ ਮਿਲਦਾ ਹੈ । ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ‘ਸੀਂ’ ਦੀ ਘਾਟ ਦੇ ਨਕਸਾਨ-ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ‘ਸੀ ਦੀ ਘਾਟ ਨਾਲ ਸਕਰਵੀ ਰੋਗ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ । ਹੱਥਾਂ-ਪੈਰਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਦਰਦ ਅਤੇ ਸੋਜ਼ ਆ ਜਾਂਦੀ ਹੈ । ਹੱਡੀਆਂ ਦਾ ਨਿਰਮਾਣ ਅਤੇ ਵਿਕਾਸ ਰੁਕ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ਅਤੇ ਹੱਡੀਆਂ ਵਿੰਗੀਆਂ-ਟੇਢੀਆਂ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ । ਜ਼ਖ਼ਮ ਨਹੀਂ ਭਰਦੇ ਅਤੇ ਜਖ਼ਮਾਂ ਵਿਚੋਂ ਲਹੂ ਸਿੰਮਦਾ ਰਹਿੰਦਾ ਹੈ । ਦੰਦ ਕਮਜ਼ੋਰ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦੇ ਹਨ | ਮਸੂੜਿਆਂ ਵਿਚੋਂ ਲਹੂ ਵਗਣ ਲੱਗ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ । ਚਮੜੀ ਦਾ ਰੰਗ ਪੀਲਾ ਪੈ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ । ਅੱਖਾਂ ਦੇ ਘੇਰੇ ਕਾਲੇ ਪੈ ਜਾਂਦੇ ਹਨ । ਛੂਤ ਦੇ ਰੋਗ ਲੱਗਣ ਦੀ ਸੰਭਾਵਨਾ ਵੱਧ ਜਾਂਦੀ ਹੈ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 6.
ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ‘ਡੀ ਕੀ ਹੈ ? ਇਸ ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ਦੀ ਘਾਟ ਨਾਲ ਹੋਣ ਵਾਲੇ ਨੁਕਸਾਨ ਲਿਖੋ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ‘ਡੀ’ (Vitamin D)–ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ‘ਡੀ’ ਚਰਬੀ ਵਿਚ ਘੁਲਣਸ਼ੀਲ ਹੈ ।
ਕੰਮ-
- ਇਹ ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ਹੱਡੀਆਂ ਤੇ ਦੰਦ ਬਣਾਉਂਦਾ ਹੈ ।
- ਹੱਡੀਆਂ ਤੇ ਦੰਦਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਮਜ਼ਬੂਤ ਵੀ ਕਰਦਾ ਹੈ ।
- ਬੱਚਿਆਂ ਨੂੰ ਸਰੀਰਕ ਵਾਧੇ ਲਈ ਇਸ ਦੀ ਜ਼ਰੂਰਤ ਹੈ ।
ਪ੍ਰਾਪਤੀ ਦੇ ਸੋਮੇ (Sources)-ਇਹ ਦੁੱਧ, ਆਂਡੇ ਦੀ ਜ਼ਰਦੀ, ਮੱਖਣ, ਘਿਓ, ਮੱਛੀ ਦੇ ਤੇਲ ਵਿਚ ਬਹੁਤ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ । ਇਹ ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ਸੂਰਜ ਦੀਆਂ ਕਿਰਨਾਂ ਦੇ ਪ੍ਰਭਾਵ ਨਾਲ ਆਪਣੇ ਆਪ ਹੀ ਬਣਦਾ ਰਹਿੰਦਾ ਹੈ ।
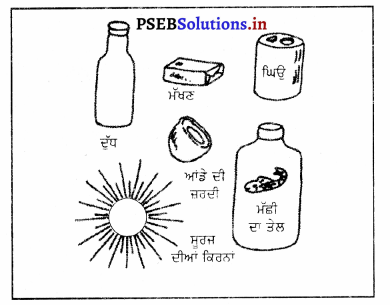
ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ‘ਡੀ’ ਦੀ ਘਾਟ ਦੇ ਨੁਕਸਾਨ-ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ‘ਡੀ’ ਦੀ ਘਾਟ ਨਾਲ ਮਾਸ਼-ਪੇਸ਼ੀਆਂ ਅਤੇ ਹੱਡੀਆਂ ਦਾ ਦਰਦ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ । ਛੋਟੇ ਬੱਚਿਆਂ ਨੂੰ ਦਮਾ ਹੋਣ ਦਾ ਡਰ ਰਹਿੰਦਾ ਹੈ । ਇਸ ਦੀ ਘਾਟ ਨਾਲ ਬੱਚਿਆਂ ਨੂੰ ਸੋਕੜਾ ਰੋਗ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ।

ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 7.
ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ‘ਈ ਕੀ ਹੈ ? ਇਸ ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ਦੀ ਪ੍ਰਾਪਤੀ ਦੇ ਸੋਤ ਲਿਖੋ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ਈ (Vitamin E)-ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ‘ਈ’ ਚਰਬੀ ਵਿਚ ਘੁਲਣਸ਼ੀਲ ਹੈ ।
ਕੰਮ-
- ਇਹ ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ਔਰਤਾਂ ਅਤੇ ਮਰਦਾਂ ਵਿਚ ਸੰਤਾਨ ਪੈਦਾ ਕਰਨ ਦੀ ਸ਼ਕਤੀ ਨੂੰ ਵਧਾਉਂਦਾ ਹੈ ।
- ਇਹ ਨਾਮਰਦੀ ਤੇ ਬਾਂਝਪਨ ਨੂੰ ਰੋਕਦਾ ਹੈ ।
ਪ੍ਰਾਪਤੀ ਦੇ ਸੋਮੇ (Sources)-ਇਹ ਬੰਦਗੋਭੀ, ਗਾਜਰ, ਸਲਾਦ, ਮਟਰ, ਪਿਆਜ਼, ਟਮਾਟਰ, ਫੁੱਲ ਗੋਭੀ ਵਿਚ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ । ਇਸ ਤੋਂ ਬਿਨਾਂ ਸ਼ਹਿਦ, ਕਣਕ, ਚੌਲ, ਬੀਜਾਂ ਦੇ ਤੇਲ, ਆਂਡੇ ਦੀ ਜ਼ਰਦੀ, ਬਦਾਮ, ਪਿਸਤੇ, ਛੋਲਿਆਂ ਦੀ ਦਾਲ ਅਤੇ ਦਲੀਏ ਵਿਚ ਬਹੁਤ ਜ਼ਿਆਦਾ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ ।

ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ‘’ ਦੀ ਘਾਟ ਦੇ ਨੁਕਸਾਨ-ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ‘ਈ’ ਦੀ ਘਾਟ ਹੋਣ ਕਰਕੇ ਔਰਤਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਬਾਂਝਪਣ ਦਾ ਰੋਗ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ । ਇਸਤਰੀਆਂ ਅਤੇ ਪੁਰਸ਼ਾਂ ਵਿਚ ਸੰਤਾਨ ਪੈਦਾ ਕਰਨ ਦੀ ਸ਼ਕਤੀ ਘੱਟ ਜਾਂਦੀ ਹੈ । ਮਾਸ-ਪੇਸ਼ੀਆਂ ਦਾ ਵਾਧਾ ਅਤੇ ਵਿਕਾਸ ਰੁਕ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ :
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 8.
ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ‘ਕੇ’ ਕੀ ਹੈ ? ਇਸ ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ਦੀ ਘਾਟ ਨਾਲ ਹੋਣ ਵਾਲੇ ਨੁਕਸਾਨ ਲਿਖੋ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ਕੇ (Vitamin K)-ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ‘ਕੇ’ ਚਰਬੀ ਵਿਚ ਘੁਲਣਸ਼ੀਲ ਹੈ ।
- ਇਹ ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ਜ਼ਖ਼ਮਾਂ ਵਿਚੋਂ ਰਿਸਦੇ ਖੂਨ ਨੂੰ ਰੋਕਦਾ ਹੈ ।
- ਉਸ ਦੇ ਜਮਾਓ ਵਿਚ ਸਹਾਇਤਾ ਕਰਦਾ ਹੈ ।
- ਇਹ ਚਮੜੀ ਦੇ ਰੋਗਾਂ ਤੋਂ ਰੱਖਿਆ ਕਰਦਾ ਹੈ ।
ਪ੍ਰਾਪਤੀ ਦੇ ਸੋਮੇ (Sources)-ਇਹ ਜ਼ਿਆਦਾਤਰ ਬੰਦ ਗੋਭੀ, ਪਾਲਕ, ਮੱਛੀ, ਸੋਇਆਬੀਨ, ਟਮਾਟਰ ਤੇ ਆਂਡੇ ਦੀ ਜ਼ਰਦੀ ਵਿਚ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ ।

ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ‘ਕੇ’ ਦੀ ਘਾਟ ਦੇ ਨੁਕਸਾਨ-ਇਸ ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ਦਾ ਨਿਰਮਾਣ ਛੋਟੀ ਆਂਤੜੀ ਵਿੱਚ ਹੋਣ ਕਰਕੇ ਇਸ ਦੀ ਘਾਟ ਬਹੁਤ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ । ਸੱਟ ਲੱਗਣ ਕਰਕੇ ਲਹੂ ਵਗਣਾ ਬੰਦ ਨਹੀਂ ਹੁੰਦਾ । ਚਮੜੀ ਖੁਰਦਰੀ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦੀ ਹੈ । ਜਿਗਰ ਦੀਆਂ ਬੀਮਾਰੀਆਂ ਅਤੇ ਦਸਤ ਲੱਗ ਜਾਂਦੇ ਹਨ | ਖੂਨ ਦੀ ਕਮੀ ਸੰਬੰਧੀ ਰੋਗ ਲੱਗ ਜਾਂਦੇ ਹਨ | ਅਗੇਤੇ (Pre-mature) ਪੈਦਾ ਹੋਣ ਵਾਲੇ ਬੱਚਿਆਂ ਵਿਚ ਇਸ ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ਦੀ ਕਮੀ ਰਹਿੰਦੀ ਹੈ ।
PSEB 8th Class Physical Education Guide ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ Important Questions and Answers
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 1.
ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ਕਿੰਨੇ ਤਰ੍ਹਾਂ ਦੇ ਹਨ ?
(ਉ) ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ‘ਏ’
(ਅ) ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ‘ਬੀ
(ਈ) ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ‘ਸੀ’ ਅਤੇ ‘ਡੀ’
(ਸ) ਇਨ੍ਹਾਂ ਵਿਚੋਂ ਕੋਈ ਨਹੀਂ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
(ਉ) ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ‘ਏ’
(ਅ) ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ‘ਬੀ
(ਈ) ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ‘ਸੀ’ ਅਤੇ ‘ਡੀ’
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 2.
ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ‘ਡੀ ਕਿੱਥੋਂ ਮਿਲਦਾ ਹੈ ?
(ਉ) ਤੇ ਦੁੱਧ ਤੋਂ
(ਅ) ਅਨਾਜ ਤੋਂ
(ਈ) ਫਲਾਂ ਤੋਂ
(ਸ) ਧੁੱਪ ਤੋਂ |
ਉੱਤਰ-
(ਸ) ਧੁੱਪ ਤੋਂ |

ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 3.
ਬੇਰੀ-ਬੇਰੀ ਰੋਗ ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ਦੀ ਘਾਟ ਨਾਲ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ –
(ਉ) ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ‘ਬੀ’
(ਅ) ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ‘ਏ’
(ਇ) ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ‘ਕੇ
(ਸ) ਕਿਸੇ ਨਾਲ ਨਹੀਂ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
(ਉ) ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ‘ਬੀ’
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 4.
ਕਿਸ ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ਦੀ ਘਾਟ ਨਾਲ ਸਕਰਵੀ ਰੋਗ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ ?
(ਉ) ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ‘ਸੀ’
(ਅ) ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ‘ਕੇ’
(ਈ) ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ‘ਡੀ’
(ਸ) ਕਿਸੇ ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ਦੀ ਘਾਟ ਨਾਲ ਨਹੀਂ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
(ਉ) ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ‘ਸੀ’
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 5.
ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ਦੀ ਕਮੀ ਨਾਲ ਕਿਹੜੇ ਰੋਗ ਮਰੀਜ਼ ਨੂੰ ਲਗ ਜਾਂਦੇ ਹਨ ?
(ਉ) ਅੰਧਰਾਤਾ ਅਤੇ ਚਮੜੀ ਦੇ ਰੋਗ
(ਅ) ਭੁੱਖ ਨਹੀਂ ਲਗਦੀ
(ਇ) ਅਨੀਮੀਆ ਰੋਗ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ
(ਸ) ਉਪਰੋਕਤ ਸਾਰੇ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
(ਸ) ਉਪਰੋਕਤ ਸਾਰੇ ।
ਬਹੁਤ ਛੋਟ ਉੱਤਰਾਂ ਵਾਲੇ ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 1.
ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ਕਿੰਨੀ ਪ੍ਰਕਾਰ ਦੇ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ ?
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ਛੇ ਪ੍ਰਕਾਰ ਦੇ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ-ਏ, ਬੀ, ਸੀ, ਡੀ, ਈ ਅਤੇ ਕੇ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 2.
ਅੰਧਰਾਤਾ ਰੋਗ ਕਿਸ ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ਦੀ ਘਾਟ ਕਰਕੇ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ ?
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਇਹ ਰੋਗ ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ਏ ਦੀ ਘਾਟ ਕਰਕੇ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 3.
ਕਿਸ ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ਦੀ ਘਾਟ ਕਾਰਨ ਸਕਰਵੀ ਰੋਗ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ?
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ‘ਸੀ’ ਦੀ ਘਾਟ ਕਾਰਨ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 4.
ਬੇਰੀ-ਬੇਰੀ ਰੋਗ ਕਿਸ ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ਦੀ ਘਾਟ ਕਾਰਨ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ ?
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ‘ਸੀ’ ਦੀ ਘਾਟ ਕਾਰਨ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 5.
ਪਾਇਉਰੀਆ ਰੋਗ ਕਿਸ ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ਦੀ ਘਾਟ ਕਾਰਨ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ ?
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਇਹ ਰੋਗ ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ਸੀ ਦੀ ਘਾਟ ਕਾਰਨ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 6.
ਬਾਂਝਪਨ ਦਾ ਰੋਗ ਕਿਸ ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ਦੀ ਘਾਟ ਕਾਰਨ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ ?
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ‘ਈ’ ਦੀ ਘਾਟ ਕਾਰਨ ।
ਤਰਾਂ ਵਾਲੇ ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 1.
ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ਏ ਦੀ ਘਾਟ ਨਾਲ ਕਿਹੜੇ-ਕਿਹੜੇ ਰੋਗ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ ?
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ‘ਏ’ ਦੀ ਘਾਟ ਨਾਲ ਛੂਤ ਦੇ ਰੋਗਾਂ ਨਾਲ ਲੜਨ ਦੀ ਸ਼ਕਤੀ ਘੱਟ ਜਾਂਦੀ ਹੈ ਅਤੇ ਵਿਅਕਤੀ ਬਿਮਾਰੀਆਂ ਦਾ ਸ਼ਿਕਾਰ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ । ਅੱਖਾਂ ਵਿਚ ਖਾਰਸ਼ ਅਤੇ ਜਲਨ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ । ਇਸ ਦੀ ਘਾਟ ਨਾਲ ਰਾਤ ਨੂੰ ਸਾਫ ਨਹੀਂ ਦਿਖਾਈ ਦਿੰਦਾ ਅਤੇ ਵਿਅਕਤੀ ਨੂੰ ਅੰਧਰਾ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ । ਹੰਝੂ ਗੰਥੀਆਂ ਕੰਮ ਨਹੀਂ ਕਰਦੀਆਂ । ਚਮੜੀ ਖੁਸ਼ਕ ਅਤੇ ਸ਼ਖਤ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦੀ ਹੈ । ਗੁਰਦਿਆਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਪੱਥਰੀ ਬਣਨ ਦੀ ਸੰਭਾਵਨਾ ਵੱਧ ਜਾਂਦੀ ਹੈ । ਦੰਦ ਜਲਦੀ ਟੁੱਟਣ ਲੱਗ ਪੈਂਦੇ ਹਨ । ਦੰਦਾਂ ਨੂੰ ਪਾਇਉਰੀਆ ਨਾਂ ਦੀ ਬਿਮਾਰੀ ਲੱਗ ਜਾਂਦੀ ਹੈ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 2.
ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ‘ਬੀ’ ਦੇ ਪਾਪਤੀ ਦੇ ਸੋਮੇ ਲਿਖੋ
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਪ੍ਰਾਪਤੀ ਦੇ ਸੋਮੇ (Sources)-ਇਹ ਦੁੱਧ, ਦਹੀਂ, ਮੱਖਣ, ਪਨੀਰ, ਸਾਬਤ ਦਾਲਾਂ, ਅਨਾਜ, ਸੋਇਆਬੀਨ, ਮਟਰ ਅਤੇ ਆਂਡੇ, ਹਰੀਆਂ ਸਬਜ਼ੀਆਂ ਦੇ ਪੱਤਿਆਂ ਜਿਵੇਂ ਬੰਦ ਗੋਭੀ, ਪਿਆਜ਼, ਪਾਲਕ, ਟਮਾਟਰ, ਸ਼ਲਗਮ ਤੇ ਸਲਾਦ ਆਦਿ ਵਿਚ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 3.
ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ‘ਡੀ’ ਦੇ ਪ੍ਰਾਪਤੀ ਦੇ ਸੋਮੇ ਲਿਖੋ ।
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਪ੍ਰਾਪਤੀ ਦੇ ਸੋਮੇ (Sources)-ਇਹ ਦੁੱਧ, ਆਂਡੇ ਦੀ ਜ਼ਰਦੀ, ਮੱਖਣ, ਘਿਉ, ਮੱਛੀ ਦੇ ਤੇਲ ਵਿਚ ਬਹੁਤ ਹੁੰਦਾ ਹੈ । ਇਹ ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ਸੂਰਜ ਦੀਆਂ ਕਿਰਨਾਂ ਦੇ ਪ੍ਰਭਾਵ ਨਾਲ ਆਪਣੇ ਆਪ ਹੀ ਬਣਦਾ ਰਹਿੰਦਾ ਹੈ ।

ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 4.
ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ‘ਕੇ ਦੀ ਘਾਟ ਨਾਲ ਕਿਹੜੇ-ਕਿਹੜੇ ਰੋਗ ਹੁੰਦੇ ਹਨ ?
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਇਸ ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ਦਾ ਨਿਰਮਾਣ ਛੋਟੀ ਆਂਤੜੀ ਵਿਚ ਹੋਣ ਕਰਕੇ ਇਸ ਦੀ ਘਾਟ ਬਹੁਤ ਘੱਟ ਹੁੰਦੀ ਹੈ । ਸੱਟ ਲੱਗਣ ਕਰਕੇ ਲਹੂ ਵੱਗਣਾ ਬੰਦ ਨਹੀਂ ਹੁੰਦਾ । ਚਮੜੀ ਖੁਰਦਰੀ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦੀ ਹੈ । ਜਿਗਰ ਦੀਆਂ ਬਿਮਾਰੀਆਂ ਅਤੇ ਦਸਤ ਲੱਗ ਜਾਂਦੇ ਹਨ | ਖੂਨ ਦੀ ਕਮੀ ਸੰਬੰਧੀ ਰੋਗ ਲੱਗ ਜਾਂਦੇ ਹਨ | ਅਗੇਤੇ (Pre-mature) ਪੈਦਾ ਹੋਣ ਵਾਲੇ ਬੱਚਿਆਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਇਸ ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨ ਦੀ ਕਮੀ ਰਹਿੰਦੀ ਹੈ ।
ਪ੍ਰਸ਼ਨ 5.
ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨਾਂ ਦੀ ਕਮੀ ਨਾਲ ਸਰੀਰ ਵਿਚ ਕਿਹੜੇ ਰੋਗ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦੇ ਹਨ ?
ਉੱਤਰ-
ਭਿੰਨ-ਭਿੰਨ ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨਾਂ ਦੀ ਘਾਟ ਨਾਲ ਹੇਠ ਲਿਖੇ ਰੋਗ ਲੱਗ ਜਾਂਦੇ ਹਨ –
- ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨਾਂ ਦੀ ਘਾਟ ਕਾਰਨ ਅੰਧਰਾਤਾ ਅਤੇ ਚਮੜੀ ਦੇ ਰੋਗ ਲੱਗ ਜਾਂਦੇ ਹਨ ।
- ਇਹਨਾਂ ਦੀ ਘਾਟ ਨਾਲ ਫੇਫੜੇ ਕਮਜ਼ੋਰ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦੇ ਹਨ ਅਤੇ ਛੂਤ ਦੀਆਂ ਬਿਮਾਰੀਆਂ ਲੱਗ ਜਾਂਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ ।
- ਭੁੱਖ ਨਹੀਂ ਲੱਗਦੀ ।
- ਅਨੀਮੀਆ ਰੋਗ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦਾ ਹੈ ।
- ਅੱਖਾਂ ਵਿੱਚ ਮੋਤੀਆਬਿੰਦ ਛੇਤੀ ਹੋਣ ਲੱਗਦਾ ਹੈ ।
- ਇਸ ਦੀ ਘਾਟ ਨਾਲ ਮਿਰਗੀ, ਹਿਸਟੀਰੀਆ, ਸਕਰਵੀ, ਪਾਇਰੀਆ ਅਤੇ ਰਿਕਟਸ ਦੀਆਂ ਬਿਮਾਰੀਆਂ ਹੋ ਜਾਂਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ ।
- ਫੋੜੇ-ਫਿਨਸੀਆਂ ਨਿਕਲ ਆਉਂਦੀਆਂ ਹਨ ।
- ਵਿਟਾਮਿਨਾਂ ਦੀ ਘਾਟ ਨਾਲ ਜ਼ਖ਼ਮ ਵਿੱਚੋਂ ਖੂਨ ਦਾ ਵਗਣਾ ਜਲਦੀ ਬੰਦ ਨਹੀਂ ਹੁੰਦਾ |











